L8// Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Structure, Function, and Cell Communication
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
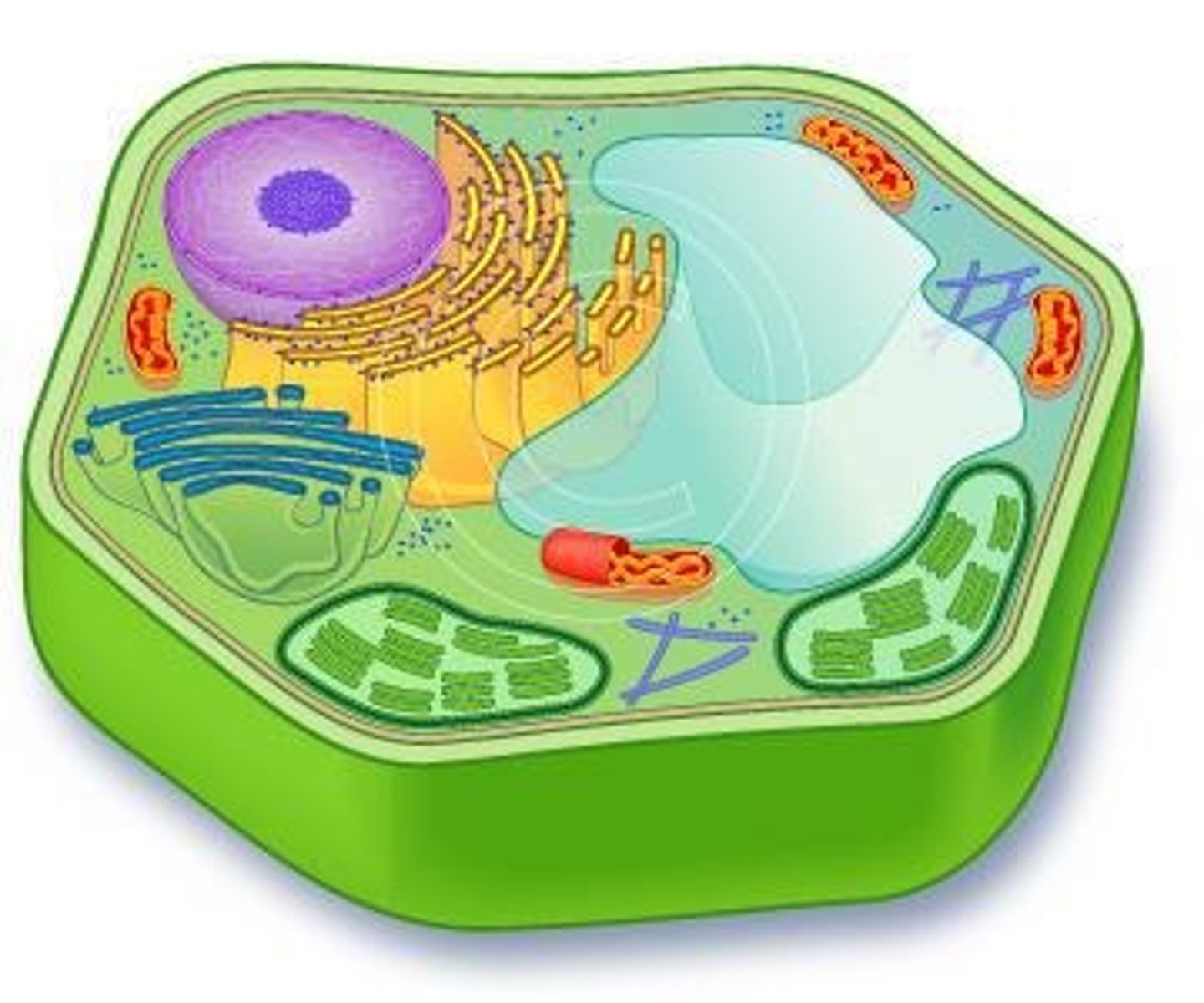
What are the main characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
- lack a membrane-bound nucleus
- lack membrane-bound organelles
