bio 6
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/349
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
350 Terms
1
New cards
movement of molecules in passive transport
substance can cross membrane
without any input of energy.
without any input of energy.
2
New cards
movement of of molecules in simple diffusion
movement of molecules from
an area of high concentration to low conc., most simple.
an area of high concentration to low conc., most simple.
3
New cards
what is concentration gradient
difference in concentration of
molecules across a distance
molecules across a distance
4
New cards
what is equilibrium
concentration of molecules are in equality
5
New cards
what is osmosis
water molecules diffuse from high to
low concentration, across a semi permeable membrane.
low concentration, across a semi permeable membrane.
6
New cards
in osmosis that type of membrane does the water molecules pass through
a semi permeable membrane
7
New cards
what is hypotonic
solution concentrate is lower that inside cell
8
New cards
what is hypertonic
solution concentrate is higher than inside cell
9
New cards
what is isotonic solution
inside and outside of cell are equal
10
New cards
what is a solvent
substance there is more of and dissolves other substance
11
New cards
what is a solute
substances that dissolve the substance
12
New cards
what is a solution
a mixture of substances that is equally mixed throughout
13
New cards
what are the functions of cell membranes
Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an
internal balance called homeostasis
Provides protection and support for the cell.
Cell membranes have pores (holes) in it.
internal balance called homeostasis
Provides protection and support for the cell.
Cell membranes have pores (holes) in it.
14
New cards
what is a selectivly permeable membrane
allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out
15
New cards
examples of diffusion
smelling cooked food
perfume
food coloring spread out in water
perfume
food coloring spread out in water
16
New cards
When smelling body spray where is the smell strongest
and where is the smell weakest?
and where is the smell weakest?
smell at the source is the strongest. diffusion means the smell spreads out and gets weaker further away from the source.
17
New cards
types of cellular transportation
passive transport
active transport
\
active transport
\
18
New cards
what are the types of passive transport
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
19
New cards
types of active transport
protein pumps
edocytosis
exocytosis
edocytosis
exocytosis
20
New cards
what is facilitated diffusion
diffusion os specific particles through transport proteins found in the membrane
21
New cards
what is diffusion
random movement
of particles from an area of high
concentration to
of particles from an area of high
concentration to
22
New cards
when does diffusion continue until
diffusion continues until all molecules are evenly space(equilibrium is reached)
23
New cards
factors that affect the rate of diffusion
size of molecules, size of pores in membrane, temperature, pressure, and concentration
24
New cards
where is diffusion occuring in our body
Diffusion occurs in the organ systems that control your
breathing, circulation, digestion and other life processes.
breathing, circulation, digestion and other life processes.
25
New cards
diffusion and breathing
Breathing involves the exchange of
gases in the lungs, a process which
occurs by diffusion.
gases in the lungs, a process which
occurs by diffusion.
26
New cards
what is the vital gas that you breathe in
oxygen
27
New cards
what is the waste you breathe out
carbon dioxide
28
New cards
why do lungs have a huge surface area
to maximize the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with each breath
29
New cards
where does gas exchange in the lungs take place
the alveoli, the tiny air sacs at the end of the bronchioles
30
New cards
what does inhaling increase
the concentration of oxygen molecules in an alveolus
31
New cards
what are transport proteins
they select only certain molecules to cross the membranes
32
New cards
what is osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane,
where water moves from high to low concentrations
where water moves from high to low concentrations
33
New cards
osmosis real life example
1\.When we water plants, we usually water the stem end and soil in which they are growing. Hence,
the roots of the plants absorb water and from the roots water travel to different parts of plants; be it
leaves, fruits or flowers. Every root acts as a semipermeable barrier, which allows water molecules to
transfer from high concentration (soil) to low concentration (roots). Roots have hair, which increases
surface area and hence the water intake by the plants.
the roots of the plants absorb water and from the roots water travel to different parts of plants; be it
leaves, fruits or flowers. Every root acts as a semipermeable barrier, which allows water molecules to
transfer from high concentration (soil) to low concentration (roots). Roots have hair, which increases
surface area and hence the water intake by the plants.
34
New cards
how does osmosos help get pure water
RO Reverse Osmosis is the process of Osmosis in
reverse. Whereas Osmosis occurs naturally, without the involvement of energy; however, to
reverse the process of osmosis, you need to apply energy to the more saline solution. A
reverse osmosis membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that allows the passage of
water molecules but not the majority of dissolved salts, organics, bacteria and pyrogens.
