2 Electrical conductance disorders
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Where are the pacemaker cells located within the heart?
SA node: wall of the right atrium
AV node: right atrial wall near autonomic parasympathetic ganglia
Bundle of his: interventricular septum
Purkunje fibers: extend to apex (bottom) of heart and out to outer ventricular walls
What is the normal path of an electrical signal through the heart?
SA node, atria, AV node, Bundles of His, Purkinje fibers
What effect do sympathetic and parasympathetic activation have on the rate of depolarization and action potentials?
Sympathetic (fight or flight) --> increased conduction velocity in AV node via increasing rate of depolarization of AP --> reduces normal delay of conduction through AV nodes --> reduces time between atrial and ventricular contraction (INCREASES)
Parasympathetic (rest and digest) --> decreased conduction velocity in AV node via decreasing slope of phase 0 of the nodal AP --> slows depolarization of adjacent cells --> reduced velocity of conduction (DECREASES)
What potential effect could an interrupted or abnormal signal at any point in the electrical pathway have on contraction of the atria and/or ventricles?
Arrhythmia
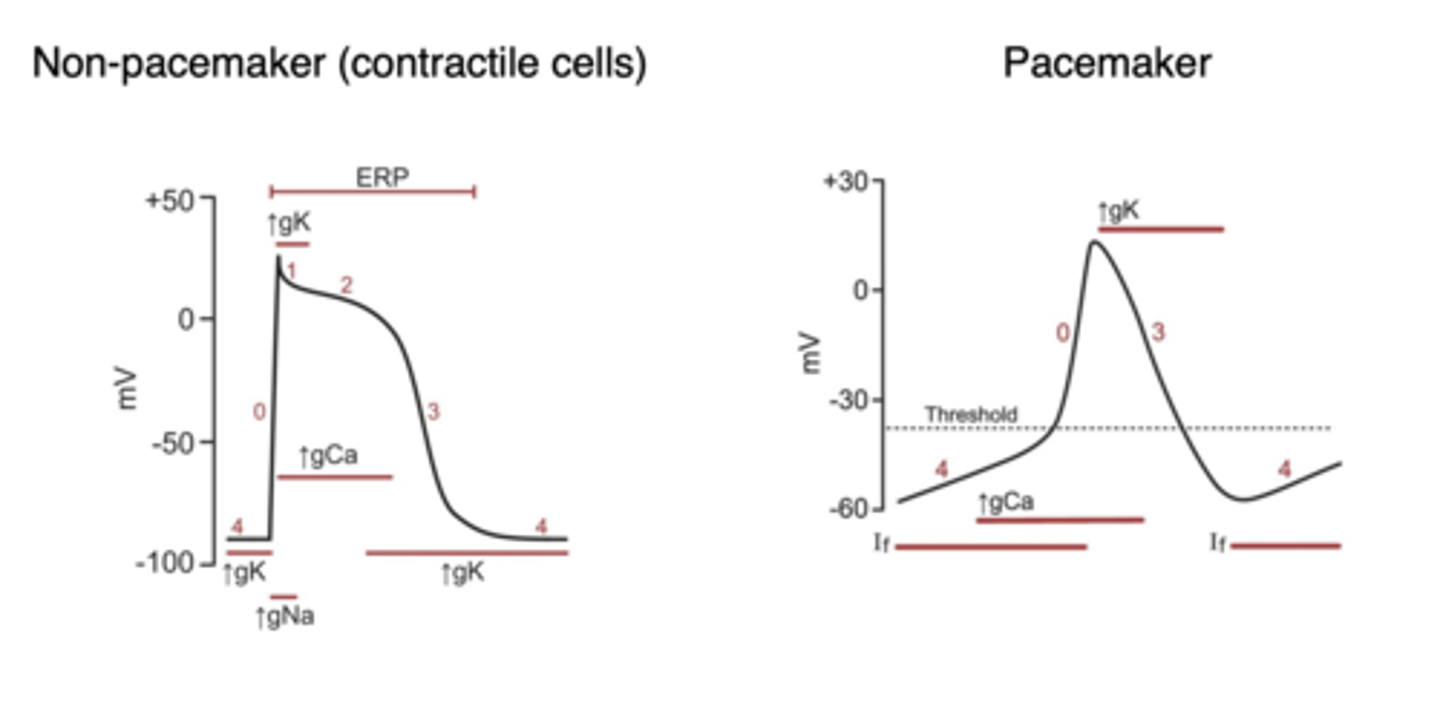
Which part of the cardiac action potential in non-pacemaker cells is denoted by which phase?
