Materials Science Chapters 1-6, 17
1/118
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
If the carbon content in common steel increases, the hardness then…
Increases
Increasing the temperature generally _________ electrical resistance.
Increases
Deformation in a material typically ________ electrical resistance.
Increases
The efficacy of heat conduction __________ as porosity increases.
Decreases
When in this structure, electron position is described in terms of proprietary density, and the aspects of this are determined by quantum numbers.
Wave
T or F: Most elements have unstable configurations.
True
1 - e(-0.25 * ΔEN2)
Percent Ionic Character
Atomic arrangement of a material that has periodic, 3D arrays of molecules.
Crystalline
Atomic arrangement of a material that has any non-periodic arrangement
Noncrystalline, Amorphous
Metals have dense atomic packing because…
Bonds are nondirectional, low bond energy, high shielding
The coordination number (C#) is the number of…
Nearest neighbors
SCC Coordination Number
6
SCS Radius (where a is edge length)
0.5a
SCS Atoms per unit cell
1
SCS Atomic Packing Factor
0.52
BCC Coordination Number
8
BCC atoms per unit cell
2
BCC Atomic Packing Factor
0.68
BCC Radius (where a is edge length)
sqrt(3) * a * 0.25
FCC Coordination Number
12
FCC Atoms per unit cell
4
FCC Radius
sqrt(2) * a * 0.25
HCP atoms per unit cell
6
Ideal ratio for c:a in HCP material structure.
1.633
HCP Radius is actually dependent on the how many factors?
Think: there are different molecules in this structure
2 (edge length a and edge length c)
What atomic facters determine crystal structure in ceramics?
Relative sizes, charge neutrality
When the ratio of cation:anion increases, the coordination number….
Increases
Bond hypridization is possible where there is significant ___________ bonding.
Covalent
The Percent Ionic Character is what percent of atoms becomes…
Hybridization
The most common elements on earth are…
Silicon, Oxygen
A polymorphic form of quartz, a type of ceramic. Known as (SiO2)
Silica
When SiO4 is bound to other stuff, we get….
Silicates
Bonds within silicates do what two things?
Maintain charge neutrality, ionically bond silicates
Structure of glass.
Amorphous
Fused silica (SiO2) with no impurities; noncrystalline stucture.
Glass
Tetrahedrally structured carbon.
Diamond
Layered parallel-hexagonal arrayed carbon
Graphite
Describe the structure of graphite
Weak van der Waal’s between layers, so the planes slide easily
Layered hexagonal arrays make the planes
When property values depend on direction; observed in single crystals.
Ansiotropy
Polycrystals where properties have random orientation.
Isotropic
Polycrystals where properties are textured.
Ansiotropic
When there are 2+ structures for the same material.
Polymorphism; allotropy
Carbon has multiple forms, such as diamond and graphite. This is an example of the trait…
Allotropy
A hydrocarbon where each carbon is singly bonded to four other atoms.
Saturated
A hydrocarbon where some carbon is doubly/triply bonded to four other atoms.
Unsaturated
The property describing that two compounds with the same chemical formula may have multiple different structures.
Isomerism
The average number of repeat monomers per chain.
Degree of Polymerization
Grains that are roughly the same dimension in all directions after solidification.
Equiaxed
Grains that are elongated in one direction after solidification.
Columnar
Something added to a substance during solidification to make smaller, more uniform, equiaxed grains.
Grain Refiner
Heat treating polymers causes % crystallinity to…
Increase
Polymers are usually a mix of straight regions (crystalline) and squiggly regions called _____ regions.
Amorphous
A type of crystals that, in polymers, are only for slow and carefully controlled growth rates.
Single Crystals
Polymer semi-crystalline structure that alternates chain-folded crystallites and amorphous regions.
Spherulite
Polymer spherulite structures have relatively ______ growth rates.
Fast
Each spherulite in polyethylene can look like what shape?
Maltese Cross
Two steps of solidification in solids.
Nuclei form
Crystals grow until their boundaries meet one another
The slight atomic disorder in grain boundaries leads to what two attributes?