- unicellular
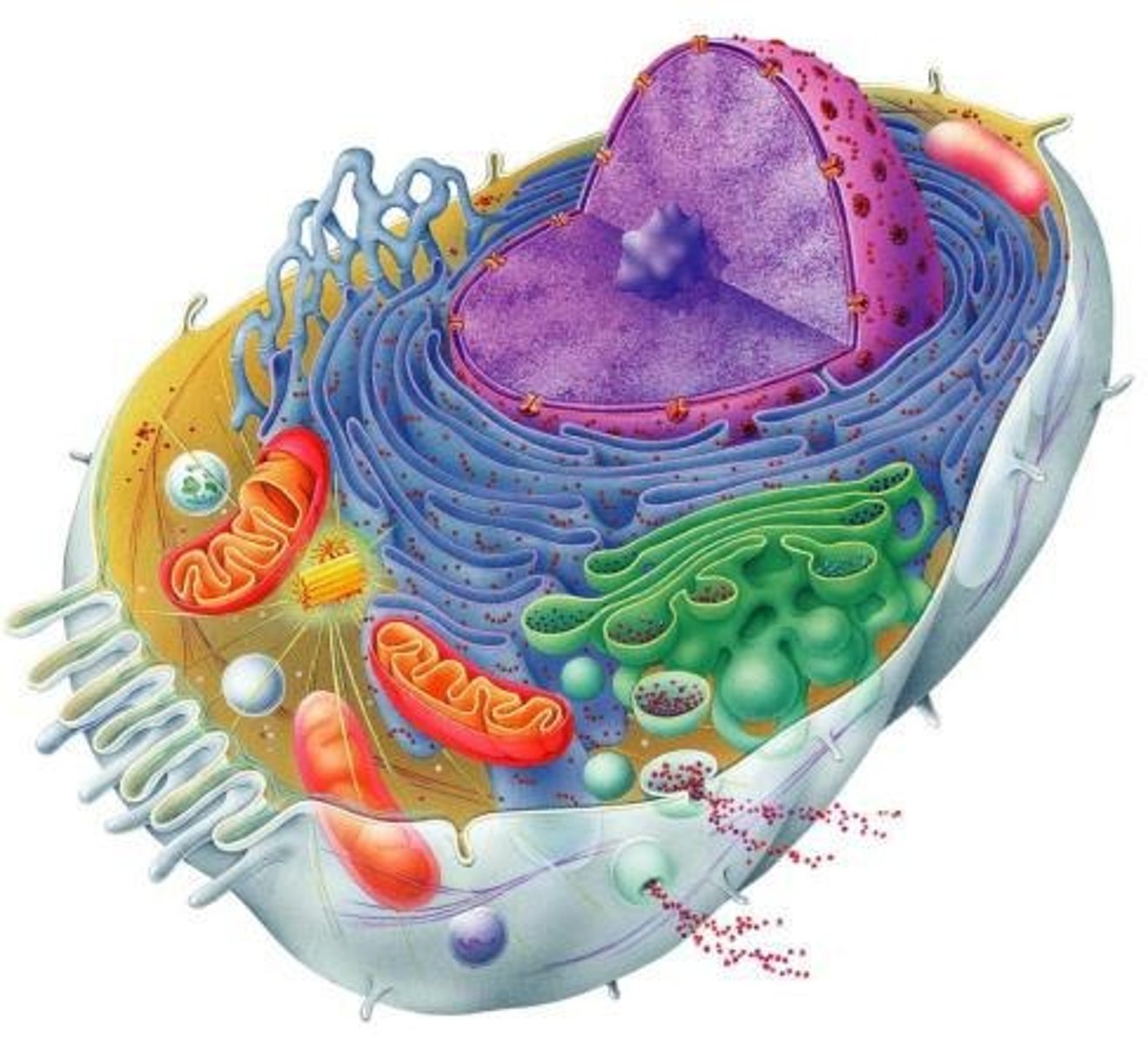
What are the main characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
- have a nucleus
- have membrane-bound organelles
- unicellular or multicellular
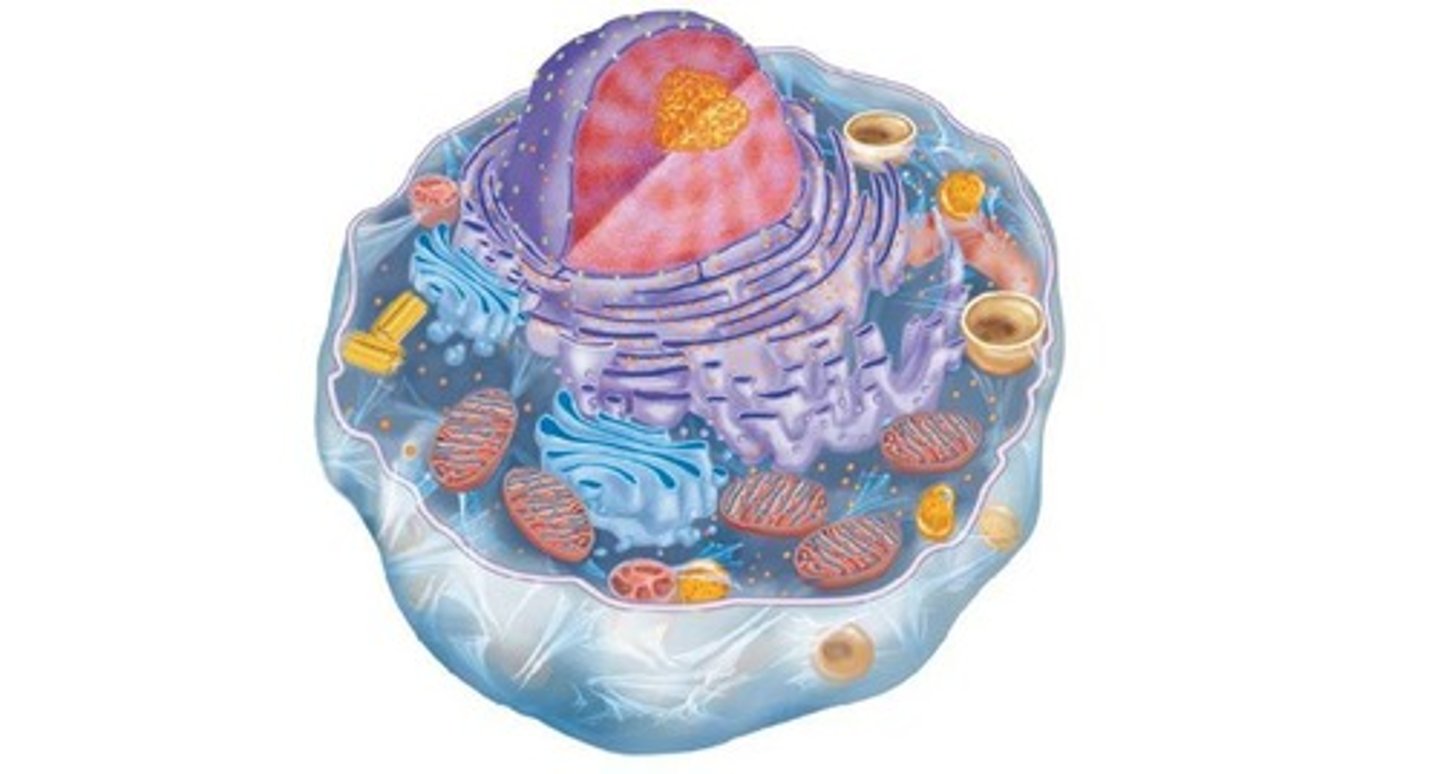
Name a type of eukaryotic cell and its unique structures.
