4- Stem cells
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is a stem cell?
An undifferentiated cell which is capable of becoming many different cell types in the organism
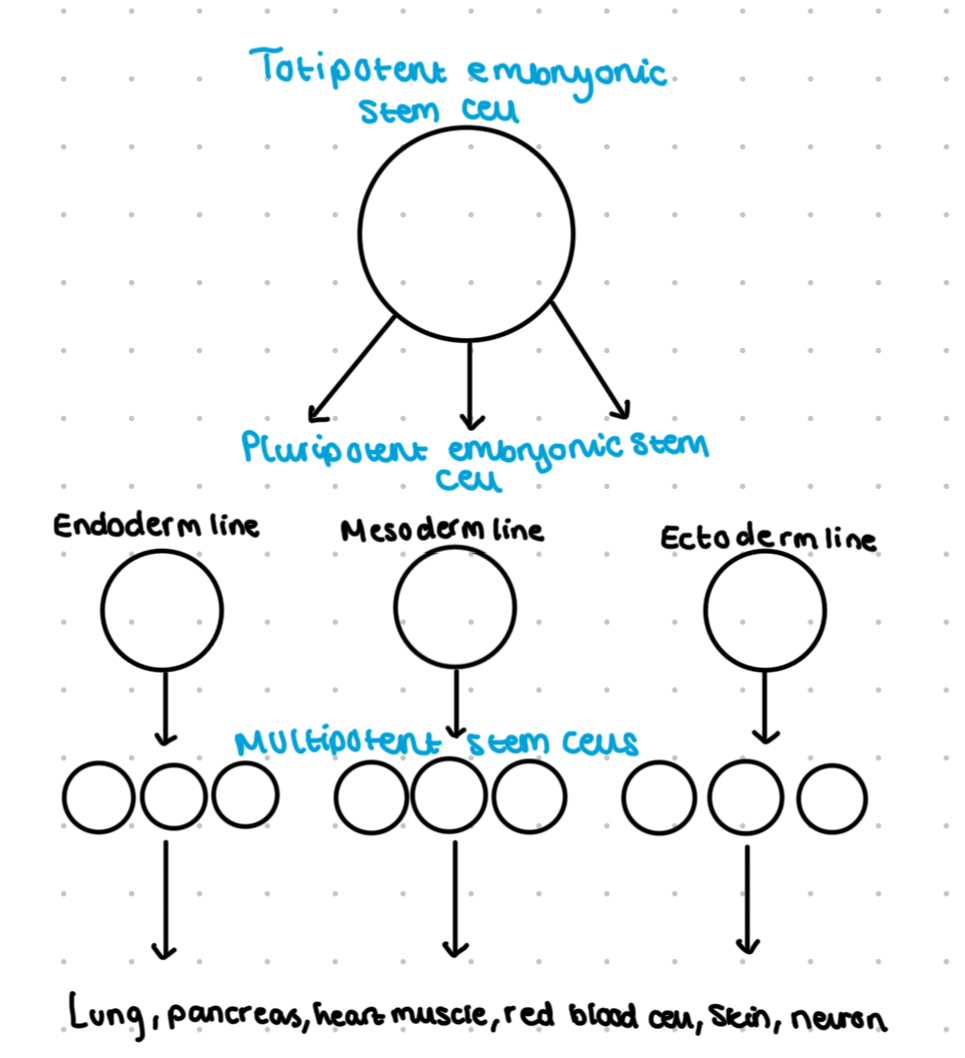
What are the 3 types of stem cell?
