APES U4
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Decomposition
Long-term storage
Combustion
Ocean exchange
Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen fixation – Atmospheric N₂ is converted into ammonia (NH₃) or similar usable forms by bacteria or lightning.
Nitrification – Ammonia is converted to nitrites (NO₂⁻) and then to nitrates (NO₃⁻) by soil bacteria.
Assimilation – Plants absorb nitrates and build organic nitrogen; animals get it by eating plants.
Ammonification (decomposition) – Decomposers turn organic nitrogen from dead matter/waste back into ammonia.
Denitrification – Specialized bacteria convert nitrates back into N₂ gas, returning it to the atmosphere.
Phosphorus Cycle
Weathering of rocks
Uptake by plants
Animals get phosphorus by eating plants or other animals.
Decomposition – decomposers return phosphate to the soil or water.
Runoff & sedimentation
Water Cycle
Evaporation
Transpiration – Plants release water vapor from leaves.
Condensation
Precipitation – Water returns to Earth as rain/snow.
Infiltration/Runoff – Water soaks into ground (groundwater) or runs over land into bodies of water.
carbon sources and sinks
Carbon sources: respiration, decomposition, combustion
Carbon sinks: photosynthesis, ocean uptake, fossil fuels
Nitrogen sources and sinks
Nitrogen sources: nitrogen fixation, lightning, fertilizer production, decomposition
Nitrogen sinks:, soil organic matter, denitrification
Phosphorous sources and sinks
Phosphorus sources: rock weathering, decomposition, fertilizer runoff
Phosphorus sinks: plant uptake, soil storage, sediments, rock formation
Water sources and sinks
Water sources: evaporation, transpiration
Water sinks: oceans, glaciers, groundwater, lakes, soil
Population vs. Community
Pop - Group of individuals of same species at same time and place
Community - All the different pops of different species
Biotic vs Abiotic Factors
Abiotic - Nonliving factors that influence living organisms
Biotic - All the living organisms in an ecosystem that interact with one another
Range of tolerance
Range of conditions within which a species can survive grow and reproduce
Limiting Factors
Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts growth of a pop
Food Chain
A linear sequence showing how energy and nutrients pass from one organism to another in an ecosystem
Food Web
A complex network of interconnected food chains showing all feeding relationships in an ecosystem
Energy Flow
The one-way movement of energy through an ecosystem from producers to consumers and decomposers
Tropic Levels
producers → primary consumers → secondary consumers → tertiary consumers → decomposers
Producer example
Grass, algae
Primary Consumer example
Grasshoppers, rabbits
Secondary Consunmer example
Frogs, small fish
Tertiary Consumer example
Hawks, lions
Decomposers example
Fungi
Ecological efficiency
percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next
10% Rule
only 10% of energy is avalible to the next tropic level
10% rule formula
Ecological Efficiency: \frac{Energy_{}athigherlevel}{Energyatlowerlevel}\cdot100
GPP
Total energy captured by producers, represents all energy produced
NPP
Energy remaining after producers use some for respiration (R)
NPP = GPP-R
C and E of EL Nino
Causes: Weakened trade winds, pressure changes
Effects: Lower fish pops, reduced amounts of nutrient rich water, crop failures, increased risk of disease outbreaks
Genetic Biodiversity
Variation of genes within a species
Species Biodiversity
Variety of species in a particular ecosystem or globally
Ecosystem Diversity
Variety of ecosystems in a region or the planet
Species Richness
The number of different species present in a given area or ecosystem
Demographic Bottleneck
A sharp reduction in the population size of a species due to environmental events or human activities, leading to reduced genetic diversity
Island Biogeography
Larger island - more species, lower extinction rates
Islands closer to mainland - more species
Species Equlibrium - Species richness reaches a equlibrium, immigration rate - extinction rate
Symbiosis Types
Mutualism: +/+
Commensalism: +/0
Parasitism: +/–
Amensalism: –/0
Neutralism: 0/0
Resource Partitioning
similar species coexist in the same habitat by dividing resources so they don’t directly compete
Describe Competitive Exclusion Principle
two species competing for the same limited resource cannot coexist indefinitely in the same niche
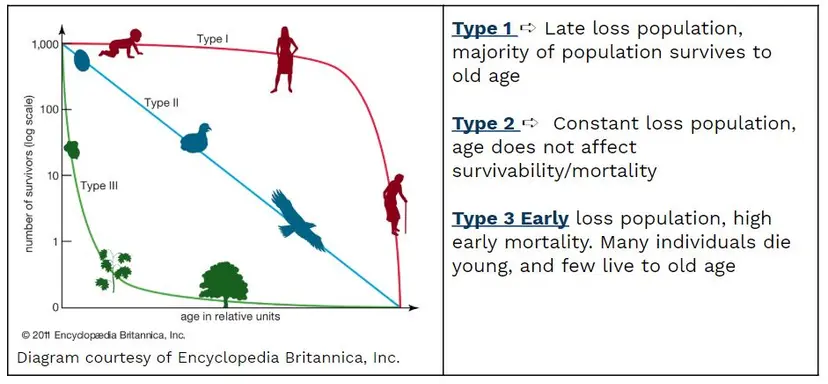
Identify types of Survivorship curves
Calculate change in Population Growth
change in pop = (#BIRTHS-#DEATHS)+(#IMMIGRANTS-#EMIGRANTS)
Keystone Species
A species that has a large effect on its ecosystem, disproportionate to its abundance
Indicator Species
A species sensitive to environmental changes, signaling ecosystem health
R-selected Species
Species that reproduce quickly, have many offspring, and little parental care
K-selected Species
Species that reproduce slowly, have few offspring, and high parental care
Characteristics of Successful Invasive Species
rapid repro, broad diet, tolerance to wide env conditions. areas w/low biodiversity more prone
Describe characteristics of species prone to extinction
Small pop size, small geographic area, specialized
Describe solutions to Endangered Species
Control of invasive species, habitat protection, captive breeding