Understanding Pavlovian Conditioning and Its Implications
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Pavlovian Conditioning
Learning process through stimulus-response associations.
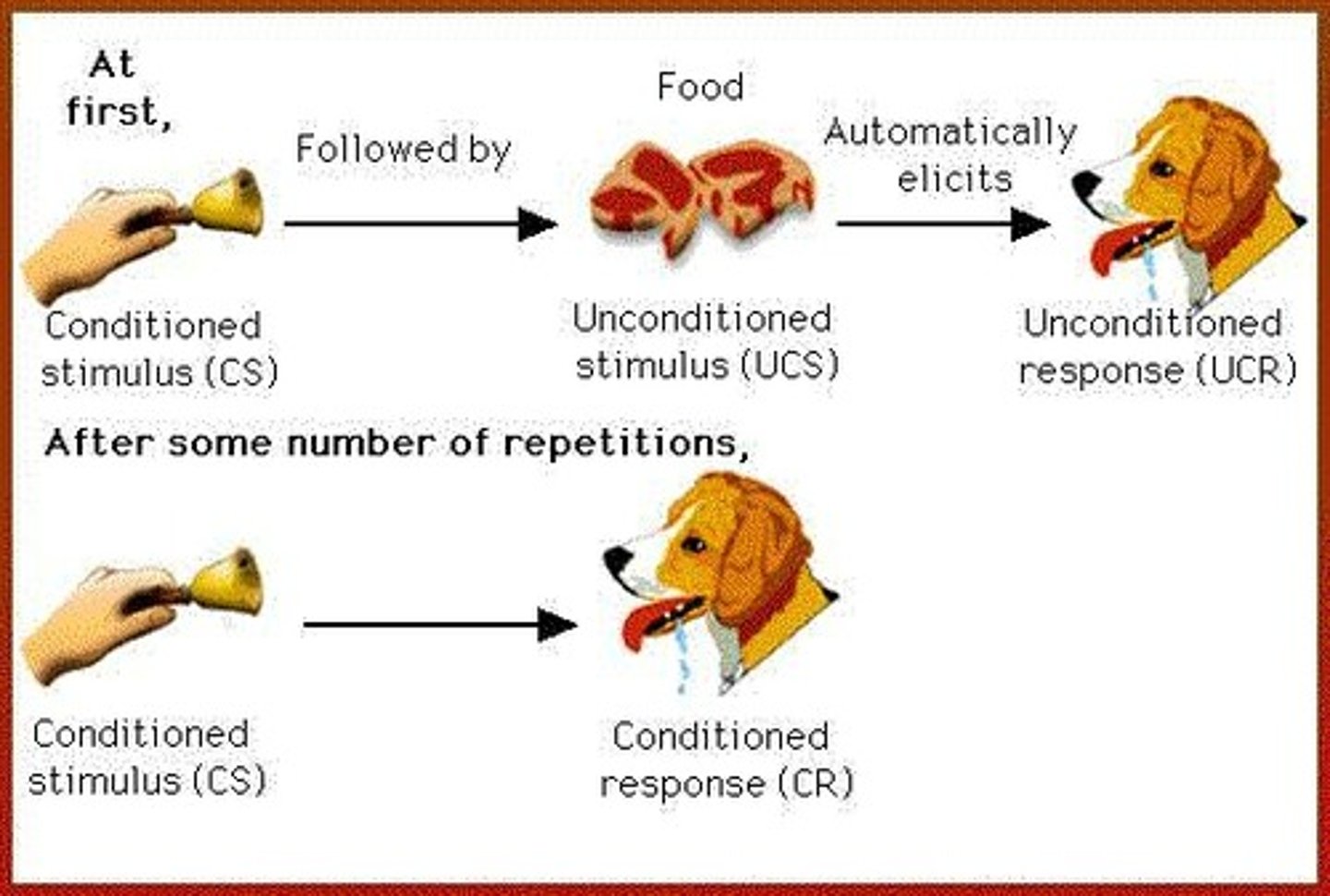
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
Stimulus that naturally triggers an unconditioned response.
Unconditioned Response (UR)
Automatic response to an unconditioned stimulus.