0: Rapid depolarization
1: Initial repolarization
2: Plateau phase
3: Repolarization
4: resting membrane potential near equilibrium potential for K+
Which ions and channels are responsible for each of the five (5) phases of the cardiac action potential in non-pacemaker cells?
0: Rapid depolarization --> increase conductance of voltage-gated Na+, Na+ moves into cell --> Long-last Ca2+ channels open when membrane depolarizes, Ca2+ moves into cell
1: Initial repolarization --> Caused by opening of K+ channels and rapid inactivation of fast Na+ channels
2: Plateau phase --> repolarization delayed due to open Ca2+ channels
3: Repolarization --> Ca2+ channels close --> K+ flows out of cell
4: resting membrane potential near equilibrium potential for K+
- Na+/K+ ATPase pump 3 Na+ out of cell 2 K+ in cell
- Na+/Ca2+ exchange 3 Na+ into cell and 1 Ca2+ out of cell
- Ca2+ ATPase pump moves Ca2+ out of cell
- Membrane permeable to K+ which allows K+ to leak out of cell and restore equilibrium
What are the differences in shape of the action potentials in pacemaker vs non-pacemaker cells?
Pacemaker cells do not have a phase 1 or 2 and have no true resting potential
- Slower depolarization
- Ca2+ is main cause of depolarization
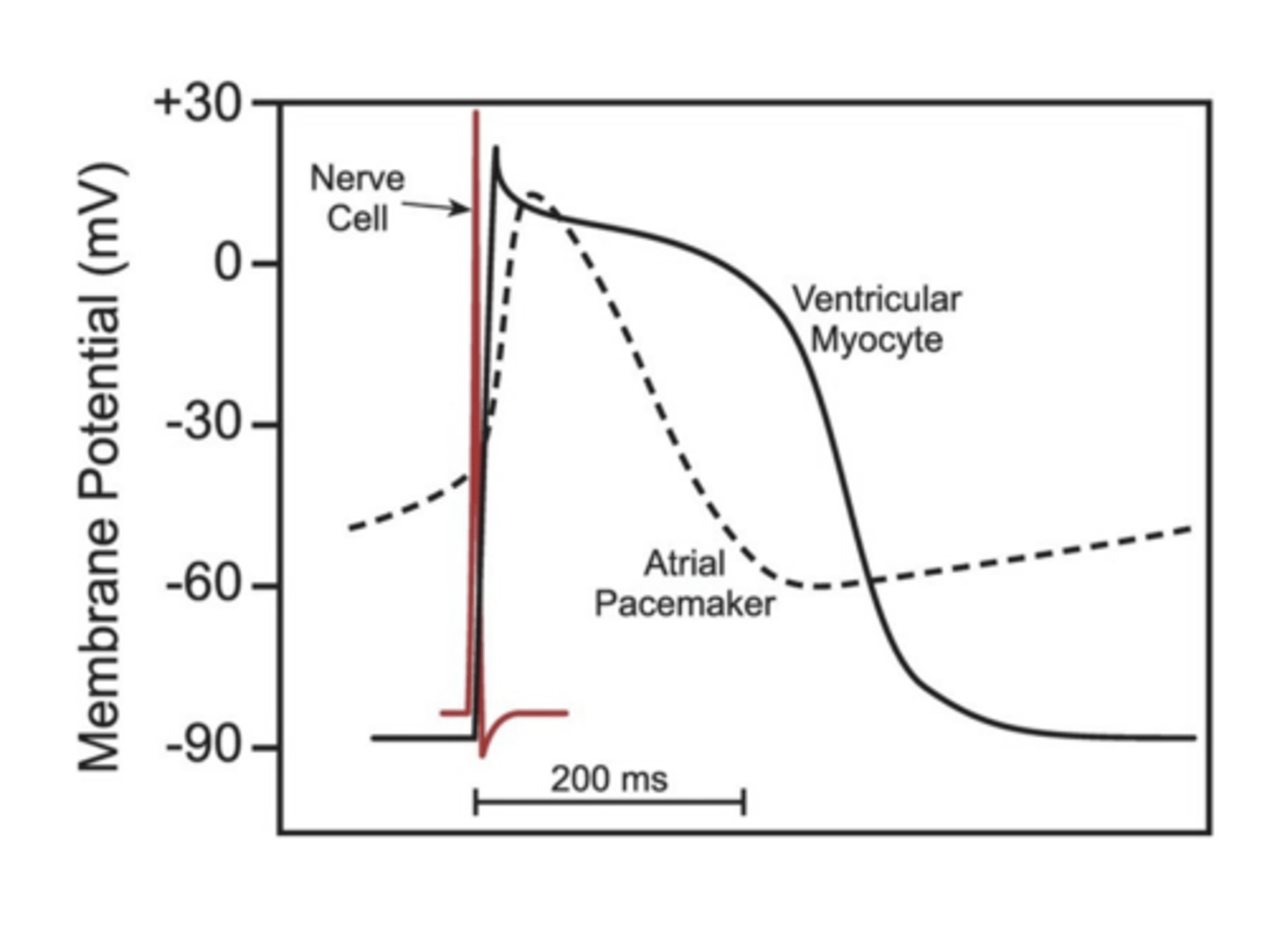
What are the differences in duration and shape of the atrial and ventricular action potentials compared to action potentials seen in skeletal muscle cells and neurons?
Nerve cell: ~1ms
Skeletal muscle cell: ~2-5 ms
Cardiac muscle cell: 200-400ms
