Unit 1 Advanced A&P summer assignment
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2025-2026 school year
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Anatomy
The structure and shape of the body and its parts
Gross anatomy
Large body structures being studied
Microscopic anatomy
Study of the Bodies structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
Cytology
Examines the features of the cells
Histology
Examines features of tissues composed of cellular structures and surrounding materials
Levels of organization
Chemical level, tissues, organs, systems, organisms, cellular
Physiology
Study of how the body and its parts function
Pathology
Study of the development of diseases and any structural and functional changes resulting from disease
Integumentary system
External covering of the body
Skeletal system
Supports the Body and provides framework for movement
Muscular system
Movement and force.
Nervous system
Controls systems using electric
Endocrine system
Control of activities using chemical signals
Cardiovascular system
Carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and wastes from the cells
Lymphatic system
Return leaked fluid from the blood back to the vessels
Respiratory system
Keeps the body supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
Digestive system
Break down food and deliver nutrients to the blood for the body
Urinary system
Removes the nitrogen containing wastes from the body
Reproductive system
Production of offspring
Characteristics for maintaining life
Organized, metabolism, respond to stimuli, grow, develop, and reproduce
Homeostasis
Ability to maintain stable internal conditions and constant environment
Negative feedback loop
To respond to the stimuli in reverse
Positive feedback loop
Any change from normal is increase and respond to stimuli is equal or same
Supine
Lying Facing up
Prone
Laying face down
Superior (Cephalic)
Towards the head or above
Inferior (caudal)
Away from the head or below
Anterior (ventral)
Toward the front, in front
Posterior (dorsal)
Towards the back, in behind
Proximal
