Chapter 6: the measurement of macroeconomic performance
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What are the main objectives of government macroeconomic policy?
economic growth, price stability (inflation), minimising unemployment and a stable balance of payments on current account(trade).
What is economic growth?
improving living standards and greater economic welfare for citizens
What is short-run economic growth?
when the economy moves from a situation where there are factors of production not being utilised (unemployment of resources including labour) towards full employment of resources. It takes up the slack by using unused capacity in the economy
What graph represents short run economic growth?
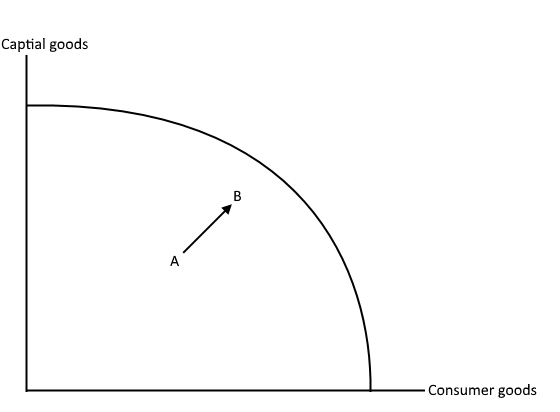
What is long-run economic growth?
this occurs when an economy’s productive capability increases, pushing the PPF curve outwards e.g due to technological advances
What is short-run negative growth?
producing less meaning you move from a point near or on the PPF curve to one further away
What is long-run negative growth?
when the PPF curve moves inwards showing a reduction in the capacity of the economy e.g due to war or emigration
How do you calculate the rate of economic growth?
(change in real national income/original national income) x100
What is gross domestic product (GDP)?
the sum of all goods and services, or level of output, produced in the economy over a period of time, e.g one year (output measure)
What is real GDP?
a measure of all the goods and services produced in an economy, adjusted for price changes or inflation
What is nominal (money) GDP?
GDP measured at the current market prices, without removing the effects of inflation
What is the difference between real and nominal GDP?
is that nominal GDP is the real GDP multiplied by the average current price level for the year in question (nominal takes into account inflation)
How do you calculate real GDP?
real GDP = nominal GDP - rate of inflation
How do you calculate nominal GDP?
nominal GDP = real GDP x average current price level
Which GDP do we look at?
real GDP
What is real GDP per capita?
this term means "per person." When you divide the Real GDP by the total population, you get Real GDP per capita
GDP is one of the main…
macroecenomic performance indicators
What is the beveridge definition of full employment?
where 3% or less of the labour force are unemployed
What is the free-market definition of full employment?
the level of employment occurring when the labour market is in equilibrium - where the number of worker whom employers wish to hire equals the number of workers wanting to work
What does the beverdige definition of full employment show about the real economy?
that there will always be some unemployment simply because the economy is constantly changing, with some jobs disappearing while new jobs are created
What is a limitation of the beveridge definition of full employment?
that the 3% figure is rather arbitrary and made-up
What are the two methods that are used to measure unemployment in the UK?
the claimant count and the labour force survey
What is the claimant count?
the method of measuring unemployment according to those people who are claiming unemployment-related benefits (jobseeker’s allowance)
What is the labour force survey (LFS)?
a quarterly sample survey of households in the UK
How do you calculate the unemployment rate?
(number of people unemployed/size of labour force) x100
Define price stability
refers to maintaining a consistent and predictable level of prices in an economy over time
Define inflation
a persistent or continuing rise in the average price level
Define deflation
a persistent or continuing fall in the average price level
Define disinflation
when the rate of inflation is falling, but still positive
What is the UK’s target inflation rate?
(+/- 1%) 2%
What happens in the UK’s rate of inflation exceeds 3% or is bellow 1%?
the governor of the bank of England (Andrew Bailey) has to write a letter to the Chancellor of Exchequer (Rachel Reeves) about why this has happened and what they intend to do about it
Define price index
an index number showing the extent to which a price, or ‘basket’ of prices, has changed over a period of time in comparison with the prices in a base year
What is consumer prices index (CPI)?
CPI is a key indicator of inflation measures the average change in prices paid by consumers for a fixed basket of goods and services
What is retail prices index (RPI)?
similar to CPI, RPI measures the change in prices of a basket of retail goods and services. RPI includes mortgage interest payments and council tax, which CPI does not. This makes RPI more sensitive to changes in interest rates
CPI and RPI are…
macroeconomic performance indicators
What is the difference between CPI and RPI?
CPI does not include housing costs
What are the balance of payments?
a record of all the currency flows into and out of a country in a particular time period
what is the current account of balance of payments?
measures all the currency flows into and out of a country in a particular time period focusing specifically on the trade of goods and services, imports and exports
What are the two main sections of the current account balance of payments?
the money value of exports, and the money value of imports
Define exports
goods and services produced in one country and sold to residents of another country
Define imports
goods and services purchased from other countries for domestic consumption
What is the balance of trade?
the difference between the money value of a country’s imports ant its exports. It is the largest component of a country’s balance of payments on current account
What is balance of trade deficit?
when the money value of country’s imports exceeds the money value of its exports : basically, when a country imports more than it exports
What is balance of trade surplus?
when the money value of a country’s exports exceeds the money value of its imports : basically, when a country imports less than it exports
What do most economics think of a ‘satisfactory’ balance of payments?
a situation in which the current account is in equilibrium, or when there is a small surplus or a small but sustainable deficit
What are the other two macroeconomic objectives?
balancing the budget (+reducing the government’s budget deficit) and achieving a fairer distribution of income
Define balanced budget
when government spending equals government revenue, which is mostly tax revenue
What is a budget deficit?
when government spending is greater than government revenue
What is policy conflict?
when two policy objectives can’t both be achieved at the same time : the better the performance in achieving one objective, the worse the performance in achieving the other
What are trade-offs between policy objectives?
when two or more desirable objectives are mutually exclusive (can’t be achieved at the same time)
What are the main policy conflicts and trade-offs?
full employment and economic growth - satisfactory balance of payments
full employment and economic growth - control of inflation
economic growth - greater income equality
current living standards - future living standards
What are keynesian economists?
people who believe that governments should manage the economy, particularly by using fiscal policy
What are pro-free market economists?
opponents of keynesian economists, who dislike government intervention in the economy and think that the market will correct itself
Define performance indicators
they provide information for judging the success or failure of a particular type of government policy such as fiscal or monetary policy
What are the two types of performance indicators?
lead indicators and lag indicators
What is a lead indicator?
one that provides information about the future state of the economy
What is a lag indicator?
one that provides information about the past and possibly current economic performance and the extent to which policy objectives such as economic growth and control inflation have been achieved
What is an index number?
a number used in an index (e.g CPI) to enable accurate comparisons to be made. The base year index number is typically 100
When do economists use index numbers?
when making comparisons over periods of time
How do you calculate index number?
index number in year Y = (data value in year Y/ base year value) x100
How do you calculate percentage change within the growth rate?
(new index number-original index number / original index number ) x100