What stage of electrical propagation do each of the waves of a normal ECG signify?
P-wave: atrial depolarization
QRS complex: ventricular depolarization
T wave: ventricular repolarization
PR interval: atrial depolarization plus AV nodal delay
ST segment: isoelectric period of depolarized ventricles
QT interval: duration of depolarization plus repolarization corresponds to AP durations throughout ventricles
How do each of the waves of a normal ECG correspond to cardiac function?
Waves show cardiac conduction
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Sinus rhythm
Normal sinus rhythm- Very regular- Minimal cyclical fluctuation- Atrial contraction always followed by ventricular contraction
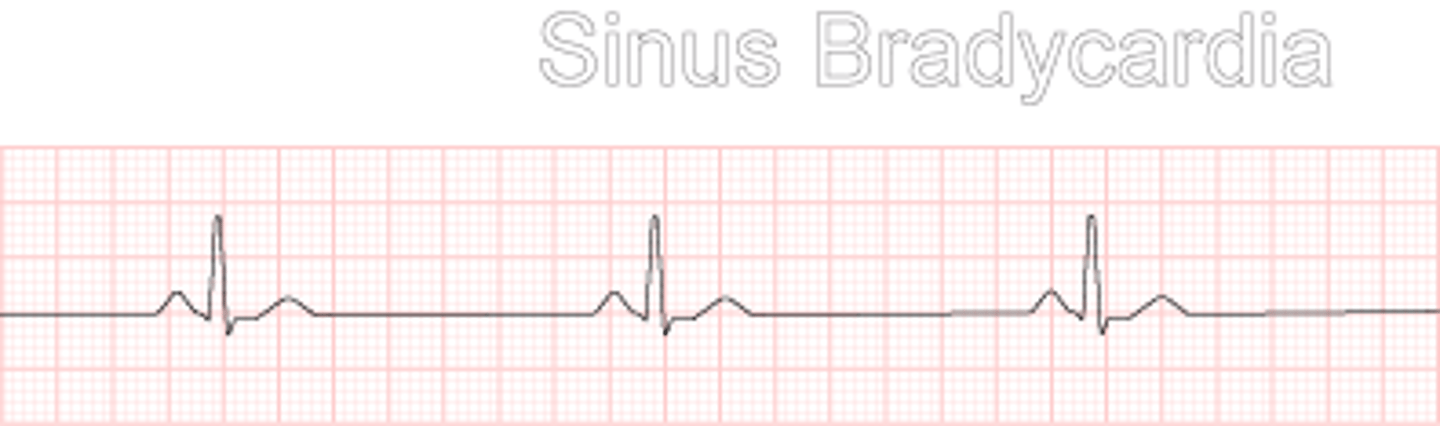
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Sinus bradycardia
Heart beats too slow, longer wider waves
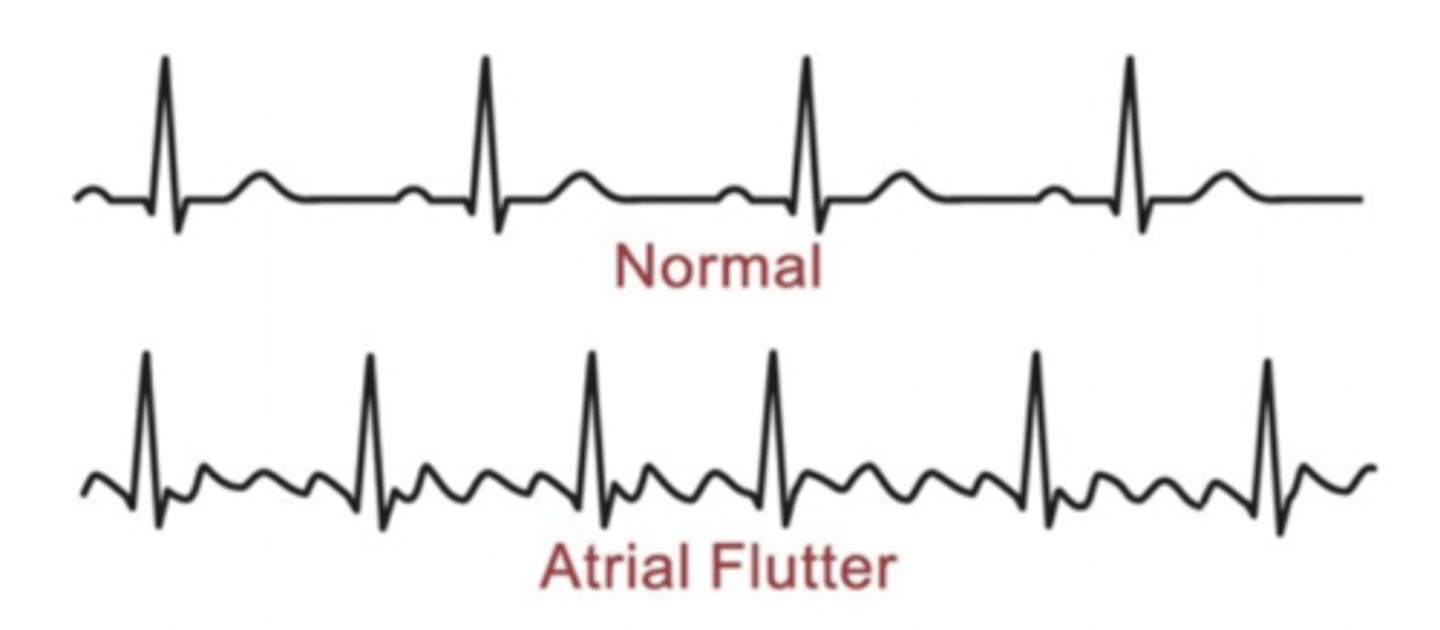
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Atrial flutter
Depolarization currents arise from SA but atrial rate too high for all impulses to be conducted through the AV node
FAST
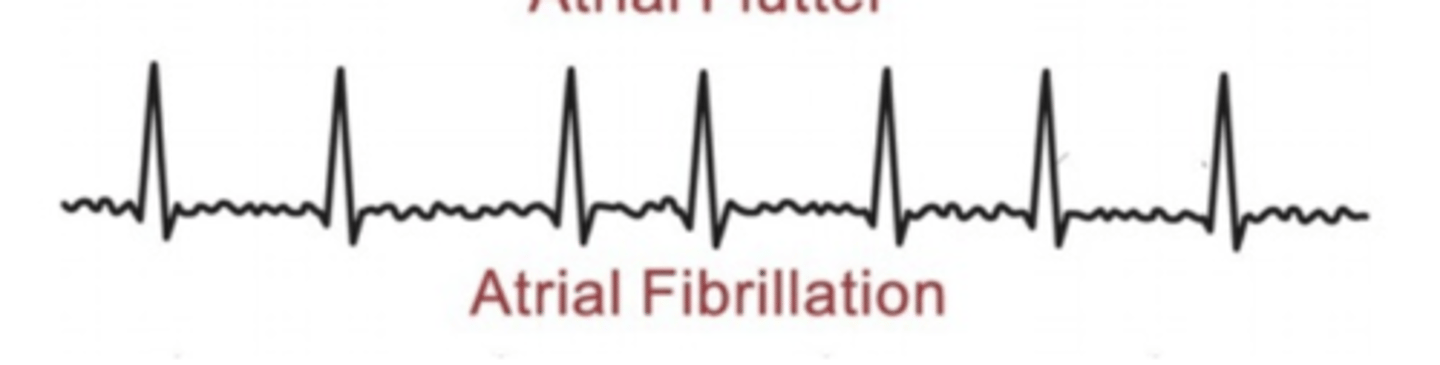
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Atrial fibrillation
Depolarization currents arise from non-SA node sites throughout the atria
No discernable P wave and irregular ventricular rate
FAST, RANDOM
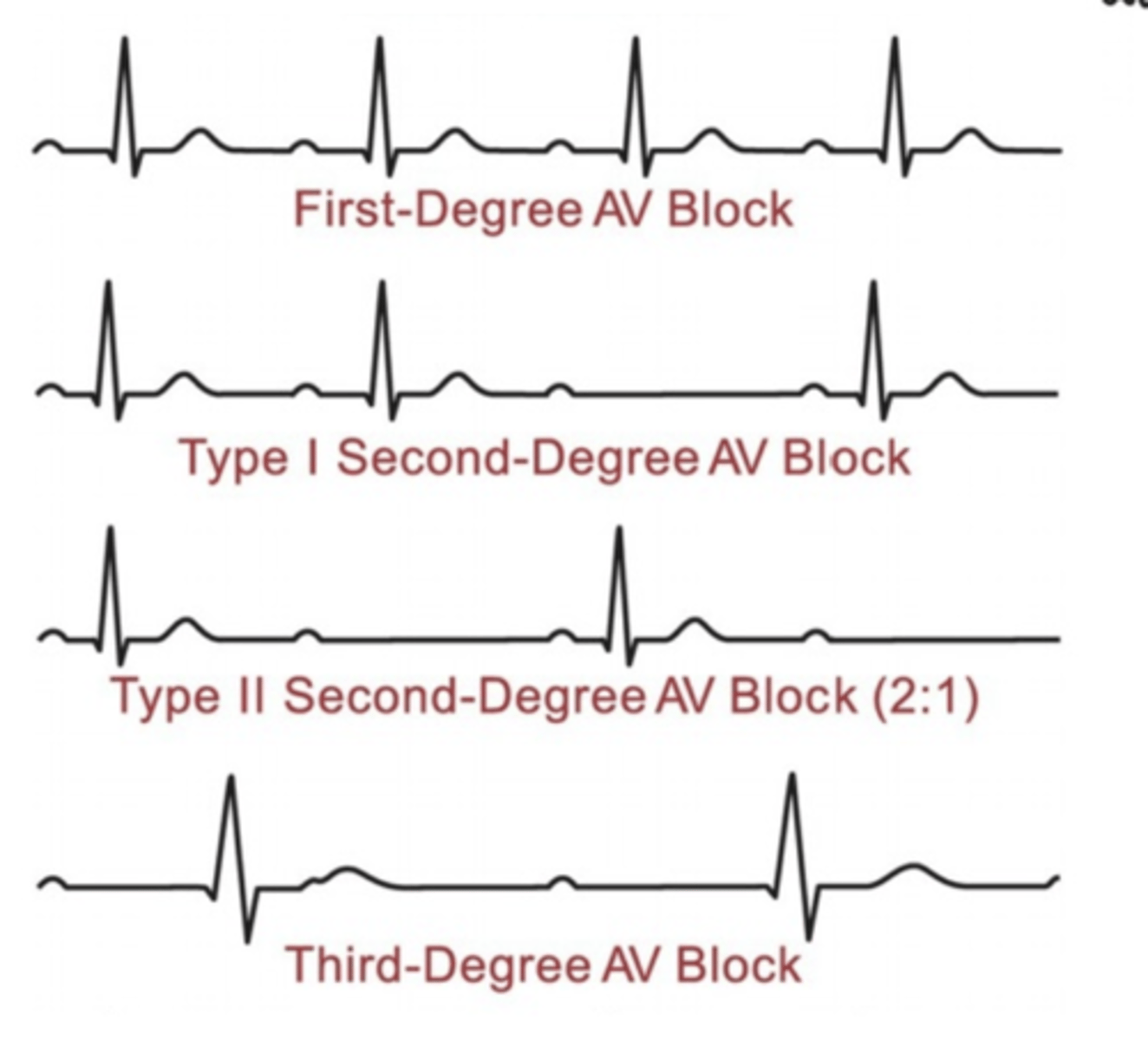
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Atrioventricular block (in general, not necessary to identify the three types)
Conduction delay in area of AV conduction system
