SCIENCE: 2ND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Genes
Small units of information inside our cells that contain instructions for how our bodies develop and function.
They code for traits like our eye color, hair color, and height.
DNA
A molecule that carries genetic information in living organisms. It looks like a ladder (double helix) and is found inside the nucleus of our cells.
Stands for “deoxyribonucleic acid”
Genetic Code
A language that DNA uses to give instructions to cells.
Nucleotides
ADENINE (A)
THYMINE (T)
CYTOSINE (C)
GUANINE (G)
(A) with (T) | (G) with (C)
Amino acids
The building blocks for proteins. Our DNA codes for different proteins that perform specific functions in our body.
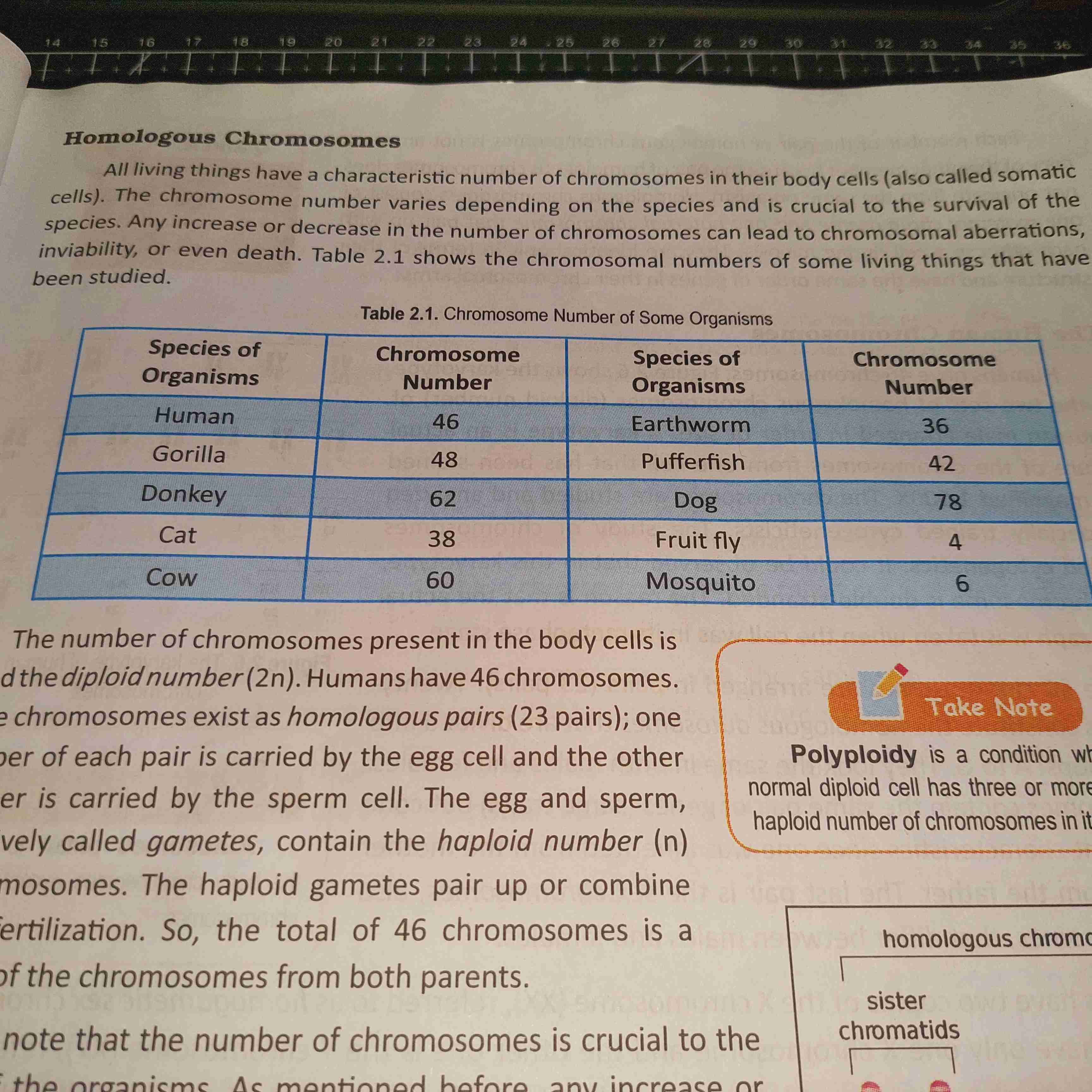
46 Chromosomes, 23
Humans have (beep) chromosomes, which come in pairs, with (beep) inherited from each parent.
Genetic Inheritance
The passing of traits from parents to their offspring.
Genotype
Refers to the alleles an organism has inherited for a particular gene.