High atomic mobility
High chemical reactivity
Dimension of Defect:
Vacancies
0
Dimension of Defect:
0 (point)
1 (linear)
2 (interfacial)
Interstitial atoms
0
Dimension of Defect:
0 (point)
1 (linear)
2 (interfacial)
Substitutions
0
Dimension of Defect:
0 (point)
1 (linear)
2 (interfacial)
Dislocations
1
Dimension of Defect:
0 (point)
1 (linear)
2 (interfacial)
Grain boundaries
2
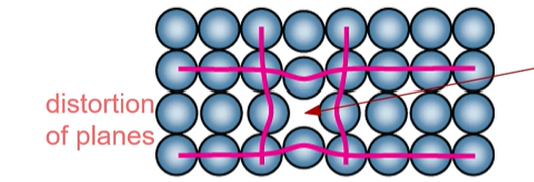
What point defect of a metal does the picture describe?
Vacancy
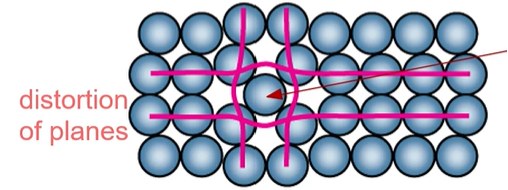
What point defect of a metal does the picture describe?
Self-interstitial
In metals, each ____________ is a potential vacancy
Lattice site
In ceramics, vacancy point defects can happen with _________.
Cations
Anions
Cations and anions
Cations and anions
In ceramics, interstitial point defects can happen with _________.
Cations
Anions
Cations and anions
Note: one option is observed more normally, because the other is usually too large
Cations
Conditions for substitutions in metals (Hume-Rothery Rules)
Difference in atomic radius < 15%
Proximity in periodic table (e.g. similar electronegativities)
Same crystal structure (pure metals)
Valences (higher valences dissolve easier)
A polymer linear dislocation where part of the polymer extends from the base in a twisting manner
Screw
A polymer point defect where the chain drops off the boundary and ends.
Dangling chain
A polymer point defect where the typically straight chain starts warping and wiggling.
Noncrystalline region
A polymer point defect where the chain trails off of the base and eventually returns.
Loose chain
A polymer point defect where the chain stops before it should.
Vacancy
A polymer point defect where two loops of the chain connect horizontally
Branch
In a screw dislocation, the measure of lattice distortion (Burger’s vector) is ________ to the dislocation line.
Parallel
A plane dislocation that occurs when an extra half-plane of atoms is inserted into the base structure, perpendicular to the dislocation line.
Edge
Dislocations _____ when stresses are applied and results in ________ deformation
Permanent (plasic)
Mirror reflections of atom positions of one side is a twin to the other; an interfacial defect
Twin boundaries
These interfacial faults occur when there is an error in the planar stacking sequence. For example, ABABC instead of ABCABC
Stacking faults
Catalytic reactions normally occur at….
Surface defect sites
Grain boundaries are (more/less) susceptible to etching.
More
Number of Grains Per Inch2 at 100x magnification.
2ASTM # - 1
Metallographic scopes often use this type of light to increase contrast.
Polarized
The best resolution for an optical microscope is….
100nm
The best resolution for an electron microscope is…
0.003nm
The best possible magnification for an electron microscope is…
1,000,000X
The best possible magnification for an optical microscope is…
1,000X
Electron beams in an electron microscope are focused by what type of lenses?
Magnetic?
Type of microscopy where surface atoms are imaged using a tiny probe that tapers to a single atom; atoms can be rearranged by pushing them with a tip.
STM (scanning tunneling microscopy)
Three types of dislocation imperfections.
Edge, screw, mixed
Gases and liquids have this diffusion mechanism.
Random (Brownian)
Diffusion of atoms of one material into another.
Interdiffusion
Atomic migration in a pure metal
Self-diffusion
The rate of vacancy diffusion depends on…
Number of vacancies, activation energy
Interstitial diffusion is (faster, slower) than vacancy.
Faster
A type of interstitial diffusion where the outer surface is selectively hardened by diffusing carbon atoms into the surface.
Case hardening
Case hardening diffuses what atoms into the surface of the material?
Carbon
Diffusion of very small concentrations of atoms of impurity (e.g. phosphorous) into the semiconductor silicon.
Doping
The target of diffusion in doping is what material?
Silicon