Prolonged PR Interval, each type is progressively longer
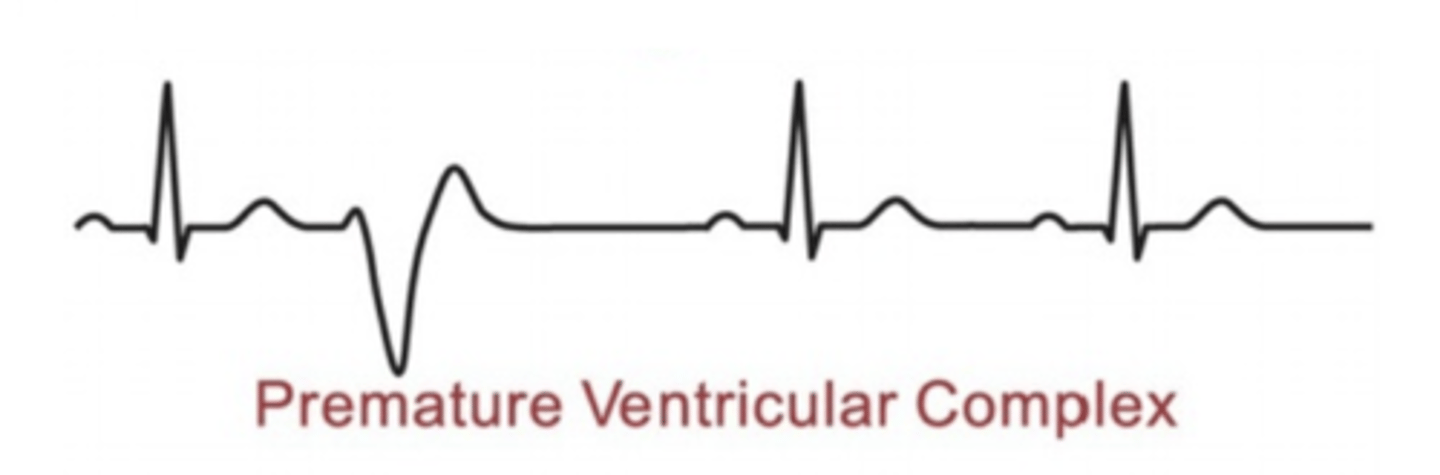
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Ectopic foci (premature ventricular complex)
No P wave
Large and inverted T wave
Premature and bizarrely shaped QRS complex
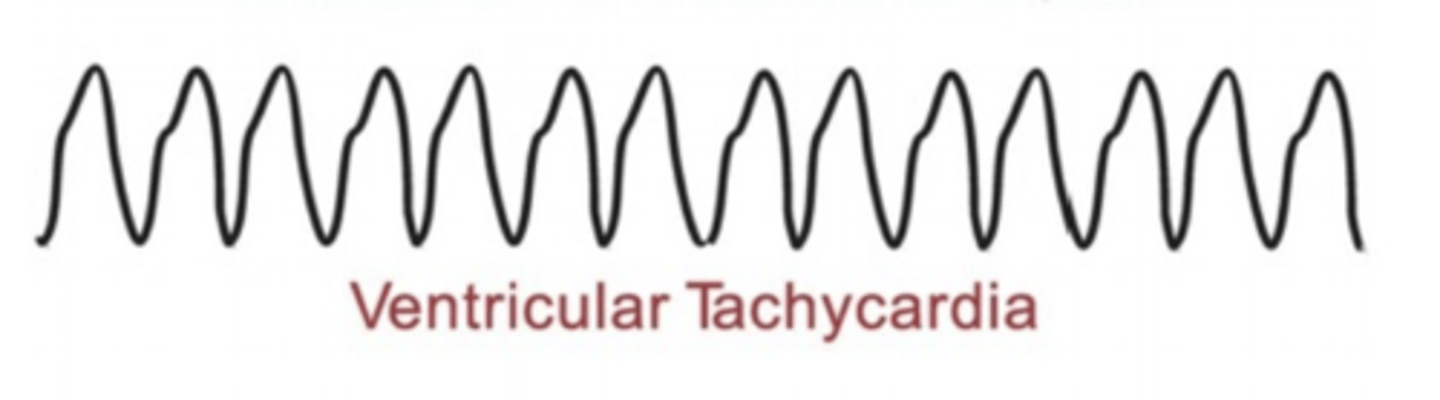
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Ventricular tachycardia
Characterized by widened QRS
Describe and/or identify the typical ECG tracings for each of the following rhythms and arrhythmias (these are the ONLY ECG strips I expect you to know): Ventricular fibrillation
Uncoordinated ventricular depolarizations

What are the most common arrhythmias in the US?
Atrial flutter
Atrial Fibrilation
What are the general symptoms of arrhythmias?
Less serious
- palpitations
- slow heart beat
- irregular heart beat
- feeling pauses between heart beats
More serious
- anxiety
- dyspnea
- syncope
- dizziness
- fatigue
- sweating
- chest pain
What techniques are typically used to diagnose arrhythmias?
- Electrocardiogram to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart
- Holter monitoring (24h portable ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Exercise stress test
- Tilt table test
What are some common risk factors for development of arrhythmia?
- Age
- Gender M>F
- Stress
- Renal failure
- HTN
- Previous MI
- Congenital heart disease
- Thyroid disorders
- OTC cough and cold medications
- Anti-arrythmia medications
- Anabolic steroids
- Diabetes
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Nicotine
- Chronic lung disease
- Pulmonary embolism
- Emphysema
- Asthma
What are some common causes of arrhythmia?
1. Coronary artery disease (CAD): Myocardial ischemia or infarction starves cardiomyocytes of oxygen, causing them to become depolarized causing altered impulse formation or conduction
2. Altered impulse formation
- Changes in rhythm
- Caused by changes in the automaticity (spontaneous activity) of pacemaker cells or
abnormal generation of action potentials at sites other than the SA node (termed ectopic
foci).
3. Altered impulse conduction
- Complete or partial block of electrical conduction
- Can lead to tachyarrhythmias
4. Changes in cardiac structure that accompany heart failure
- E.g., dilated or hypertrophied cardiac chambers
5. Electrolyte disturbances
- Primarily K+ and Ca2+
Describe the basic symptoms, effect on cardiac output (if any) and treatment approaches (if any) for each of the following arrhythmias (these are the ONLY arrhythmias I expect you to know): Sinus bradycardia
Symptoms:
- Decreased cardiac output --> decreased arterial pressure
- Syncope and other symptoms related to hypotension
Treatment: Pacemaker
Describe the basic symptoms, effect on cardiac output (if any) and treatment approaches (if any) for each of the following arrhythmias (these are the ONLY arrhythmias I expect you to know): Atrial flutter
Symptoms:
- Palpitations
- Fluttering
- Dyspnea
- Anxiety
Treatment:
- Ventricular rate control
- Electrical or pharmacological cardioversion