However, you need to ‘push’ the water through the reverse osmosis membrane by applying
pressure that is greater than the naturally occurring osmotic pressure in order to desalinate
(demineralize or deionize) water in the process; allowing pure water to pass through while
holding back a majority of contaminants. Reverse Osmosis is also used in large scale
desalination of seawater; turning it into drinking water.
reverse. Whereas Osmosis occurs naturally, without the involvement of energy; however, to
reverse the process of osmosis, you need to apply energy to the more saline solution. A
reverse osmosis membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that allows the passage of
water molecules but not the majority of dissolved salts, organics, bacteria and pyrogens.
However, you need to ‘push’ the water through the reverse osmosis membrane by applying
pressure that is greater than the naturally occurring osmotic pressure in order to desalinate
(demineralize or deionize) water in the process; allowing pure water to pass through while
holding back a majority of contaminants. Reverse Osmosis is also used in large scale
desalination of seawater; turning it into drinking water.
35
New cards
what is reverse osmosis
the process of osmosis in reverese
36
New cards
what is a reverse osmosis membrane
a semi-permeable membrane that allows the passage of
water molecules but not the majority of dissolved salts, organics, bacteria and pyrogens.
However, you need to ‘push’ the water through the reverse osmosis membrane by applying
pressure that is greater than the naturally occurring osmotic pressure in order to desalinate
(demineralize or deionize) water in the process; allowing pure water to pass through while
holding back a majority of contaminants.
water molecules but not the majority of dissolved salts, organics, bacteria and pyrogens.
However, you need to ‘push’ the water through the reverse osmosis membrane by applying
pressure that is greater than the naturally occurring osmotic pressure in order to desalinate
(demineralize or deionize) water in the process; allowing pure water to pass through while
holding back a majority of contaminants.
37
New cards
how is osmosis responsible for pruned or wrinkled fingers
Fingers-When we sit in the bathtub or
submerge our fingers in water for a while they got wrinkly. And that is too because of
osmosis. The skin of our fingers absorb water and get expanded or bloated; leading to the
pruned or wrinkled fingers.
submerge our fingers in water for a while they got wrinkly. And that is too because of
osmosis. The skin of our fingers absorb water and get expanded or bloated; leading to the
pruned or wrinkled fingers.
38
New cards
why dod we feel thirsty after eating slaty food
Fingers-When we sit in the bathtub or
submerge our fingers in water for a while they got wrinkly. And that is too because of
osmosis. The skin of our fingers absorb water and get expanded or bloated; leading to the
pruned or wrinkled fingers.
submerge our fingers in water for a while they got wrinkly. And that is too because of
osmosis. The skin of our fingers absorb water and get expanded or bloated; leading to the
pruned or wrinkled fingers.
39
New cards
how does kidney dialysis a example os osmosis
In this process, the dialyzer removes waste products from a patient’s
blood through a dialyzing membrane(acts as a semi-permeable membrane) and passes them
into the dialysis solution tank. The red blood cells being larger in size cannot pass through
the membrane and are retained in the blood. Thus, by the process of osmosis waste materials
are continuously removed from the blood.
blood through a dialyzing membrane(acts as a semi-permeable membrane) and passes them
into the dialysis solution tank. The red blood cells being larger in size cannot pass through
the membrane and are retained in the blood. Thus, by the process of osmosis waste materials
are continuously removed from the blood.
40
New cards
what are the differnces and simalarities between osmosis and diffusion

41
New cards
what are the 3 types of osmotic solutions
isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic
42
New cards
what is a hypotonic solution
The solution has a lower concentration of solutes and a higher concentration of water outside side than inside of the cell. (Low solute; High water) so the water moves from the solution to inside the cell and the cell swell and busrts and open
43
New cards
what is cytolysis
when the cell swells burst and open
44
New cards
what is a hypertonic solution
The solution has a higher concentration of solutes and a lower concentration of water than inside the cell. (High solute; Low water) so the water moves from inside the cell into the solution and the cell shrinks
45
New cards
what is plasmolysis
when the cell shrinks
46
New cards
what is isotonic solution
The concentration of solutes in the solution is equal to the concentration of solutes inside the cell. so the water moves equally in both directions and the cell remains the same size which is dynamic equilibrium
47
New cards
what is dynamic equilibrium
Water moves equally in both directions and
the cell remains same size!
the cell remains same size!
