Midterm — Branding Based on Presentations
“brand”- Old nurse word. MEANING
Brandr. It means “to burn”
Used to identify this is my cow, sheep, or nowadays these are my designer shoes
Definition of a brand
A brand is a name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a
-combination of them,
-intended to identify the goods and services of one seller or group of sellers and
-to differentiate them from those of competition
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards of key terms and definitions from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
“brand”- Old nurse word. MEANING
Brandr. It means “to burn”
Used to identify this is my cow, sheep, or nowadays these are my designer shoes
Definition of a brand
A brand is a name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a
-combination of them,
-intended to identify the goods and services of one seller or group of sellers and
-to differentiate them from those of competition
Brand elements
Name, Sign / Symbol, Design, Tagline or slogan, Positioning, Brand Voice
What does Airbnb represent (identity)
Belonging, connecting, Sharing, safety, A home away from home, Be a local anywhere

Core benefit
Basic need or want that the customer satisfies when they buy the product
Values
The brand represents the company’s values or belief system
Brand Positioning
-A short statement that identifies your unique value to your clients and your promise to them
-It should set the expectation in your customer’s mind
Brand positioning
It is about owning a unique space in the minds of your customers
Crucial when you have a lot of competition
Established relative to that competition
Expresses the value of the brand for your customers and potential customers
Price
Focus on how you offer market-leading value
Quality/ Luxury
The quality of your product is more important than its price
Challenger
You take advantage of your underdog position in the market
Brand Voice
It is there every time your company speaks
Use
The way your product is used can help you find a point of differentiation, a unique audience, and memorable brand positioning

Creator
Desire: Create the perfect product/services
Goal: Innovation
Strategy: Use creativity to solve problems
Brand Message: “Be original”
Traits: Innovation, Originality, Expression, Vision, Individuality
Fears: Stagnation, Duplication, Familiarity, Disillusion, Indifference

Sage
Desire: Find the Truth
Goal: Understanding
Strategy: Seek information and knowledge
Brand Message: “The truth will set you free”
Traits: Wisdom, Intelligence, Expertise, Information, Influence
Fears: Lies, Misinformation, Ignorance, Inaccuracy, Stupidity

Caregiver
Desire: Care, Protect and nurture
Goal: Helping others
Strategy: Do things for others
Brand Message: “Treat others as yourself”
Traits: Compassion, Caring, Reassuring, Nurturing, Warm
Fears: Helplessness, Selfishness, Ingratitude, Instability, Neglect

Innocent
Desire: Love, Peace, and happiness for all
Goal: Happiness
Strategy: Do the right thing
Brand Message: “The glass is half full”
Traits: Optimistic, Charming, Honest, Loyal, simplistic
Fears: Depravity, Deceit, Complexity, Punishment, Confusion
Jester
Desire: Enjoy life and have fun
Goal: Entertainment
Strategy: Be playful, be fun
Brand Message: “If you’re not having fun you’re doing it wrong”
Traits: Playful, humorous, Positivity, Togetherness, Funny
Fears: Boredom, Negativity, Seriousness, Gloom, Misery

Magician
Desire: Turn dreams into reality
Goal: Magical Moments
Strategy: Create a unique vision and stand by it
Brand Message: “Make the impossible, possible”
Traits: Transformational, Charisma, Imaginative, Idealistic, Insightful
Fears: Repetition, Boring, Stagnation, Doubt, Ignorance

Ruler
Desire: Control
Goal: Success
Strategy: Lead and create exclusivity
Brand Message: “Power is everything”
Traits: Power, Status, Success, Wealth, Loyalty
Fears: Losing power, being undermined, rule breakers, rebels

Hero
Desire: Mastery
Goal: Improve the world through courage
Strategy: Motivate and encourage
Brand Message: “Where there’s a will there’s a way”
Traits: Bravery, Courage, Honor, Inspiration, Growth
Fears: Weakness, incapability, injustice, cowardice, incompetence

Everyman
Desire: Connection with others
Goal: Belonging
Strategy: Down-to-earth and trustworthy
Brand Message: “Live together in harmony”
Traits: Dependable, Realistic, Pragmatic, Inclusive, Equality
Fears: Exclusion, Standing out, Hostility, Isolation, Separation

