Forestry
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Roots
All belowground parts of trees, may sometimes be above ground
Act as an anchor, gets/stores food n water, may be part of reproduction
Trunk
Aboveground woody part, below canopy
Transports water/nutrients throughout tree
Canopy
Leaves and branches
Photosynthesis, hormones, and transpiration
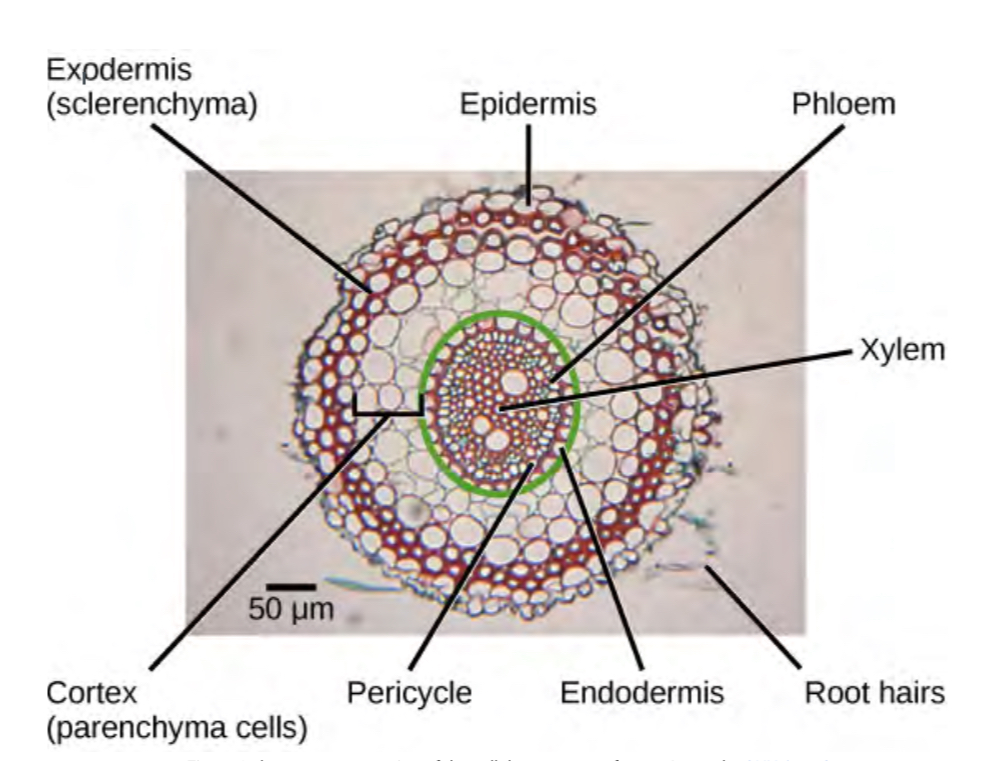
Root hairs
small outgrowths from lateral roots, continuously being created, die off in 2-3 weeks, main purpose to increase surface area to allow for absorb more water and nutrients
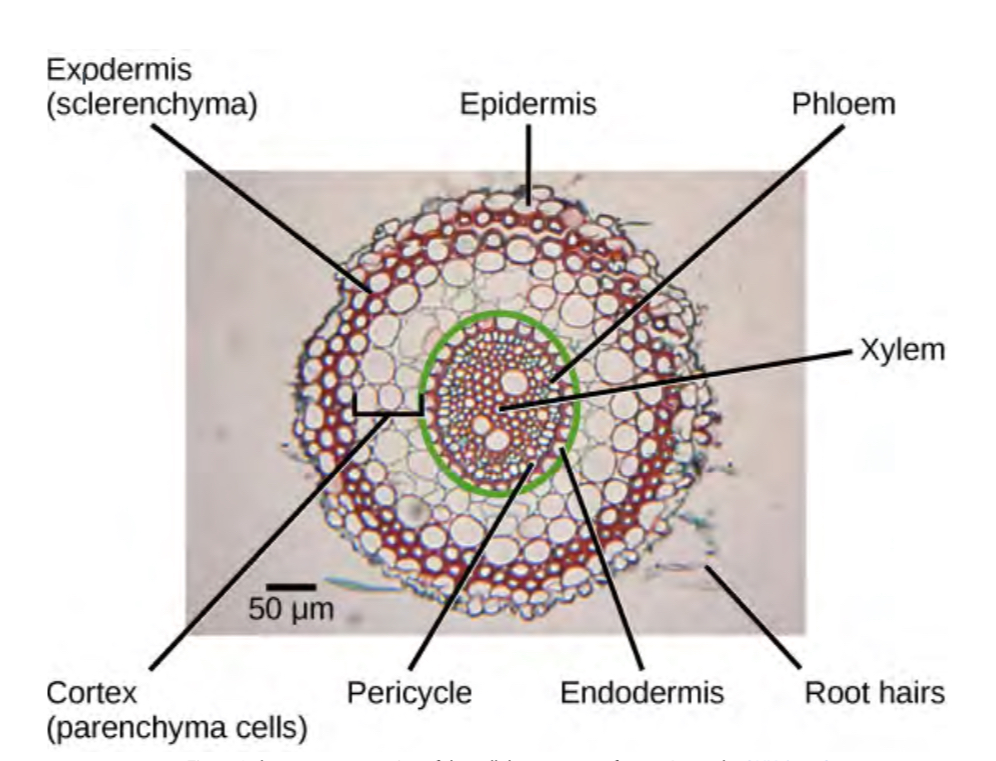
lateral roots