Phenotype
A result of the expression of one or more genes.
Example: Brown hair, AB blood type, Blue eye color
Dominant
Only ONE allele is needed for the trait to be expressed.
Recessive
TWO alleles are needed for the trait to be expressed.
Incomplete Dominance
Both alleles are partially expressed in an phenotype.
(It will mix together)
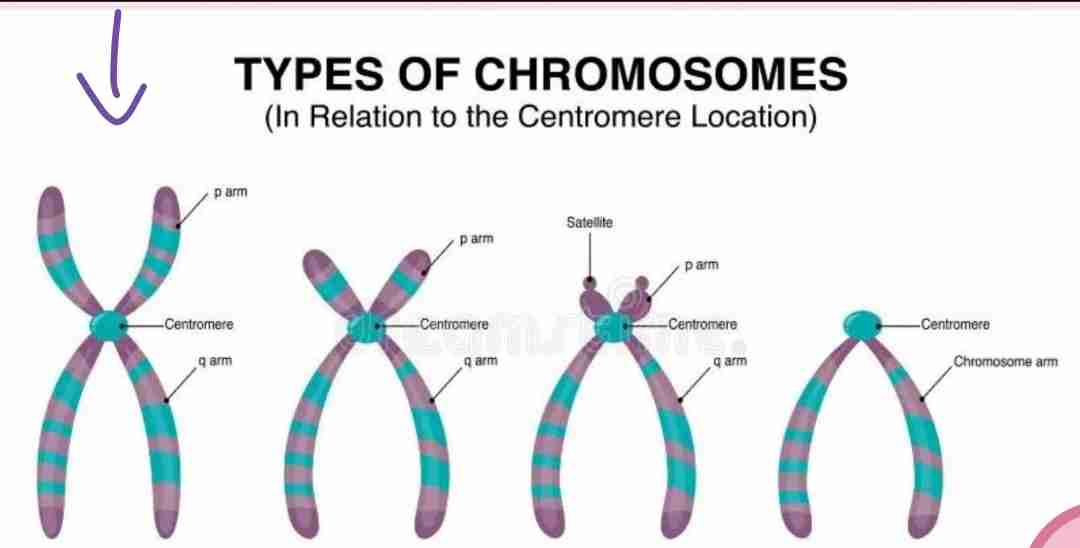
Metacentric
The centromere is located at the center of the chromosome, forming two equal arms.
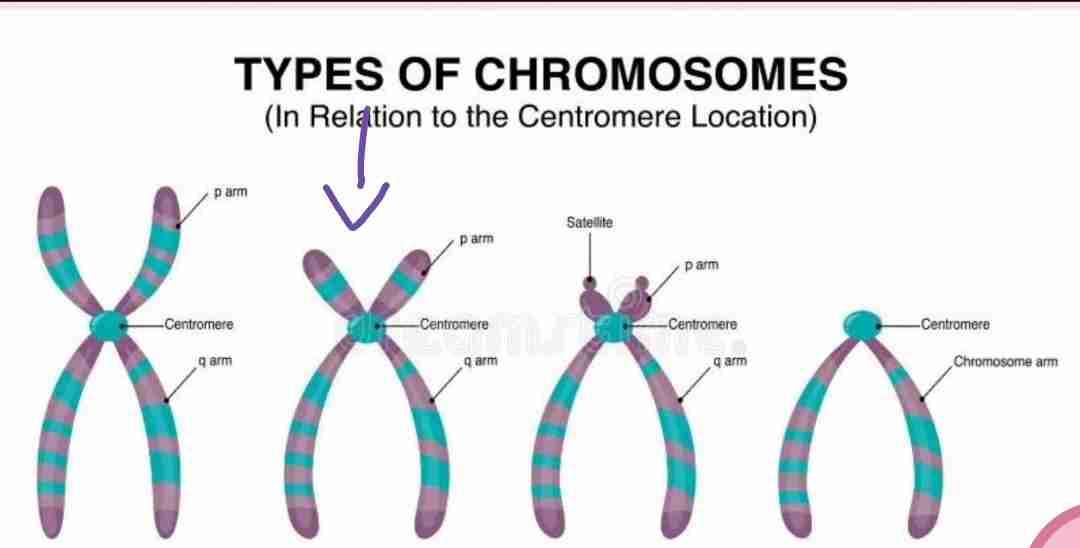
Subtemetacentric
The centromere is slightly off center, resulting in one long arm and one shorter arm.
