Magnetism_gr 10
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Magnetic Filed
A region in space where a magnet or ferromagnetic material will experience a non-contact force.
Ferromagnetic materials
Materials that are strongly attracted by magnets and are easily magnetized. E.g Iron, Cobalt and Nickel.
Non-contact forces
A force exerted on an object without touching the object.
How do magnetic fields originate?
All magnetic fields originate as a result of moving charges.
Electric field
A region in space where an electric charge will experience an electric force.
Gravitational field
A region in space in which MASS will experience a gravitational force.
Magnet
An object that has a pair of opposite poles, called north and south or north-seeking and south-seeking poles.
Monopoles
There are NO MONOPOLES. Even if an object is cut into tiny pieces, it will still have North and South poles.
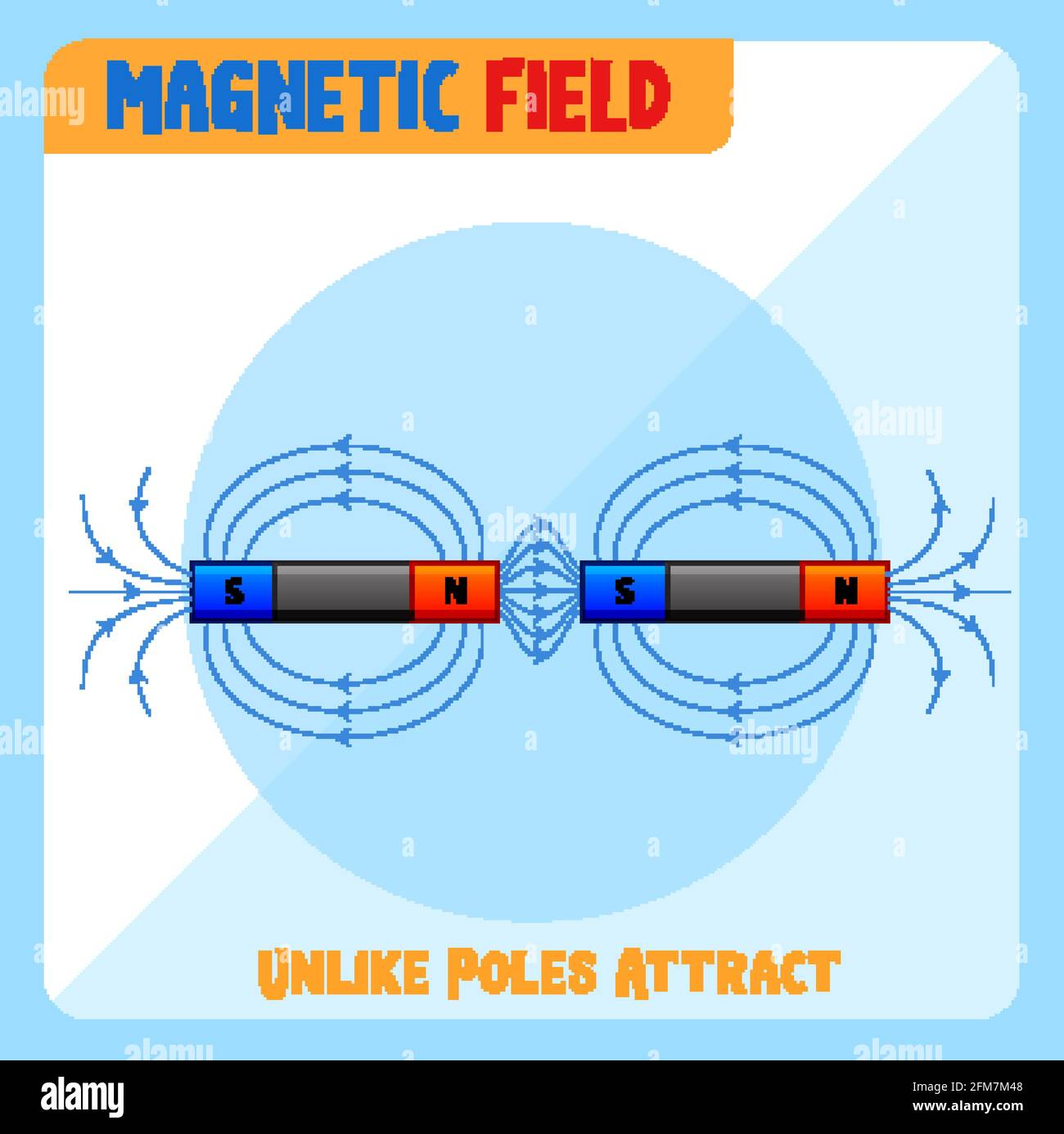
Attraction of magnets:
UNLIKE POELS ATTRACT EACH OTHER. Go closer to each other.
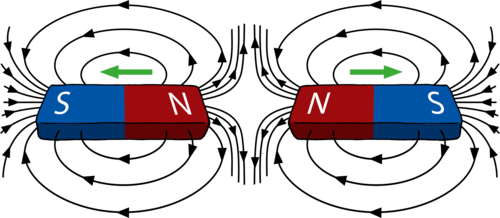
Repulsion of poles
LIKE POLES REPEL EACH OTHER. meaning they push away from each other.
Permanent magnets
Magnets (bar magnets) that keep their magnetism once they have magnetised.
How to Magnets lose their magnetism?
If they are hit with a hammer repeatedly
Dropped repeatedly
Heated to very high temperatures.
Temporary magnets
Magnets that are only magnetic if they are placed in another magnetic field.
Magnetic Field Lines
are imaginary lines that are used to represent the 3-dimensional force field that exists around a magnet.
Propeties of field lines
They point from North to South
Magnetic field lines never cross each other.
Arrows are drawn to represent the direction of the field.
The more closely spaced the field lines the greater the magnetic field at that point.
Compass
An instrument used to indicate where North is at any point on Earth.
How a compass indicates the direction of a magnetic field:
A compass needle moves freely on its axis. When placed anywhere on Earth’s magnetic field, the needle will come to rest with the N-pole of the compass, pointing to the direction called magnetic North.
Earth’s magnetic field
In Earth’s core there’s molten magnetic metals like nickel and iron that results in Earth being a giant magnet. The magnetic field of Earth is similar to that of a bar magnet, including a North Pole and South Pole.
Geographic North vs Magnetic North
Geographic north pole: Point in the northern hemisphere where the rotation axis of the Earth meets the surface.
Magnetic north pole: The point where the magnetic field lines of the Earth enters the Earth. It is the direction in which the north pole of a compass points.
Solar Wind
A stream of radioactive and charged particles sent into space at high speeds due to reactions on the sun.
Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights):
An atmospheric phenomenon consisting of bands of light at the north pole caused by charged solar particles following the Earth's magnetic lines of force.
Magnetic storm
A disturbance in the Earth's outer magnetosphere, usually caused by streams of charged particles given off by solar flares.
Magnetosphere:
A region surrounding the Earth in which charged particles are trapped and their behaviour is dominated by the Earth's magnetic field.