Rebel
Desire: Revolution
Goal: Disruption
Strategy: Shake things up and do things differently
Brand message: “Rules are made to be broken”
Traits: Disruptive, Liberator, Confrontational, Independent, Change
Fears: Conformity, Rules, Repetition, Rigidity, Status Quo

Explorer
Desire: Freedom of discovery
Goal: Excitement and fulfillment
Strategy: Take your own path
Brand message: “Seek out new things and set yourself free”
Traits: Discovery, Adventure, Independence, Exploration, Pioneering
Fears: Aimlessness, Safety, Confinement, Short Sightedness

Lover
Desire: Connection
Goal: Intimacy
Strategy: Be desirable
Brand Message: “Love makes the world go round”
Traits: Passionate, Sensual, Romantic, Affectionate, Indulgent
Fears: Rejection, Isolation, Loneliness, Unloved, Invisible
Pre-purchase
Points of contact with the brand BEFORE completing a purchase
Advertising
Public Relations
Social media
Website and online presence
Purchase
Points of contact with the brand THROUGHOUT the actual purchase process
Packaging
Welcome kit
Environment
Check-out, offline, and online
Staff
Post-purchase
Points of contact with the brand AFTER completing a purchase
Loyalty programs
Customer service
Product experience
Follow-up
Brand culture
The set of values and beliefs that a company cultivates to make the brand come alive for customers
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
The continuing commitment by businesses to contribute to economic development while improving the quality of life of the workforce and their families, as well as the community and society at large.
CSR
Public responsibility and private enterprise
Public Responsibility
- Private companies entering “public” areas
-Beyond traditional CSR
Strategies that firms develop to address public problems in the absence of effective governmental infrastructure or process
Owned
Online media that an organization owns and controls
Paid Media
Online media where you pay to appear
Earned
Stakeholder-generated word-of-mouth
The PARC principles of success
Participatory, Authentic, Resourceful, Credible
Disruptive marketing
Disruptive marketing is about challenging and reshaping traditional marketing practices to stand out in the industry
What connects and touches everything? GIVE THE 4
The BRAND.
Brand concept.
Brand Attributes.
Customer Journey
Products and Services
What are the definitions of brand Direct Identification
This product is manufactured by X
Consistent experience
I know what to expect, decisions made easy
What are the definitions of Identification with the brand itself:
This brand is about X
This brand is for people like me
This brand will make me feel sexy, successful, cool, rich, free…
Brands make you feel stuff: design + experience + advertising + other people’s opinions
LINK between the BRand with the Idea
Your brand must embody an idea
This idea must have emotional resonance to be memorable
The brand will help you stand out
The brand will help you sell
Its elements must be aligned with the big idea
Product vs brand- Give the name of the Theory
Kolter’s 5 Levels of Meaning for Products
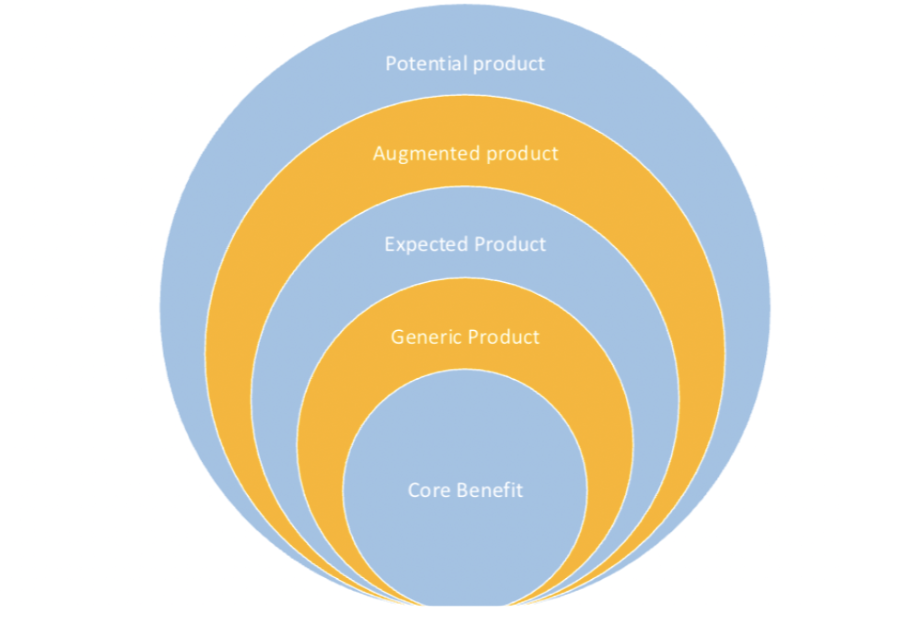
NAME Kolter’s 5 Levels of Meaning for Products
Core Benefit
Generic Product
Expected Product
Augmented product
Potential product

