CH 29 Seedless Plants
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
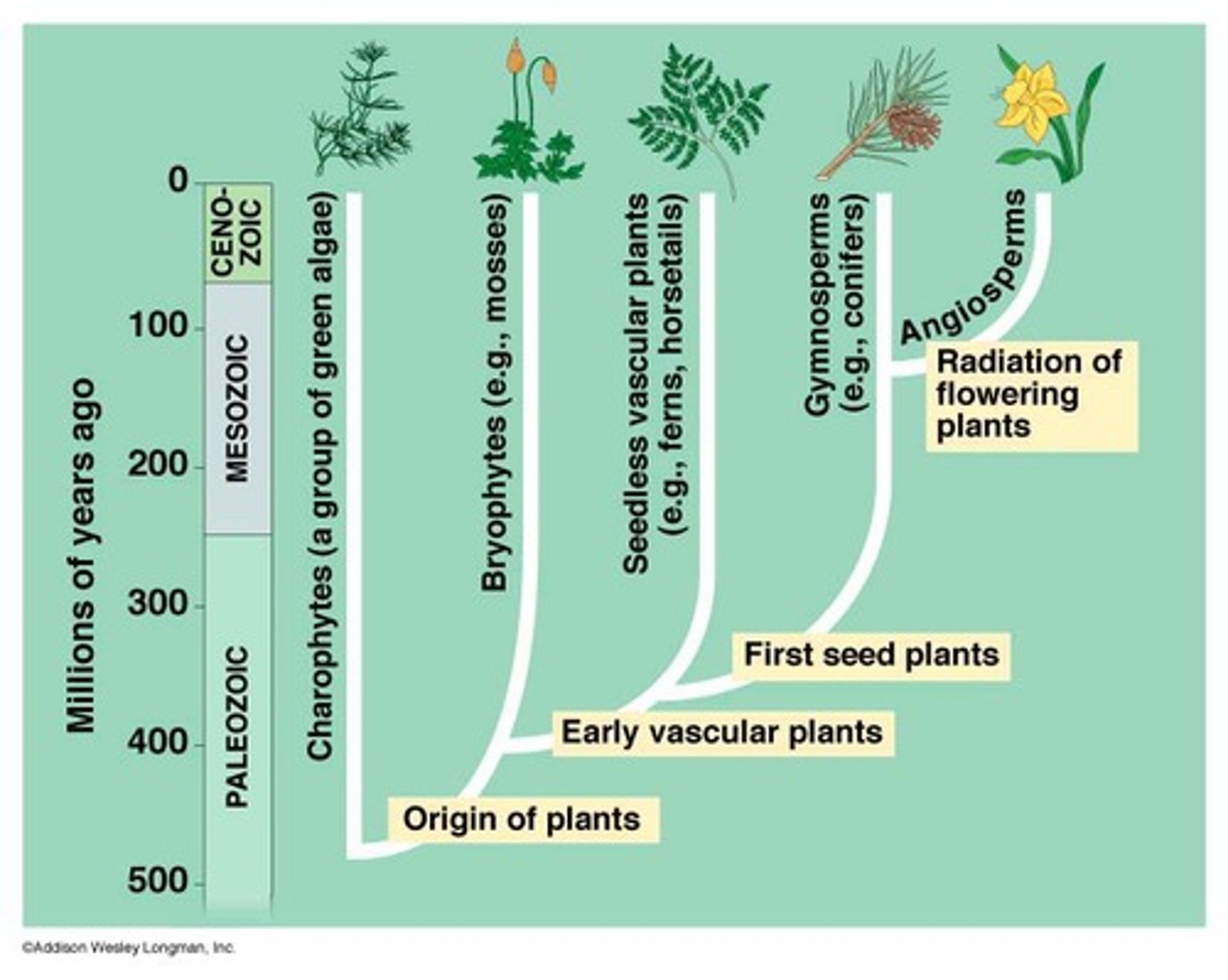
Origin of land plants
Green Algae (shared common ancestor 1 BYA)
Charophytes
Green plants = green algae + land plants
Issues plants had to over come to move to land?
Water loss
Protection from harmful effects of sun
Ability to effectively disseminate gametes for production
Chlorophytes
never made it to land, green algae
Charophytes
sister clade to all land plants
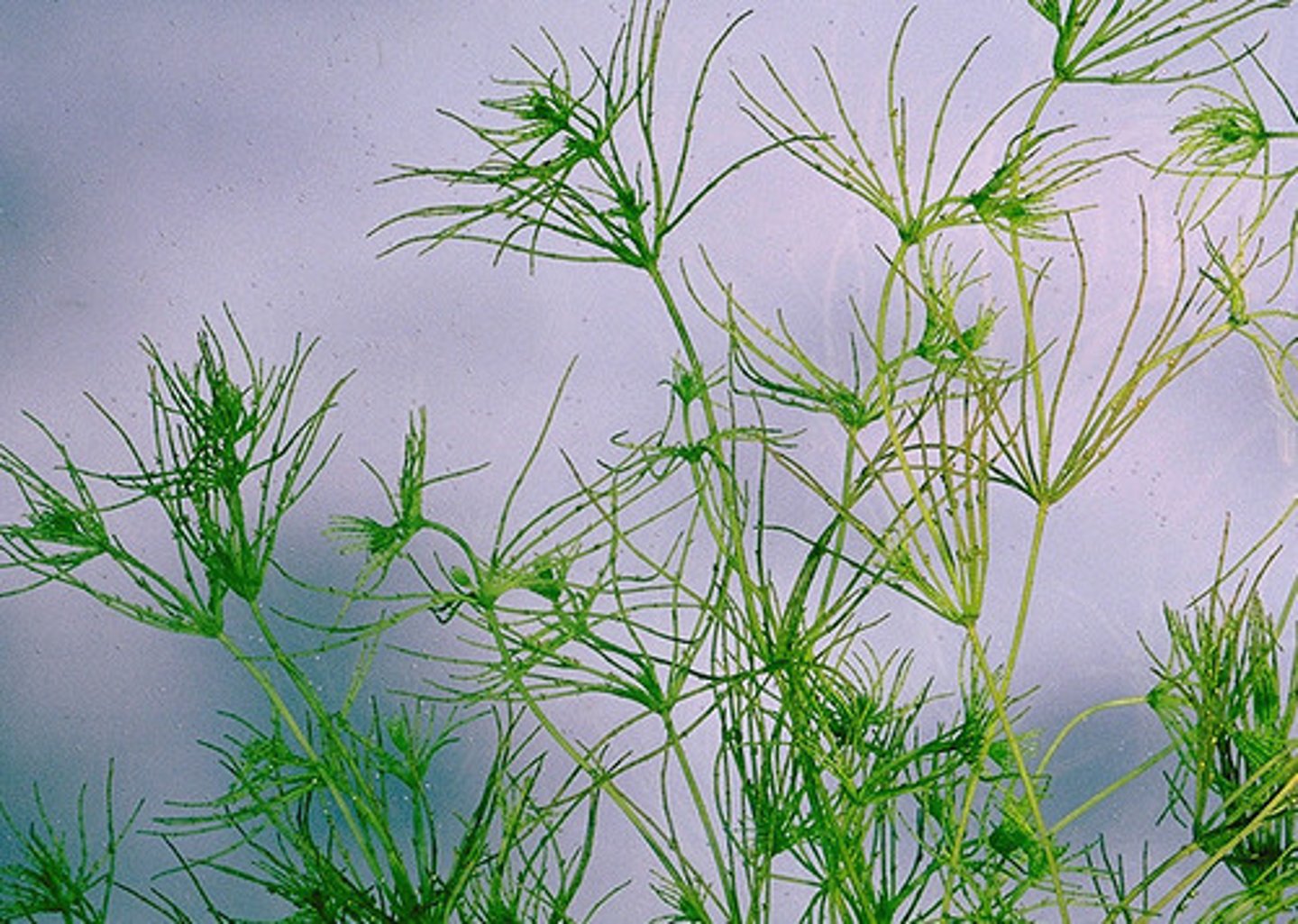

Streptophytes (green plants)
Includes charophytes and all land plants. (twisted-phytes; for the morphology of the sperm of some members)
Adaptations to Terrestrial Life
Waxy cuticle & stomata (protect from drying out)
Vascular system (moving water)
Shift to Dominant diploid generations (deal w/ UV mutations)
Haplodiplontic Life Cycle
Alternation between multicellular haploid and diploid stages.
