Unit 8 - Nasal Cavity and Pharynx
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is the nasal planum (nasal plate)?
- Bare skin around the nostrils
What is the philtrum?
- Slit in the nasal planum and upper lip
The nostril opens into what?
- Into the nasal vestibule
What is the wing of the nostril?
- Thickened dorsolateral portion of the nostril
The external nose is formed of _________ and ___________.
- Bone
- Cartilage
What bones make up the external nose?
- Incisive bone
- Maxilla
- Nasal bone
Cartilage forms the __________ part of the external nose.
- Mobile
What cartilages make up the external nose?
- Septal cartilage
- Dorsal lateral nasal cartilage
- Ventral lateral nasal cartilage
- Accessory cartilage
The nasal cavity is the ___________ part of the respiratory tract. What is it divided into by the nasal septum?
- Facial
- Divided into right and left halves by the nasal septum
What is the cranial boundary of the nasal cavity? The caudal boundary?
- Cranial: Nostrils (external nares)/nasal aperture
- Caudal: Choanae (internal nares)
Where are the choanae located?
- Located between the nasal cavity and the nasopharynx
The bony portion of the nasal septum forms the caudal __________ of the septum. What bones is it formed by?
- 1/3
- Formed by ethmoid, frontal, nasal, and vomer bones
What is the cartilaginous portion of the nasal septum?
- Rostral continuation of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
Where is the membranous portion of the nasal septum located?
- Located in the region of the nasal aperture
What does the membranous portion of the nasal septum connect?
- Connects cartilaginous septum with moveable cartilage of the nose
What is the nasal vestibule?
- Initial portion of the nasal cavity
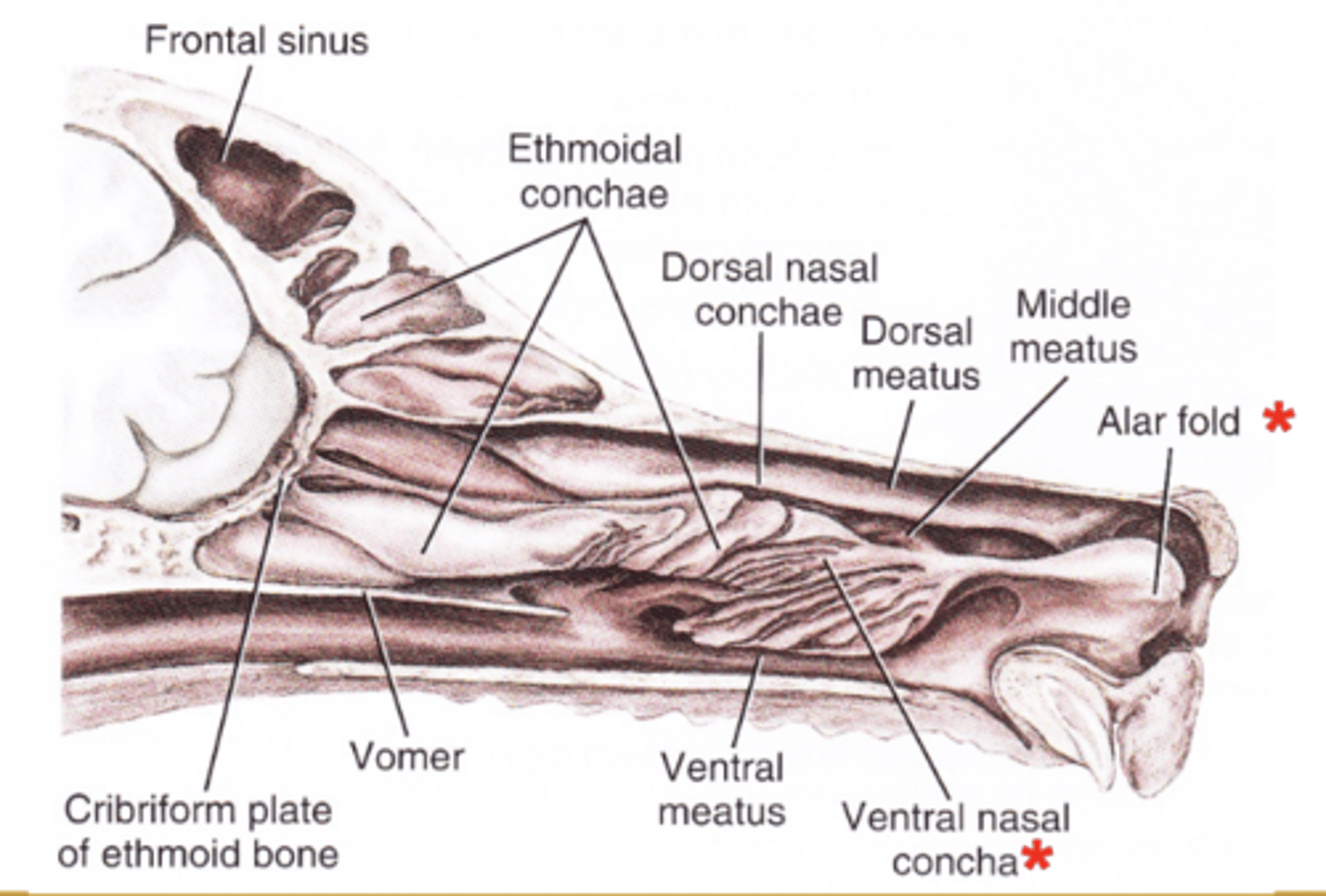
What is the alar fold? Where does it terminate?