Generic Product
Basic version made up of only those features necessary for it to function

Expected product
Additional features that the customer might expect

Augmented product
Variations or extra features to help differentiate from its competitors
Potential product
Improvements the product could have in the future
Name the Six dimensions where you can anchor a brand
1.Product benefits
2.Intangible attributes
3.Culture
4.Personality
5.User emulation
6.Values

Definition of Product benefits
You base your brand on the most attractive benefits of your offering

Definition of Intangible attributes
You associate yourself to one or more intangible attributes

Definition of Culture
A brand chooses to represent the customer’s social/cultural features

Definition of Personality
A brand adopts personality patterns of the consumers it targets

Definition of User emulation
A brand emulates its users-imitates or copies. embodies values

Definition of Values
The brand represents the company’s values or belief system

Brand equity = brands have value
A value premium that a company generates from a product with a recognizable name when compared to a generic equivalent
Steps to create your brand positioning:
Who - You are targeting
What - Is the need you are serving
Why - Your audience should believe you
Positioning strategies
Price
Characteristics
Use
Quality/ Luxury
Challenger
Characteristics
Focus on one or several of your product/service features
Carl Jung (1875-1961) WHO IS HE
A pioneer in Psychology
Studied the structure of our mind
CARL JUNG studied Brand Archetypes
How we perceive and classify things
It determines how:
We see the world
We see others and ourselves
We behave as persons and as consumers
Brand archetypes → they fit into pre-shaped areas of our brain
What do brands use research for?
Thoughts
Feelings
Images
Perceptions
Attitudes
Use
STUDY NAME FOR Market Research
The Mason Haire Study of 1953
The Mason Haire Study of 1953
Nestlé related to lazy
Another example of Study for Market research
The New Coke fiasco of 1985
Benefits of Brand research
Take the guesswork away
Make informed decisions
Actionable insights
Be aware of shifts in consumer attitudes and trends
Shape, manage and grow your brand
Types of research
Qualitative
Quantitative
Qualitative Research
for insights
Uncover consumer insights
Explore opinions, experiences, attitudes
Creative
Multiple methods
No statistical significance
Non-numerical data
Open to different interpretations
Not scientific
Main Methods Qualitative Research
Qualitative Good or Bad Questions
Quantitative Research
for confirmation
Objectively collect numerical information
Use it to test a theory, to prove or disprove it
Mathematical, statistical significance
Allows for rapid analysis
Limits participants' opinions and reactions
Findings are influenced by the context
Likely to reflect the assumptions you bring to the research
Smaller samples may not be accurate
Quantitative research main methods:
Survey Research
Descriptive Research
Survey Good questions
Brand Territory:
The place a brand occupies in the minds of consumers, based on a company’s values, expectations of its customers, and communication
To define it, brands establish distinctive communication elements or touchpoints (logo, slogan, editorial line, etc.)
Brand territory is a key differentiating factor
Based on the long term
Brands must follow it over time to build a solid awareness
can be a tangible or an intangible space
What are the market’s expectations?
Examine the competitive landscape
Is there a place in it that your brand can claim?
How do customers think about a certain market?
Can you create a new space?
Can you leverage social trends?
Lots of research required
What is the brand’s DNA?
What’s your brand about?
What do you want to achieve in your market?
What do you offer?
What is your look & feel?
How are you different?
How do you communicate your brand to the market?
Visuals
Speech: tone, words
Communication strategy
Relationship with customers
Social media presence

