Neural Development: Determination, Differentiation, Diversification
Determination
Process of defining cell fate during development.
Differentiation
Specialization of less specialized cells into specific types.
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
Determination
Process of defining cell fate during development.
Differentiation
Specialization of less specialized cells into specific types.
Diversification
Further specialization of postmitotic cells for functions.
Neural Circuits
Complex networks formed by interconnected neurons.
Postmitotic Fate
Specific identity acquired by a cell after division.
Oligodendrocyte Fate
Acquisition of oligodendrocyte identity via Olig2 expression.
Molecular Diversity
Variety of molecular identities among neurons and glia.
Functional Heterogeneity
Different functions performed by diverse neuron types.
Progenitor Cells
Undifferentiated cells that can become specialized neurons.
Spinal Cord Motor Neurons
Neurons that control muscle movement in the spinal cord.
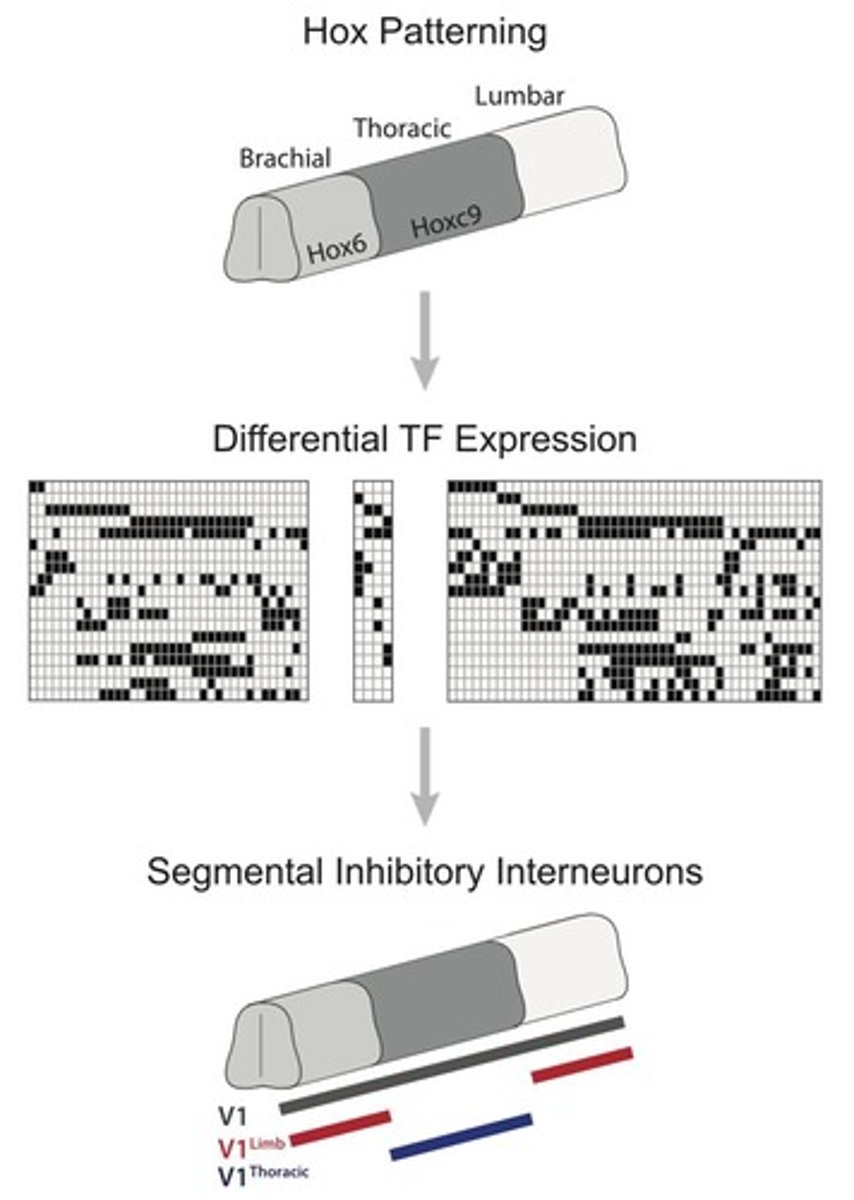
Hox Genes
Genes that specify positional identity in developing neurons.
