2.3 aggregate supply
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
aggregate supply
the total level of output
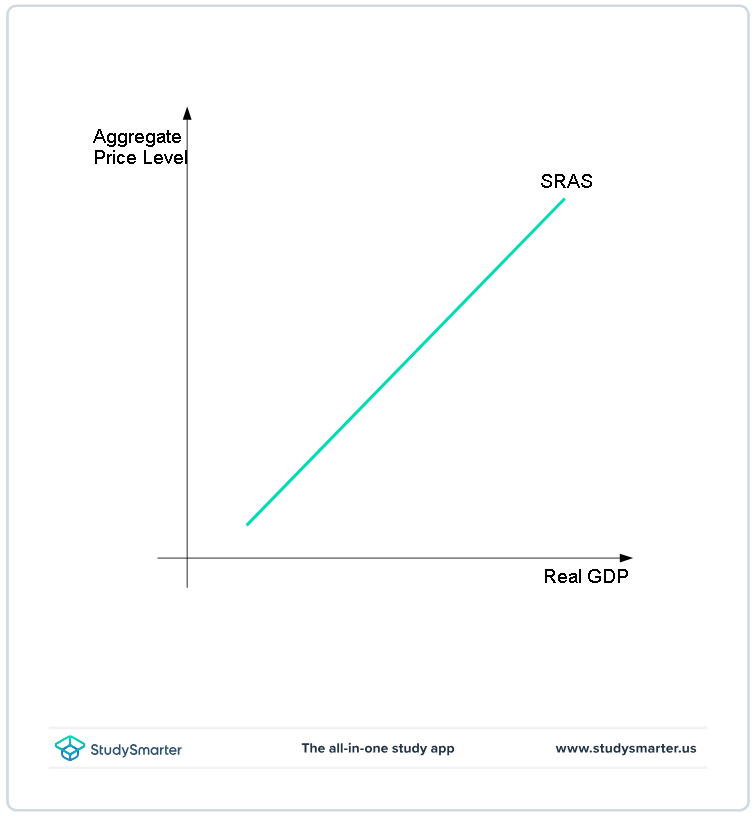
SRAS curve
in short run theres a positive correlation between price and output
shifts in AS curve
technological advances
relative productivity
changes in education/skills
changes in government regulation
other factors that affect SRAS
wage rates
indirect taxes
exchange rate
worker productivity
LRAS
long run aggregate supply curve
in long run as more resources are used to increase output
AS becomes more inelastic i.e increase in price may not increase AS due to no spare capacity
2 types of LRAS
Keynesian AS curve
Classical AS curve
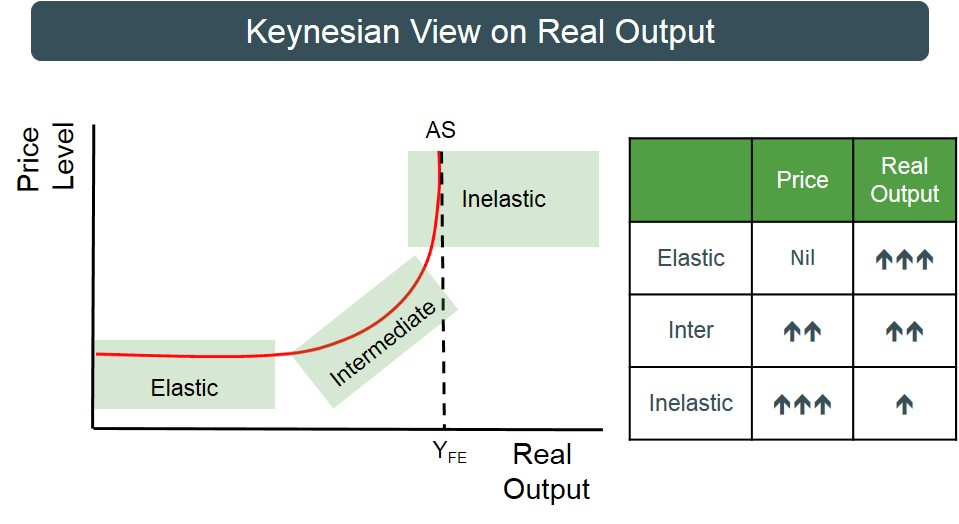
Keynesian AS curve
at low-levels of output,Real GDP can be increased without significant pressure on price to rise - plenty of spare capacity
however as demand increases and we approach full capacity AS becomes more vertical i.e inelastic i.e run out of resources
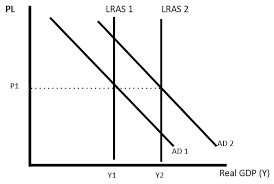
classical AS curve
here the classical approach assumes that in the long run output will always be at full capacity level
its best to shift AS because it will increase output while decreasing price
why is infrastructure spending important for LRAS
reduces inflation
boosts economic growth
increases output
increase transport
increase AD. AS
examples of Govt regulation which affect LRAS
increase Investment into infrastructure
changes in direct taxes levels
changes to business rates
however wether a business decides to invest or not is down to them
demographic changes and migration affect on LRAS
increase immigration - increase labour supply
increase life expectancy - increase pension age
increase population