sporophyte-> Diploid stage = haploid spored by meiosis (4 haploid spores that b/c first cells of gametophytes)
gametophyte-> Haploid stage = spores divide by mitosis & fuse to form diploid zygotes (b/c first cell of sporophytes)
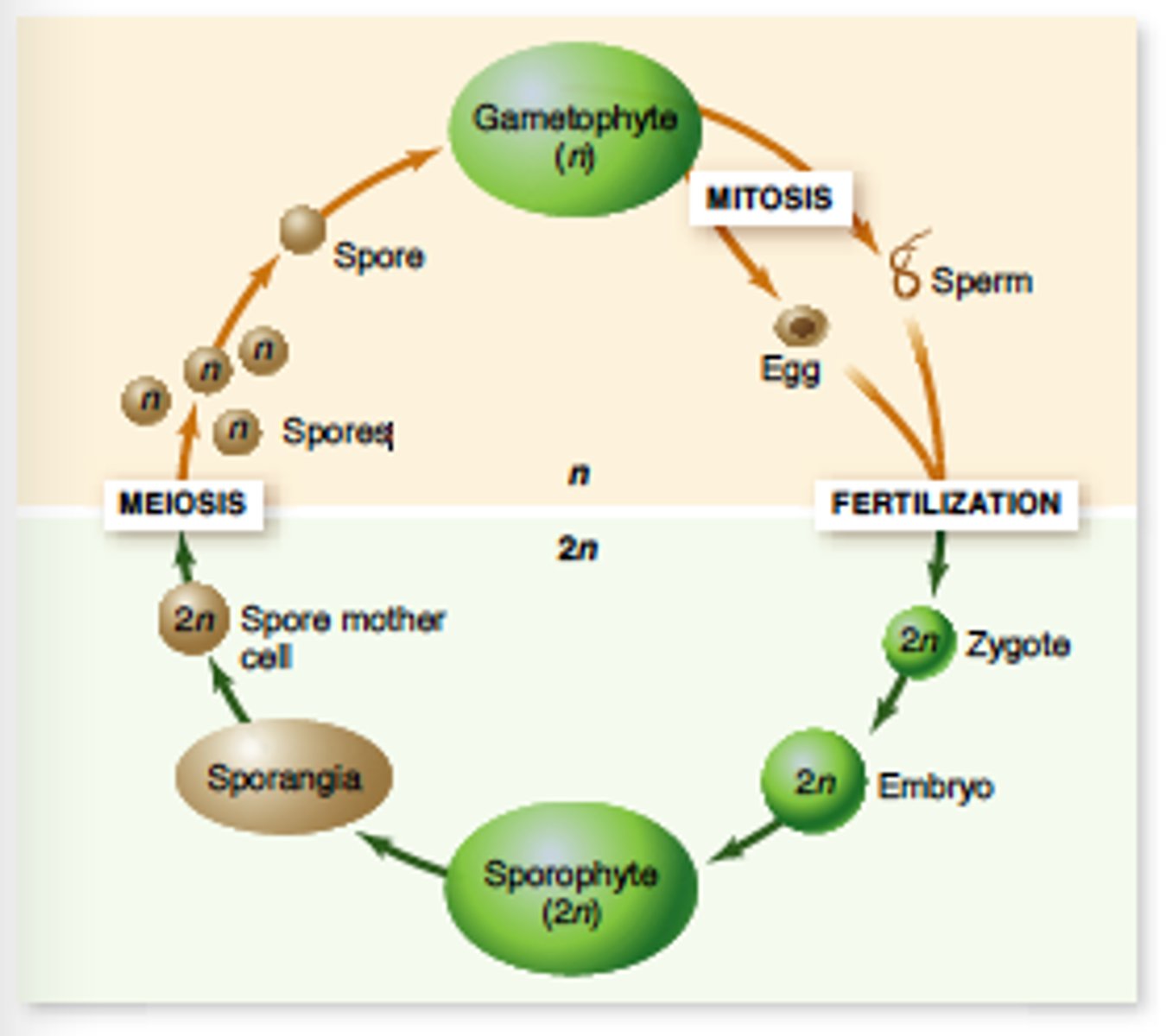
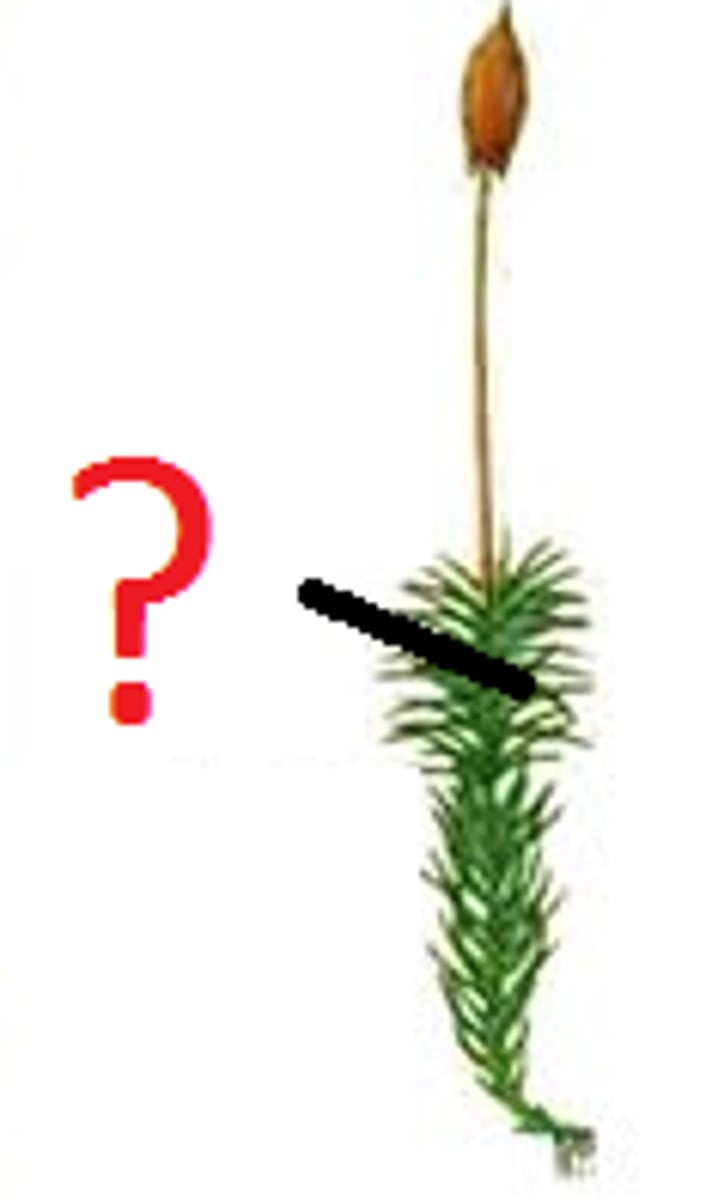
Sporophyte
Multicellular diploid stage producing haploid spores. (4 haploid cells via meiosis)
usually top of plant, or big structure
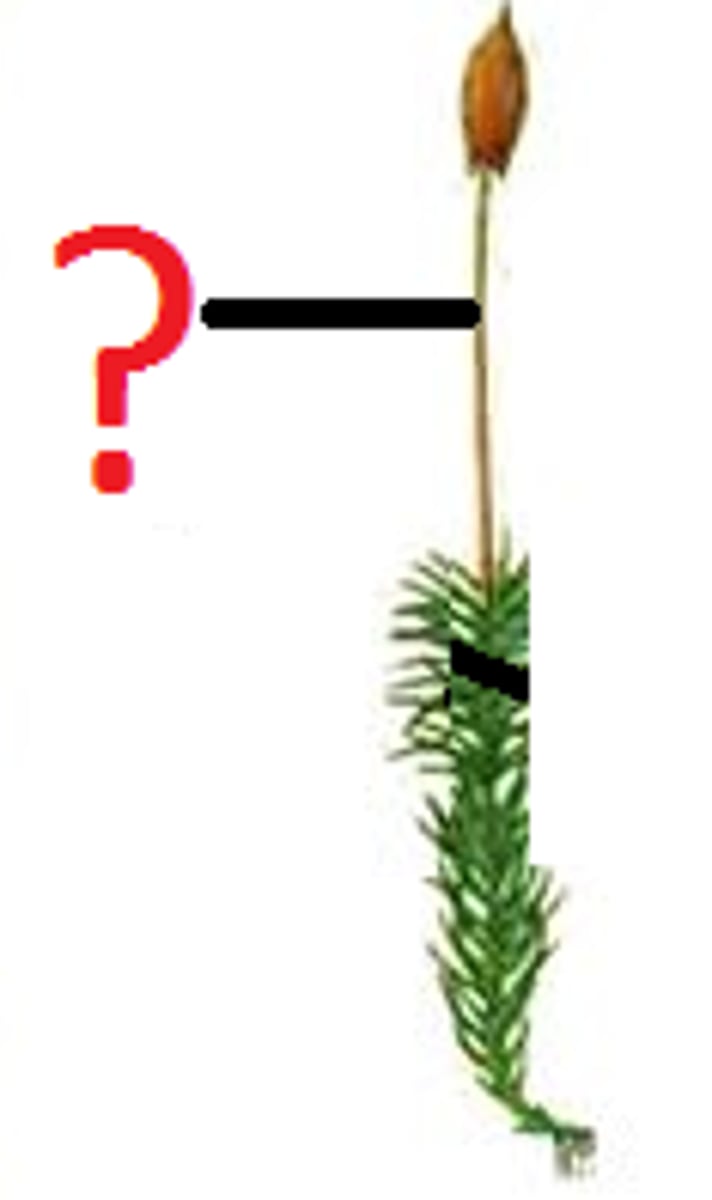

Gametophyte
Multicellular haploid stage producing gametes. (pores divide by mitosis & fuse to form diploid zygotes)
usually bottom of plant, or very small

Land plants
Have multicellular haploid & diploid stages