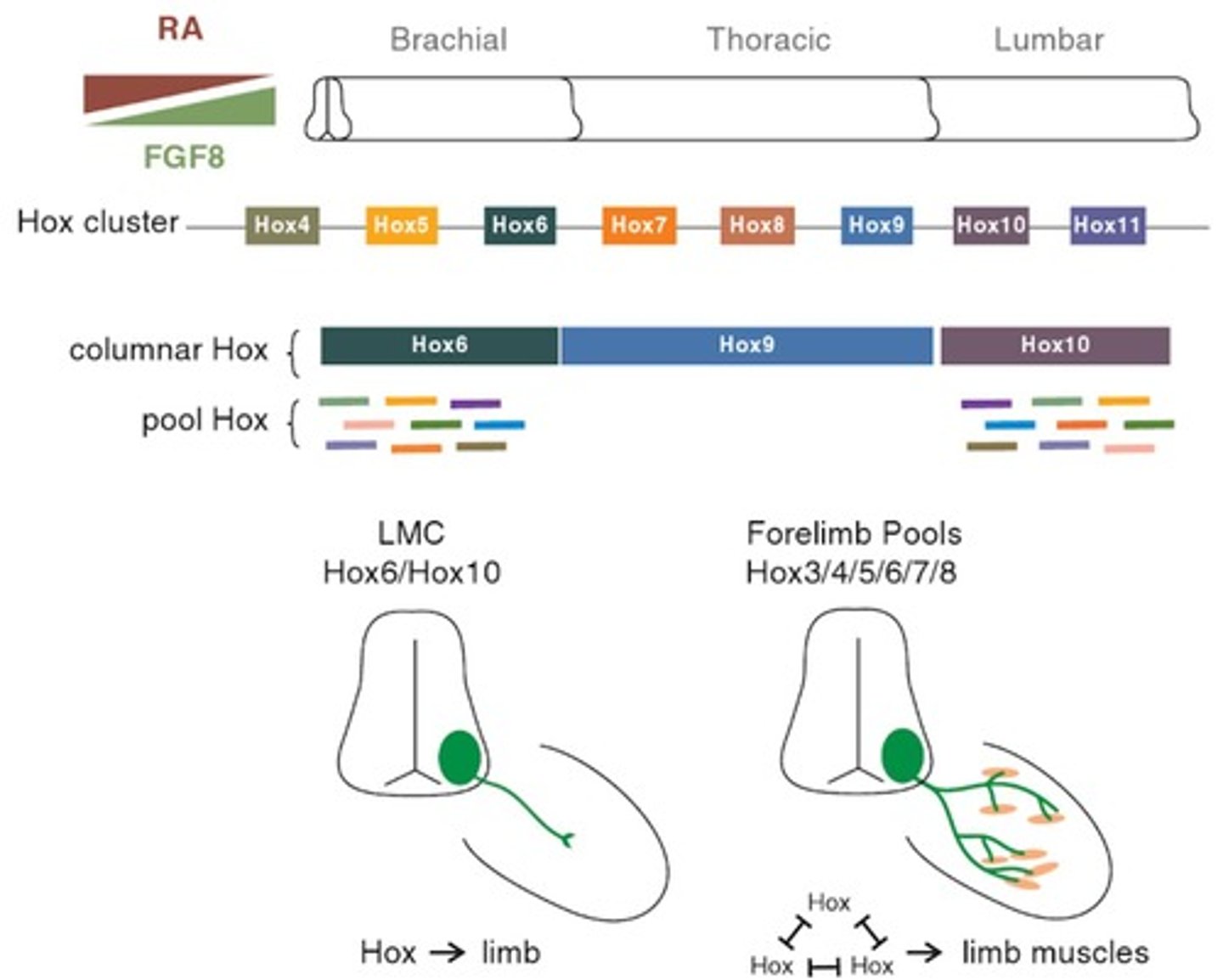
Positional Identity
Determines motor pool identities and axon targeting.
Gene Expression Programs
Patterns of gene activity during development and maturity.
Electrophysiological Properties
Electrical characteristics of neurons measured for classification.
Synaptic Specificity
Target identification of neurons based on synapse formation.
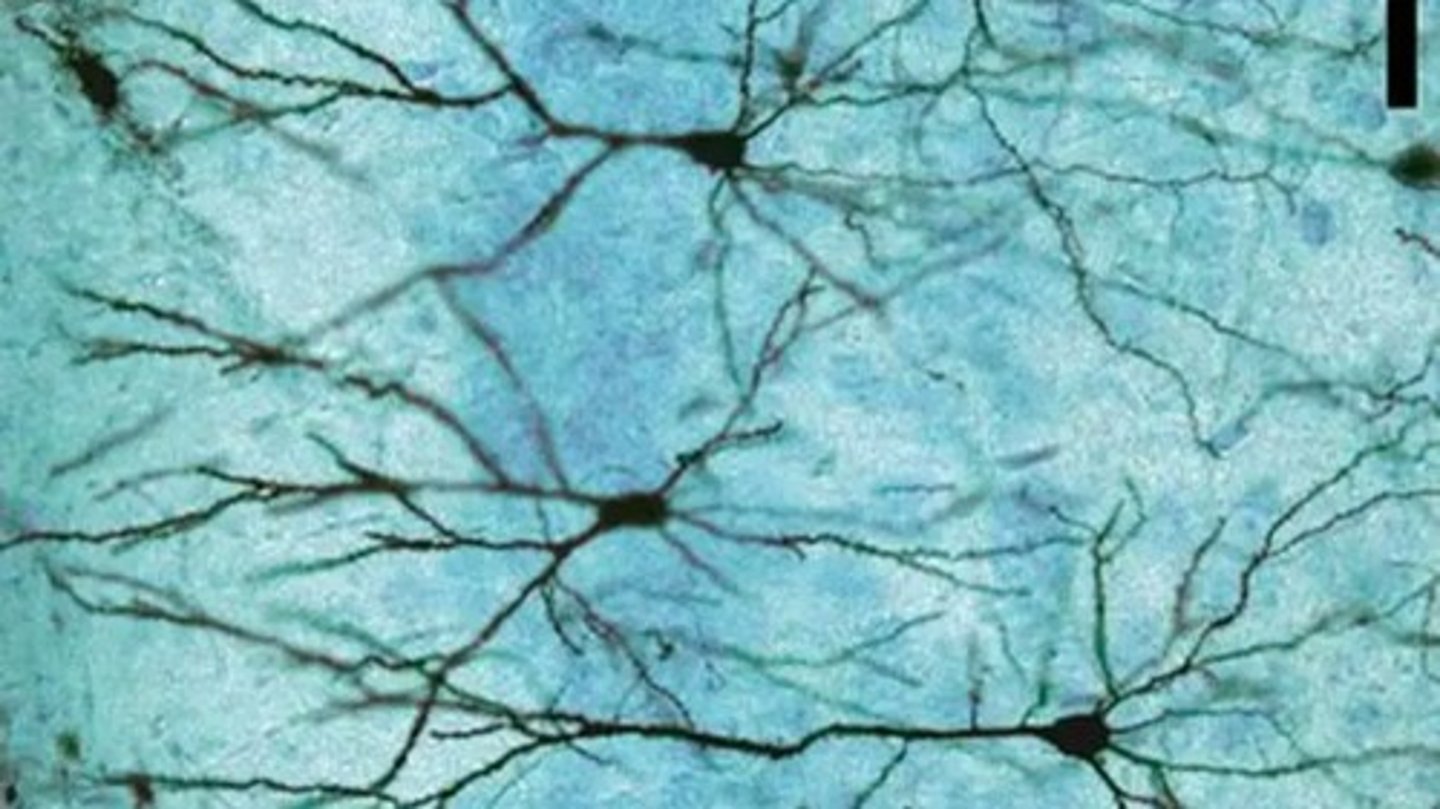
Cellular Morphology
Shape and structure of cells used for classification.