- Catheter based radio frequency (RFA)
- Anti-coagulant medication
- Anti-arrhythmic meds
Describe the basic symptoms, effect on cardiac output (if any) and treatment approaches (if any) for each of the following arrhythmias (these are the ONLY arrhythmias I expect you to know): Atrial fibrillation
Symptoms: during activity, shortness of breath and impaired perfusion of active muscles
Treatment: Cardioversion, anti-coagulant medication
Describe the basic symptoms, effect on cardiac output (if any) and treatment approaches (if any) for each of the following arrhythmias (these are the ONLY arrhythmias I expect you to know): Atrioventricular block (in general, not necessary to identify the three types)
Symptoms: Asymptomatic
- Except 3rd degree: fatigue, dizziness, light-headed, presyncope, syncope
Treatment: pacemaker
Describe the basic symptoms, effect on cardiac output (if any) and treatment approaches (if any) for each of the following arrhythmias (these are the ONLY arrhythmias I expect you to know): Ectopic foci (premature ventricular complex)
Symptoms:
- Asymptomatic
- Palpitations and neck and/or chest discomfort
- Feeling of heart “stopping”
- Syncope
- Hypotension
Treatment:
- Oxygen if hypoxic
- Antiarrhythmic meds
- Beta-blockers
- Electrolytes
- Ca2+ channel blockers
Describe the basic symptoms, effect on cardiac output (if any) and treatment approaches (if any) for each of the following arrhythmias (these are the ONLY arrhythmias I expect you to know): Ventricular tachycardia
Symptoms:
- Palpitation
- Light-headedness and syncope
- Chest pain
- Anxiety
- Sensation of neck fullness
- dyspnea
Treatment:
- cardioversion
- implantable carioverter defibrillator
- catheter base radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
Describe the basic symptoms, effect on cardiac output (if any) and treatment approaches (if any) for each of the following arrhythmias (these are the ONLY arrhythmias I expect you to know): Ventricular fibrillation
Symptoms:
- complaints of chest pain, fatigue, palpitations, and other nonspecific complaints up to 4 weeks prior to VF
Treatment:
- Immediate defibrillation
- Catheter-based radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
What are afterdepolarizations and what causes them?
Early afterdepolarizations
- Occur during late phase 2 or phase 3
- Likely to occur when AP durations are prolonged
- EAD characterized by long QT interval
- Can be cause by anti-arrhythmia drugs
- Blocked by magnesium
Delayed afterdepolarization
- Occurs at end of phase 3 or early in phase 4
- Results in tachyarrhythmias
- Caused by abnormal Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Can also be caused by digoxin
- Blocked by verapamil or quinidine
Cardiac action potentials have a much longer action potential than both nerve and skeletal muscle action potentials. True or False
True
The normal path of an electrical signal through the heart would be best described as:
a. SA node, atria, AV node, Bundles of His, Purkinje fibers
b. SA node, ventricles, AV node, Bundles of His, Purkinje fibers