- Extension of the ventral nasal concha
- Terminates in the nasal vestibule
What does the alar fold fuse with? Where does it divert air?
- Fuses to the wing of the nostril
- Diverts air medially and ventrally
What is the location of the nasolacrimal duct opening?
- Nasal vestibule
What are nasal conchae? What do they occupy?
- Cartilaginous or slightly ossified scrolls covered with nasal mucosa
- Occupy the major portion of each half of the nasal cavity
What are the two nasal conchae?
- Dorsal
- Ventral
Describe the dorsal nasal concha and its attachments.
- Elongated, slightly curled scroll which attaches to the ethmoid and nasal bones
Describe the ventral nasal concha and its attachments.
- Several tightly folded scrolls which attaches to the maxilla at the conchal crest
The dorsal nasal concha is continued rostrally by what?
- By a mucosal fold into the nasal vestibule
Where is the ventral nasal concha located?
- Located the level of the first to third maxillary premolar teeth
The ethmoid labyrinth (concha) are also referred to as what?
- As middle nasal concha
What is the ethmoid labyrinth (concha)?
- Outgrowths of ethmoid bone covered with nasal mucosa
The ethmoid labyrinth (concha) fill the __________ part of the nasal cavity and extend into the ____________ _____________ and the cavity in the _______________ ______________.
- Caudal
- Frontal sinus
- Presphenoid bone
What does meatus mean?
- Passageway
Where is the dorsal nasal meatus located? Where does it present air to?
- Located dorsal to the dorsal nasal concha
- Presents air to the olfactory mucosa
Where is the middle nasal meatus located? What does it access?
- Between the dorsal and ventral nasal conchae
- Accesses the frontal sinus
Where is the ventral nasal meatus located? What does it communicate with?
- Located ventral to the ventral nasal concha
- Communicates with the pharynx
Where is the common nasal meatus located?
- Along the nasal septum
What are the paranasal sinuses?
- Frontal sinus
- Maxillary sinus/recess
- Sphenoid sinus
In the dog, how is the frontal sinus divided? How does this differ in the cat?
- Divided into lateral, medial, and rostral parts
- In the cat, the frontal sinus is undivided
In the dog, which part of the frontal sinus is the largest?
- Lateral frontal sinus
Describe the frontal sinus in Persian cats.
- Reduced or absent
Frontal sinuses open into the nasal cavity via what?
- Via ethmoid meatuses
Where is the maxillary sinus/recess located in the dog? What does it communicate with? What does it contain?
- Located dorsal to the roots of the last 3 cheek teeth.
- Freely communicates with the nasal cavity
- Contains the lateral nasal gland
What is the lateral nasal gland innervated by?
- Facial nerve (CN VII)
How is the maxillary sinus/recess formed in the dog?
- Lateral wall is formed by maxillary bone, medial wall is formed by lateral lamina of ethmoid bone
Describe the maxillary sinus/recess in the cat.
- Maxillary sinus is almost nonexistent
The sphenoid sinus is present in which species? Where is it located?
- The cat
- Located ventral to the cranial cavity
Why is the sphenoid sinus only a potential cavity in the dog?
- Because it is filled by an endoturbinate scroll
The pharynx is a passageway for which systems? Where does it extend from and to?
- For both respiratory and digestive systems
- Extends from the orbits to approximately the second cervical vertebra
What are the regions of the pharynx?