Animal cells
- lysosomes
- centrioles
What structures are found in plant cells but not in most animal cells?
- cell wall
- chloroplasts
- large central vacuole
What is the function of the endomembrane system in eukaryotic cells?
connects all internal membranes of the eukaryotic cell
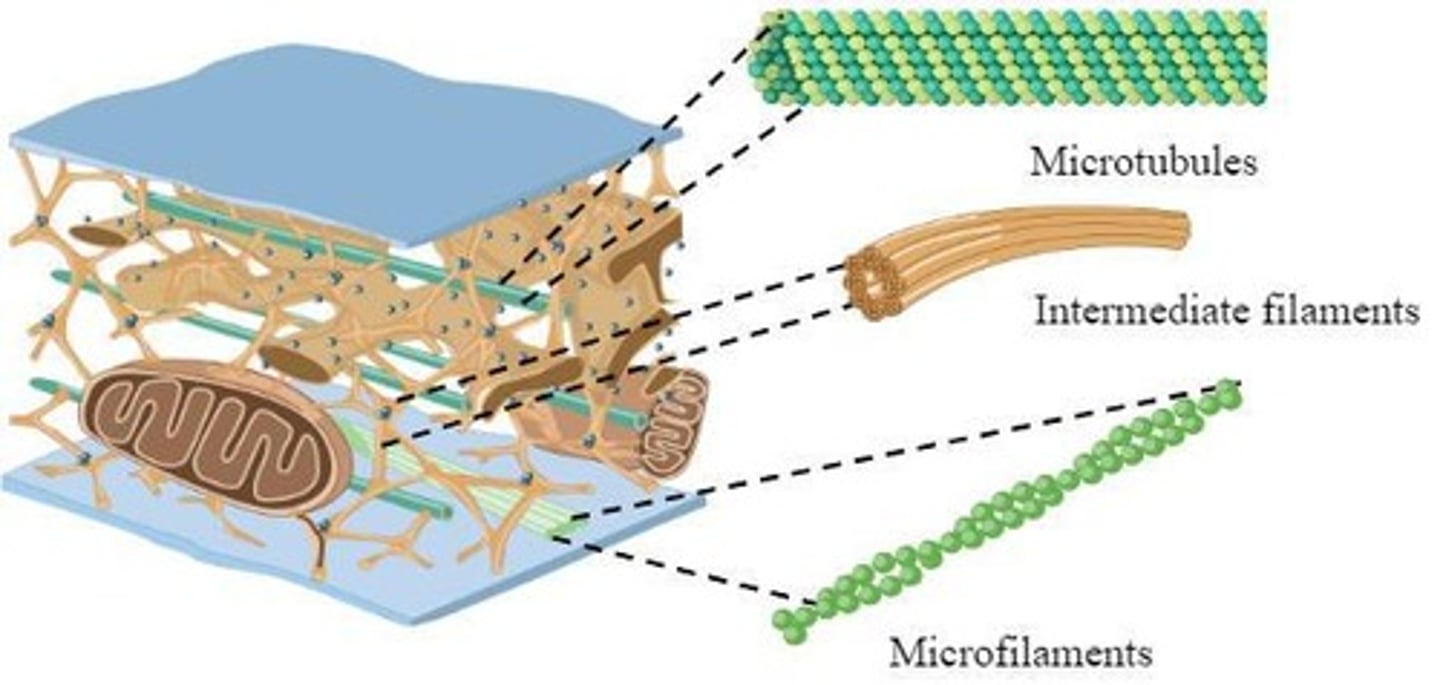
What role does the cytoskeleton play in a cell?
- provides structure
- serves as tracks for movement within cell
What is the extracellular matrix (ECM) and its function?
- integrates cell into tissue
- provides strength and resiliency
- assists in cell signaling
What are integral proteins and where are they found?
