Anatomy and Physiology: Skeletal System Functions, Bone Types, and Fractures
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
Support, Mineral storage, Production of Red Blood Cells, Protection, Movement (with muscles ONLY)
Name the types of bone and give examples.
Long - Femur/Humerus, Flat - Skull/Ribs/Sternum, Short - Carpals/Tarsals/Ankle, Irregular - Vertebral/Hip
What does the periosteum do?
Protects, secures, and provides blood and nutrients to bone; it is the outside cover of the bone shaft.
What is the difference between yellow and red bone marrow?
Yellow - in adults, fat storage; Red - in children, produces red blood cells.
What is an epiphyseal plate?
It is a growth plate; when present, it means the bone length is increasing.
What is the difference between compact and spongy bone?
Compact - dense/homogenous (shaft); Spongy - needlelike (head).
What is a fossa?
A depression.
What is an epicondyle?
A protrusion or bump.
What is a foramen?
A hole (e.g., Foramen magnum in the occipital bone).
What is a tubercle?
A bump.
What is a cavity?
A hole.
What is a tuberosity?
A bump.
What type of cartilage is present in an embryo?
Hyaline cartilage.
What are the 4 steps in bone repair?
1. Hematoma, 2. Fibrocartilage callus, 3. Bony callus, 4. Bone remodeling.
What is the axial skeleton?
Skull, vertebral column, ribs.
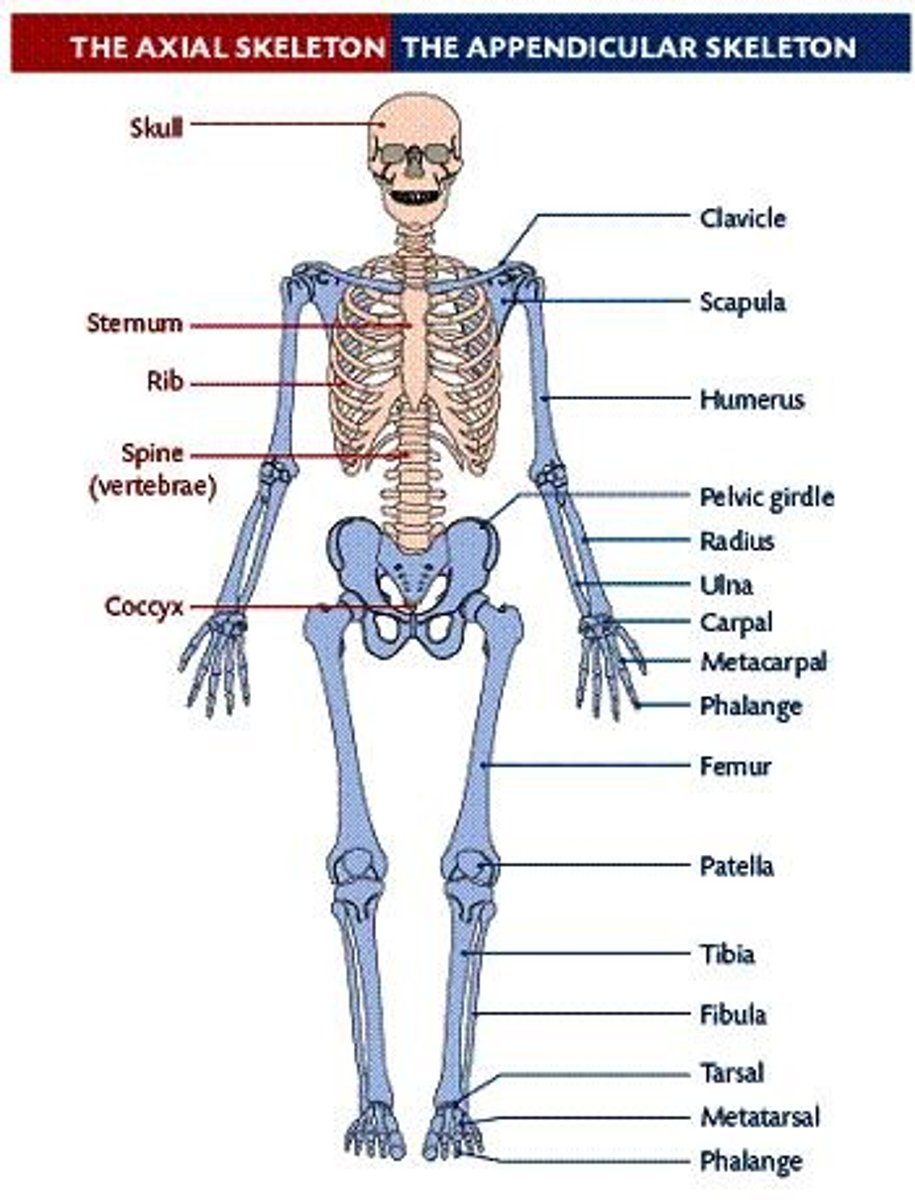
What is the appendicular skeleton?
Arms, legs, shoulders, hips.
What is the hyoid bone?
It is in the anterior neck where the tongue attaches; it is unique because it doesn't articulate with any other bone.
Name the regions of the vertebral column from superior to inferior.
Cervical - 5, Thoracic - 12, Lumbar - 5, Sacral - 5 fused, Coccyx - 4 fused.
Name the ribs from superior to inferior.
True (7), False (5 - 2 of them are floating).
What bone structure makes up the point of the shoulder?
Acromion.
What is the purpose of fontanels in children?
They allow for the brain to grow.
What is the most common fracture for children?
Greenstick.
Describe a comminuted fracture.
It has many fragments.
Describe a compression fracture.
It is compressed.
Describe a compound fracture.
It is outside of the skin.
Describe an impacted fracture.
The two ends are forced together.
Describe a greenstick fracture.
A fracture common in children (bendy).
Describe a simple fracture.
It is inside.
What are synovial joints?
Freely movable joints.
What are cartilaginous joints?
Slightly movable joints.
What are fibrous joints?
Immovable joints.
What are lacunae?
Small spaces containing bone cells.
What is Volkmann's canal?
Channels in bone that transmit blood vessels.
What are Haversian canals?
Channels in bone that contain blood vessels and nerves.
What is lamella?
Thin layers of bone matrix.
What is the anatomical position of the radius?
The radius is lateral.
What is the tibia?
The shin bone.
What is the acromion?
The point of the shoulder.
What is an osteoblast?
A bone-building cell.
What is an osteoclast?
A bone-collapsing cell.
What is the major portion of the coxal bone?
Ilium.
What is the zygomatic bone?
The cheekbone.