Exam 2 flashcards
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What diet is recommended for CKD patients (without dialysis)?
Low protein, low sodium, low Phosphorus
What diet is recommended for a kidney transplant?
Balanced diet with low sodium and food safety precautions
What foods should someone with a kidney transplant avoid?
Grapefruit, raw seafood, undercooked meats
What are the two main causes of CKD?
Diabetes and HTN
What is the hallmark late finding of CKD (stage 5)?
Oliguria → anuria
What happens if a CKD patient misses dialysis?
Increased BUN/Ct and uremic buildupWh
What symptoms do you expect to see from someone who has uremic buildup after skipping dialysis?
Fatigue, headache, altered LOC.
What is the most life-threatening complication of CKD/AKI?
Hyperkalemia (leads to dysrhythmias and cardiac arrest)
What are three causes of intrarenal AKI?
ATN (most common), glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis.
If a patient hasn’t urinated for days, what electrolyte is most concerning to see?
Hyperkalemia
How do you correct hyperkalemia in AKI?
IV insulin + D10W (shifts K into cells w/out tanking pt)
What is the best way to monitor fluid balance on CRRT?
Obtaining daily weights
What is the first thing you do for chemical eye trauma?
Irrigate with MorganLens
If a patient has an object in their eye, such as a nail, what is the first thing you do?
Stabilize the object (do not remove).
What is the first thing you assess in a SCI?
Airway and breathing
What is paradoxical breathing?
Chest and abdomen move in opposite directions.
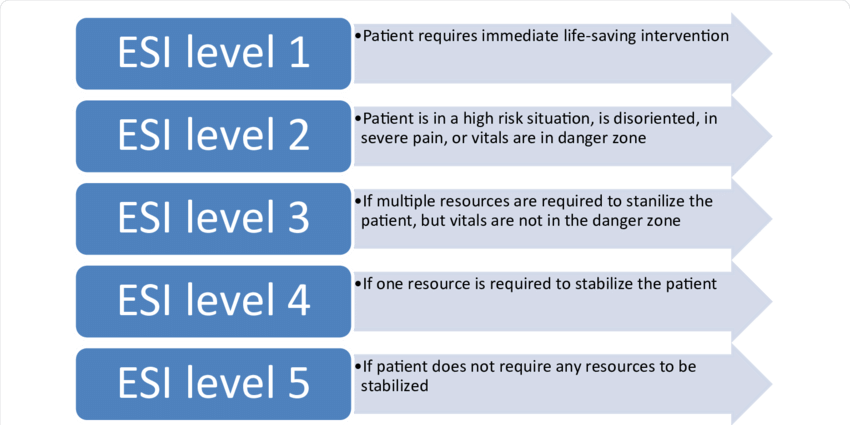
What is 1 and 5 on the ESI triage scale?
1 = life-threatening and 5= stable/minimal resources
Cardiac arrest, intubated trauma patient, overdose with bradypnea, severe respiratory distress, anaphylactic shock, hypoglycemia with change in mental status.
Using the ESI triage scale, which category do these patients fall under?
1= life-threatening conditions
Chest pain from ischemia, multiple trauma unless responsive, suicidal patient, immunocompromised patient with a fever, acute stroke.
Using the ESI triage scale, which category do these patients fall under?
2 = urgent conditions requiring timely intervention
Abdominal pain or gynecologic disorders unless in severe distress, hip fracture in older patient, vomiting, hypertension.
Using the ESI triage scale, which category do these patients fall under?
3 = non-urgent conditions requiring evaluation (vitals aren’t in danger zone)
Closed extremity trauma, simple laceration, cystitis.
Using the ESI triage scale, which category do these patients fall under?
4 = low priority cases requiring evaluation but not immediate intervention
Cold symptoms, minor burn, poison ivy, recheck (e.g., wound), prescription refill.
Using the ESI triage scale, which category do these patients fall under?
5 = lowest priority cases that can wait for evaluation and do not require intervention for stability
A patient has an airway obstruction and another has shock, which is immediate and life-threatening, which MCI tag would this be?
Red (first priority)
A patient has an open fracture, which is urgent but stable. What MCI tag would this be?
Yellow
A patient has a sprained ankle, which is minor. Which MCI tag is this?
Green
A patient suffers a massive head trauma during a mass casualty event, where there are limited/no resources and likely will die. Which MCI tag is this?
Black (last priorty)
What does redness/swelling around external fixation pins indicate?
Infection
What should you do if you notice external fixation pins look infected?
Clean the pins individually and notify the PCP.
A patient has severe leg pain and swelling (without external fixation pins), what do you suspect it is?
Compartment syndrome
What should you do if you suspect compartment syndrome?
Notify the PCP
What treatment will be performed for compartment syndrome?
Fasciotomy
What are the 6 P’s of compartment syndrome?
Pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia, paralysis, pressure
What is roconium’s MOA?
Non-depolarizing paralytic
Succinylcholine MOA?
Depolarizing paralytic
Midazolam MOA?
Benzodiazepine that sedates and causes amnesia.
Propofol MOA?
Sedative-hypnotic with rapid induction
Atropine MOA?
Anticholinergic that increases HR Wa
What medication would you expect to give to someone with bradycardia?
Atropine
What are classic signs of DKA?