c. AV node, ventricles, SA node, Bundles of His, Purkinje fibers
d. AV node, atria, SA node, Bundles of His, Purkinje fibers
a. SA node, atria, AV node, Bundles of His, Purkinje fibers
Phase 0 of the cardiomyocyte action potential represents
a. Rapid depolarization
b. There is no Phase 0
c. The plateau phase
d. Rapid repolarization
a. Rapid depolarization
The most effective initial treatment for ventricular fibrillation is:
a. Valsalva maneuver
b. Immediate defibrillation
c. Nothing as this is not a pathological condition
d. Anti-coagulation medication
b. Immediate defibrillation
The blood vessels with the thickest layer of smooth muscle are:
A: Arteries
B: Arterioles
C: Capillaries
D: Veins
A: Arteries
Phase 0 of the action potential in cardiac contraction cells involves:
A: Potassium channels
B: Sodium channels
C: Calcium channels
D: Hydrogen channels
B: Sodium channels
The QRS complex in the ECG represents:
A: Atrial depolarization
B: Ventricular depolarization
C: Ventricular repolarization
D: Nothing
B: Ventricular depolarization
General symptoms of arrhythmia include all of the following EXCEPT:
A: Palpitations
B: Anxiety
C: Dizziness
D: Death
D: Death
Treatment options for arrhythmia include all of the following EXCEPT:
A: anti-arrhythmic medication
B: Exercise stress test
C: Cardioversion
D: Pacemaker
B: Exercise stress test
The P wave in the ECG indicates the beginning of:
A: Atrial contraction
B: Atrial conduction
C: Ventricular contraction
D: Ventricular conduction
A: Atrial contraction