- embedded in the lipid bilayer
- can penetrate its hydrophobic interior
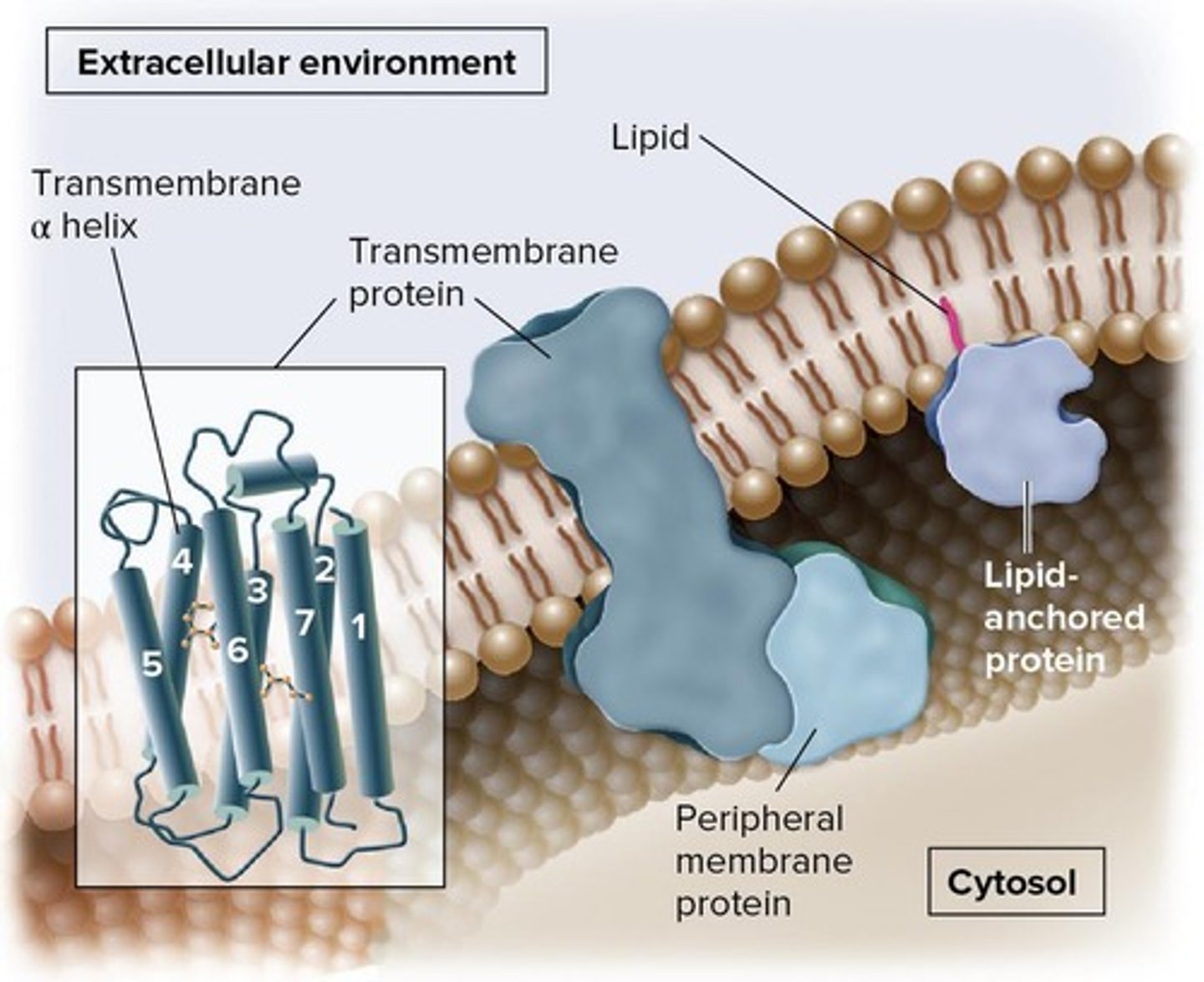
What are the six major functions of membrane proteins?
1. Transport
2. Enzymatic activity
3. Attachment to cytoskeleton and ECM
4. Cell-cell recognition
5. Intercellular joining
6. Signal transduction
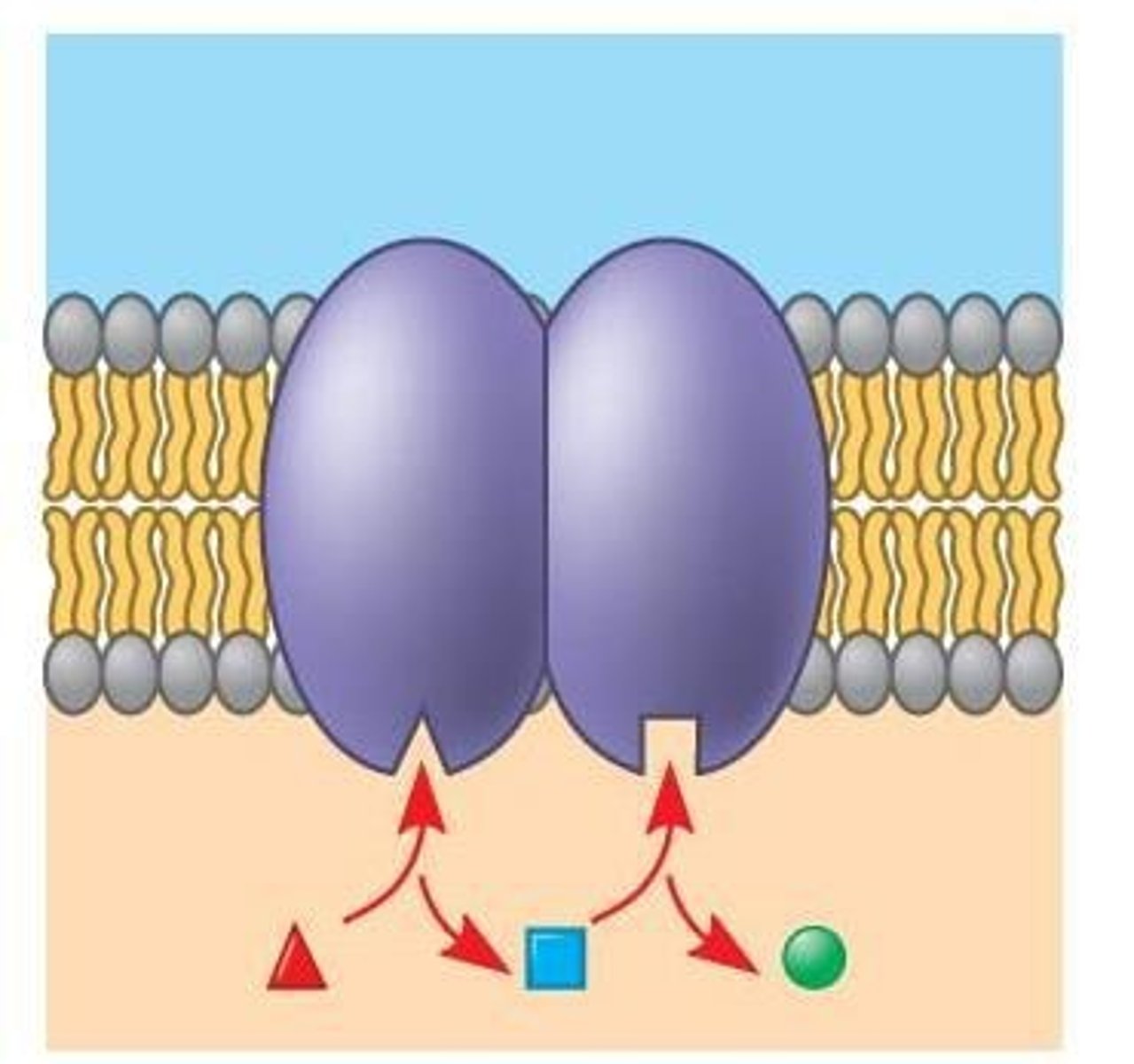
How do transport proteins function in cell membranes?