the bigger root structure made of vascular tissue that helps transport nutrients and water throughout the tree
Epidermis
Outer layer of root that protects, insulates, and controls gas and moisture. Absorbs some water and nutrients, continuously dying off and replaced by cella from exodermis—like shark teeth
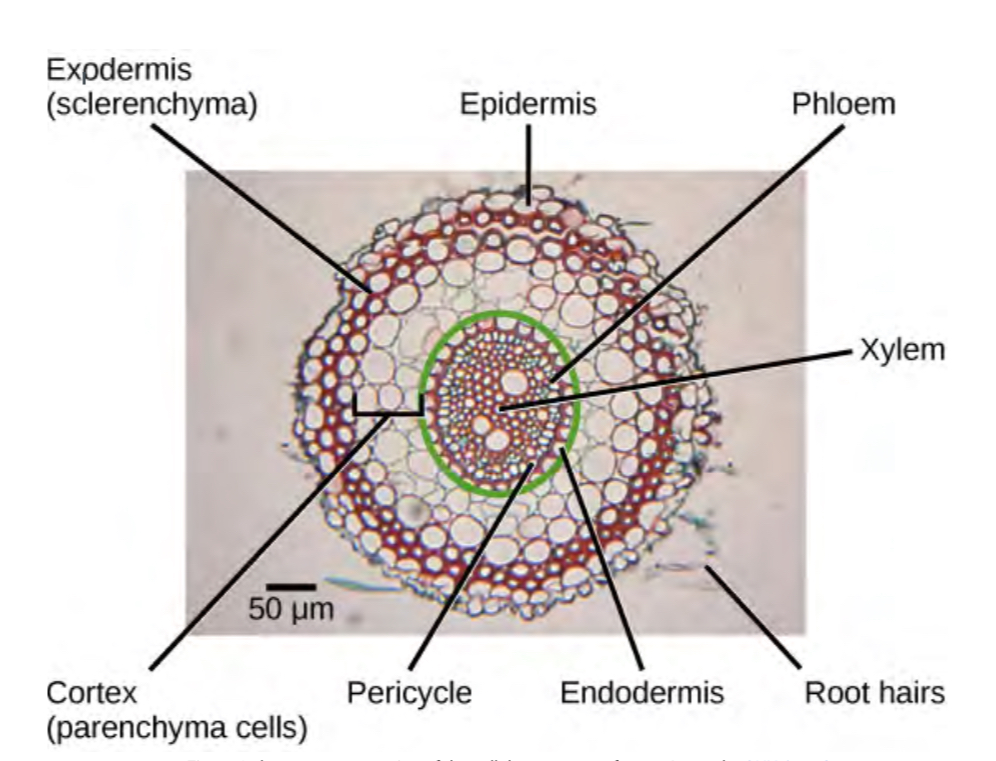
Exodermis
Layer underneath epidermis that replaces it—”epidermis heir”
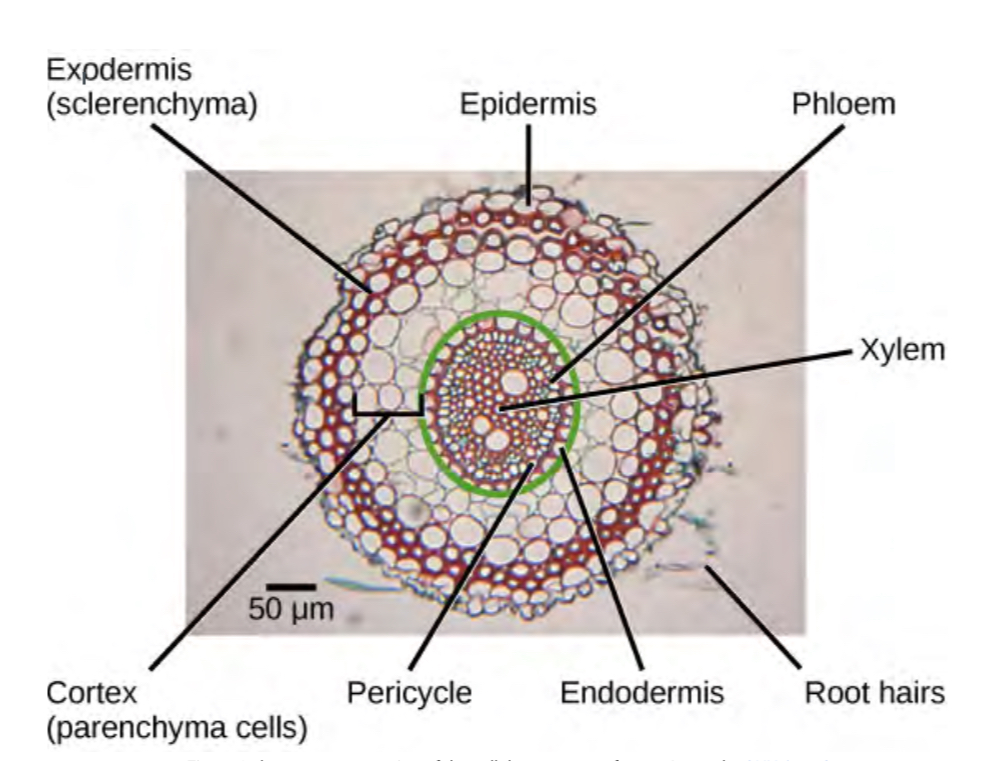
Cortex
Stores energy and transfers nutrients from root hairs to vascular tissue
Between exo and endo dermis
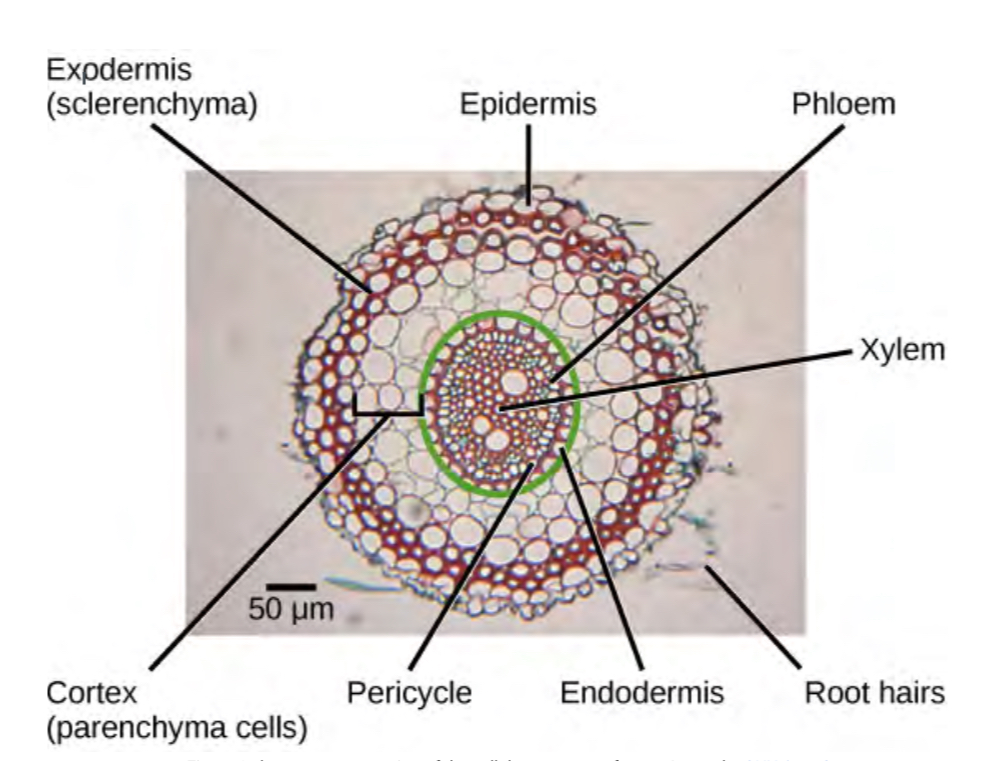
Endodermis
Innermost layer of cells with thick cell walls, may be coated in suberin, regulates water and nutrients movement. Between cortex and pericycle