Single Cell Morphology
Individual cell shape analysis for neuron classification.
Multicellular Morphologies
Group structures of cells indicating distribution patterns.
Developmental Lineage
Line of descent determining cell specialization.
Mosaic Spacing
Regular spacing of similar neuron types in the retina.
Technological Advances
New methods enhancing understanding of cell identities.
Transcriptional Networks
Gene regulatory networks guiding early neural development.
Neural Circuitry Development
Process of forming functional neural connections.
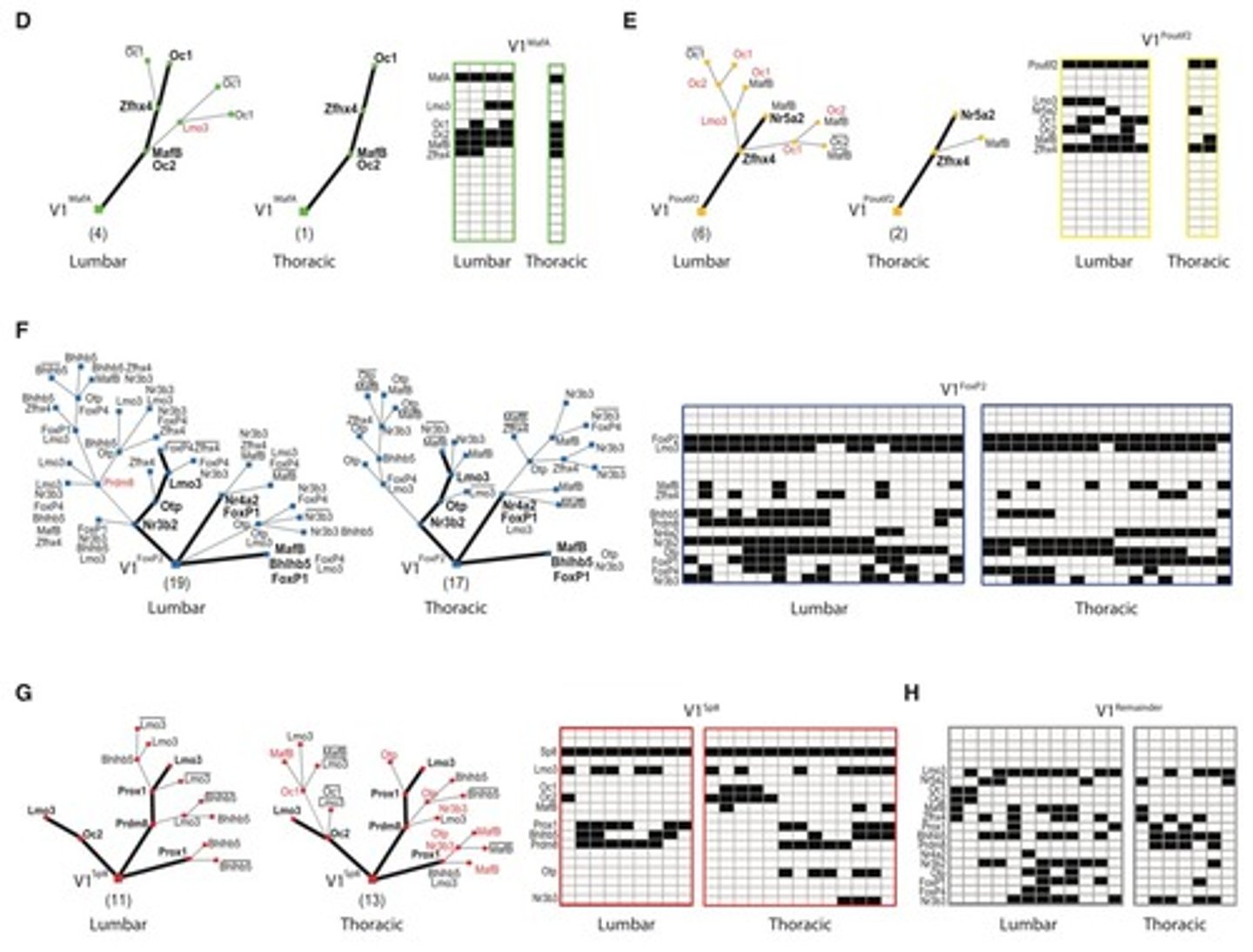
Developmental lineage
The historical path of cell development.
Cellular morphology
Study of cell shape and structure.
Single cell morphology
Characteristics of individual neuron shapes.
Multicellular morphologies
Cell arrangements in clusters or layers.
Gene expression programs
Patterns of gene activity during development.
Uniform physiological properties
Consistent functional characteristics across neurons.
Electrophysiological recordings
Measurements of electrical activity in neurons.
Optical imaging
Visualizing cellular structures using light.
Synaptic specificity
Target identification for synaptic connections.
Location
Physical positioning of neurons in tissue.
Spacing
Regular distribution of similar neuron types.