48
New cards
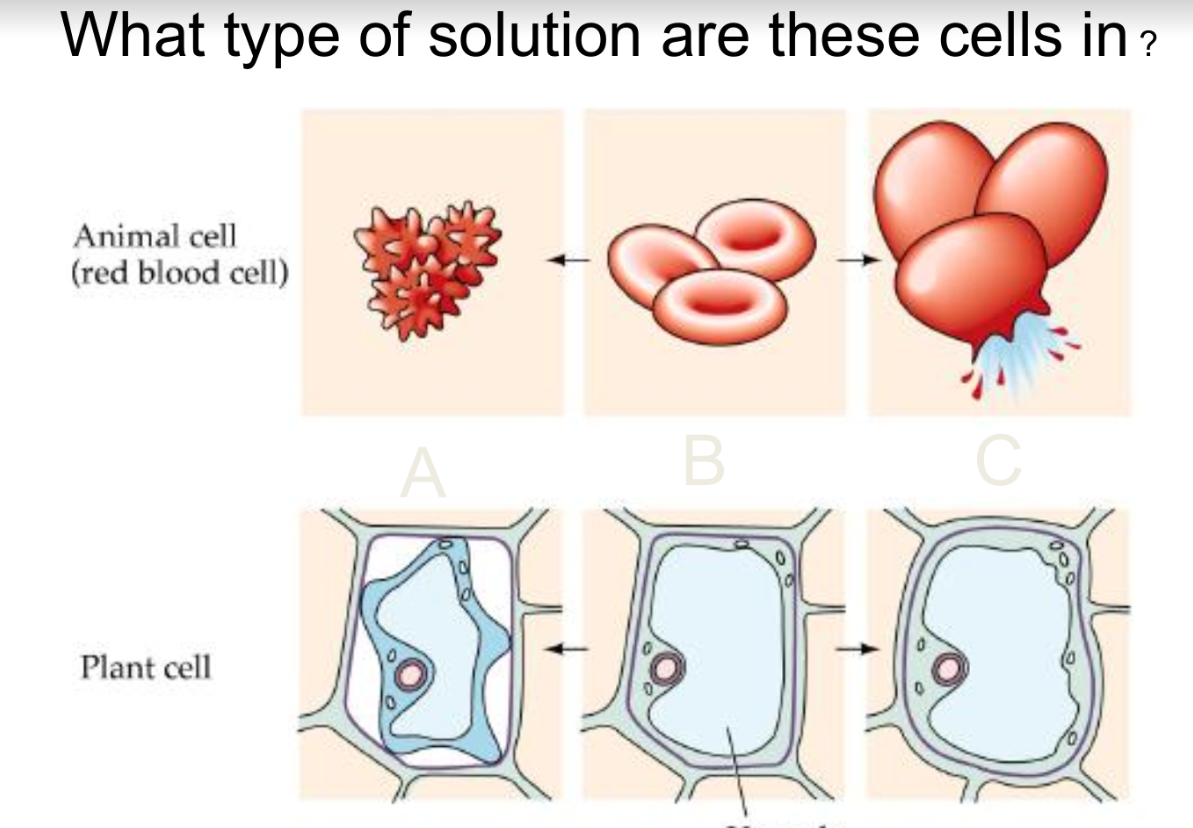
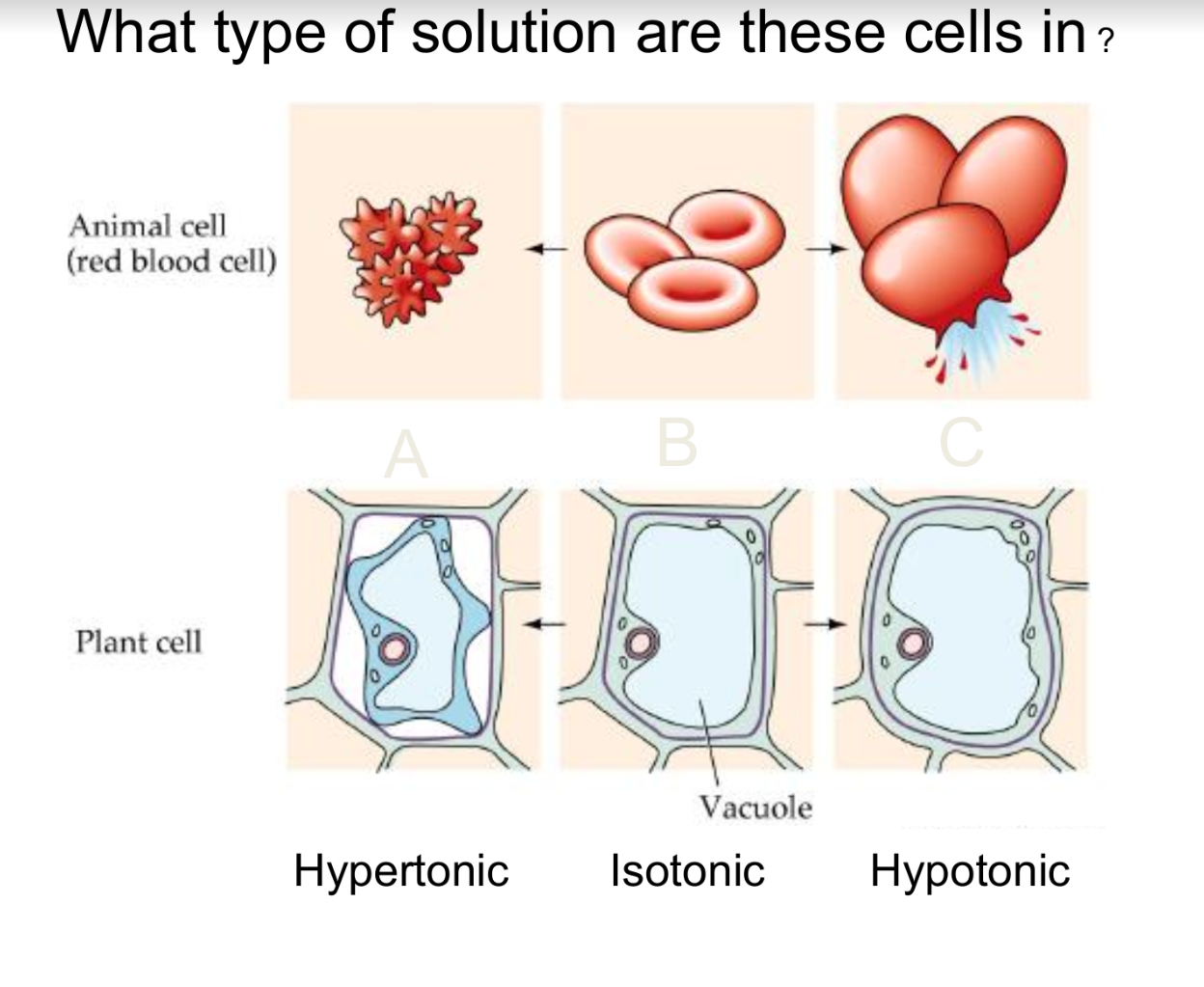
49
New cards
what is cytoplasm
a solution of water and solids
50
New cards
why does the water move into and out of the cells
because of the different concentrations of the solutes
51
New cards
how does bacteria deal with osmotic pressure
Bacteria and plants have cell walls that prevent them
from over-expanding.
from over-expanding.
52
New cards
what is turgor pressure
In plants the pressure exerted on the cell wall is called turgor pressure.
53
New cards
how does protists deal with osmotic pressure
A protist like paramecium has contractile vacuoles that
collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them
from over-expanding.
collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them
from over-expanding.
54
New cards
what is active transport
Movement from an area of low concentration
to an area of high concentration
to an area of high concentration
55
New cards
what are the types of active transport
protein pumps
edocytosis
exocytosis
edocytosis
exocytosis
56
New cards
what is protein pumps
transport proteins that require energy to do work
57
New cards
what is endocytosis
it forms food vacuole and digests food, this is how hite blood cells eat bacteria.
\
engulfs substances by enclosing in a membranous vesicle
\
engulfs substances by enclosing in a membranous vesicle
58
New cards
what are the 2 types of endocytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
pinocytosis
59
New cards
what is phagocytosis
cell eating
60
New cards
what is pinocytosis
cell drinking
61
New cards
what is exocytosis
Endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large
molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell.
molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell.