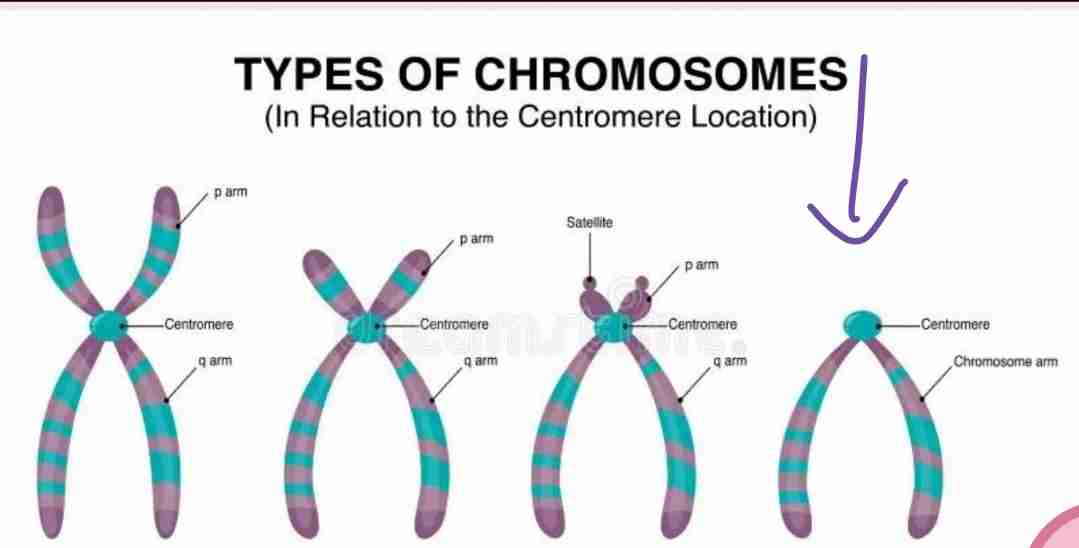
Telocentric
The centromere is located at the end of the chromosome.
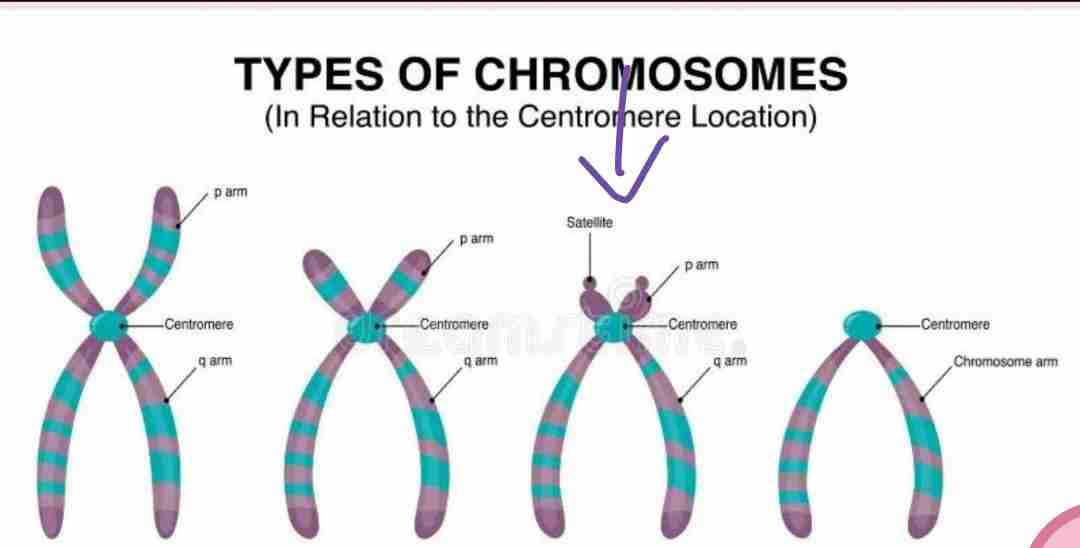
Acrocentric
The centromere is significantly off-center, resulting in one extremely short arm and one extremely long arm.
Homologous Chromosomes
They have the same location of the centromere.
They contain the sate set of genes in the same order along the entire length of their chromosomal arms.
Their chromosomal arms are of the same length.