- Oropharynx
- Nasopharynx
- Laryngopharynx
Is the larynx part of the pharynx?
- No
What are the cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral and lateral boundaries of the oropharynx?
- Cranial: Palatoglossal arch/fold
- Caudal: Caudal border of the soft palate; base of the epiglottis
- Dorsal: Soft palate
- Ventral: Root of tongue
- Lateral: Tonsilar fossa and palatine tonsil
What are the palatine tonsils located?
- Located in the lateral wall of the oropharynx just caudal to the palatoglossal arch
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
- Tonsillar fossa
The medial wall of the tonsillar fossa is formed by what?
- The tonsillar fold
The palatine tonsils are _________ in the cat.
- Small
Efferent lymphatic vessels of the palatine tonsils drain into what?
- Into the medial retropharyngeal lymph node
What are the cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral, and lateral boundaries of the nasopharynx?
- Cranial: Choanae
- Caudal: Intrapharyngeal ostium formed by patatopharyngeal arch
- Dorsal: Base of the skull and longus capitis m.
- Ventral: Small portion of hard palate and all of soft palate
- Lateral: Palatine and pterygoid bones
What does the nasopharynx contain?
- Pharyngeal opening of the auditory tubes
- Pharyngeal tonsils: Lymphoid tissue, adenoids in humans
What is the intrapharyngeal ostium? What is it formed by?
- The opening of the nasopharynx into the laryngopharynx
- Formed by right and left palatopharyngeal arches and caudal border of soft palate
What are other names for the auditory tube?
- Internal auditory canal
- Internal auditory meatus
- Eustachian tube
What does the auditory tube connect?
- Connects middle ear to nasopharynx
What happens to the opening in the nasopharynx during swallowing and yawning?
- It expands, allowing air pressure within the tympanic cavity to equalize with air pressure in the external ear canal
The laryngopharynx is the portion of the pharynx located __________ to the larynx.
- Dorsal
What are the cranial, caudal, dorsal and ventral boundaries of the laryngopharynx?
- Cranial: Palatopharyngeal arches
- Caudal: Pharyngoesophageal limen (at the level of the axis)
- Dorsal: Longus colli and longus capitis muscles at the level of C1 and C2
- Ventral: Larynx
The pharyngoesophageal limen is located between what two things?
- Located between the laryngopharynx and the esophagus
Somatic muscles of the head are muscles of ___________ origin. This includes what two muscle groups?
- Somatic
1) Extrinsic eye muscles
2) Tongue muscles
The visceral muscles of the head are muscles of _________________________ origin. This includes what five muscle groups?
- Pharyngeal arch
1) Muscles of mastication
2) Muscles of facial expression
3) Pharyngeal constrictors
4) Muscles of pharynx, larynx, esophagus
5) COST muscles and laryngeal muscles
The pharyngeal muscles are primarily associated with what?
- With the laryngopharynx
What are the pharyngeal muscle constrictors (which we need to know)? The dilator?
- Constrictors: Hypopharyngeus m., thyropharyngeus m., and cricopharyngeus m.
- Dilator: Stylopharyngeus m.
Where does the hypopharyngeus m. course? What is its action? What is it innervated by?
- Courses from the thyrohyoid and ceratohyoid bones to the mid-dorsal raphe of the pharynx
- Constricts the rostral part of the pharynx
- Innervated by CNs IX and X.
Where does the thyropharyngeus m. course? What is its action? What is it innervated by?
- Courses from the thyroid cartilage lamina to the mid-dorsal raphe of the pharynx
- Constricts the middle part of the pharynx
- Innervated by CNs IX and X
The cricopharyngeus m. is also referred to as what?
- As the upper esophageal sphincter
Where does the cricopharyngeus m. course? What is its action? What is it innervated by?
- Courses from the lateral surface of the cricoid cartilage to the mid-dorsal raphe of the pharynx
- Constricts the caudal part of the pharynx
- Innervated by CNs IX and X
Where does the stylopharyngeus m. course? What is its action? What is it innervated by?
- From the stylohyoid bone to the rostrodorsal wall of the pharynx
- Dilates, elevates and draws the pharynx forward
- Innervated by CNs IX and X
Where does the palatinus m. course? What is its action? What is it innervated by?
- From the caudal edge of the horizontal part of the palatine bone to the caudal free border of the soft palate
- Shortens the soft palate
- Innervated by CNs IX and X