allow passage of hydrophilic substances across membrane
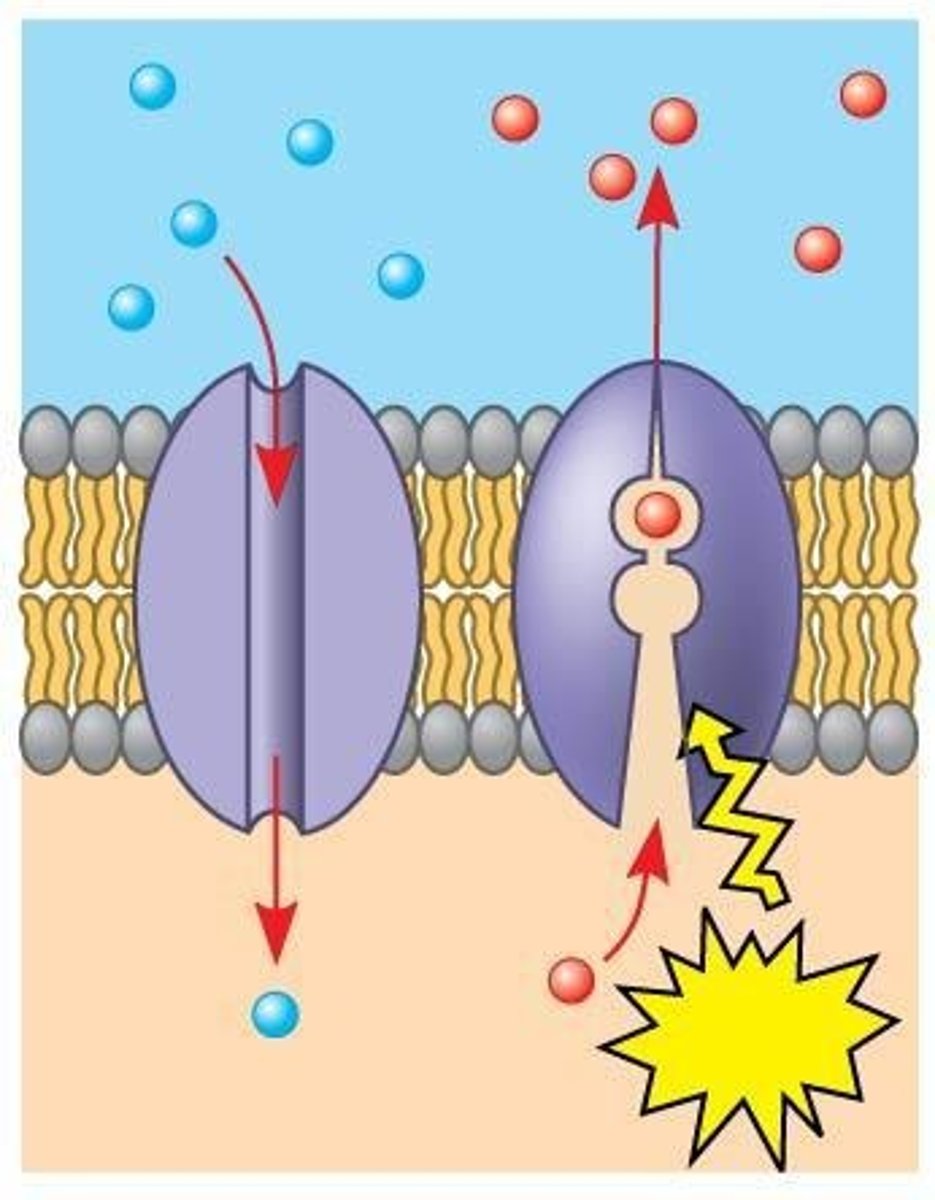
What is passive transport and what does it involve?