Diploid Cells
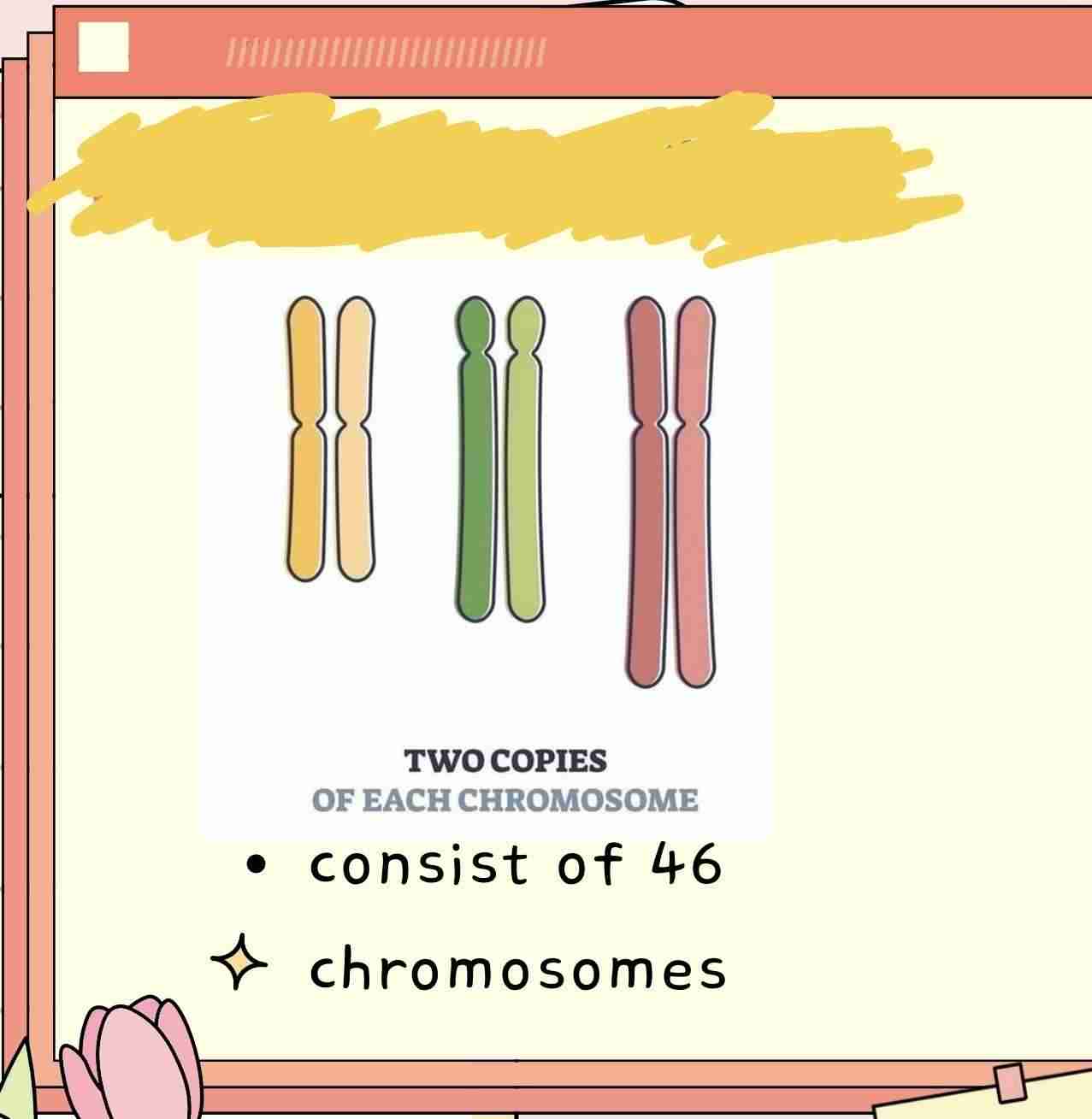
Haploid Cells

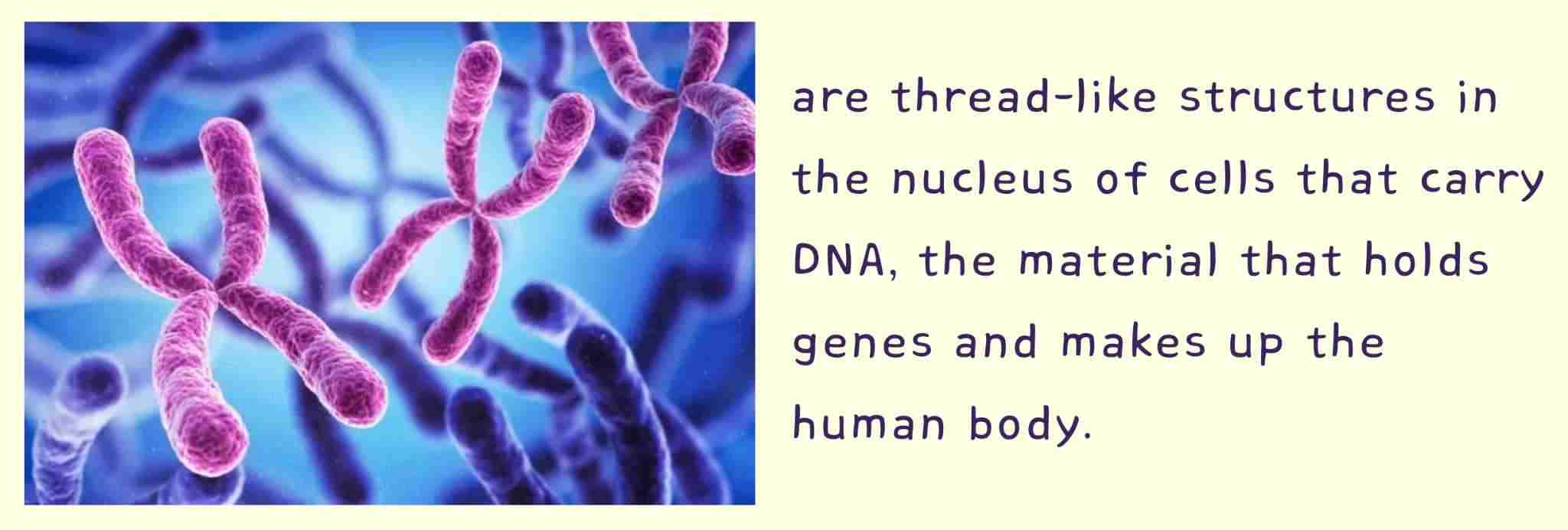