Suberin
Water-repellant substance that helps keep endodermis watertight
Pericycle
Site of new lateral root growth, provides internal support and protection. inside of endodermis
Vascular tissue
Bundle of cells that helps transport nutrients and water from roots to rest of tree
Tree osmosis
They increase salt concentration in roots so water flows in, carrying dissolved minerals
bark purpose
protection, insulation, moisture control
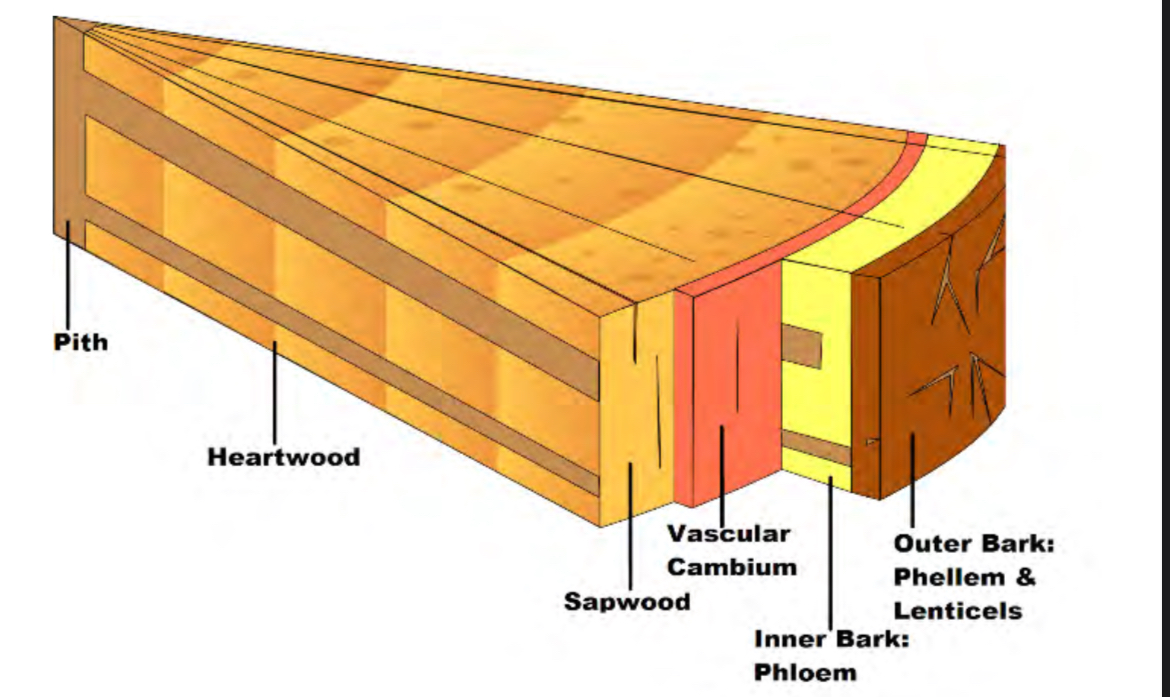
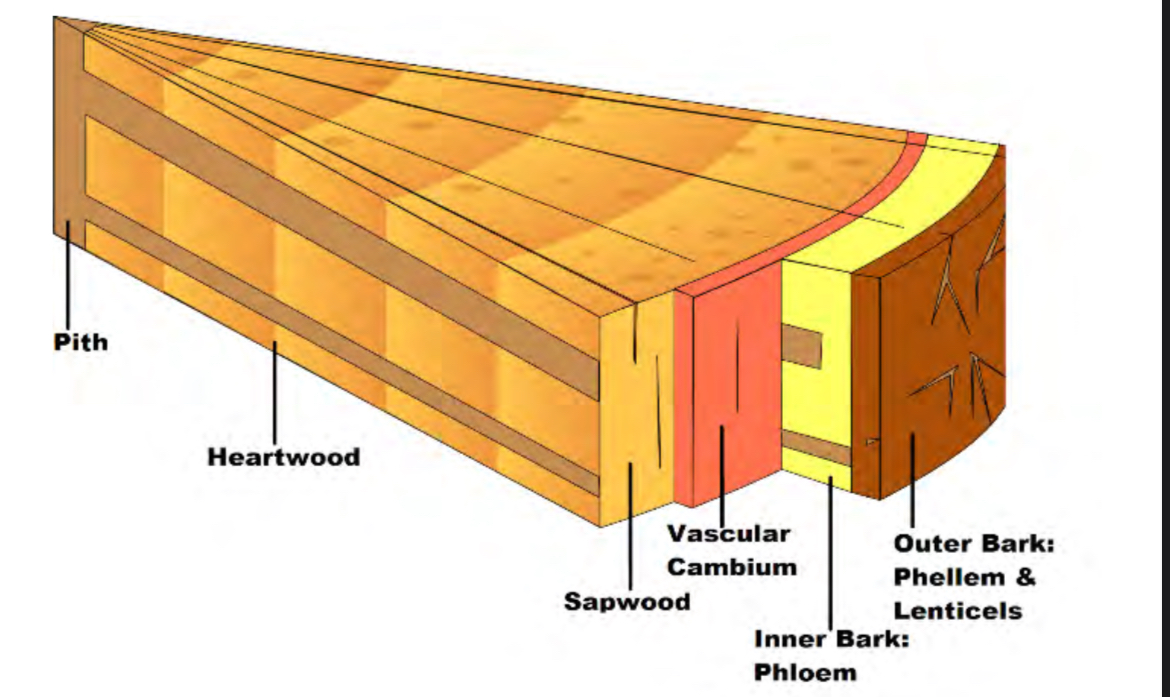
Outer bark
Made of dead cells(cork). Has lenticels and phellem. Is on the very outside
Inner bark
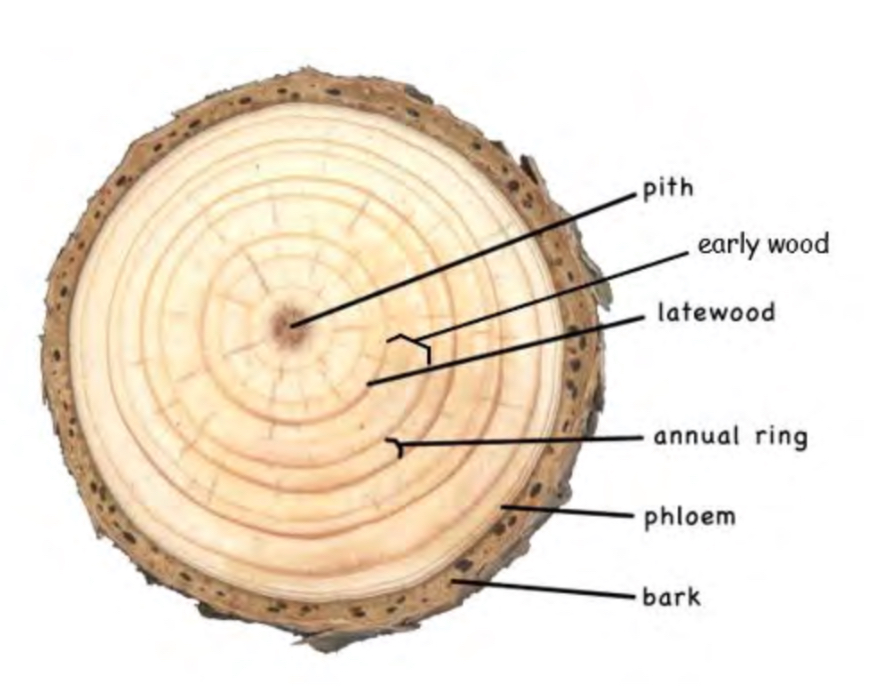