- moves materials down concentration gradient without energy input
- involves diffusion and facilitated diffusion
What is active transport?
moves materials against their concentration gradient
requires energy (ATP)
What is facilitated diffusion?
passive movement of molecules across membrane by transport proteins
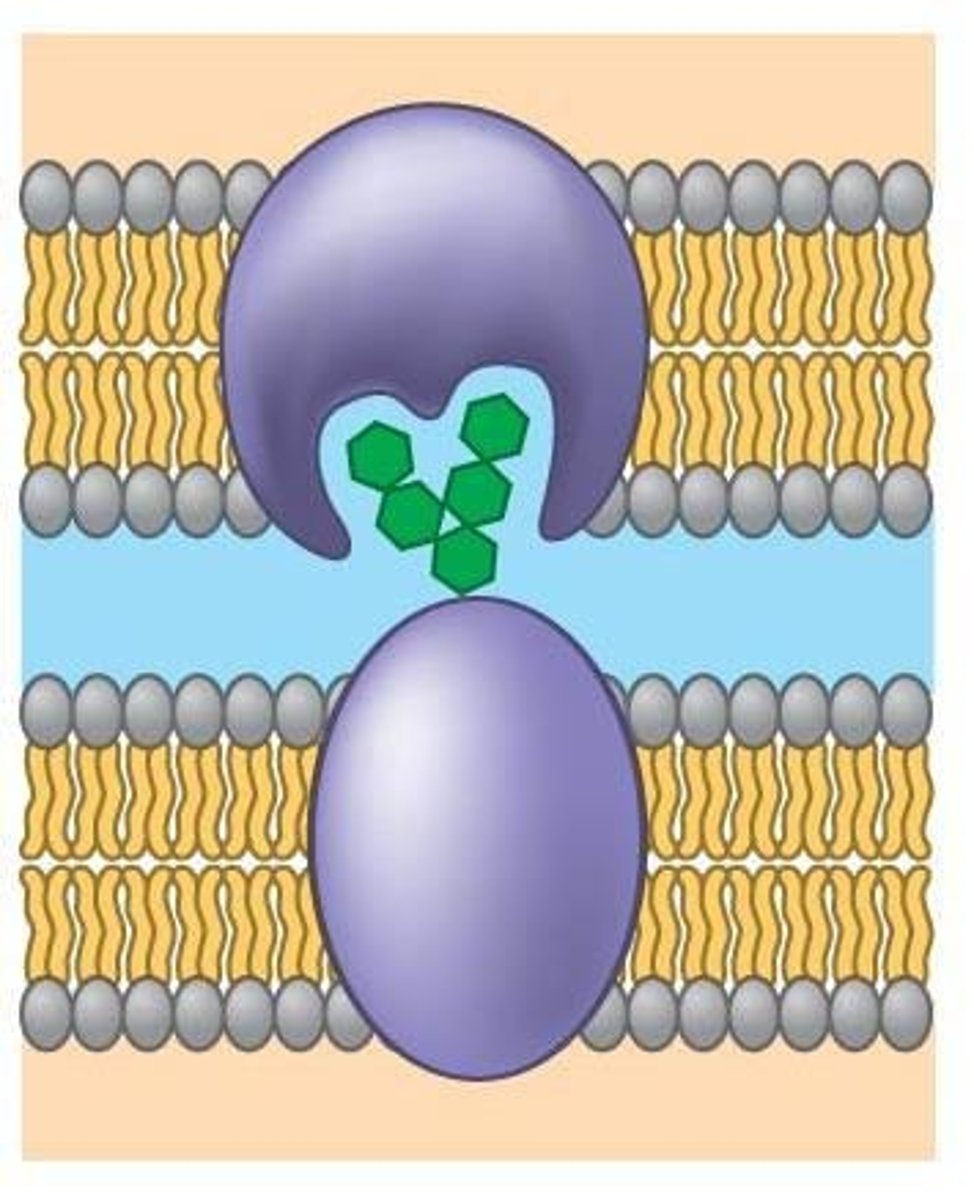
What are channel proteins and their role?