Chromosomes
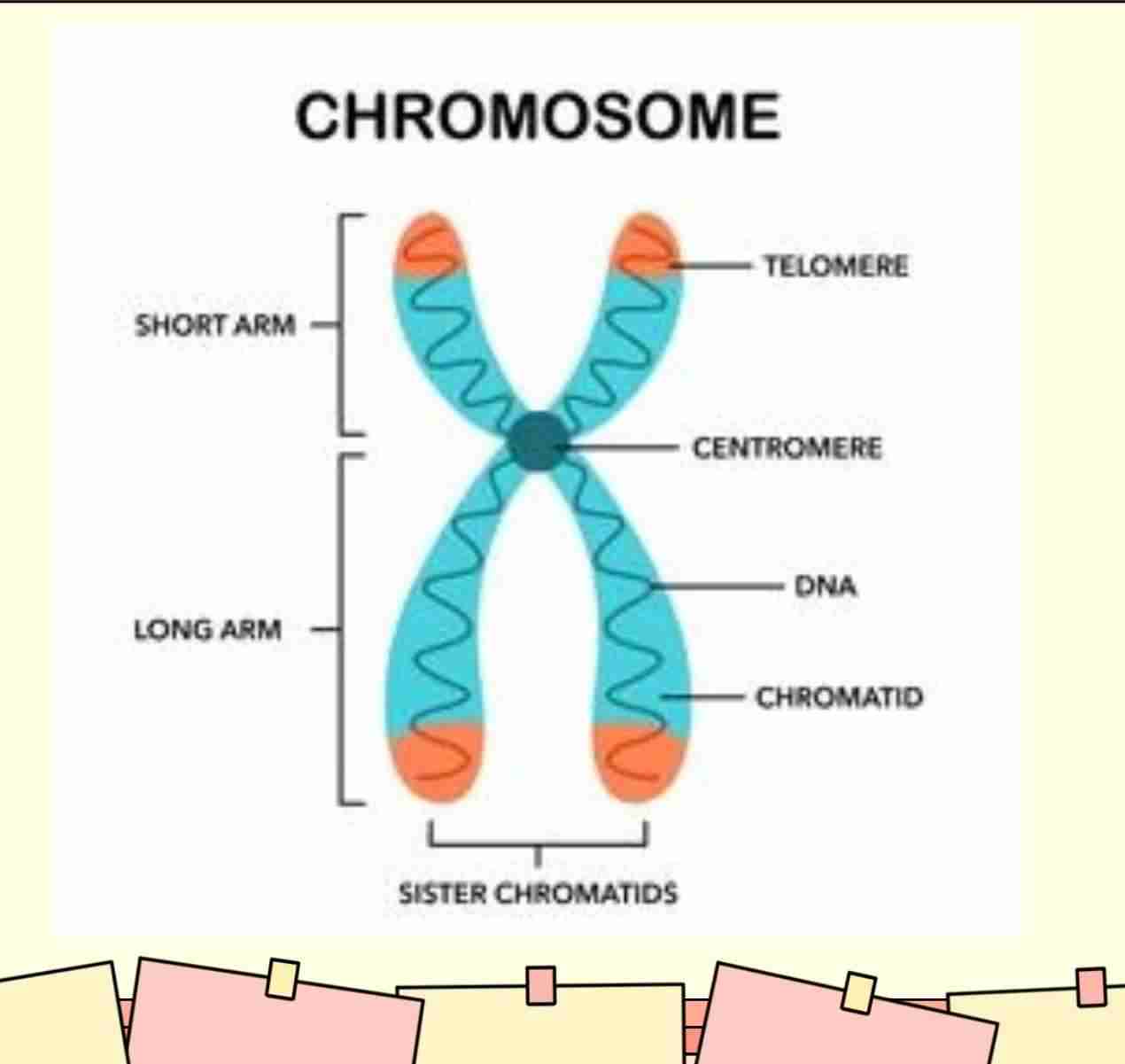
Structure Of Chromosomes