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
Initially neutral stimulus that gains significance through conditioning.
Conditioned Response (CR)
Learned response to a previously neutral stimulus.
Physiological Response
Body's automatic reaction to stimuli, like drugs.
Operant Conditioning
Learning through consequences of voluntary behavior.
Involuntary Response
Automatic reaction not under conscious control.
Voluntary Response
Conscious action influenced by previous consequences.
Prediction in Conditioning
Conditioning involves anticipating important events.
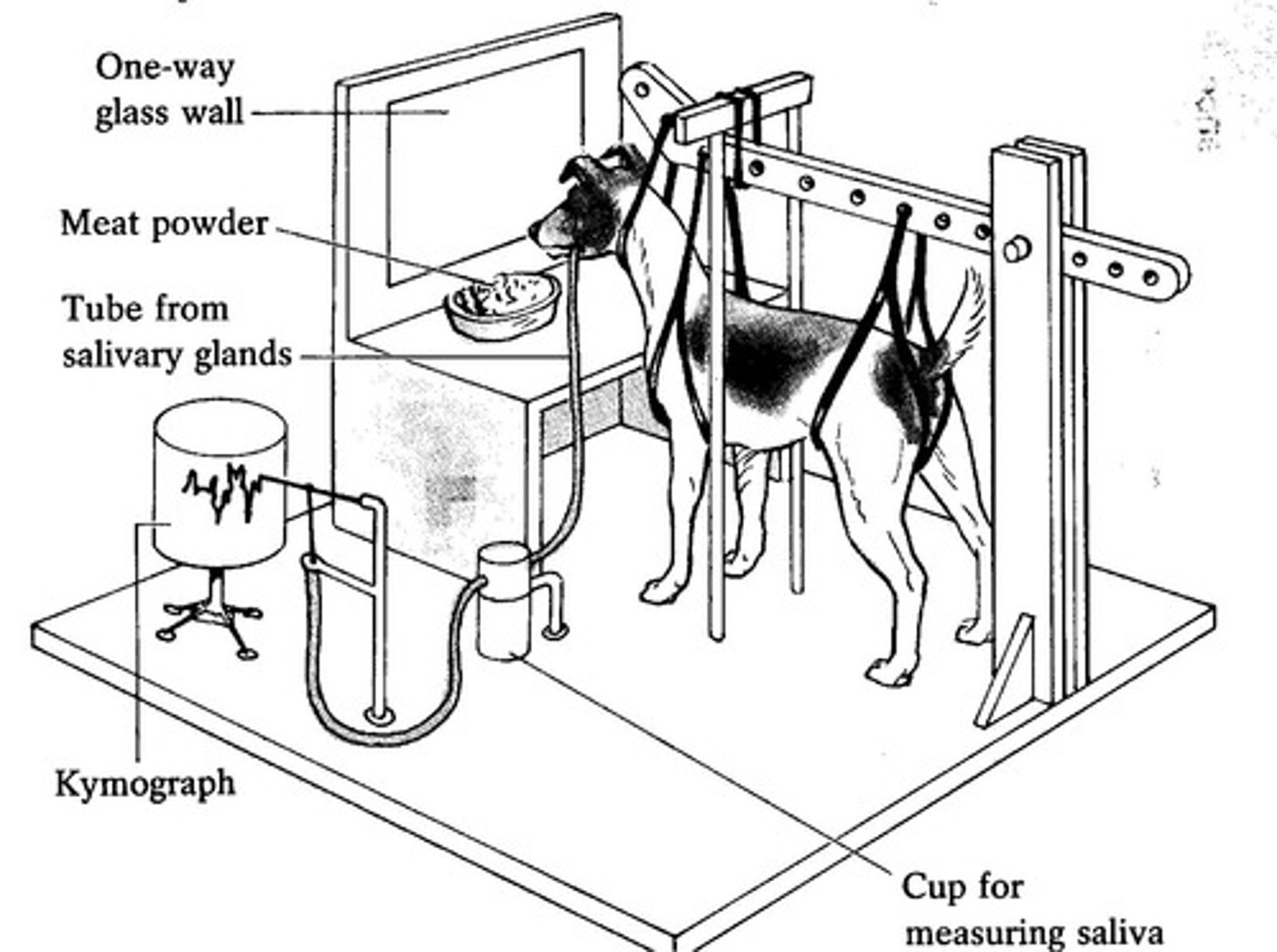
Ivan Pavlov
Physiologist known for research on conditioning.