provide corridors for molecules or ions to cross membrane
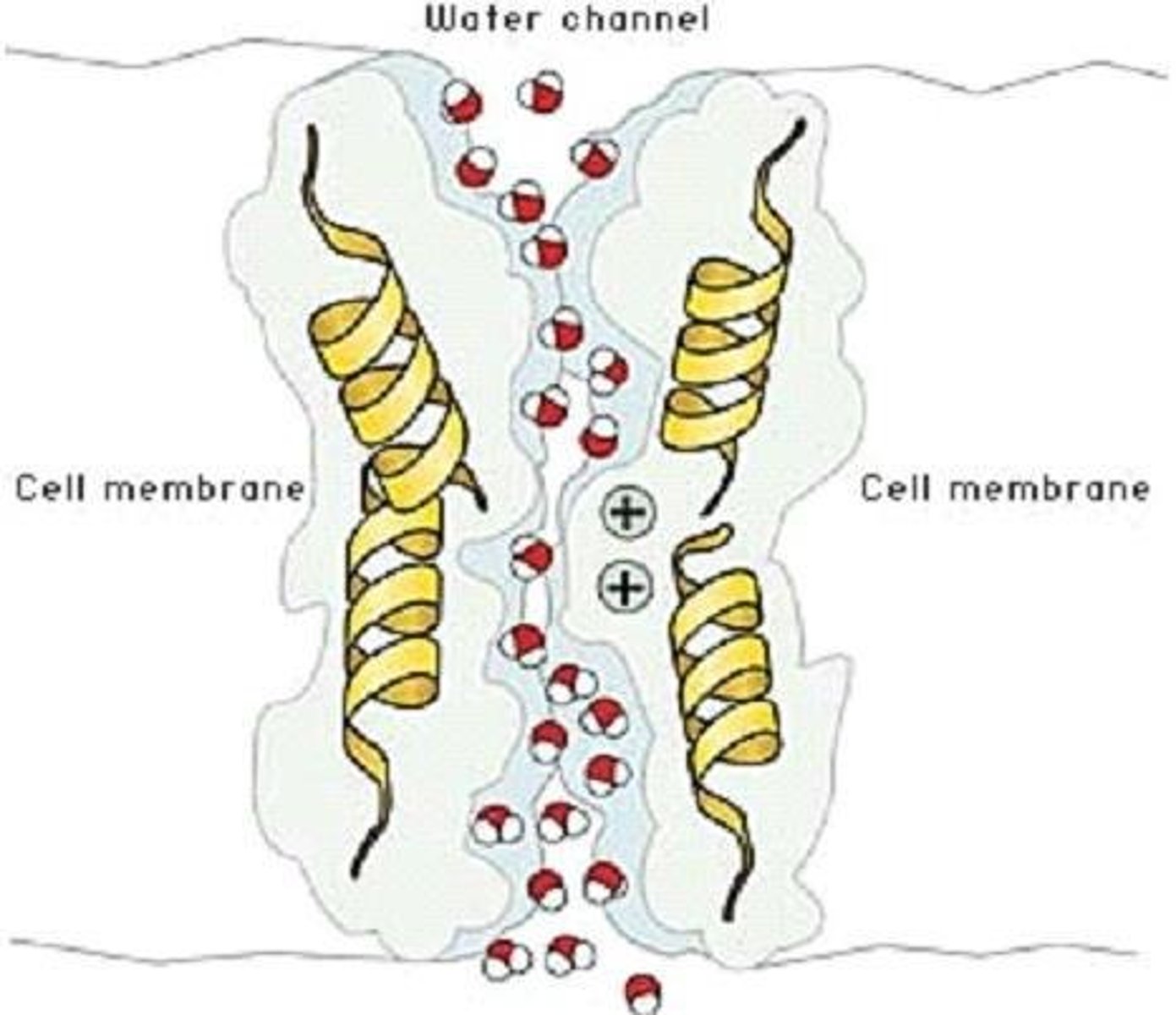
What are aquaporins?
channel proteins that facilitate passage of water across cell membranes
What is the role of glycoproteins in cell membranes?
- serve as ID tags
- recognized by proteins on surface of other cells facilitating cell-cell recognition
What is the significance of the nuclear envelope in eukaryotic cells?
surrounds the nucleus
separates it from cytoplasm
What is the function of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells?
protein synthesis
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
- modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to organelles
What is the role of lysosomes in animal cells?
- contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cell debris
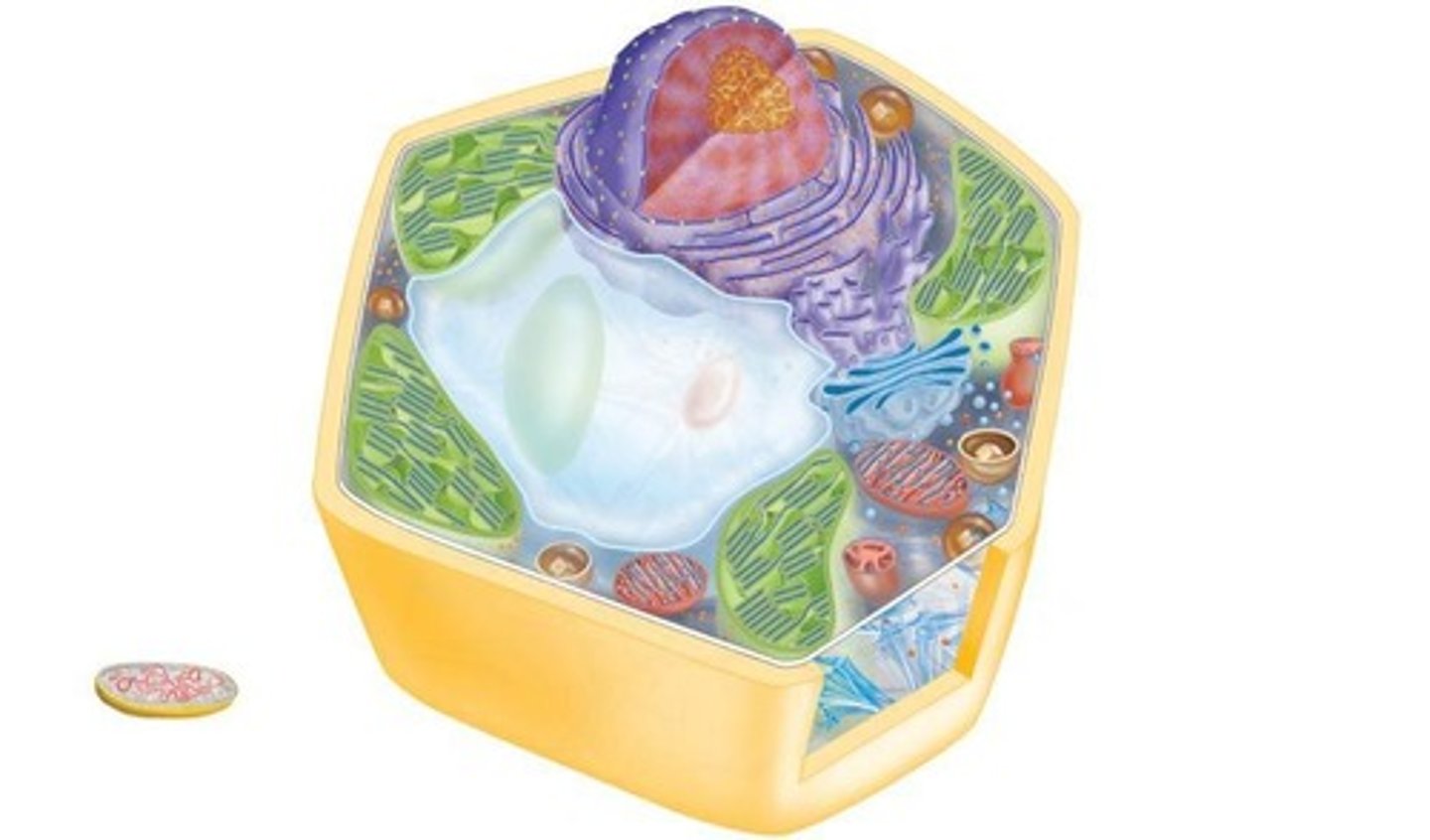
What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy

What is the function of vacuoles in plant cells?