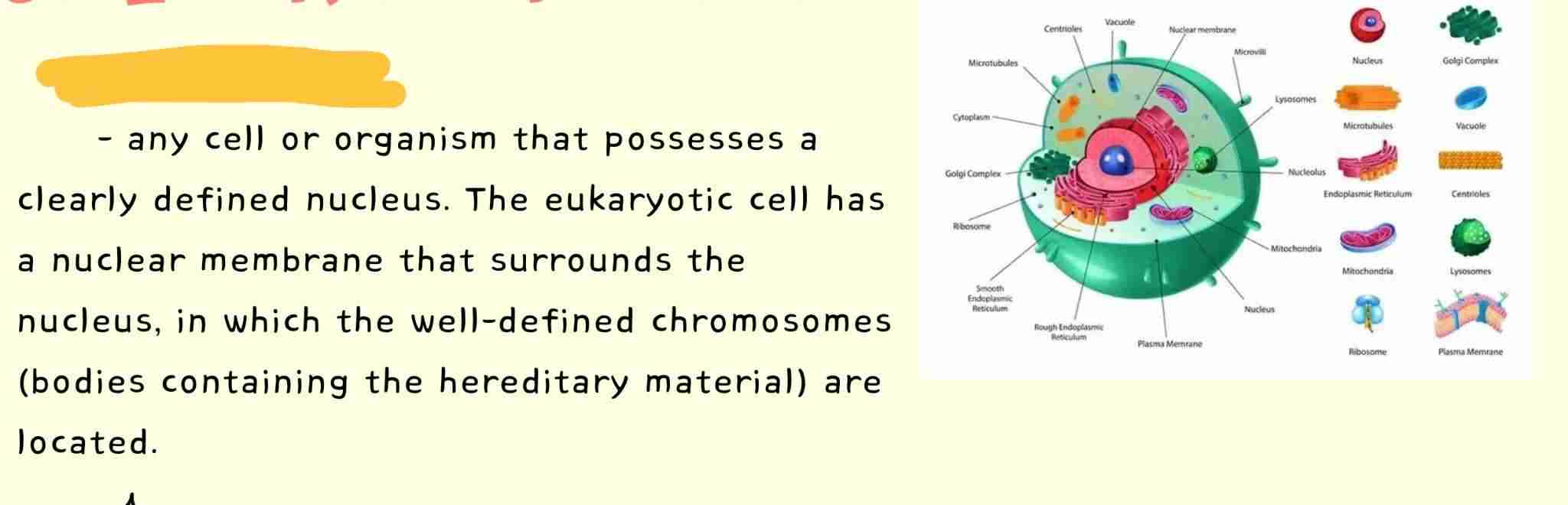
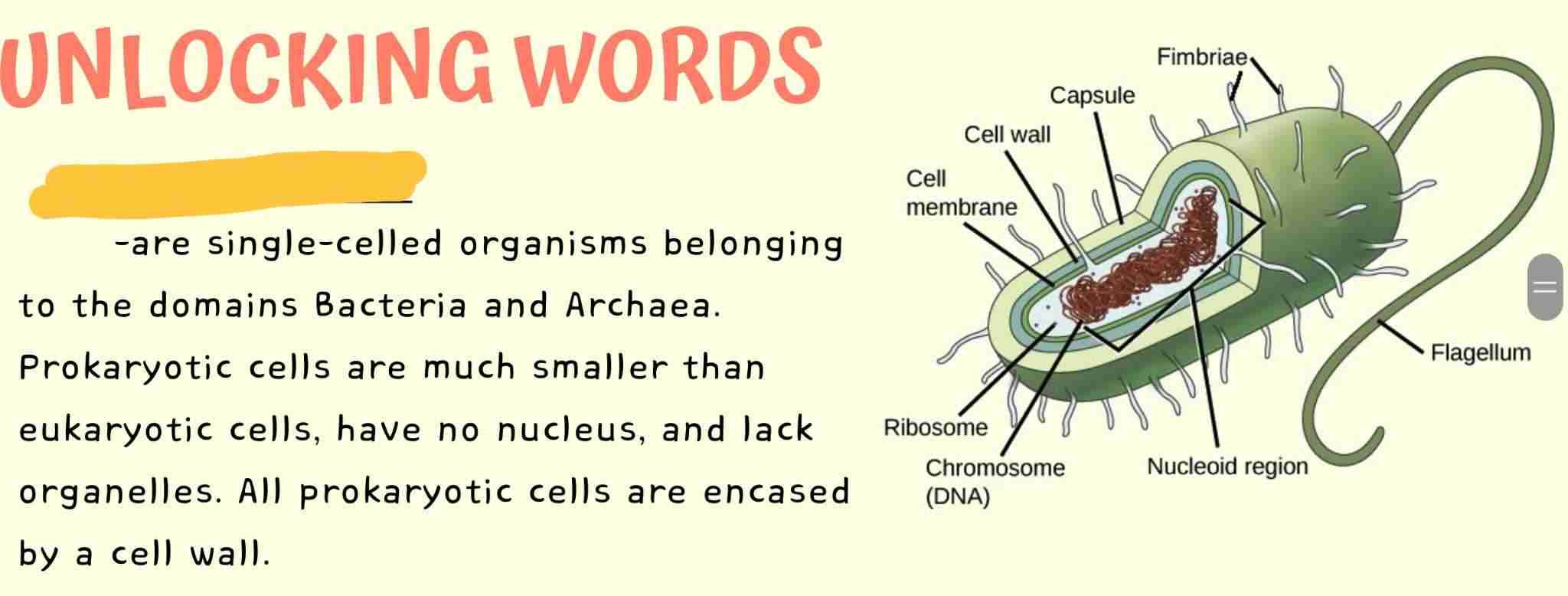
Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic Cells
Chromosome Number
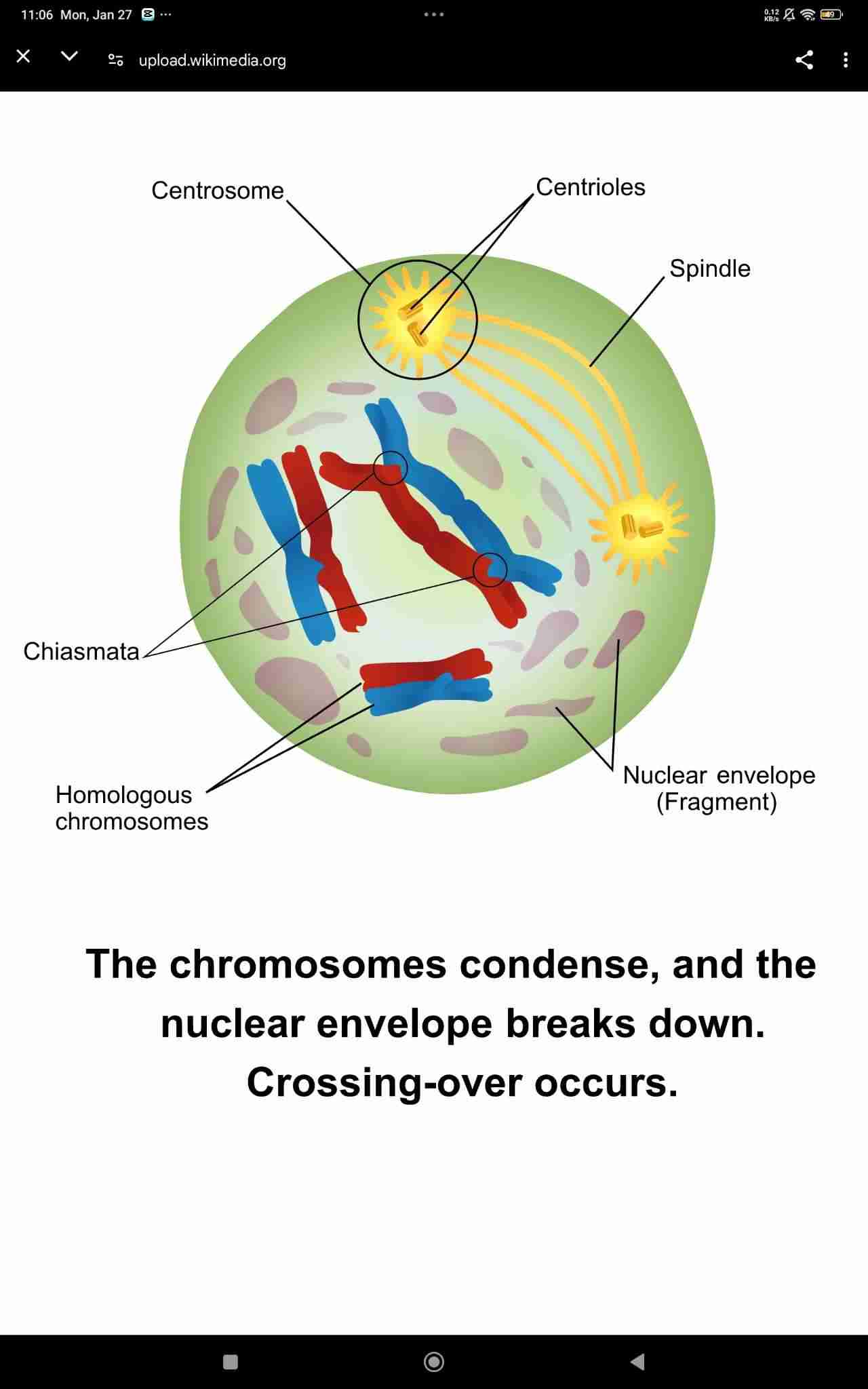
Prophase I