Totipotent- first 8 cells after 3 divisions, can differentiate into any cell of the body and placenta
Pluripotent- ‘embryonic’ stem cells- inner cells of the blastocyst, can make most but not all types of cell of the adult
Multipotent- can form more they one cell type, these are present in the adult e.g. bone marrow, also obtained from the umbilical cord
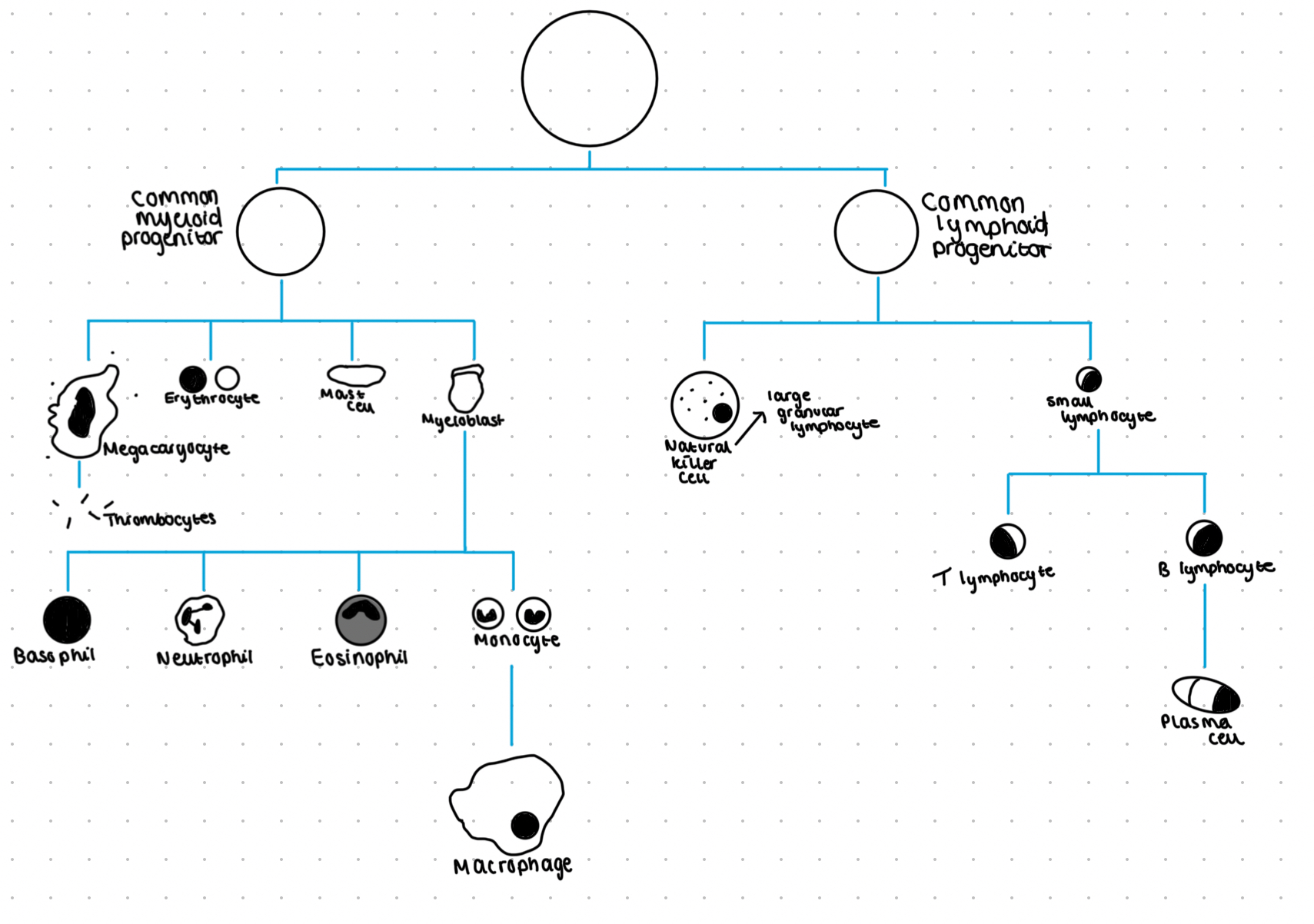
Formation of blood cells from bone marrow
Xylem and phloem
Xylem and phloem develops from meristem
In plants, the only cells which undergo mitosis are meristem cells (cambium)
Xylem:
Lignin is deposited in cell walls which reinforces, waterproofs and kills cells
The ends of the cell break dew on so that xylem forms continuous columns with wide lumens to carry water and dissolved nutrients
Phloem, sieve tubes and companion cells:
Sieve tubes lose most of the organelles and sieve plates develop between them
Companion cells retain their organelles and continue metabolic functions to provide ATP for active loading
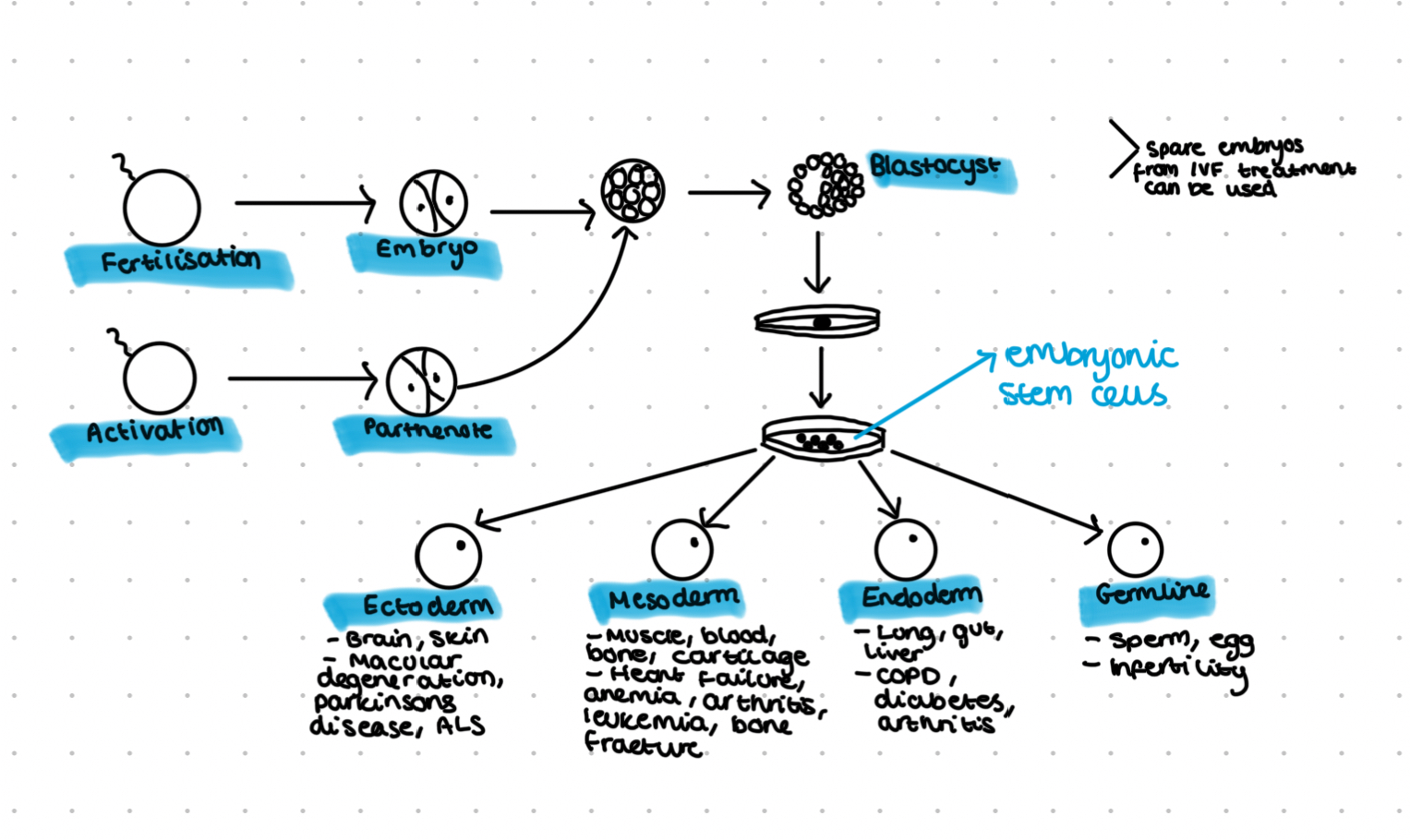
Sources of stem cells: embryonic stem cells
Sources of stem cells: umbilical cord stem cells
Taken after birth and stored by freezing
15 cm sample taken
Wharton’s jelly contains MSCs
Artery used in extraction of cord blood stem cells
Vein used in extraction of cord blood stem cells
Sources of stem cells: adult stem cells
Found in blood, brain, muscle, bone, adipose, tissue and skin
Sources of stem cells: Induced pluripotent stem cells
Creation:
Isolate cells from patient (skin/ fibroblasts), grow in a dish
Treat cells with reprogramming factors
Wait a few weeks
Pluripotent stem cells
Change culture conditions to stimulate cells to differentiate into a variety of cell types: blood cells, gut cells, cardiac muscle cells
Ethical issues
Adult stem cells have been used for many years in bone marrow transplants
Embryos from IVF are discarded
Embryos created in as lab for stem cells
Religious objections (life begins at conception)
Embryo can’t give consent for research
Uses of stem cells
Bone marrow transplants
Drug research
Developmental biology
Repair or replacement of damaged tissues
Bone marrow transplants
Can be used to treat sickle cell anemia and leukaemia, sever combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
Can be used to restore the blood system after treatment for some types of cancer
Drug research
can use stem cells to develop tissues
New drugs can be tested directly on tissue instead of animals
Developmental biology
Develop better understanding of how multicellular organisms develop and grow
Can study cell differentiation
Can study effect of disease on cell types
Can research if the capacity of embryos to grow and have tissues repair can be extended into later life
Repair or replacement of damaged tissues
Treating diabetic mice with programmed iPS cells to become pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin
Bone marrow stem cells can be made to develop into I’ve cells
Stem cells could be used to treat Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
Regenerative medicine
Arthritis, stroke, burns, vision and hearing loss