- store nutrients and waste products
- help maintain turgor pressure in plant cells
What are gated ion channels?
channels that open or close in response to a stimulus
What is passive transport?
facilitated diffusion by proteins without energy investment
How do carrier proteins function in facilitated diffusion?
they undergo a shape change that translocates solute-binding site across membrane
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
active transport system that exchanges Na+ for K+ across cell membrane
What is membrane potential?
voltage across a membrane created by differences in the distribution of positive and negative ions
What is an electrogenic pump?
- transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane
- ex.) sodium-potassium pump in animal cells
What role do proton pumps play in plants, fungi, and bacteria?
- main electrogenic pump
- generates a proton gradient for cellular work
What is cotransport?
active transport of one solute indirectly drives transport of another solute against its gradient
What is secondary active transport?
- aka cotransport
- diffusion of one ion provides the energy to move another ion against its gradient
What is a symporter?
a type of cotransporter that moves solutes in the same direction
What is an antiporter?
a type of cotransporter that moves solutes in opposite directions.
How do local signals function in cell communication?
- secreted by a specific cell type and travel short distances
- ex. ) neurotransmitters between neurons
What is an example of long-distance signaling?
hormones released from brain travel through bloodstream to stimulate distant target cells
What triggers the release of neurotransmitters?
an electrical signal along a nerve cell
What happens when a target cell binds a hormone?
target cell is stimulated to perform a specific function
What is the role of the extracellular fluid in transport mechanisms?
- provides the environment for ion exchange
- transport processes across membrane
What is the relationship between the electrochemical gradient and ion diffusion?
electrochemical gradient combines chemical and electrical forces to drive ion diffusion across a membrane
How does phosphorylation affect the sodium-potassium pump?
- changes protein shape
- reducing its affinity for Na+
- allowing it to be released outside the cell
What restores the original shape of the sodium-potassium pump?
the loss of the phosphate group after K+ binds, which has a lower affinity for K+
What are the three stages of cell signaling?
1. Reception
2. Transduction
3. Response
What occurs during the reception stage of cell signaling?
- highly-specific binding of a signal molecule (ligand) to a receptor
- may change shape
What is transduction in cell signaling?
signal is sent through multiple relay molecules
What is the response in cell signaling?
action taken by proteins or genetic response triggered by signal
What are the two main types of membrane receptors?
- G protein-coupled receptors
- Ligand-gated ion channels
How do G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) function?
- they work with the help of a G protein
- binds to GTP to become activated
What happens when GTP binds to a G protein?
- G protein is activated
- acts as an on-off switch for signaling
What is the role of ligand-gated ion channels?
act as gates for ions
allowing specific ions to pass through when a ligand binds
What is the significance of intracellular receptors?
- found in the cytosol or nucleus
- respond to small or hydrophobic chemical messengers
What is an example of a hydrophobic messenger?
steroid hormones
- ex.) testosterone
What is signal transduction?
converting an extracellular signal into an intracellular response
What is phosphorylation?
- addition of phosphate groups to proteins
- activating them
What is dephosphorylation?
- removal of phosphate groups from proteins
- inactivating them
What is the role of protein kinases?
- transfer phosphates from ATP to proteins
- regulating activity
What are tight junctions?
specialized proteins that form watertight seals between adjacent animal cells
What are desmosomes?
- structures that link the cytoskeletons of adjacent cells
- common in epithelial and muscle tissue
What are gap junctions?
- channels that connect adjacent cells
- allows the flow of small molecules between them
What is plasmodesmata?
- structures in plant cells
- connect cytoplasm of adjacent cells through gaps in cell wall
How do cells communicate in multicellular organisms?
- through cell-to-cell communication
- allowing coordination of activities
What is the function of signaling molecules?
bind to receptors to initiate the signaling process
What is the outcome of signal amplification in cell signaling?
- signal is transduced through multiple steps
- enhancing the cellular response
What is the role of transcription factors in cellular response?
activate genes needed for specific cellular functions or characteristics
What is the importance of cell signaling pathways?
- regulate cellular activities
- responses to external signals
What is the difference between local signaling and long-distance signaling?
- local signaling: direct connections between adjacent cells
- long-distance signaling: hormones traveling through bloodstream