Trend toward more diploid embryo protection
Trend toward reduced haploid stage
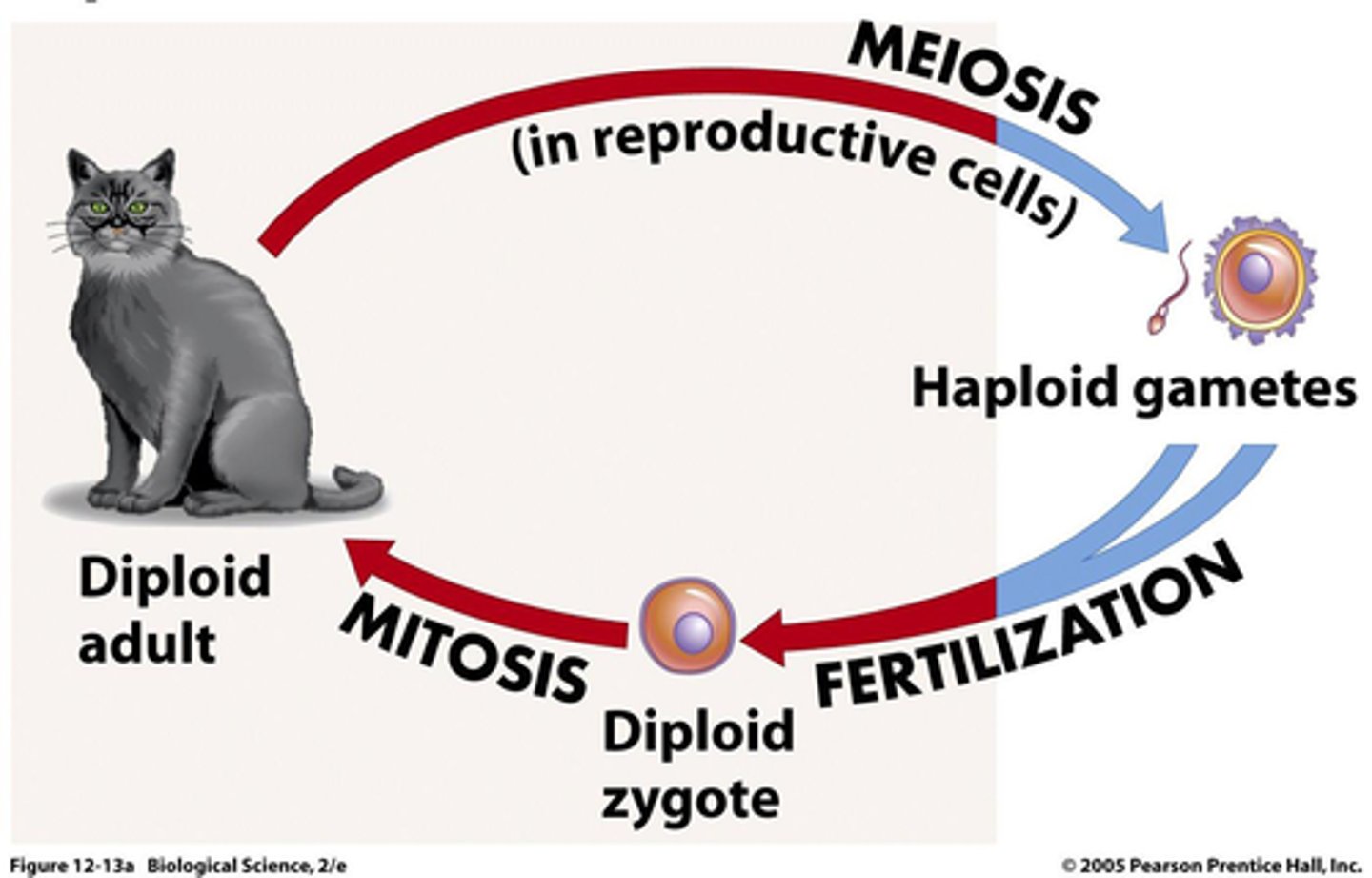
Diplontic Life cycle
Human and animal lifecycle; always a diploid
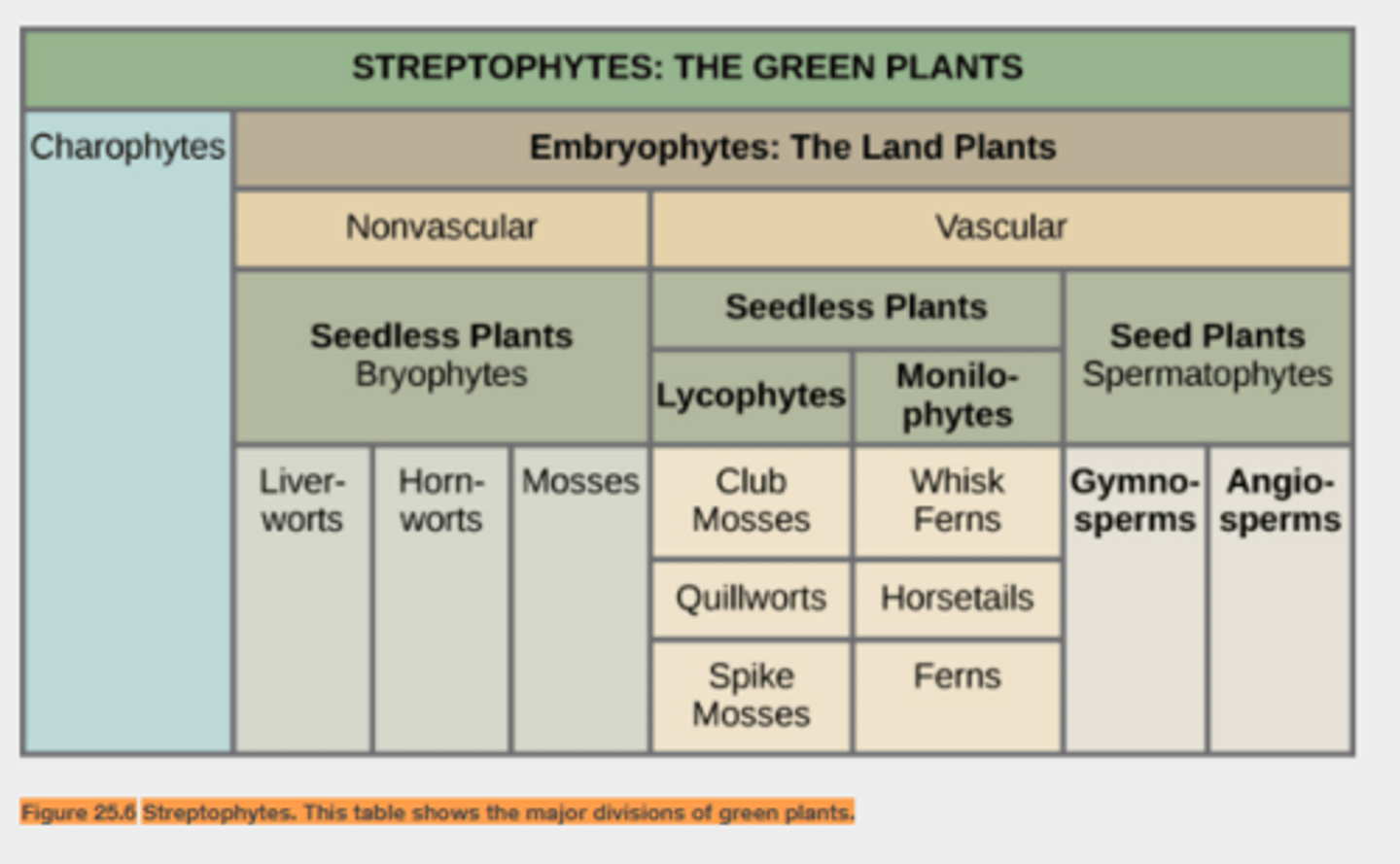
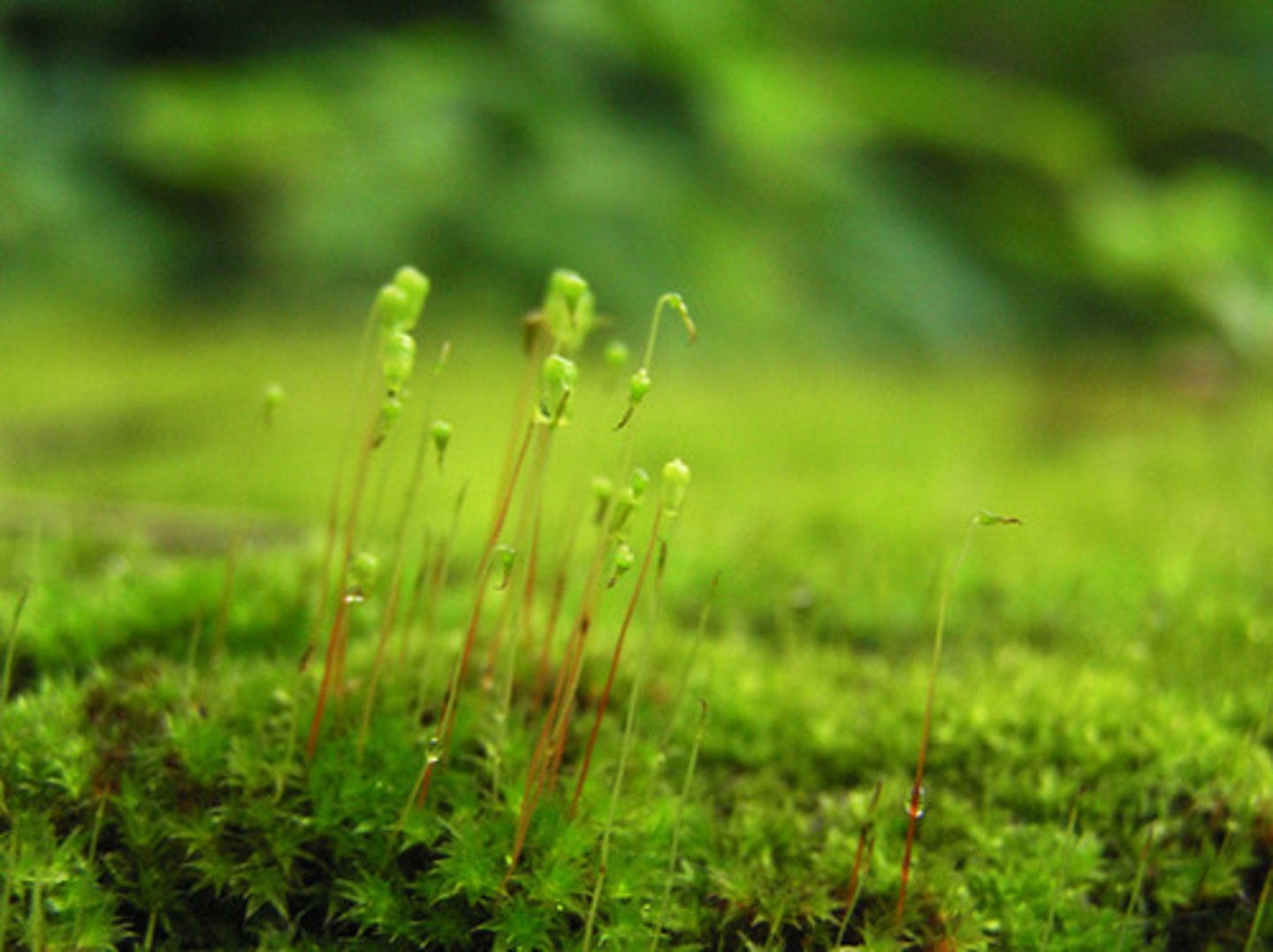
Bryophytes
Closest living descendants of first land plants
no seeds or vascular system
three clades
liverworts
mosses
hornworts

Tracheophytes
no seeds but has vascular system
xylem & phloem
include
lycophytes (club mosses)
pterophytes (ferns)
seed plants

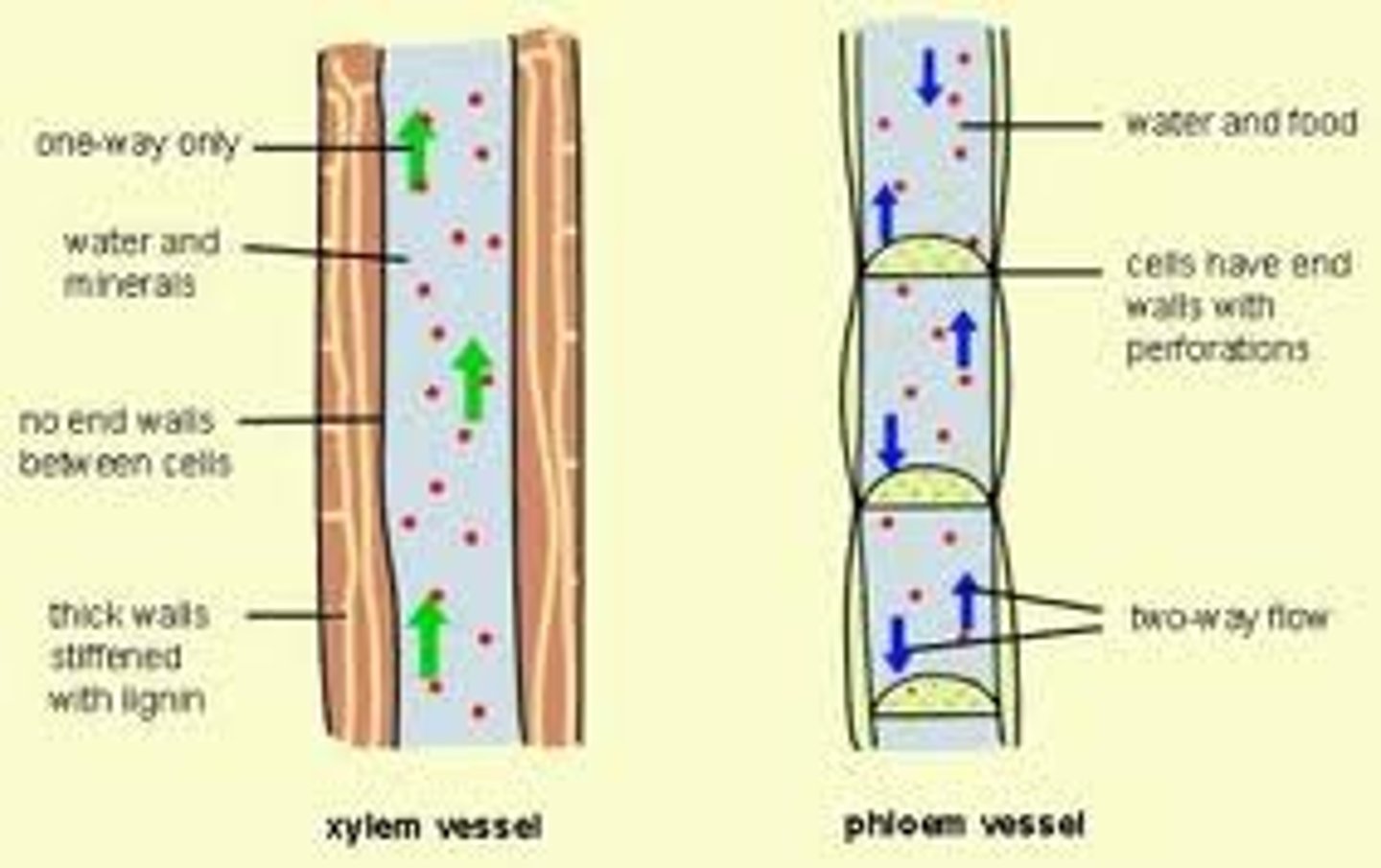
Xylem
conduct water & dissolved minerals upward from the roots

Phloem
conducts sucrose & hormones throughout the plant