Close of the origin or point of attraction
Distal
Further from the origin or point of attachment
Medial
Toward the middle of the body or midline
Lateral
Away from the middle of the body or midline
Superficial
Close to the surface of the body
Deep
Toward the interior of the body
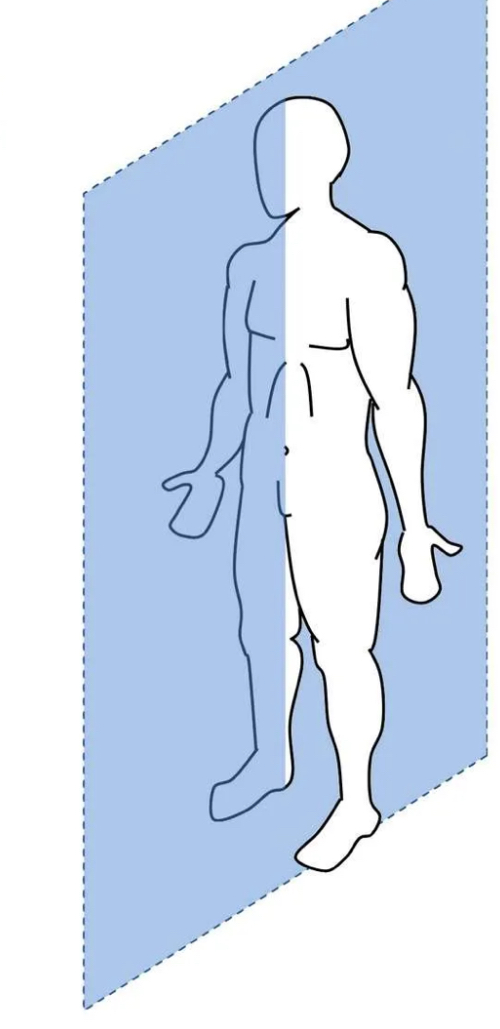
Sagittal plane
Runs vertically through the body, separating it right to left
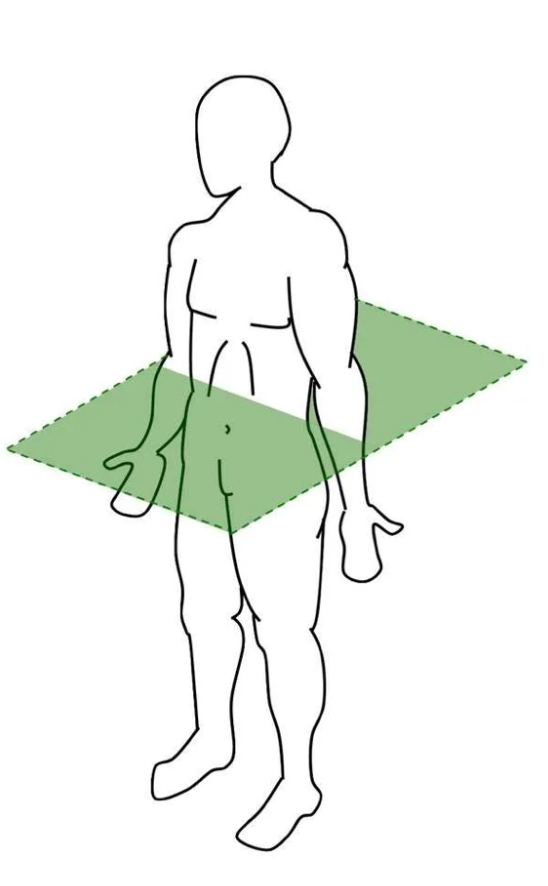
Transverse
Runs parallel to the ground dividing the body into superior and inferior portions
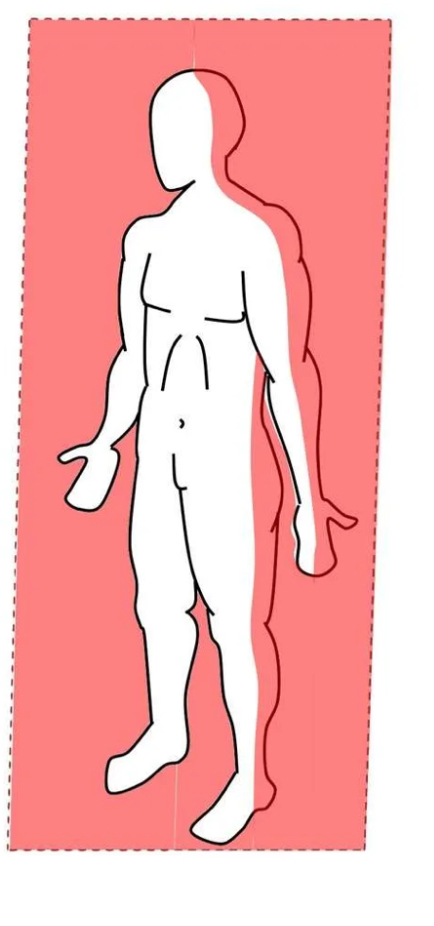
Frontal
Runs vertically to divide the body into anterior and posterior parts.
What area is the Thoracic cavity
Rib cage and diaphragm
What area is the Abdominal cavity
Diaphragm and pelvic crest
What area is the pelvic cavity
Pelvic bones
What area is the cranial and spinal cavity
Brain and spinal cord
Open cavities
Oral, digestive, nasal, orbital, middle ear.
Abdominal cavity quadrants
Right upper, left upper, right lower, and left lower
Nine abdominal regions
Right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right Iliac, hypogastric, and left iliac.
Organization
Refers to the specific interrelationships among the parts of an organism and how these parts interact and perform specific functions
Metabolism
Refers to all of the chemical reactions taking place in the cells and internal environment of an organism
Responsiveness
Ability to sense changes in its external or internal environment and adjust to those changes
Growth
Increase in size or number of cells which produces an overall enlargement of all or part of an organism
Development
Changes of an organism undergoes through time, beginning with fertilization and ending at death
Reproduction
Reformation of new cells or new organisms
Abdominal
Stomach
Acrominal
Shoulder
Axillary
Armpit
Brachial
Upper arm
Carpal
Wrist
Cephalic
Cranial or cranium
Cervical
Neck
Digitals
Toes and fingers
Femoral
Femur or thigh
Fibular
Calf or shin
lumbar
Loin
Patellar
Knee cap
Pedal
Foot
Pelvic
Pelvis
Scapular
Shoulder blade
Sternal
Breastbone or sternum
Umbillical
Belly button
Gluteal
Butt