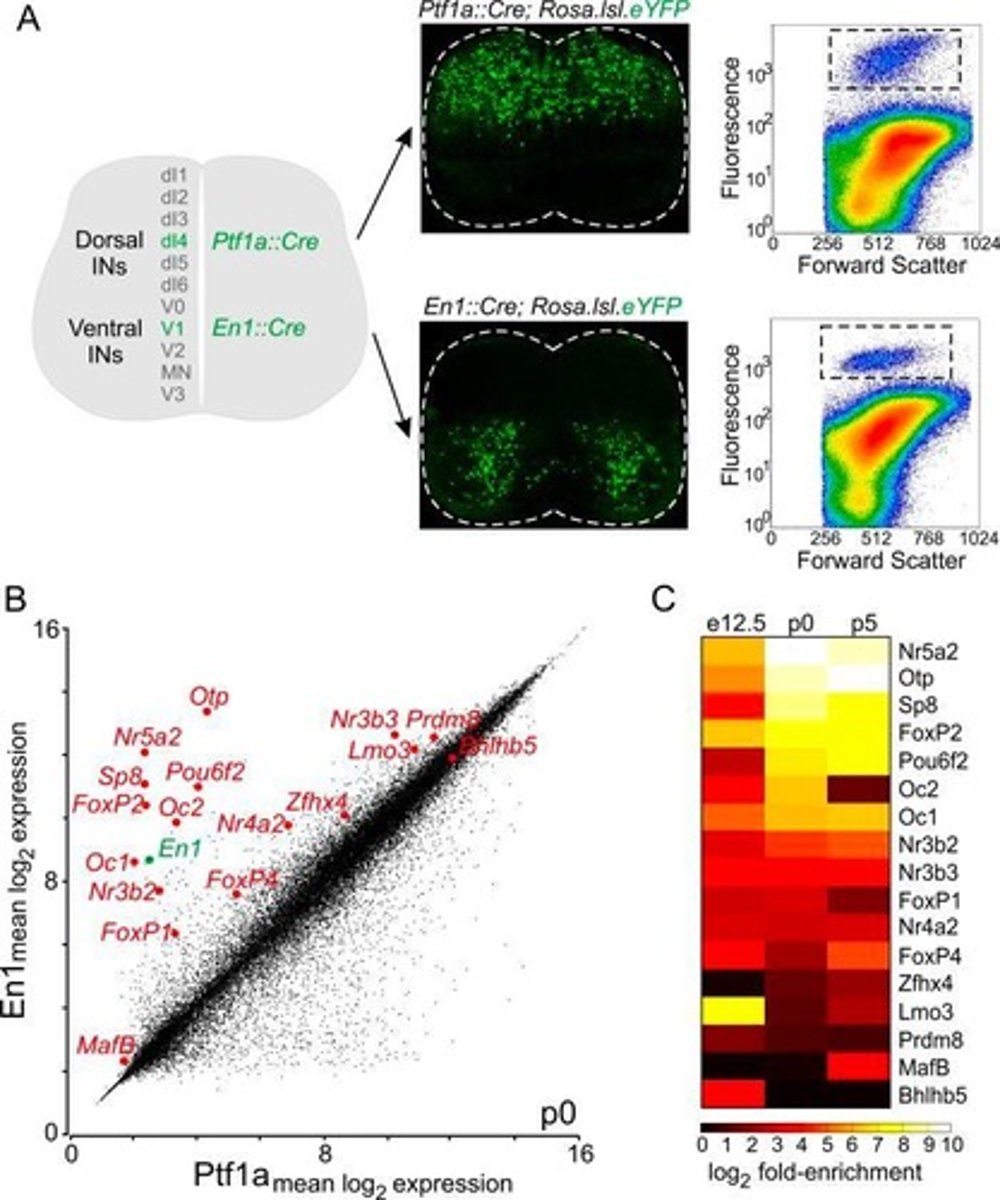
V1 interneurons
Specific spinal cord interneurons with unique functions.
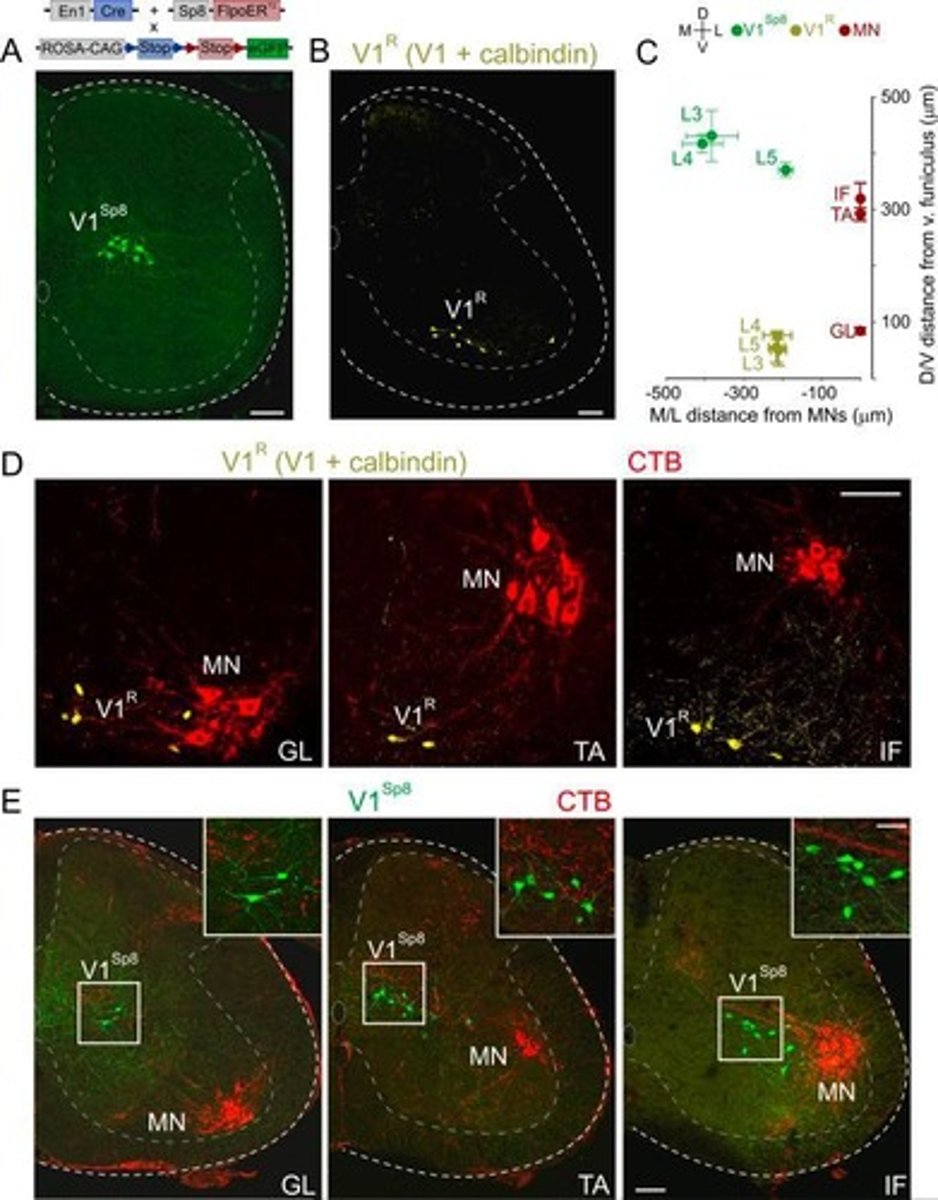
Transcriptionally defined subtypes
Neuron classifications based on gene expression.