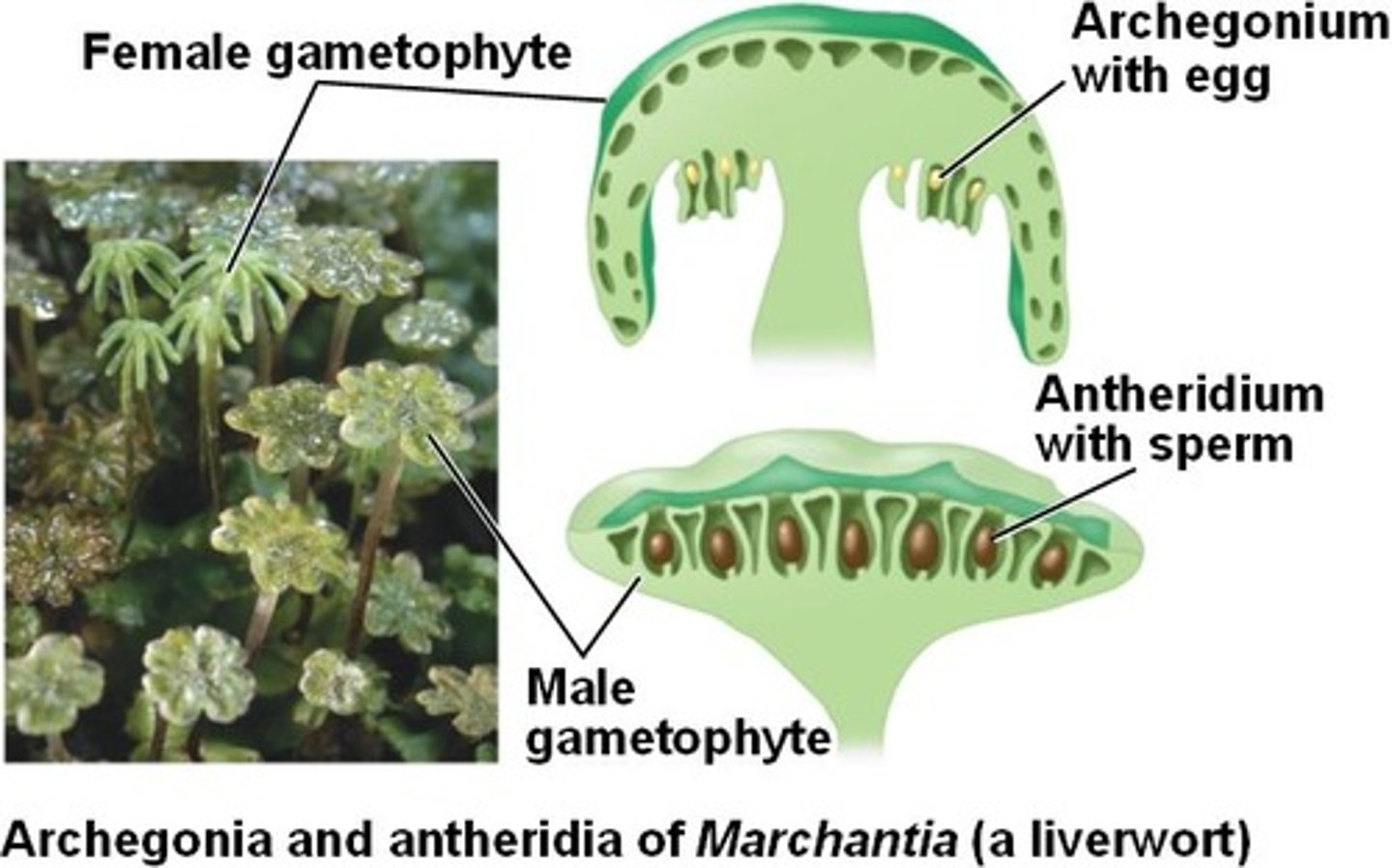
Liverworts
Best known are lobed liverworts that have flattened gametophytes (BUT 80% are leafy & look like mosses)
- Form umbrella-shared gametangia (gamete-producing structures)
- Also undergo sexual repro.
Mosses
Gametophytes consist of small, leaflike structures around a stemlike axis
Not true leave (no vascular tissue)
Anchored to substrate by rhizoids (like roots)
Multicellular, but cannot absorb nearly the vol. Of water absorbed by vascular plant root
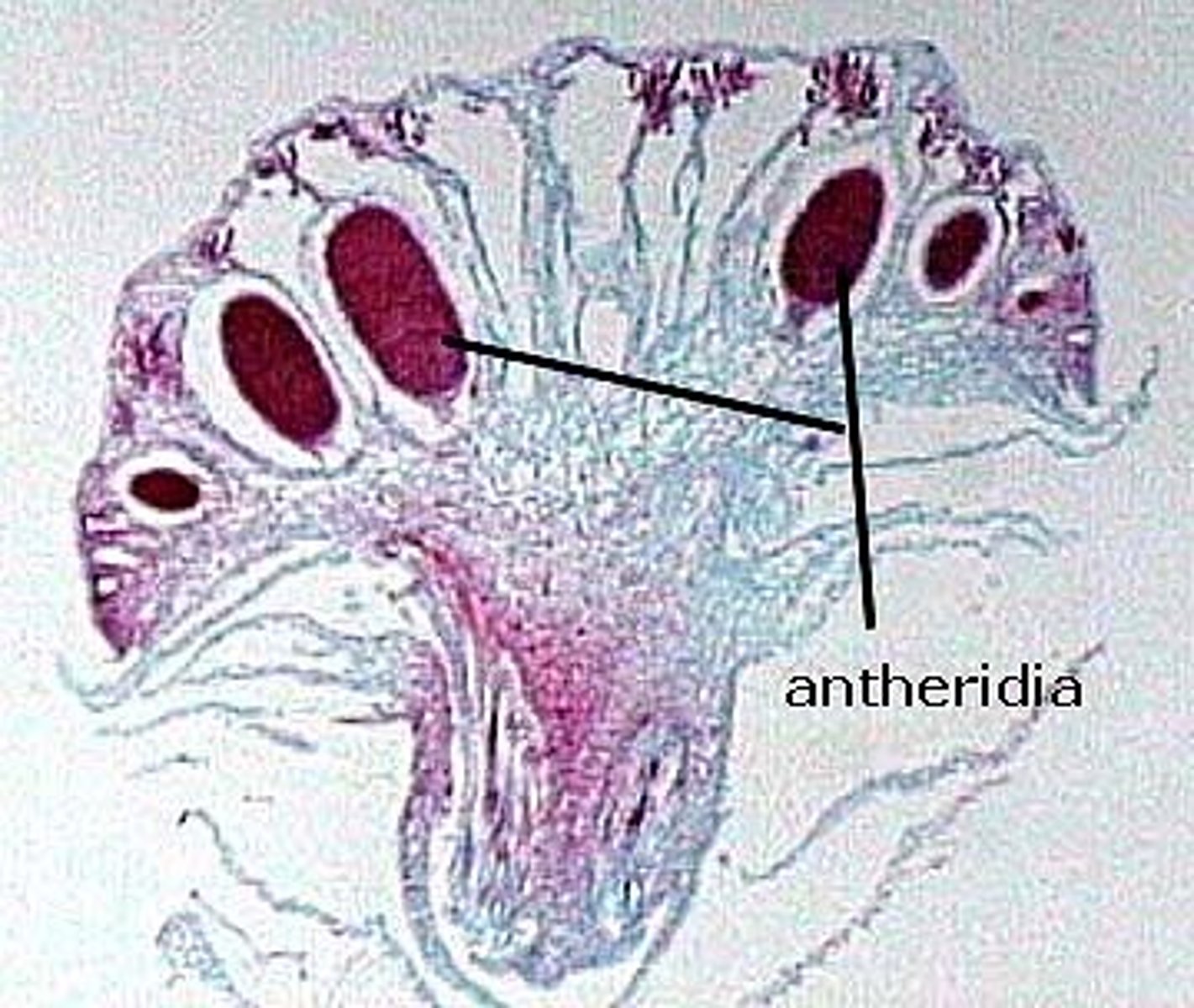
gamentangia form at tips of gametophytes

Archegonia
Female reproductive part of plant
Antheridia
male gametangia (flagellated and need water for repro.)