62
New cards
active transport in plants
Plants need mineral elements from the soil for healthy
growth. Minerals enter a plant though its roots.
growth. Minerals enter a plant though its roots.
63
New cards
how do mineral enter a root cell
active transport.
The plant uses energy to move minerals up the
concentration gradient from the soil into its root cells.
The plant uses energy to move minerals up the
concentration gradient from the soil into its root cells.
64
New cards
why is diffusion important int he human body
breathing
calcium
kidneys
liver
\
calcium
kidneys
liver
\
65
New cards
how is diffusiion used in breathing
oxygen only gets into your bloodstream when the O2
molecules you breathe in diffuse into deoxygenated blood. Breathing in and out is a mechanical action,
not diffusion, but the oxygen actually enters your bloodstream through diffusion.
molecules you breathe in diffuse into deoxygenated blood. Breathing in and out is a mechanical action,
not diffusion, but the oxygen actually enters your bloodstream through diffusion.
66
New cards
67
New cards
how does diffusion occur in the kidneys
Kidneys filter dangerous
chemicals from your bloodstream through microscopic tubes called nephrons. Nephrons separate blood from
waste chemicals and toxins, then reabsorb the water and nutrients in the blood through diffusion. The rest
goes through the bladder and out.
chemicals from your bloodstream through microscopic tubes called nephrons. Nephrons separate blood from
waste chemicals and toxins, then reabsorb the water and nutrients in the blood through diffusion. The rest
goes through the bladder and out.
68
New cards
how does diffusion occur in the liver
Your liver does all sorts of interesting things, but at the top of the list, it synthesizes proteins. You
need those. Your body is made of them. In the process, it produces a potentially dangerous waste product
called urea. Thankfully for you and your liver, the urea then diffuses into the bloodstream just upstream of
your aforementioned kidneys, where it's filtered out.
Water
need those. Your body is made of them. In the process, it produces a potentially dangerous waste product
called urea. Thankfully for you and your liver, the urea then diffuses into the bloodstream just upstream of
your aforementioned kidneys, where it's filtered out.
Water
69
New cards
what is the difference between breathing and respiration
Breathing is the process in which living
organisms take in oxygen and give out carbon
dioxide.
Respiration is the process in which the glucose
is burnt in the presence of oxygen to produce
carbon dioxide, water and energy .
Breathing takes place outside the body
Respiration takes place inside the body
organisms take in oxygen and give out carbon
dioxide.
Respiration is the process in which the glucose
is burnt in the presence of oxygen to produce
carbon dioxide, water and energy .
Breathing takes place outside the body
Respiration takes place inside the body
70
New cards
what is respiration
Respiration is a series of metabolic/chemical
reactions that takes place in every living cell.
It is a chemical reaction in which oxygen combines
with food in a cell to release the energy.
reactions that takes place in every living cell.
It is a chemical reaction in which oxygen combines
with food in a cell to release the energy.
71
New cards
what is the purpose of respiration
The purpose of respiration is to break down nutrient
molecules in living cells to release energy.
molecules in living cells to release energy.
72
New cards
what are the 2 types of respiaration
aerobic and anaerobic respiration
73
New cards
what is aerobic respiration
The release of a relatively large amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food
substances in the presence of O2.
substances in the presence of O2.
74
New cards
what is anaerobic respiration
the release of a relatively small amount of energy by the
breakdown of food substances in the absence of O2.
breakdown of food substances in the absence of O2.