Physiological signatures
Distinct functional characteristics of neuron types.
Mediolateral axis
Orientation from the middle to the side.
Dorsoventral axis
Orientation from the back to the belly.
Wiring diagram
Connections between neurons in a circuit.
Motor pools
Groups of neurons controlling muscle movements.
Hox genes
Genes determining body segment identity.
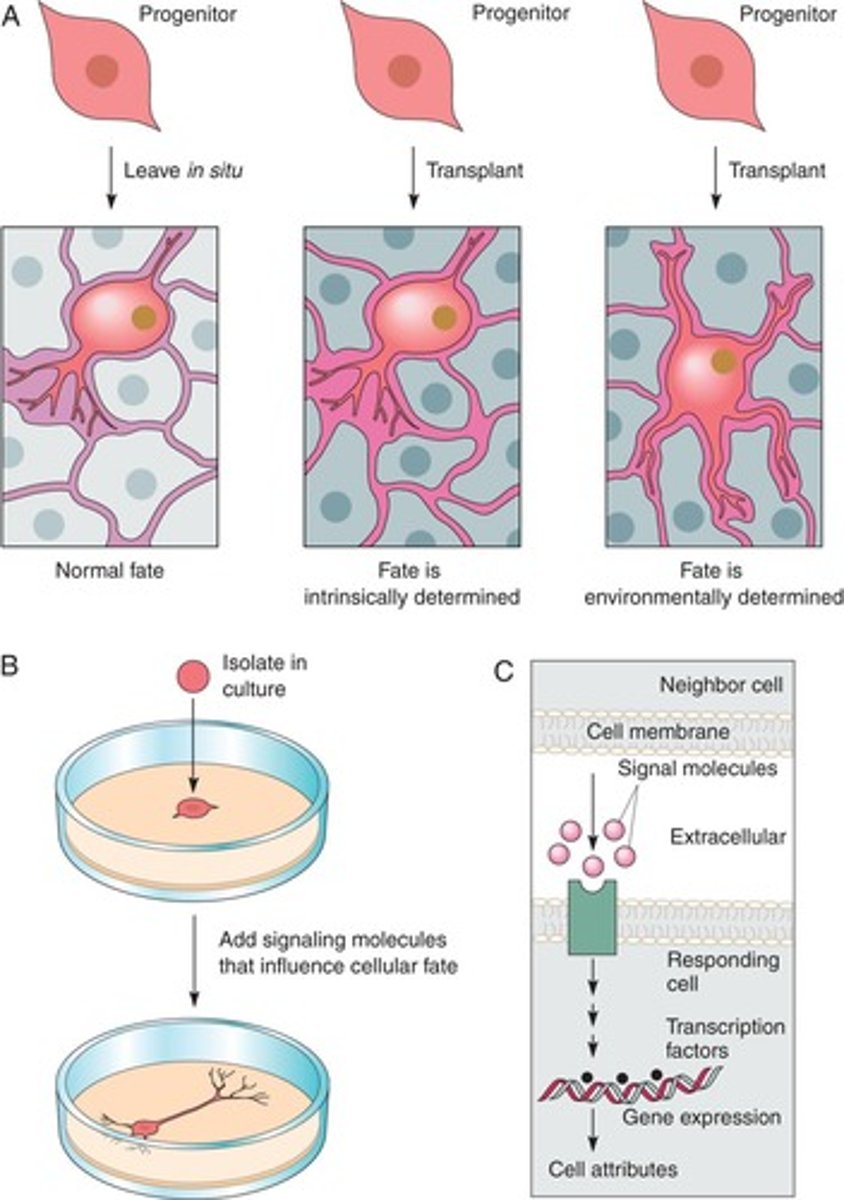
Intrinsic factors
Internal influences on cell fate determination.
Extrinsic factors
External influences affecting cell differentiation.
Cell fate plasticity
Ability of cells to change fate based on environment.
Intrinsic fate determination
Process by which neural progenitors develop specific identities.