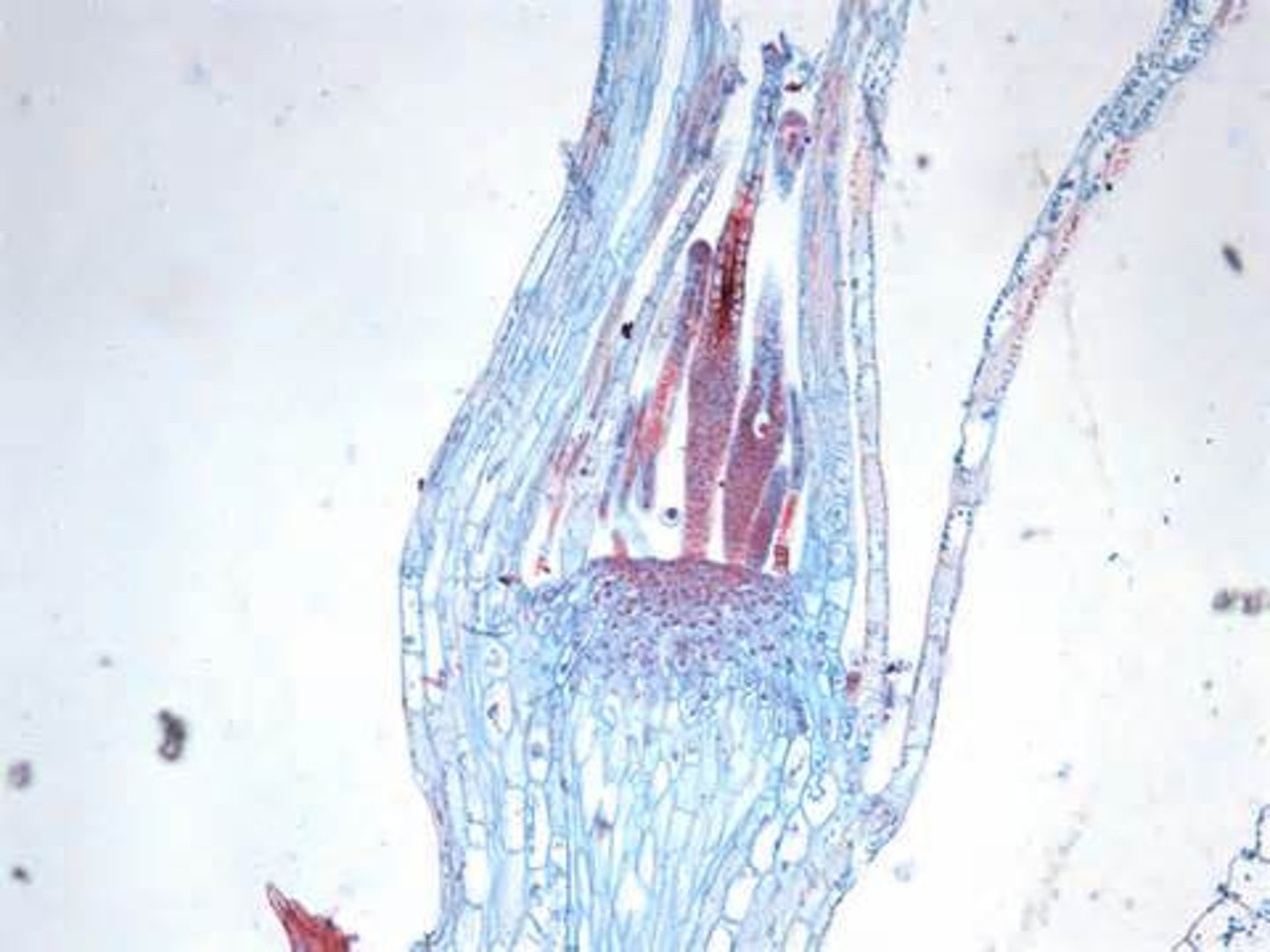
Cooksonia
First known vascular land plant
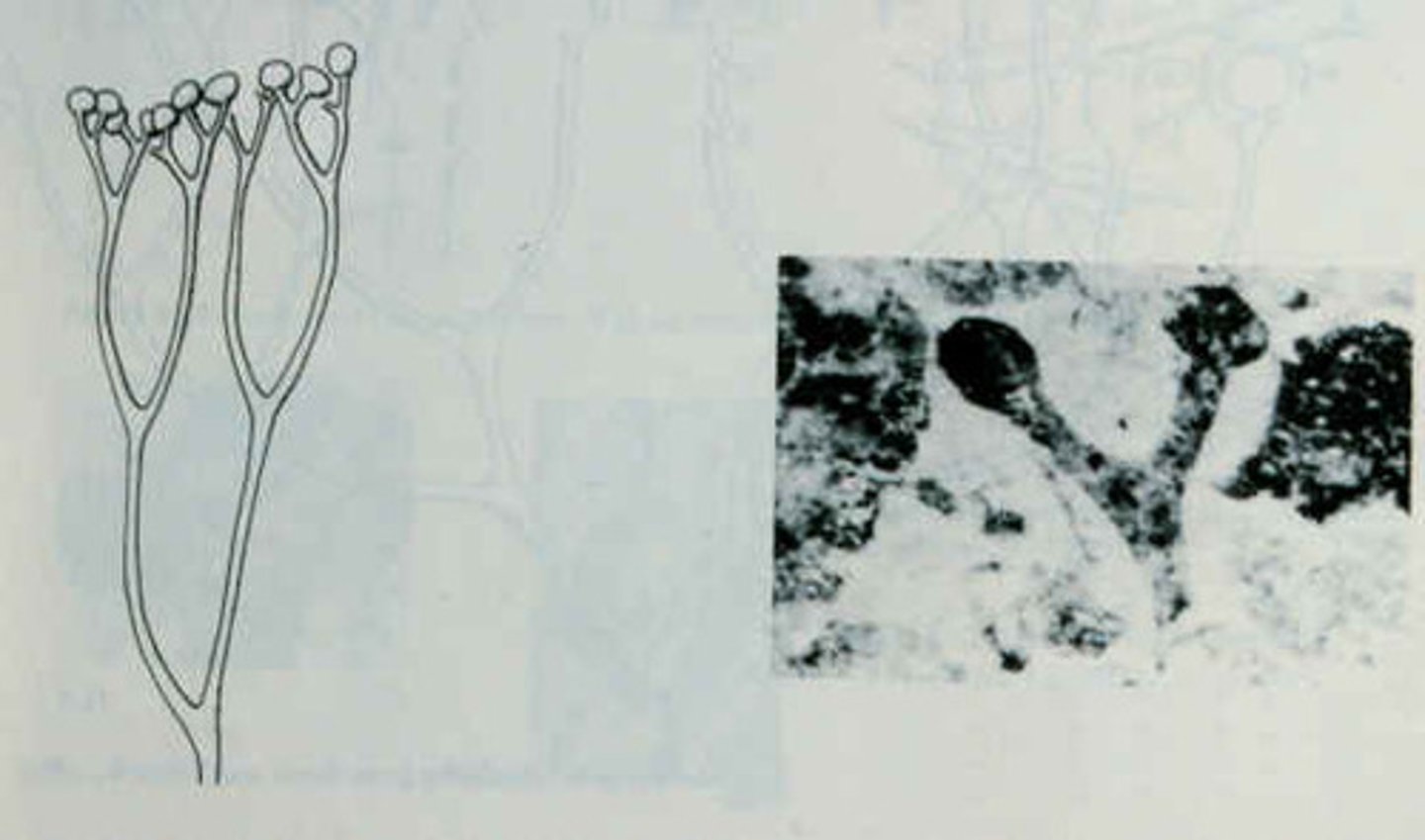

Hornworts
- Photosynthetic sporophyte looks like green horn
-S porophyte base is embedded in gametophyte tissue from which it derives some of its nutrition
- Cells have a single large chloroplast

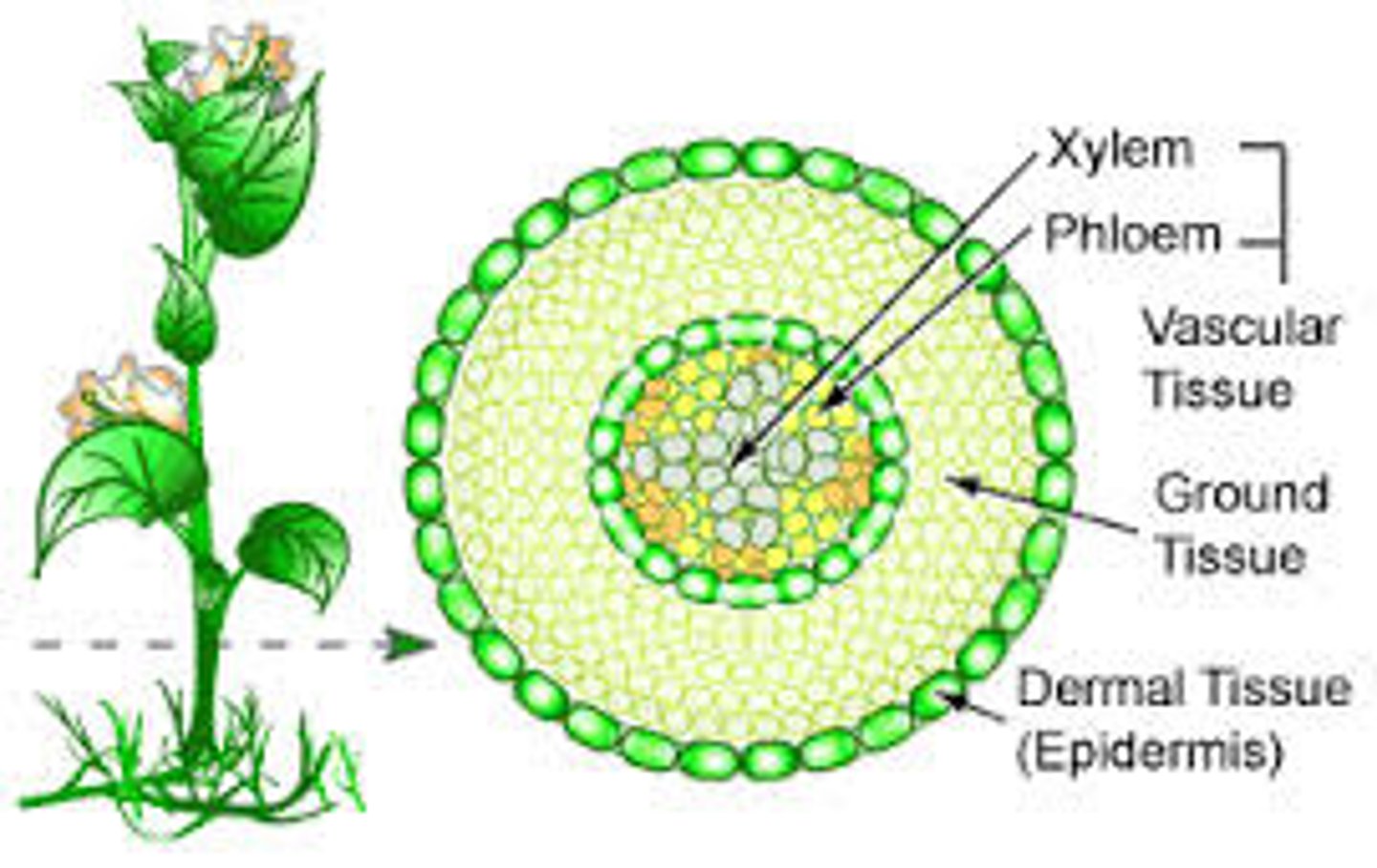
Vascular Tissue
Allows for distribution of nutrients
Xylem: conduct water & dissolved minerals upward from the roots
Phloem: conducts sucrose & hormones throughout the plant
Homosporous
Produces one type of spore in sporangia.