Nobel Prize in Medicine
Awarded to Pavlov for his physiological studies.
Chemotherapy Example
Chemo induces nausea, linked to food cues.
Allergic Response
Sneezing triggered by pollen as a CS.
Antabuse Treatment
Conditioned aversion to alcohol through nausea.
Autoshaping
Training where animals learn to associate cues with rewards.
Morphine Response
Pain sensitivity increases due to conditioning with morphine.
Alcohol Conditioning
Environmental cues lead to physiological responses to alcohol.
Lightfoot Study
Location affects intoxication levels during drinking.
Siegal's Heroin Study
Mortality rates differ based on drug context.
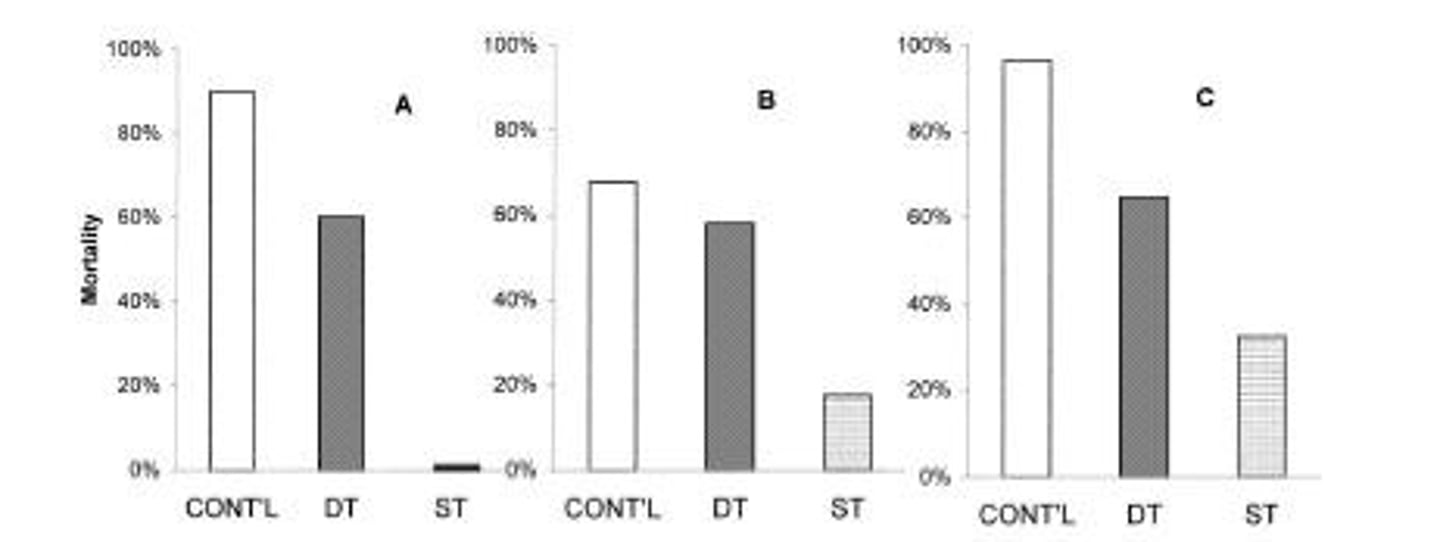
Conditioned Tolerance
Tolerance developed through environmental cues predicting drug use.
Withdrawal Effects
Physiological reactions when stopping drug intake suddenly.
preceding stimulus
that signals an upcoming unconditioned stimulus in Pavlovian conditioning.
previous consequences
that influence future behavior based on past experiences.
US to UR
no learning yet
CS to US to UR
Learning taking place
Test: CS to CR
Evidence of learningthat occurs when a conditioned stimulus produces a conditioned response.