Improving Medication Safety in Community Pharmacy
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Define medication errors
Any preventable event that has the potential to lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm during prescribing, transcribing, dispensing, administering, adherence, or monitoring a drug
Discuss the extent of medication errors and their impact on patient care: What is a medication error that stopped before harming the pt?
“Near misses” or “a potential adverse drug event:”
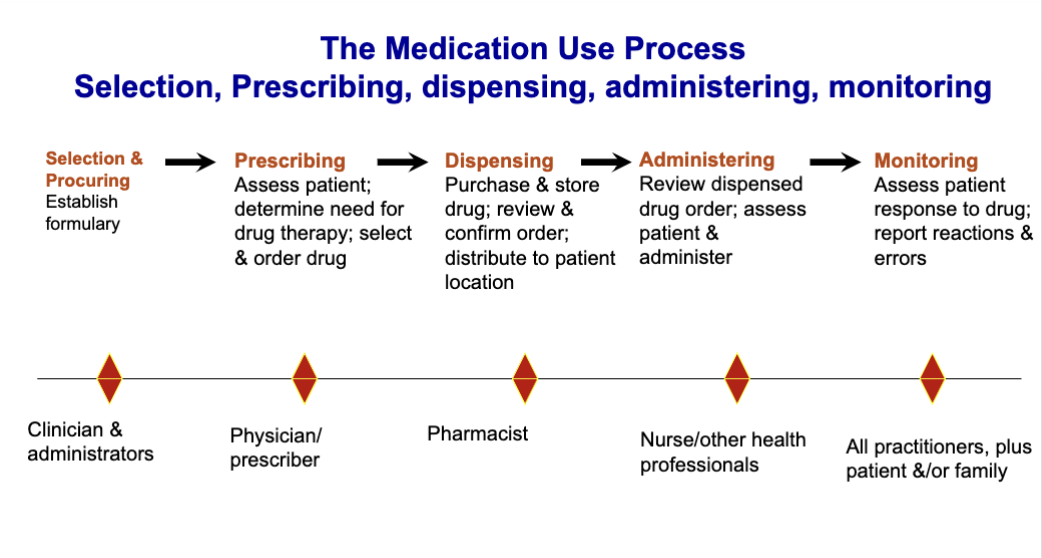
Discuss the extent of medication errors and their impact on patient care: What is the medication use process?
Selection + Procuring
Prescribing
Dispensing
Administering
Monitoring
Discuss the extent of medication errors and their impact on patient care: How often, and what is the extent of medication errors in the US?
Medications harm at least 1.5 million people per year
Pt deaths: 198,000 in 1995 to 218,000 in 2000
Cost: $177 billion per year
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: What are the key elements in medication safety?
Patient Information
Drug Information
Communication of drug orders and other drug information
Drug labeling, packaging, and nomenclature
Drug standardization, storage and distribution
Medication device acquisition, use and monitoring
Environmental factors, workflow and staffing patterns
Staff competency and education
Patient education
Quality processes and risk management
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss what patient information is typically provided and where there could be an error
Basic demographic and clinical information
serious, ADEs stem from insufficient information about pt’s before prescribing, dispensing, and administering
Correctly dispensed prescription handed to a patient for whom it was not intended is an error - avoid by consistent use of a second patient identifier
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with drug information
preventable adverse drug events (ADEs) are directly related to inadequate dissemination of drug information
Overall lack of knowledge about drug therapy was the most common cause of medication errors during both drug prescribing and drug administration, with dosing errors occurring most frequently
miscalculations or incorrect expression of measurement or drug concentration
Wrong dose and wrong drug choice
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with communication of drug orders and other drug information
Methods of communicating prescription orders and other drug information are standardized and automated to minimize the risk for error
use of incorrect drug names, confusing expressions of dosage forms, decimal places, and misunderstood abbreviations
Illegible and legible handwriting
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with Drug labeling, packaging, and nomenclature
drug products that have similar or confusing manufacturer labeling/packaging and/or drug names that look and/or sound alike
ensure prescription labels clearly identify the patient, product, directions for use, the dispensing pharmacy, and any other important information that the patient may need to take the medication accurately and safely
Tall man (mixed case) letters call attention to a drug's name and help with look-alike/sound-alike drugs
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with Drug standardization, storage and distribution
Never allow food or drink in any refrigerator used to store medications
Need to review stock for short-dated products that need to be removed from inventory
Need to store expired, returned or recall medications in an area away from regular stock
Avoid cluttered shelves
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with Medication device acquisition, use and monitoring
Appropriate safety assessment of drug delivery devices prior to their purchase and during their use is key to safe medication administration
Competency in using drug delivery devices
new devices come to the market, it is essential that training tools for proper use and potential hazards be available to train healthcare providers and patients
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with Environmental factors, workflow and staffing patterns
poor lighting, cluttered work-spaces, noise, interruptions,
and non-stop pharmacy activity
process of transcribing orders and order entry, as pharmacy staff are frequently answering telephones
and requests for information while carrying out these responsibilities
Reduced staff levels and increased workload
Poorly designed systems, processes and workflow
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with Staff competency and education
New medications being used in the pharmacy
High-alert medications which have the greatest potential to cause patient
harm if an error occurs, or drugs with unusual or critical dosing considerations
Protocols, policies and procedures related to medication use, including those related to the use of drug delivery/administration devices
Medication errors that have occurred within the organization or occurred in other organizations, and the error prevention strategies
Discuss the factors that contribute to medication errors: Discuss where there could be an error with Patient education
the final link in the medication-use process
ongoing education by physicians, pharmacists and nurses about drug brand and generic names, indications, usual and actual doses, expected and possible adverse effects, drug or food interactions and how to protect themselves from errors
Examine approaches to minimize the risk of medication errors
Traditional efforts at error reduction have focused on individual practitioners (training, exhortation, rules and disciplinary action to improve performance)
Human factors specialists and error experts reject this approach - more effective to change the system as a whole than to target individuals for improvement
redesign the systems and processes that lead to errors rather than focus efforts on correcting the individuals who make errors