Euphylls
True leaves found in ferns and seed plants.
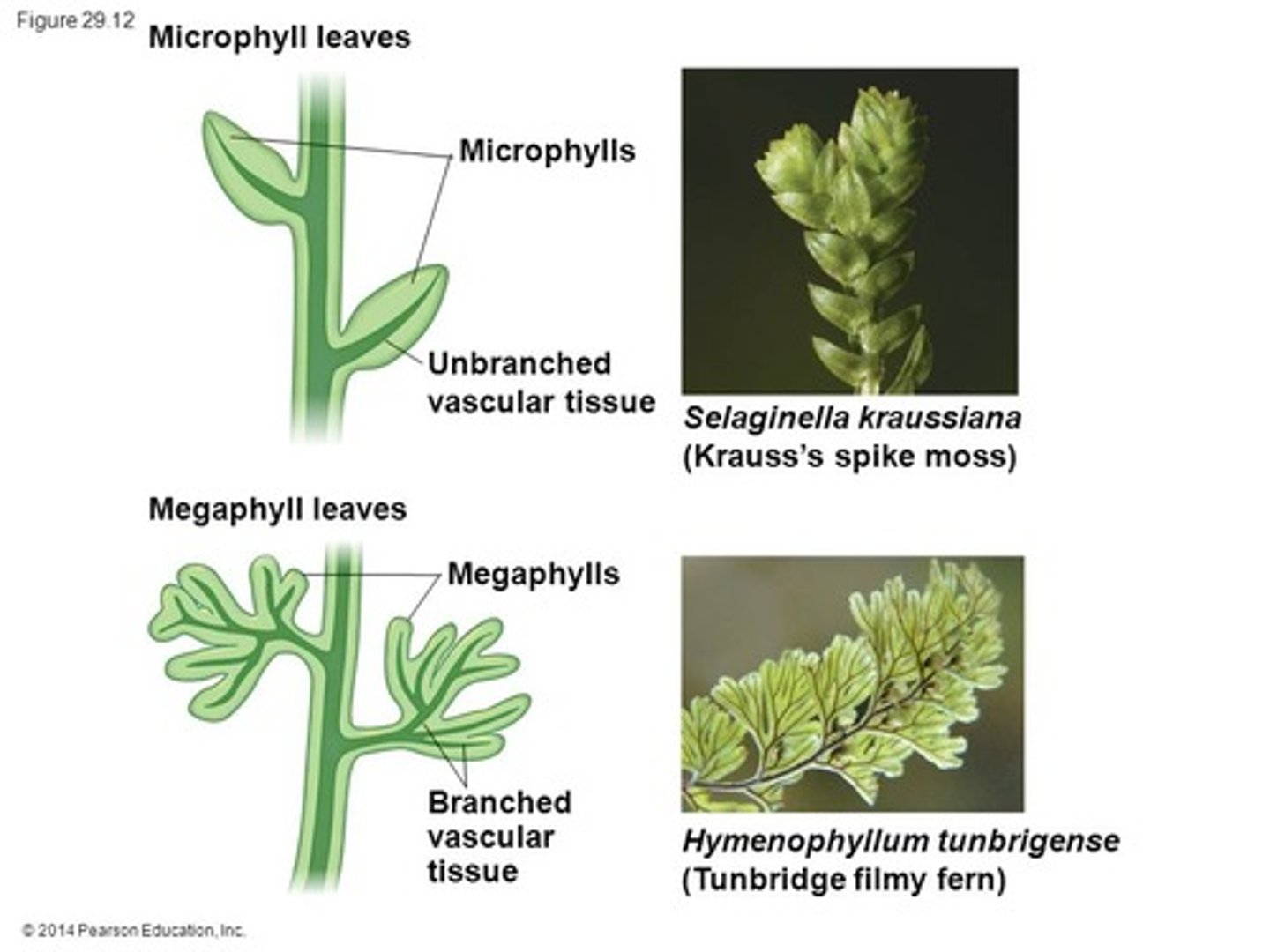
Lycophylls
Leaves found in lycophytes, evolved independently.
Seeds
Highly resistant structures; protect embryos from environmental stresses
Contain food supply for young plant
Angiosperms
Flowering plants with fruits aiding seed dispersal.

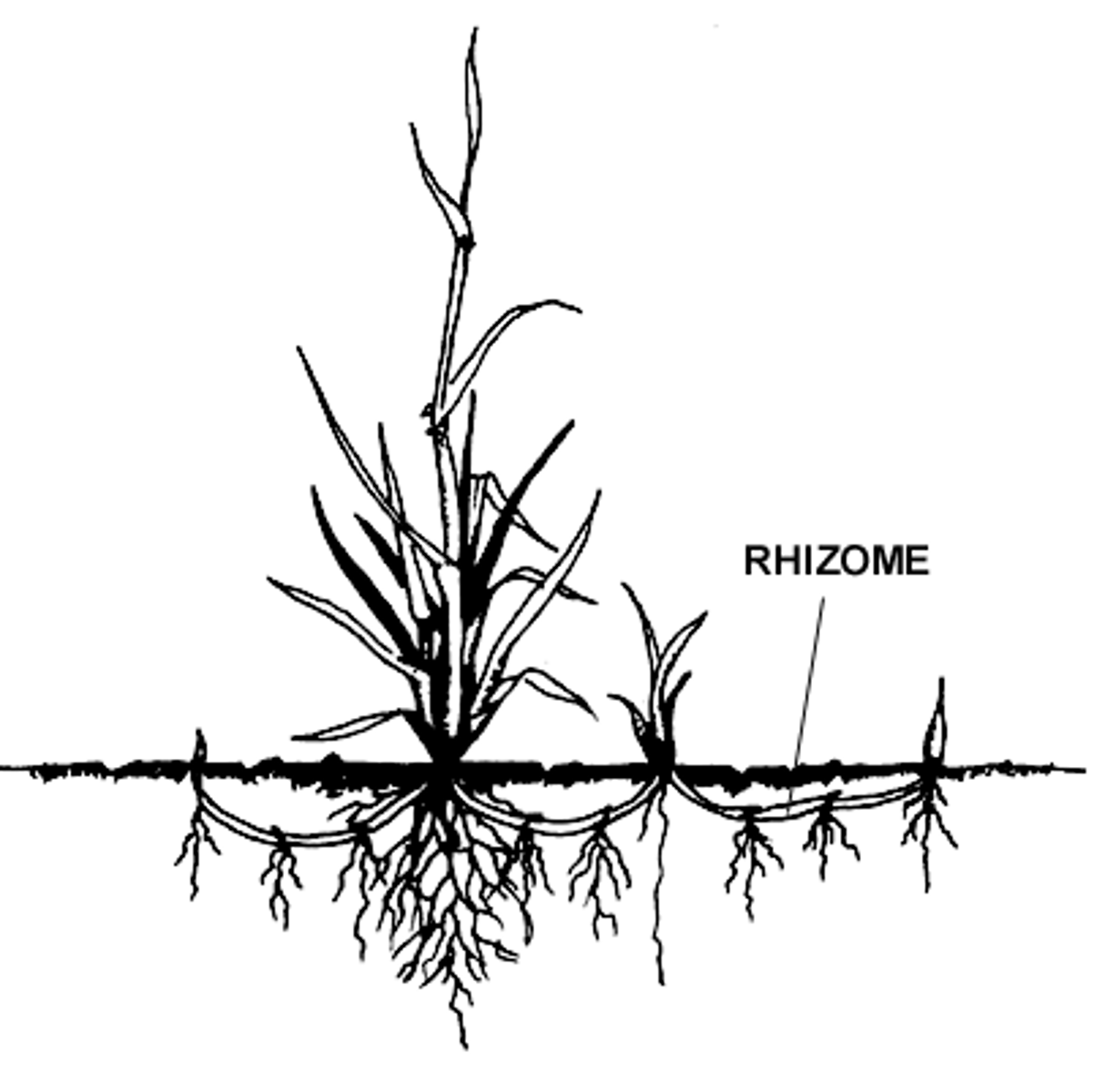
Rhizomes
like but not root b/c no vascular tissue
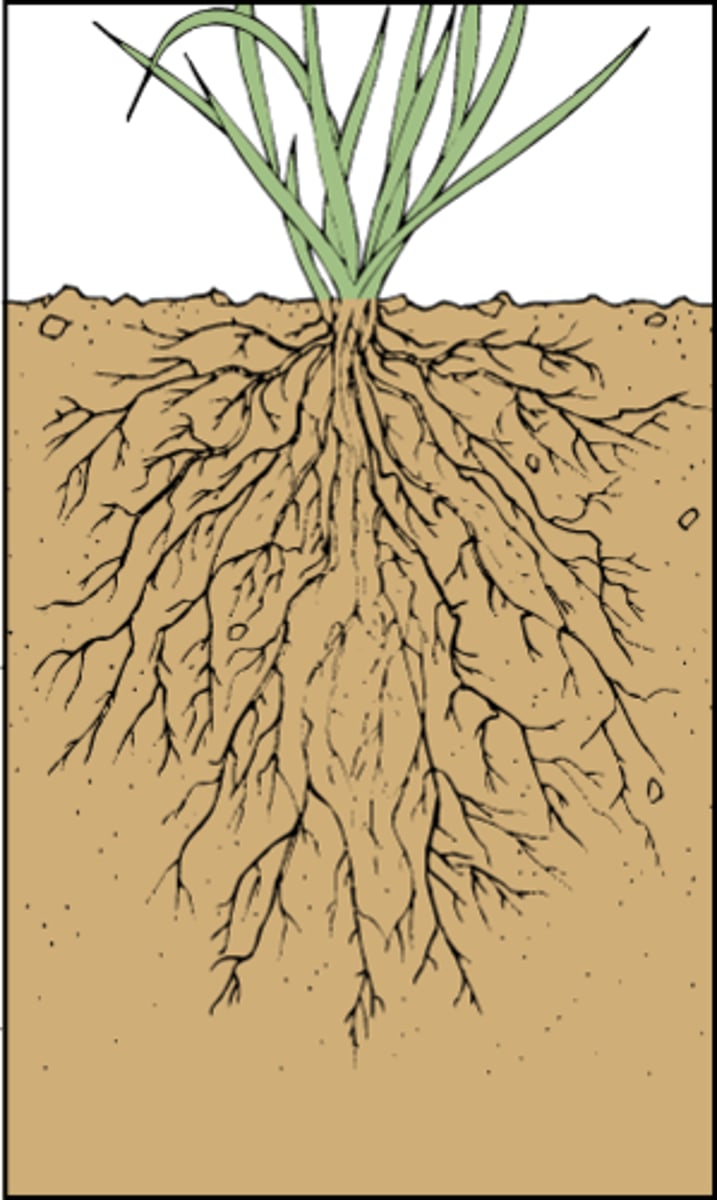
Roots
True roots are found only in tracheophytes
Only roots provide both transport & support
It appears roots evolved at least twice
Lycophytes
Sister groups to all other vascular plants