Transports sap and nutrients throughout tree. becomes outer bark when it ages. Has phloem
Vascular Cambium
Basically the stem cells of tree where most growht happen-differentiates into phloem and xylem
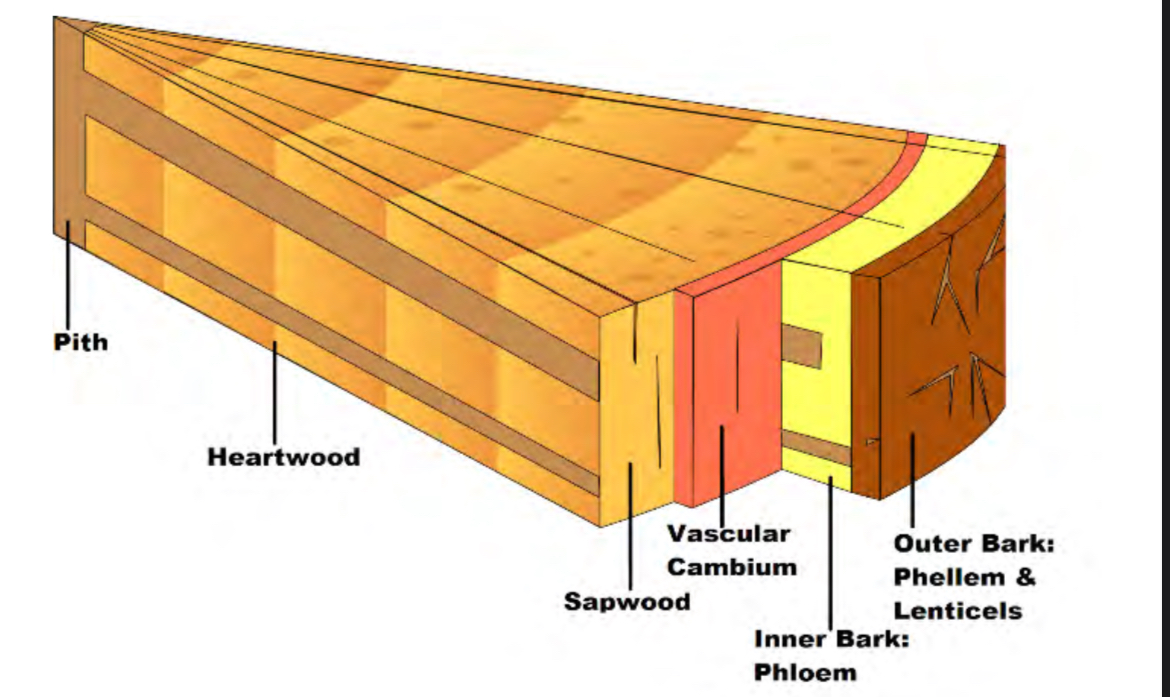
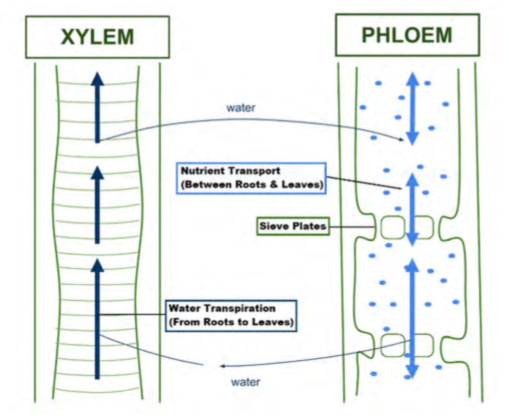
Phloem
Transports sap (sugar and other nutrients) up AND down tree. cells make sieve tubes (hollow tubes) with sieve plates that make them into smaller sections allowing for 2 direction movement
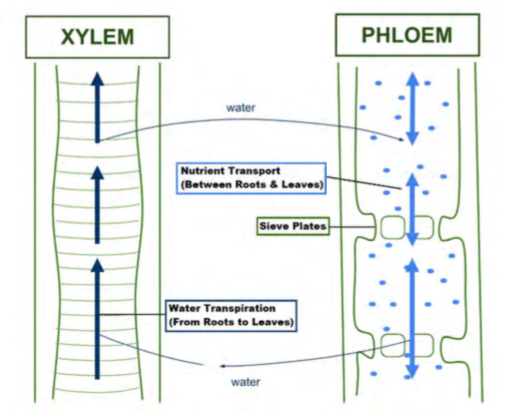
Xylem
Transports water and minerals only up the tree. They form vessel elements (hollow tubes)
Lenticels
Oxygen pores for tree
Sapwood