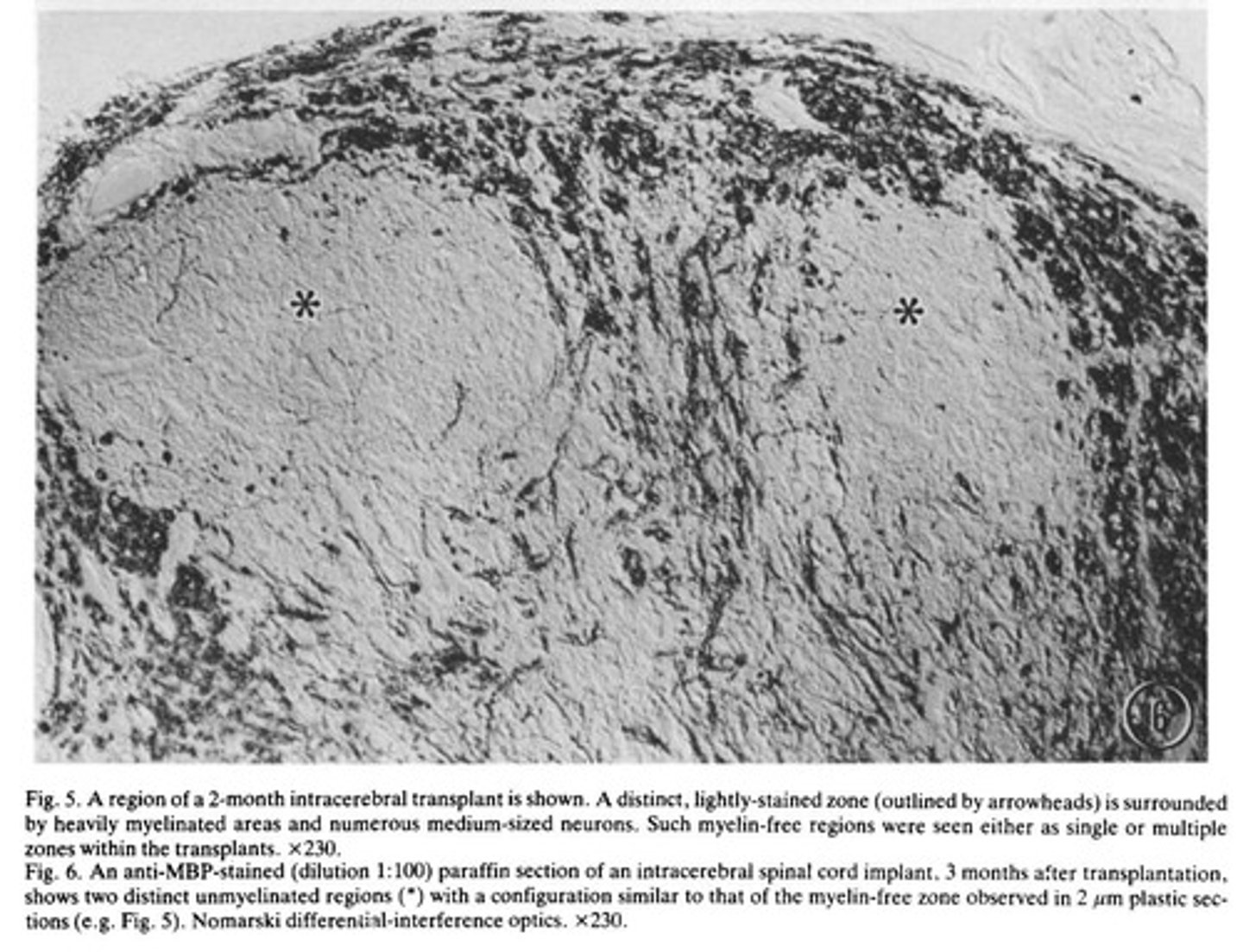
Fetal spinal cord transplantation
Transplanting fetal spinal cord tissue into adult hosts.
Graft survival
The ability of transplanted tissue to remain viable.
Cellular differentiation
Process by which cells become specialized in function.
Myelination
Formation of a myelin sheath around neurons.
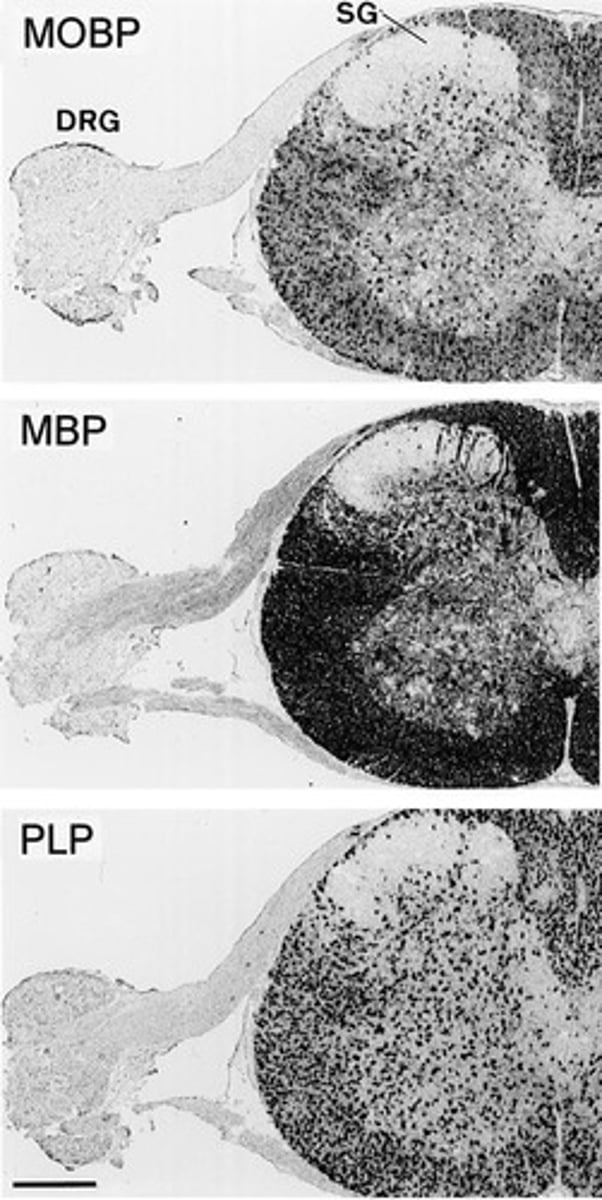
Neurons of different sizes
Diverse neuron types found in spinal cord transplants.
