Environmental Ethics in Nature and Tourism: Key Figures and Case Studies
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is environmental ethics?
A field that answers questions about the right and wrong ways to act in nature and towards the non-human world.
What are the two competing biblical interpretations regarding nature?
Dominion Thesis (humans dominate nature) and Stewardship (humans care for and protect nature).
What is anthropocentrism?
An ethical standpoint that places humans at the center of moral consideration.
What is ecocentrism?
An ethical perspective that values all living things and ecosystems, placing them at the center of moral consideration.
Who is John Locke and what is his view on property?
John Locke defined property as the mixing of human labor with nature, asserting that nature has no value unless transformed by human effort.
What are the two ethical rules proposed by John Locke?
1. Do not take more nature than you can use.
2. Do not take more land than you can work.
Who is Gifford Pinchot and what is his contribution to environmental ethics?
Father of Forestry, advocated for conservation and the sustainable use of resources.
What is John Muir's perspective on nature?
Viewed nature as having spiritual qualities and argued for its preservation for its own sake.
What is the significance of the Hetch Hetchy Valley debate?
It represents the conflict between conservation (Pinchot) and preservation (Muir) regarding resource use.
What is Aldo Leopold's Land Ethic?
Believed that a broader community exists including: humans, soils, waters, and animals, advocating for interdependence.
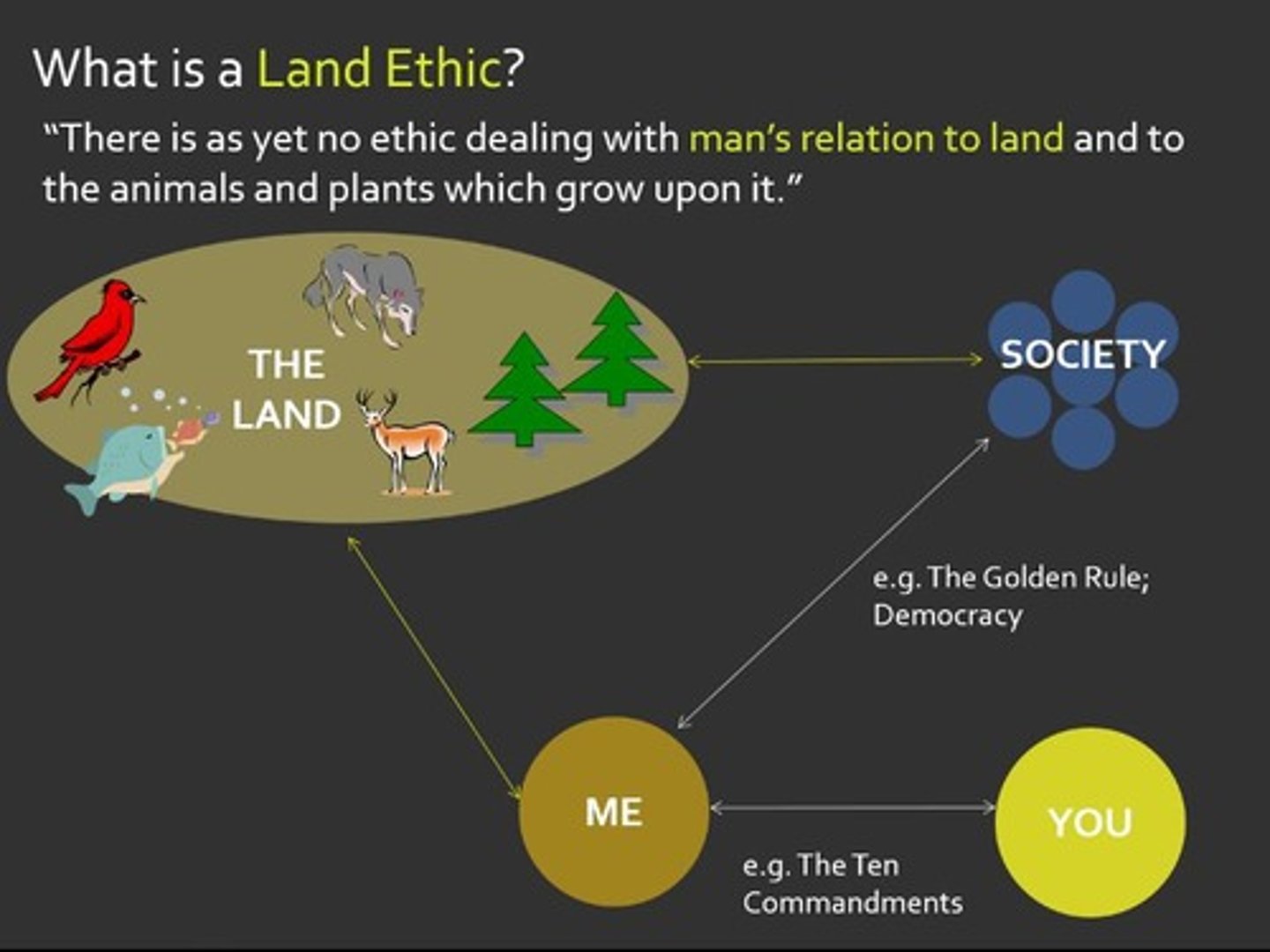
What is Deep Ecology according to Arne Naess?
Promotes biospheric egalitarianism, asserting that all living things have intrinsic value independent of their usefulness to humans.
What is Social Ecology as proposed by Murray Bookchin?
Emphasizes that environmental problems are rooted in social structures and relationships, requiring social solutions.
What is the role of ethics in environmental discussions?
A more inclusive environmental ethics is needed, recognizing the value of different ethical perspectives.
What are the economic implications of conservation ethics?
A conservation ethic based on economic value can marginalize communities that do not have immediate commercial value.
What environmental issues arise from tourism on Mt. Everest?
Issues include waste management, the impact on local livelihoods, and the ethical considerations of tourism in sacred spaces.
What is the average cost per person for climbing expeditions to Everest?
$40,000 to $60,000, potentially reaching $150,000 for luxury experiences.
How much waste is generated annually by climbers on Everest?
Approximately 165,000 lbs of waste is produced each year.

What ethical considerations should be made regarding advertising on Everest?
Considerations include the sanctity of the site for Buddhists and the impact on the environment and local culture.