Main water transporter, becomes heartwood once it ages
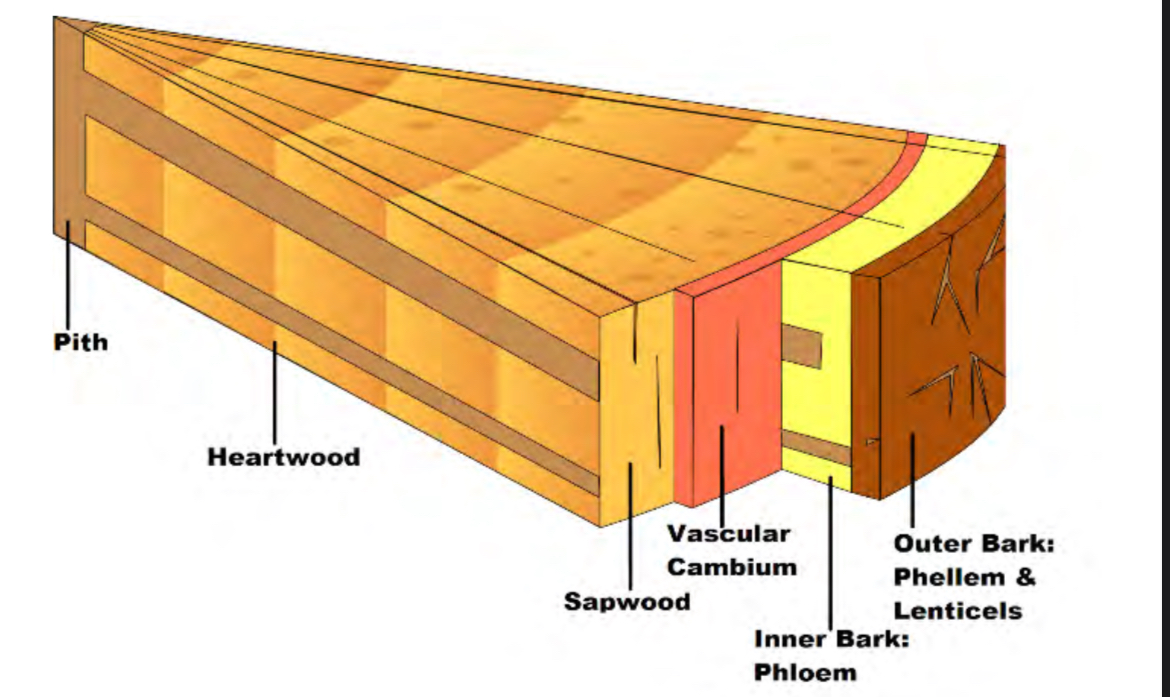
Heartwood
Rot resistant and strong, made of dead xylem and fiber bundles. supports tree
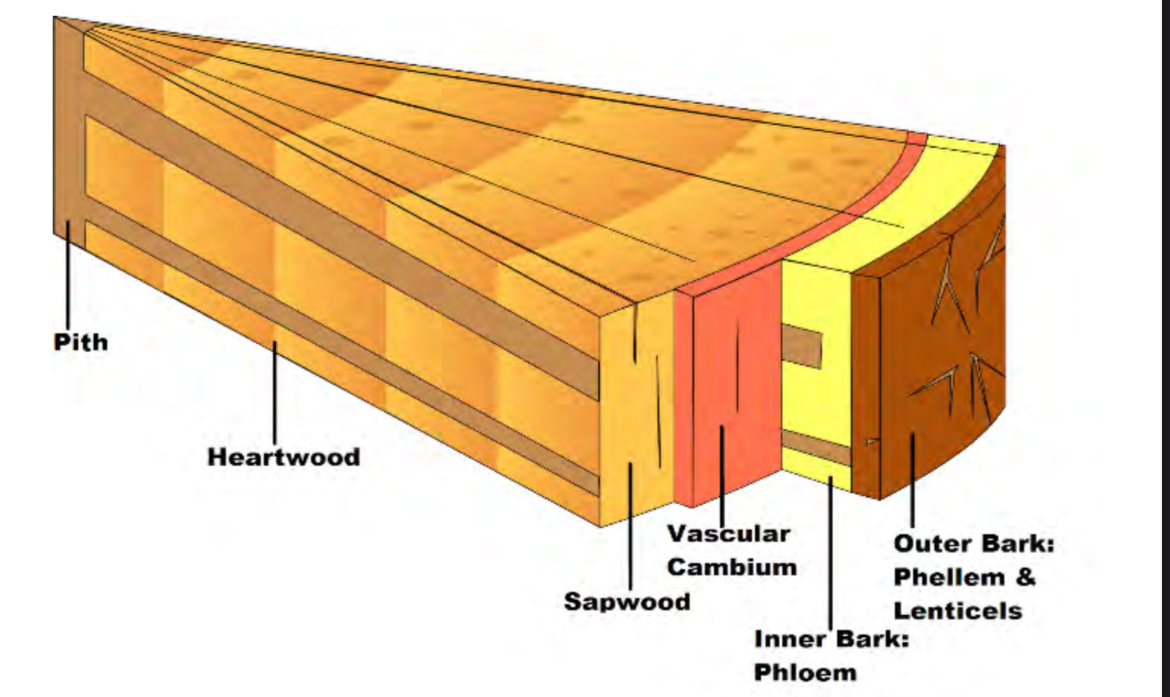
pith
Made of parenchyma cells, soft and spongy. Transports/stores water and nutrients
Parenchyma cells
Make of majority of plant cells and give support and nutrients to xylem and phloem
Fiber bundles
Bundles of long thin cells mostly made of cellulose that provide support
Early wood
When good conditions (like enough water, sun, etc) tree grow fast make light, less dense wood growth ring
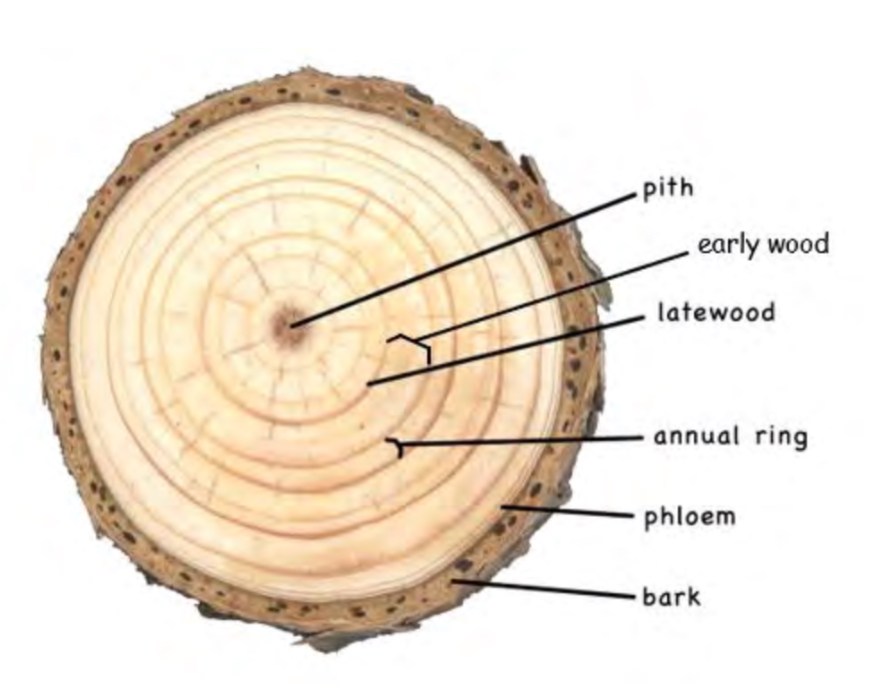
Late wood