75
New cards
comparison between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
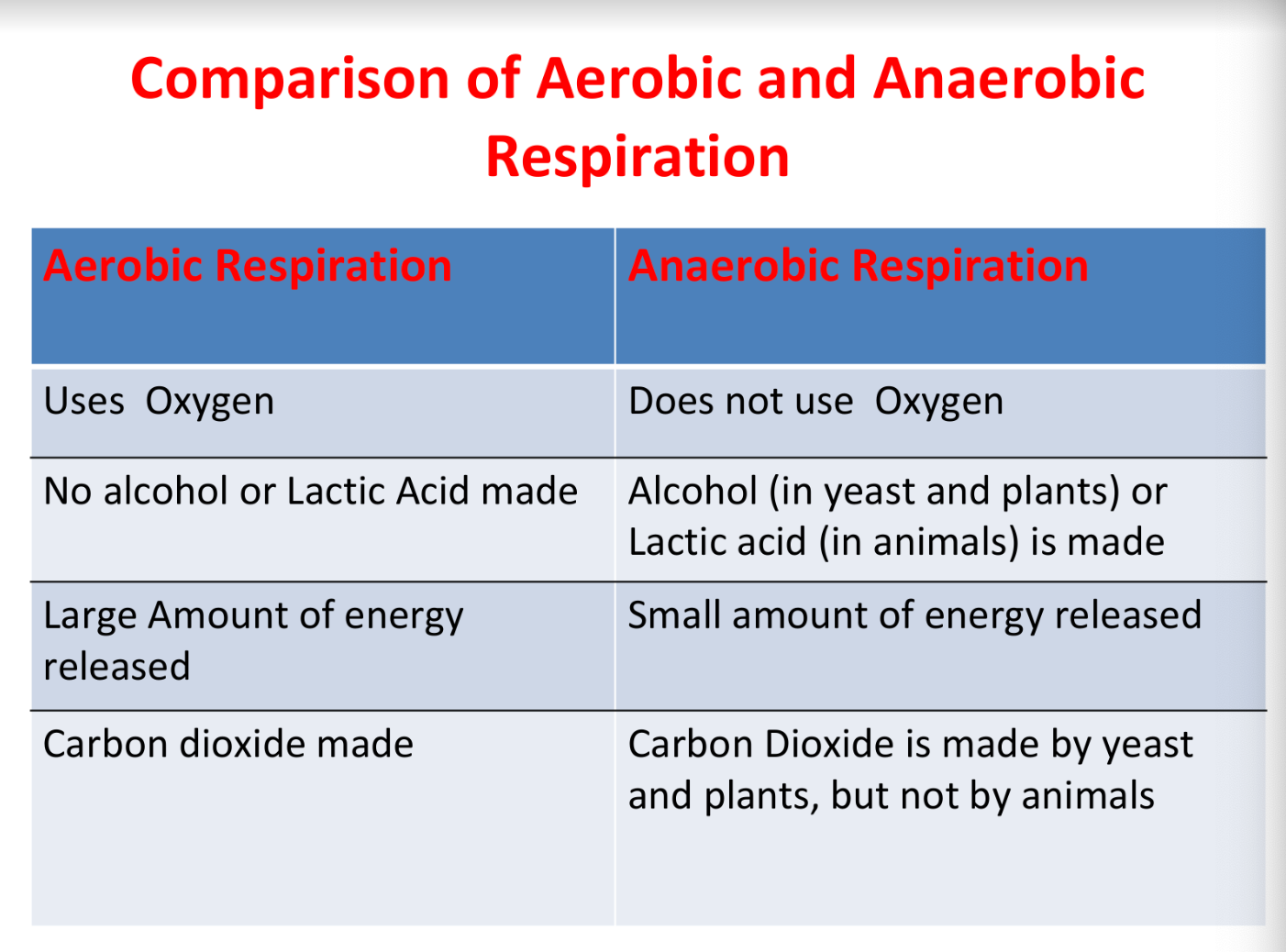
76
New cards
which types of respiration uses oxygen
aerobic respiration
77
New cards
which type of respiration does not use oxygen
anaerobic respiration
78
New cards
how much energy is released in aerobic respiration
large amount of respiration is released
79
New cards
how much energy is released in anaerobic respiration
small amount of energy is released
80
New cards
examples of anaerobic respiration through fermentation in bread making and brewing
* yeast is mixed with water to activate it then added to flour to make dough
* mixture -----> warm place ------> rise
* yeast releases CO2 ------> dough rises
* a warm to is important because fermentation is controlled by enzymes
* when dough is cooked, high to kills yeast and evaporates any formed
ethanol.
air spaces are left where CO2 was trapped
* mixture -----> warm place ------> rise
* yeast releases CO2 ------> dough rises
* a warm to is important because fermentation is controlled by enzymes
* when dough is cooked, high to kills yeast and evaporates any formed
ethanol.
air spaces are left where CO2 was trapped
81
New cards
examples of anaerobic respiration through fermentation in physical excersice
Muscles respire anaerobically when exercising vigorously, because the
blood cannot supply enough oxygen to maintain aerobic respiration.
However, the formation and build-up of lactic acid in muscles causes cramp
(muscle fatigue). Glucose-----Lactic acid + Energy
The lactic acid that is made is transported to the liver, and later is broken
down by combining it with O2. This extra O2 is breathed in after the exercise
has stopped, and it is known as the oxygen debt.
blood cannot supply enough oxygen to maintain aerobic respiration.