Leaves developed independently
Sporophyte dominant
Lack seeds, have vascular tissue
Worldwide distribution
Pterophytes
Common ancestor rise to 2 clades
Line of ferns & horsetails
Another line of ferns & whisk ferns
Phylogenetic relationships among ferns & their relationships is still being sorted
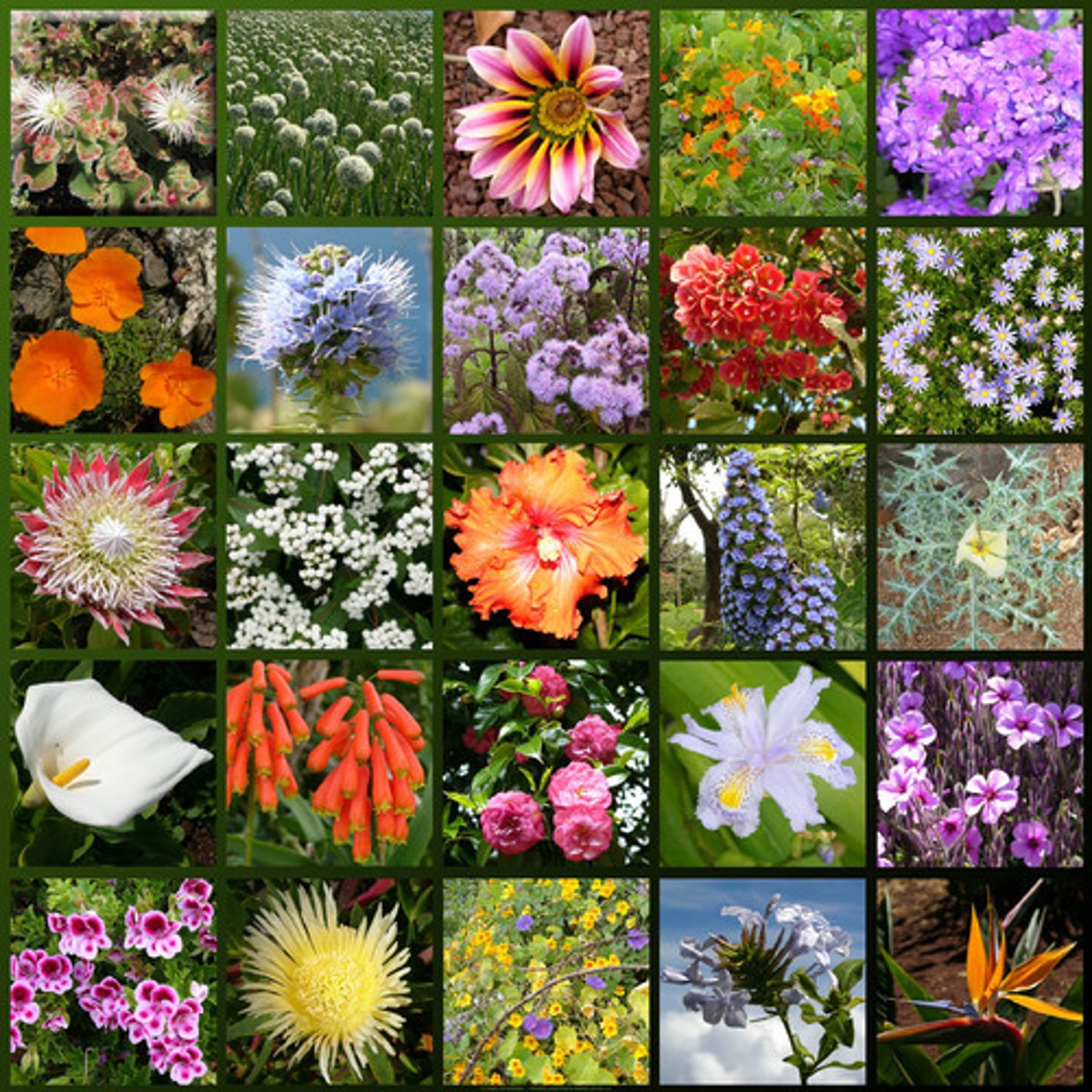
Wisk Ferns
Found in tropics
Sporophyte consists of evenly forking green stems without true leaves or roots
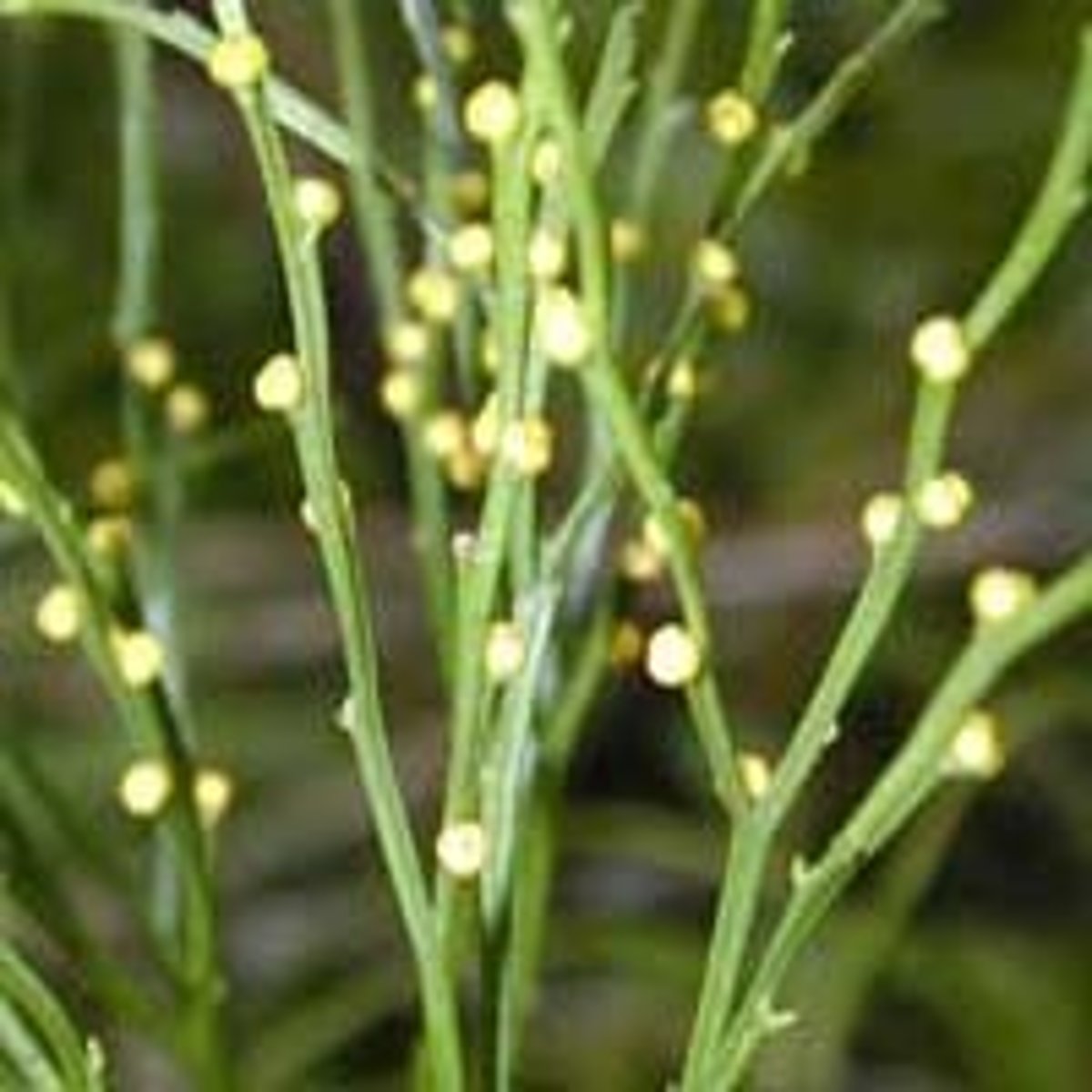

Horsetails
Sporophyte consists of ribbed jointed photosynthetic stems that arise form branching rhizomes with roots at nodes
Whorl of non-photosynthesis scale like leaves emerges at each node