Conditions (approaching winter) causing darker denser growth ring
Epidermis
Outer layer for protection and insulation. Has waxy cuticle
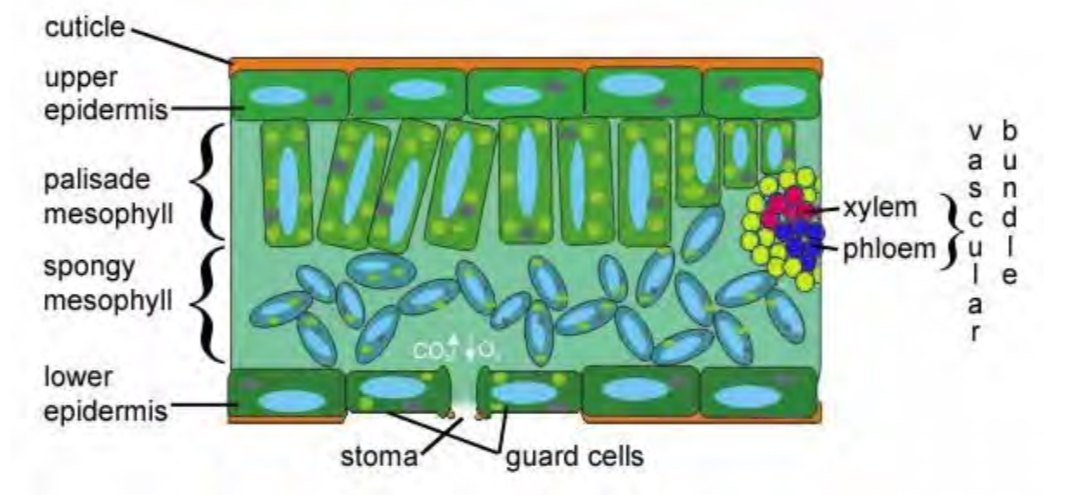
Mesophyll
Tube arranged parenchyma cells
Palisade mesophyll
Tightly packed parenchyma for lots of chloroplasts for photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll
Loosly packed parenchyma to allow gas movement and get CO2 to the chloroplasts
Stoma
Air holes that are opened and closed by guard cells, regulate gas exchange
Vascular bundle
Xylem/phloem bundles that provide water and nutrients for transpiration + photosynthesis, and take photosynthesis sugars to other parts of tree
6 reqs of trees
Sugar
Water
nutrients
CHOPKNSCaFeMg
Hormones + enzymes
Mycorrhizae
Correct environment
See hopkins cafe? It might be good
C HOPKNS CaFe Mg
essential tree elements!!
Opposite branching
branches symmetrical
Alternate Branching
Branches ate not directly across from each other
Whorled branching
Multiple branches coming out of one point
MAD Cap HORSE
Plants with opposite branching
Maple
Ash
Dogwood
Caprifoliacae
Hose chestnut
Simple leaf
There is only one leaf next to the axillary leaf bud
Pinnate leaf
There is a stalk with leaves coming off the stalk after the axillary bud
Bipinnate leaf
there is a stalk and on that stalk there are more stalks after the axillary bud
Palmately compound leaf
after the axillary bud, there is a stalk where leaves all stem from one point
Dominant Trees Crown
The Crown is higher than general canopy and receives full light from above as well as some light from the side
Codominant trees crown
The crown makes up most of the general canopy, and it gets direct light from above but little light from the sides.
intermediate trees crown
generally narrow and shorter than general canopy, and receive some direct light from above
suppressed trees crown
the tree is shortest and receive no direct light from anywhere.
Massachusetts state tree
American Elm
Forest canopy/overstory
the topmost level of the forest, made of dominant and codominant tall trees