However, the formation and build-up of lactic acid in muscles causes cramp
(muscle fatigue). Glucose-----Lactic acid + Energy
The lactic acid that is made is transported to the liver, and later is broken
down by combining it with O2. This extra O2 is breathed in after the exercise
has stopped, and it is known as the oxygen debt.
82
New cards
anaerobic respiration in yeast cells
it is also known as fermentation.
83
New cards
what is oxygen debt
Anaerobic respiration provides enough energy to
keep the muscles working for a short time.
However lactic acid builds up in the blood which
causes cramps.
The lactic acid has to be broken down using
oxygen.
The volume of oxygen needed to completely
oxidise the lactic acid that builds up in the body
during anaerobic respiration is called oxygen
debt.
keep the muscles working for a short time.
However lactic acid builds up in the blood which
causes cramps.
The lactic acid has to be broken down using
oxygen.
The volume of oxygen needed to completely
oxidise the lactic acid that builds up in the body
during anaerobic respiration is called oxygen
debt.
84
New cards
what are the methods of lactate clearence
oxidation
conversion to glucose
conversion to glucose
85
New cards
what is oxidation
Most of the lactate that accumulates during exercise is oxidized to
produce energy. Lactate remaining in your muscles is transported
into organelles within the muscle cells called mitochondria. Inside
the mitochondria, often called the powerhouse of the cell, lactate
is converted into a compound called pyruvate, which, in turn, can
be oxidized aerobically to produce energy.
produce energy. Lactate remaining in your muscles is transported
into organelles within the muscle cells called mitochondria. Inside
the mitochondria, often called the powerhouse of the cell, lactate
is converted into a compound called pyruvate, which, in turn, can
be oxidized aerobically to produce energy.
86
New cards
what is conversion to glucose
Your liver converts lactate into glucose, or blood sugar, a process
called gluconeogenesis. Glucose, released into the bloodstream,
serves as a fuel source for many tissues in the body, including
your brain and muscles.
called gluconeogenesis. Glucose, released into the bloodstream,
serves as a fuel source for many tissues in the body, including
your brain and muscles.
87
New cards
what happens to glucose in cellular respiration
it loses it hydrogen atoms and bceomes reduced to Co2
88
New cards
what happens to oxygen in cellular respiration
gains hydrogen molecules and becomes reduced to H20
89
New cards
what is the first stage of cellular respiration
glycolysis
90
New cards
where does glycolosis take place
in the cells cytoplasm/cytosol
91
New cards
what is glycolysis
Glucose and oxygen are supplied to cells by the bloodstream. The energy
molecule NAD acts as a shuttle for electrons during cellular respiration. At various
chemical reactions, the NAD+ picks up an electron from glucose, at which point it
becomes NADH.
molecule NAD acts as a shuttle for electrons during cellular respiration. At various
chemical reactions, the NAD+ picks up an electron from glucose, at which point it
becomes NADH.
92
New cards
in glycolysis how mnay molecules of ATP are produced
2
93
New cards
in glycolosis how mnay molecules of pyruvic acid and NADH are produced
2
94
New cards
what is NADH
(Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide +
Hydrogen)
Hydrogen)
95
New cards
what is produced in glycolysis
2 ATP, 2 pyruvic acid, 2 NADH
96
New cards
what are the reactants of glycosis
NAD+, glucose, ADP+o2
97
New cards
where does krebs cycle/citric acid cycle take place
This cycle takes place in the matrix of cell mitochondria.
98
New cards
what is the first thing that happens in the krebs cycle
pyruvic acid converts to acetyl-Coa
99
New cards
what happens to the acetyl-Coa in the second step of the krebs cycle
acetyl-CoA, which reacts with the four-carbon molecule known as OAA
(Oxaloacetate). During the bonding with OAA, it produces citric acid.
(Oxaloacetate). During the bonding with OAA, it produces citric acid.
100
New cards
what is produced during the krebs cycle
.
4 ATP (contains 2 molecules from Glycolysis)
10 NADH (contains 2 molecules from Glycolysis)
2 FADH2
4 ATP (contains 2 molecules from Glycolysis)
10 NADH (contains 2 molecules from Glycolysis)
2 FADH2