Ventral horn cells
Neurons located in the ventral part of the spinal cord.
Myelin-free regions
Areas in grafts lacking myelin, indicating specific neuron types.
Substantia gelatinosa
Region in the spinal cord associated with pain processing.
Topographical features
Spatial organization of neurons in the spinal cord.
Neural progenitor cells
Undifferentiated cells capable of developing into neurons.
Immunohistochemical markers
Techniques to identify specific proteins in tissue samples.
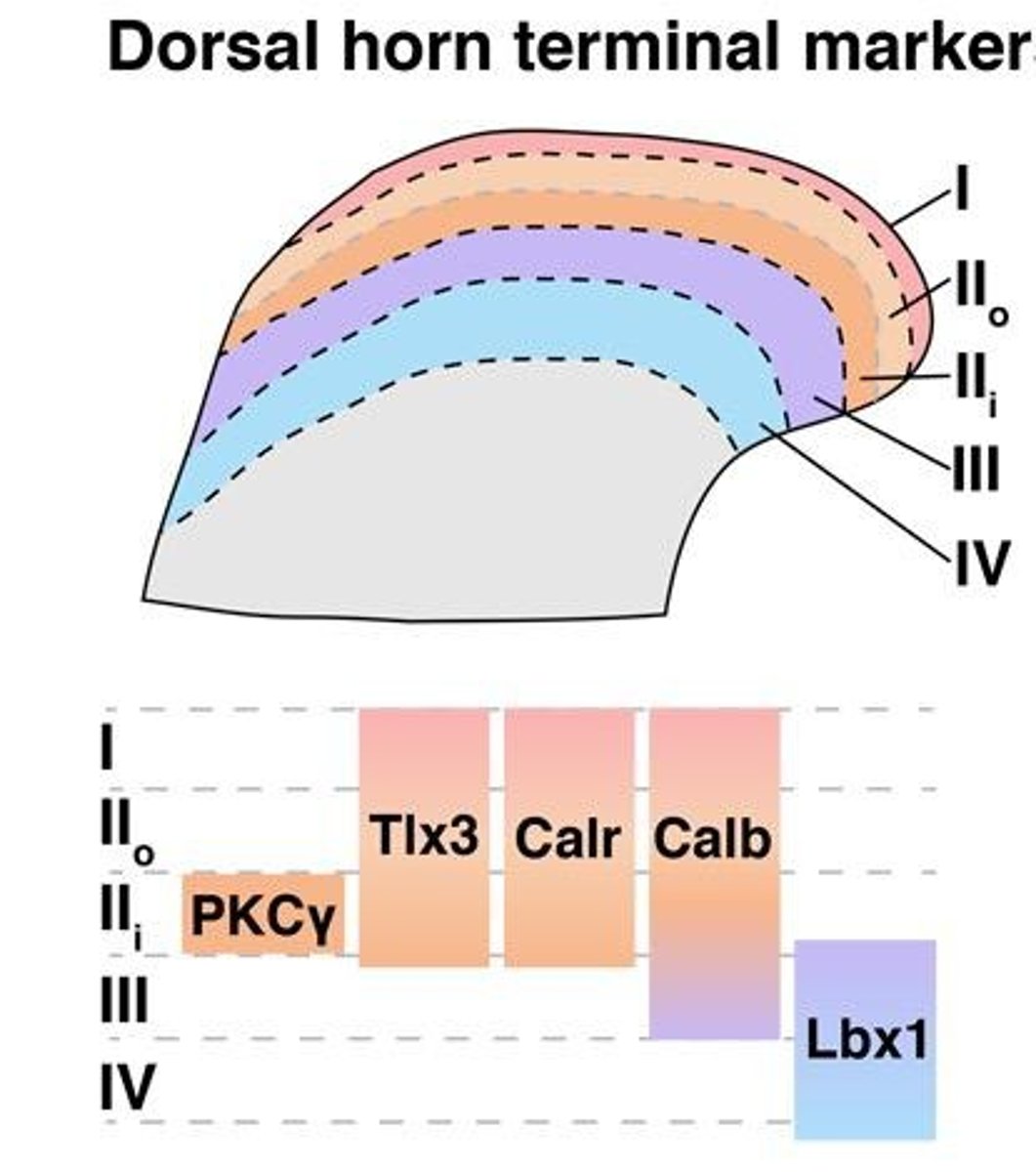
Dorsal horn neurons
Neurons located in the dorsal part of the spinal cord.
Laminae organization
Layered structure of neurons in the spinal cord.
Calbindin
Calcium-binding protein used as a neuronal marker.
