Unit 0 Test Review (Lab Safety, Scientific Method, Experimental Design, Lab Equipment)
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Chemistry
The study of matter and the changes it goes through
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Mass
The amount of matter in an object
Weight
The effect of gravitational pull on a mass
Scientific Method
A systematic approach used in scientific study
Observation
Using your 5 senses to develop a testable question
Hypothesis
Educated guess about the outcome of an experiment
Experiment
A set of controlled, repeatable trials that test the hypothesis by gathering data
Conclusion
Judgement based on one set of data about the question/hypothesis
Theory
Explanation supported by many experiments
Law
Relationship that has never been disproved/refuted yet
Quantatative
Data that is numeric
Qualitative
Data that is descriptive
Title
The effect of (independent variable) on (dependent variable)
Hypothesis
If…then…because….
Independent Variable (IV)
The variable YOU change or manipulate
Levels of IV
A list of the different IV's you're going to test
Number of Trials
How many times you're going to complete your experiment (at least 3)
Dependent Variable (DV)
The variable that responds to the changes that you made
Control
One of the IV levels that is the standard for comparison (not all experiments have this)
Constants
Things that CANNOT be changed in the experiment
Nature of Science (NOS)
The 6 foundational concepts that govern the way scientists formulate explanations about the natural world
First foundational concept of science
The natural world is understandable
Second foundational concept of science
Science is based on evidence
Third foundational concept of science
Science is a blend of logic and innovation
Fourth foundational concept of science
Scientific ideas are durable yet subject to change as new data are collected
Fifth foundational concept of science
Science is a complex social endeavor
Sixth foundational concept of science
Scientists try to remain objective and engage in peer review to help avoid bias
Goggles must be worn when there is:
Chemicals, glassware, and/or heat
Fume hood
Make sure sash is pulled down, vent is on, and all experiments take place at least 6 inches inside the hood
Fire extinguisher
Use for equipment on fire
P.A.S.S.
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
Fire Blanket
Use for people on fire
Safety Shower
Use for large chemical spills on the body
Eyewash
Use for chemical spills in eyes
Gas shut off
Turn lever horizontally to quickly shut off gas
Emergency call button
Calls the front office

Environment
Aquatic Toxicity

Health Hazard
Respiratory sensitizer

Flame
Flammable/Self-Reactive

Exclamation mark
Irritant (skin and eye)

Gas Cylinder
Gases under pressure
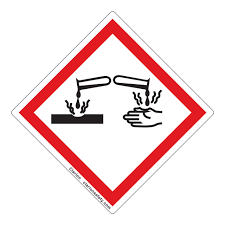
Corrosion
Skin Corrosion/Burns

Exploding Bomb
Explosive

Flame Over Circle
Oxidizer

Skull and Crossbones
Acute Toxicity

Triple Beam Balance
Weighs materials, equipment, and chemicals

Beaker
A glass container used for storing, mixing, pouring, and heating liquids that do not release gas or splatter

Buret/Burette
Long glass tube that dispenses liquids in very accurate quantities

Erlenmeyer Flask
A glass container used for liquids that may release gas or splatter but do not need to be heated evenly

Test Tube Holder
Tongs that are used specifically for holding tubes

Tripod
A three legged platform used to hold something above a bunsen burner

Pipette
A thin, plastic tube that is used to transfer a few drops of a liquid

Tongs
Metal forceps that can be used to pick things up

Ring Stand
A metal stand that can hold other pieces of equipment at varying heights

Florence flask
A glass container used for liquids that may release gas or splatter and need to be hearted evenly
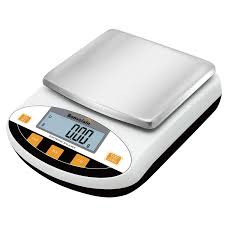
Electronic Balance
A device used to measure mass

Graduated Cylinder
A glass container used to measure volumes of liquid

Ruler
A device used to measure length

Thermometer
A device used to measure temperature

Test Tube
A thin, finger length glass container used for small samples of liquid

Funnel
A v-shaped tube used to transfer liquid from one container to another

Bunsen Burner
A device that is attached to a gas supply and used for heating things up

Pipe Clay Triangle
Holds a crucible while being heated over a Bunsen burner

Mortar and Pestle
Grinds solids into tiny pieces

Wire Gauze
Holds glassware in place over an open flame

Flint Striker
Creates a spark to light a Bunsen Burner

Watch Glass
Provides a surface for evaporating liquids; can also be used to cover a beaker

Stir Rod
Stirs combinations of materials

Crucible
Cup shaped container that allows solids to be heated to very high temperatures

Dropper Bottle
Dispenses drop-sized amount of liquids

Spatula/Scoopula
Long rod with a flattened or curved end, used to scoop small amounts of substances

Test Tube Rack
A metal, plastic, or wooden stand that can hold test tubes

Goggles
Provides eye protection

Hot Plate
Small appliance used to heat materials in glassware