Selyes general adaptation syndrome
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
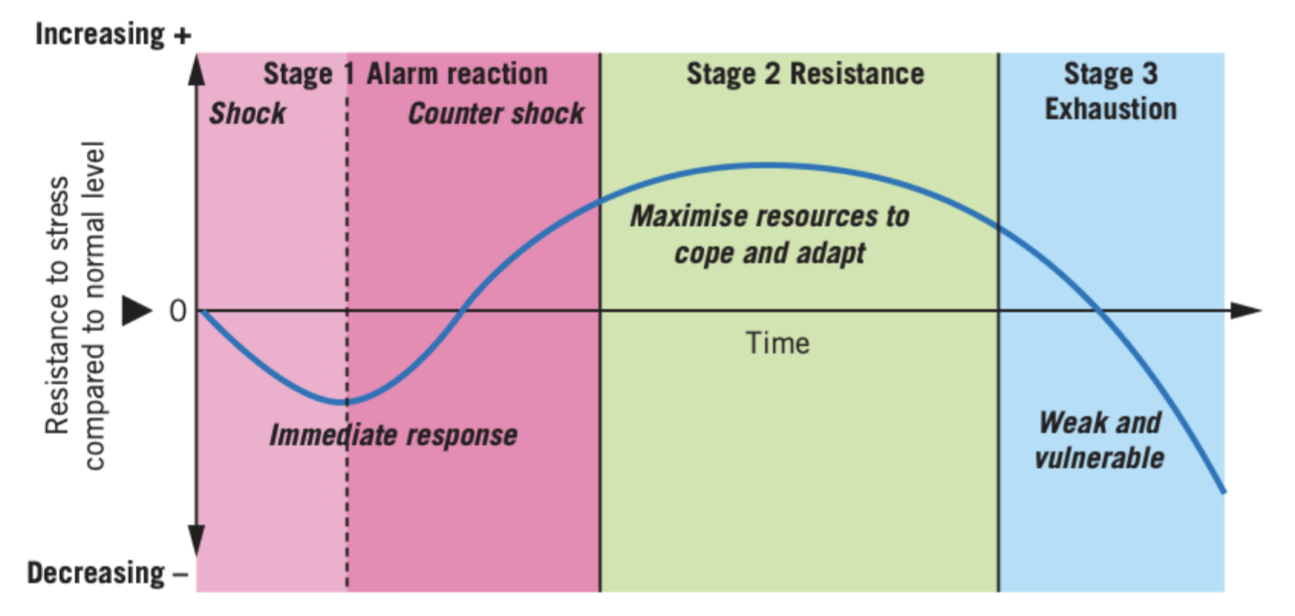
General Adaptation Syndrome
a biological model of stress that suggests we have a non-specific biological response to stress that occurs in 3 stages.
elements emphasised
its non-specific, meaning its the same regardless of the stressor an organism is faced with.
its identical within all members of a species, in this case rats.
alarm reaction
first stage of GAS in which we become aware of the stressor; it consists of shock and countershock.
shock
first stage of alarm reaction in which the bodies ability to deal with the stressor falls below the baseline resistance. It’s an acute stress response and is associated with decrease in muscle tone, body temperature and blood glucose levels.
countershock
second stage of alarm reaction in which the bodies ability to deal with the stressor rises above normal. It’s helped by the release of adrenaline and cortisol and activation of the flight-or-fight-or-freeze response to deal with stressor. It doesn’t usually last very long and associated changes include increased muscle tension, heart rate, breathing rate, blood glucose and temperature.
resistance
second stage of GAS in which stressor persists and the bodies resources are maximised to adapt and cope over time. Cortisol levels are at their highest which helps repair damage to body and maximise resources, which over time can lead to symptoms of wear and tear and social withdrawal/ irritability.
exhaustion
last stage of GAS in which the continued depletion of energy reserves and high levels of hormones such as cortisol decrease resistance to the stressor and impair the immune system. We become more susceptible to infection, stomach ulcers, sleep disturbances, irritability, fatigue, anxiety and depression.
strengths
model suggests predictable pattern of responses which can be easily tested in a laboratory.
identifies biological processes that can occur in stress response such as hormone secretion and immune depletion.
one of the first theories to suggest that stress can weaken bodies resistance to illness.
there’s research and evidence which suggest that the 3 stages of GAS exists and our bodies non-specific response to stress is a physiological reality (at least in rats)
limitations
humans and rats are physiologically different e.g. human stress responses are more complex.
doesn’t acknowledge psychological and cognitive processes in stress response, which can influence how much a person experiences stress.
doesn’t account for individual differences in stress response e.g. many different types of conditions are associated with high stress such as hypertension, PTSD and major depression.