Kussumaul respirations, n/v, abdominal pain, fruity breath, dehydration.
Name this condition using the provided labs:
BG >250, pH <7.3, HCO3 <16, ketones present, and increased anion gap.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
What is the treatment order for DKA based on lab results?
NS IV fluids → IV insulin drip → replace K+ → cardiac monitor
What risk must be monitored on an insulin drip for DKA?
Hypokalemia
Can a patient eat while on an insulin drip for DKA?
No
What are key identifying factors in DKA compared to HHS?
Ketones present, acidosis, rapid onset, and seen in DM1
What are key identifying factors in HHS compared to HHS?
No ketones, severe hyperglycemia, neuro symptoms, slow onset, seen in DM2, hyperosmolar
What are signs of hypoglycemia?
Cool, clammy, shaky, confused
Treatment for hypoglycemia if awake?
Juice/glucose tabs
A patient has a BG of 30 and is unconscious, what do you give?
Glucagon IM
A patient is bleeding in a mass casualty event and tagged, but there is also someone with airway compromise. Who should be seen first?
Airway compromise
How fast should the triage process take?
15 seconds
Cardiac arrest is an example of which ESI level?
1 - Immediate
Severe chest pain is an example of which ESI level?
2 - Emergent (high risk)
Moderate exacerbation of a chronic illness is an example of what ESI level?
3 - urgent, multiple resources
What does AVPU stand for and which survey is it used in?
Alert, Voice, Pain, Unresponsive - primary
What does an emergency primary survey focus on?
Identifying life-threats through ABCDE
What does an emergency secondary survey focus on?
Head-to-toe assessment after stabilization and history
What happened right before this started? Any allergies? Last meal? Event details?
These questions are an example of which emergency survey?
Secondary
What are examples of biologic warfare agents?
Anthrax, smallpox, botulinum toxin
What is proper traction site care?
Clean pin sites with saline and apply antibiotic ointment
What is the formula for the anion gap?
(Na + K) - (Cl + HCO3)
What is the first treatment for DKA and HHS?
Fluids
What is the fluid restriction calculation formula?
600 mL + previous 24 hour urine output
Fluid retention and edema are manifestations of which stage of CKD?
5
What is the GFR for stage 5 CKD?
<15 or dialysis
How do you treat prerenal hypovolemia?
Fluids
What are examples of postrenal AKI?
Urinary obstruction, kidney stones, BPH
What should be done if a patient has postrenal AKI?
Relieve the obstruction
What symptom of AKI requires fluid restriction?
Oliguria
How would hyperkalemia be corrected?
Insulin, sodium bicarbonate, and calcium gluconate.
Peritoneal dialysis (PD)
A treatment method for kidney failure that uses the lining of the abdomen to filter waste from the blood.
Hemodialysis (HD)
A procedure that uses a machine to filter waste and excess fluid from the blood, typically performed outside the body.
Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT)
A form of dialysis that provides continuous, slow, and gentle removal of waste and excess fluid from the blood, often used in critically ill patients.
What are nurse teaching points for someone on PD?
Sterile technique and monitor for peritonitis
Is PD or HD home-based?
PD
What is the nurse responsible for during HD?
Monitor vascular access and hypotension
What should the nurse auscultate and feel with an AV fistula?
Bruit and thrill
What are signs of a kidney transplant rejection?
Fever, increased creatinine, and tenderness
How do you prevent a fat embolism after a fracture?
Stabilize it
Elevate HOB 30 degrees, anticipate surgery, and monitor for vision loss are examples of interventions for what injury?
Eyes
What should you avoid doing if someone has an eye injury?
Apply pressure and nose blowing
If a penetrating eye injury is expected, what should the nurse avoid doing?
Irrigation
If a patient’s insulin is stopped and they suddenly feel dizzy, what should you do?
Check blood glucose
Humalog (lispro)
Rapid-acting insulin
Lantus (glargine)
Long-acting insulin
Levemir (detemir)
Long-acting insulin
Short-acting insulin
Onset 30-60 min, peak 2-4 hr, duration 5-8 hr; used for meals (bolus)
What is the order of treatment when someone is admitted for DKA?
Check sugars → fluids → potassium and insulin → cardiac monitor
Regular insulin
Short-acting insulin
Long-acting insulin
Onset 1-2 hr, no peak, duration 18-24 hr; basal coverage, once daily.
How soon should a patient eat after giving short-acting insulin?
Within 30 minutes
What are signs of hypoglycemia?
Shakiness, sweating, confusion, irritability
pH 7.2, HCO3 15, PaCO2 30
DKA (acidosis with respiratory compensation)
If the anion gap is >10, what does this indicate?
DKA
List different shocks
Cardiogenic, hypovolemic, distributive, obstructive
Anaerobic metabolism leading to metabolic acidosis is a characteristic of what shock stage?
Progressive
Tachycardia, hypotension, crackles, oliguria, and cool/clammy skin are examples of which shock?
Cardiogenic
Tachycardia, narrow pulses, cool/clammy, oliguria, AMS are s/s of which shock?
Hypovolemic
Hemorrhagic, trauma, ruptured spleen, dehydration, burns, penetrative wounds, and ascites are causes of which type of shock?
Hypovolemic
What is the first line treatment for septic shock?
Fluids