Brand manifesto
An emotionally charged statement
A brand tells what their customer can expect (and can’t)
What you stand for (and what you won’t stand for)
They are memorable, not bland
They feel personal
They inspire or revolt
They make the brand powerful and vulnerable at the same time
How do you write a manifesto?
Start with why
Paint a picture of a different world
Make it your rallying cry
Make people (your customers) care
Start with why
We are X
We believe in Y
And that is why we do Z
Paint a picture of a different world
How would you like our world to be different?
Make it your rallying cry
Not just a piece of prose
The anger of an activist
The beauty of a story
The hope of a vivid dream
A call to action
Make people (your customers) care
Understand your customers
Speak to their challenges and aspirations
Write in a collective voice: you, we, them
Brand touchpoints
Brand touchpoints are any engagement or communication between a company and its customers.
The brand creates touchpoints in order to deliver the best possible experience
Some touchpoints are carefully managed by the brand, who anticipates its customers’ journey
Others are “involuntary”
Brand touchpoints and customer journey: a restaurant
Social media review
Website to see the place and make a reservation
Restaurant entrance sign
Interior decor
Menu
Uniforms
Hospitality and service
Post-visit survey
Why are brand touchpoints important?
They create a good customer experience (a bad experience affects the brand’s reputation and performance)
Increased customer loyalty and word of mouth: more sales
Increased brand awareness and reputation
Collect data and customer feedback
Stand out from competitors
Gain a competitive advantage
What does Brand Culture do?
It shapes the actions and decisions of every member of the organization
Impacts managers and employees alike
Framework for relationships, communication, and performance
Provides orientation and clarity
Impacts productivity, employee morale, and reputation
REMEMBER THE HOW
Advantages of a strong brand culture
Attracts the best talents
Better work environment
Better employee motivation: a sense of community and purpose
Better products and services
More customer loyalty: shared values
How to build your brand culture
Start by defining (or using) your values.
Communicate your values to employees and customers.
Lead by example:
Empower your employees to make culture come true:
Take action
Measure and evaluate
Challenges OF CSR
If your organisation is not a “responsible citizen,” it may lose its “legitimacy” to operate (clients, authorities, investors…)
People are sensitive to how companies behave and punish those who don’t seem to be doing the right thing
Opportunities OF CSR
Having the respect of the communities you operate in is good for business
It is about doing CSR work and communicating it well
The triple bottom line of CSR
People
Considers employees: fair wages, humane working conditions, “giving back” to people in the community (school, grants…)
Planet
Considers the environment: less waste, reduced emissions, improved logistics….
Profit
Finding ways to make a profit without being in contradiction with the other two
CSR approaches
DEFENSIVE:
CHARITABLE:
PROMOTIONAL:
STRATEGIC:
TRANSFORMATIONAL
DEFENSIVE CSR
Ad hoc investment in social or environmental practices
Example: you reduce your waste to avoid regulation or a fine
Responsibility: Public Affairs team
Primary stakeholders: shareholders and governments
CHARITABLE STAKEHOLDERS
The organisation supports local charities or programmes
Example: donations and sponsorships, but a limited approach
Responsibility: Community Relations team
Primary stakeholders: local communities
PROMOTIONAL CSR
The organisation sees its CSR only as a way to enhance its reputation
Danger: staying in the surface (supporting an environmental group while continuing to pollute a river)
Responsibility: PR and events managers
Primary stakeholders: the general public
STRATEGIC CSR
The organisation looks for the social and environmental issues that connect with its strategy and core business operations
Not tactical or local
Example: fair trade practices for a coffee maker. Creates codes and management systems and reports them regularly
Responsibility: spread across the organisation
Primary stakeholders: the general public
TRANSFORMATIONAL CSR
The organisation focuses its activity on the root causes of sustainability & social responsibility
Invent business models and products to change society
Example: Unilever Sustainable Living Plan
Responsibility: spread across the organisation, including the brand
Primary stakeholders: current and future generations
What are community relations?
A specific part of a company’s CSR
Relates to engagement with the local communities in which your company operates
If badly managed, it can have negative consequences for your reputation
Old and new approaches to Community Relations
Philanthropy (prior to 1980)
Volunteer programmes (1980 - 90)
Partnerships (1990 - Present)
Philanthropy (prior to 1980)
Cash contributions to local charities
They send a strong symbolic signal that the company cares about the community