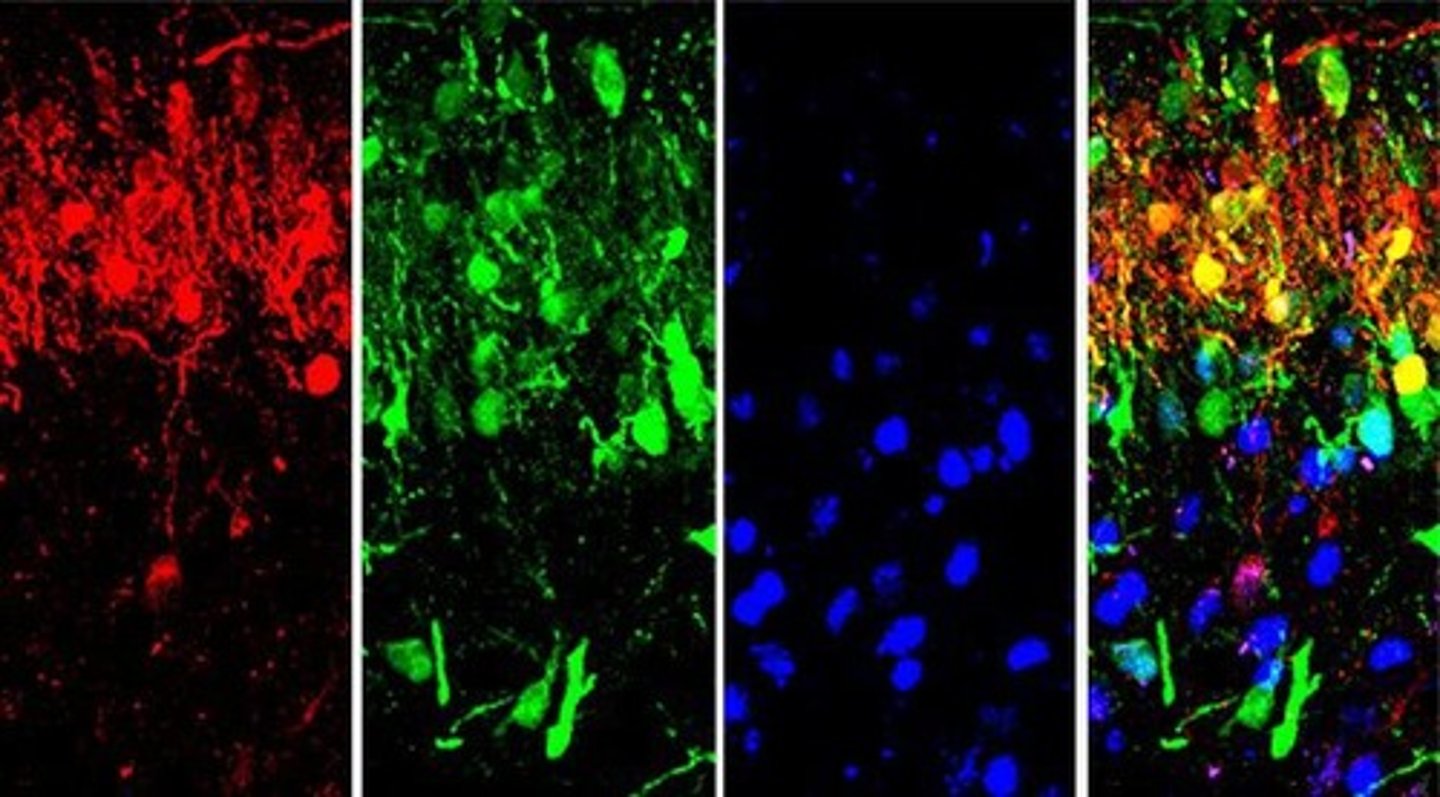
Calretinin
Calcium-binding protein indicating specific neuron types.
Lbx1
Transcription factor associated with spinal cord development.
Organotypic domains
Specific areas in grafts where neurons differentiate appropriately.
In vitro culture
Growing cells outside their natural environment for study.
Neuronal subtypes
Distinct classes of neurons based on function and markers.
Spinal cord injury
Damage to the spinal cord affecting neural function.
Neural regeneration
The process of regrowth or repair of nervous tissue.
Spinal cord neural progenitors
Cells with predetermined fates for spinal cord neurons.
Organotypic domains
Specific regions where progenitor cells differentiate.
Intrinsic factors
Internal determinants guiding cell fate decisions.
Extrinsic factors
Environmental influences affecting cell differentiation.
Calbindin
Calcium-binding protein, marker for certain neurons.
Calretinin
Calcium-binding protein, involved in neuronal signaling.
Lbx1
Transcription factor important for neuronal identity.
Pax7
Transcription factor crucial for muscle progenitor cells.
Olig2
Transcription factor for oligodendrocyte precursor cells.
Nkx2.2
Transcription factor involved in neural patterning.
Gradient-dependent induction
Differentiation influenced by concentration gradients.
Shh (Sonic Hedgehog)
Morphogen regulating neural tube development.
Mini dorsal horn
Organized structure mimicking spinal cord regions.
6 weeks in vivo
Time frame for observing graft integration.
Neural tube explants
Tissue samples used to study neural differentiation.
Diffusible morphogens
Signaling molecules that influence cell fate from distance.
Extracellular matrix components
Structural proteins affecting cell behavior and fate.
Notch signaling
Pathway influencing cell fate through lateral inhibition.
Transcriptional programs
Gene expression patterns determining cell identity.
Environmental factors
External conditions shaping progenitor cell differentiation.
Cell fate determination
Process by which cells acquire specific identities.
Olfactory epithelium
Specialized tissue with olfactory sensory neurons.
Olfactory sensory neurons
Neurons expressing odorant receptor genes (~1000).
Dorsal-ventral axis
Orientation of neuron subtypes in olfactory epithelium.
Rhinotopy
Spatial coding of olfactory sensory neuron targeting.
Olfactory bulb
Brain structure receiving input from olfactory neurons.
Stem cells of the OE
Multipotent cells in the olfactory epithelium.
Spatial patterning
Arrangement of neurons affecting axon travel.
TdTomato+ reporter mouse
Mouse model used for tracking transplanted cells.
Region-specific markers
Identifying dorsal (NQO1) and ventral (OCAM) OSNs.
Graft-derived OSNs
Neurons originating from transplanted olfactory tissue.
Ventral OSNs
Olfactory sensory neurons located in the ventral region.
Dorsal OSNs
Olfactory sensory neurons located in the dorsal region.