Silica deposits in cells (also called scouring rushes b/c pioneers in American West used them to scrub pans)
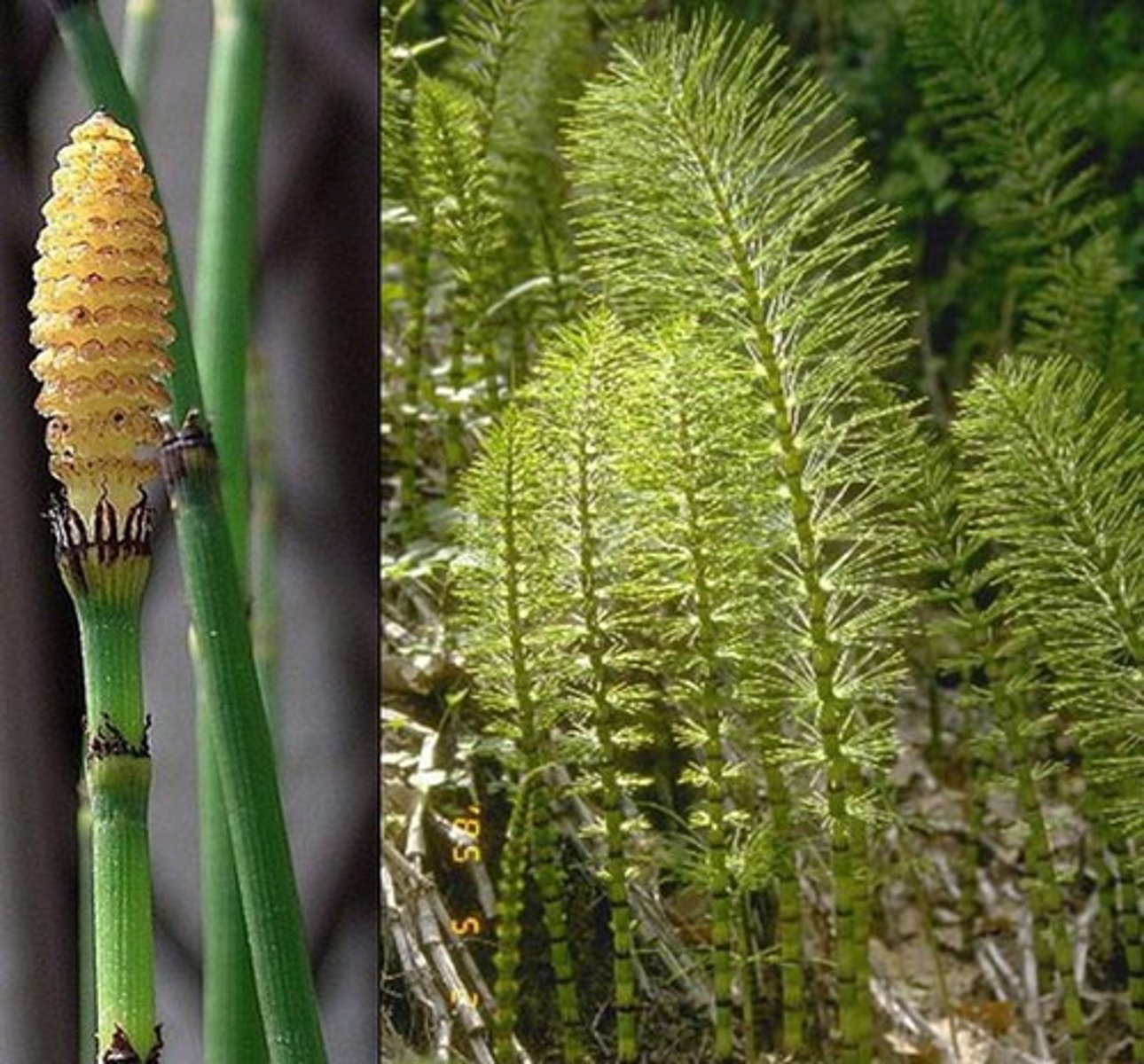

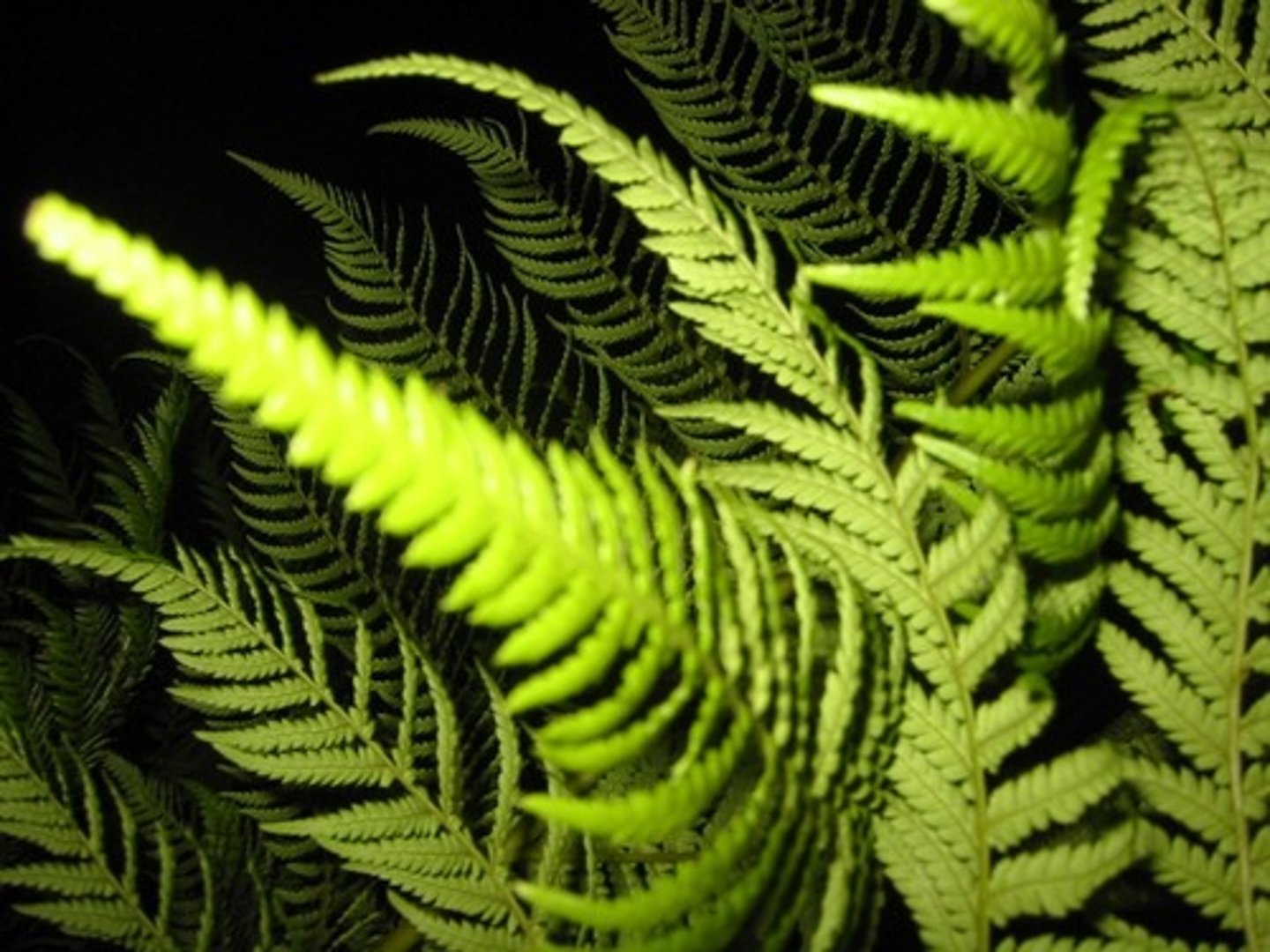
Ferns
Most abundant group pf seedless vascular plants (a/t 11,000 species)
Coal formed from forests 300 MYA
Conspicuous sporophyte & much smaller gametophyte are both photosynthetic

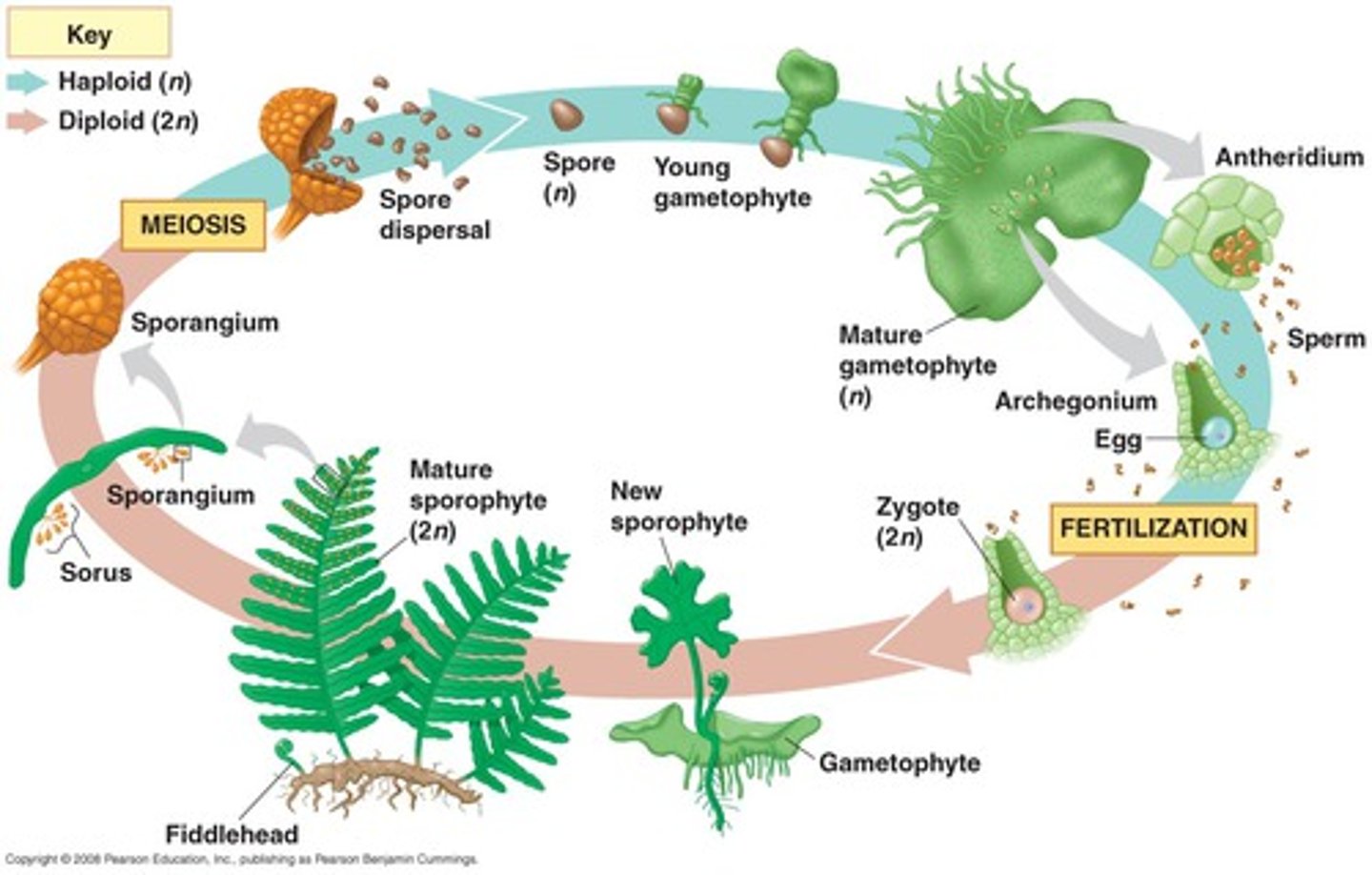
Fern Life Cycle
Produce distinctive sporangia in clusters called sori on back of fronds
Diploid spore mother cells in sporangia produce haploid spored by meiosis
Spores germinate into gametophyte
Flagellated sperm