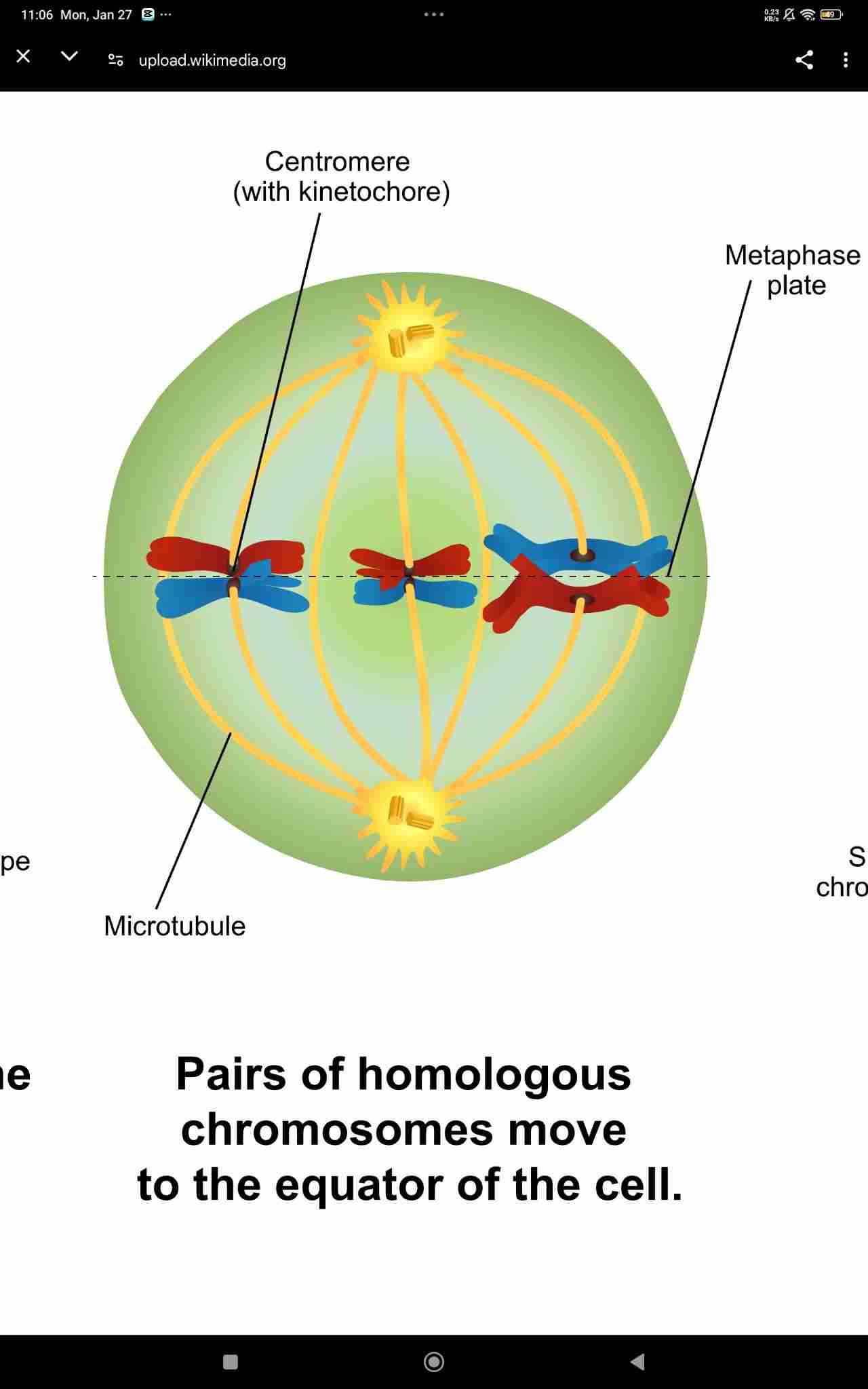
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
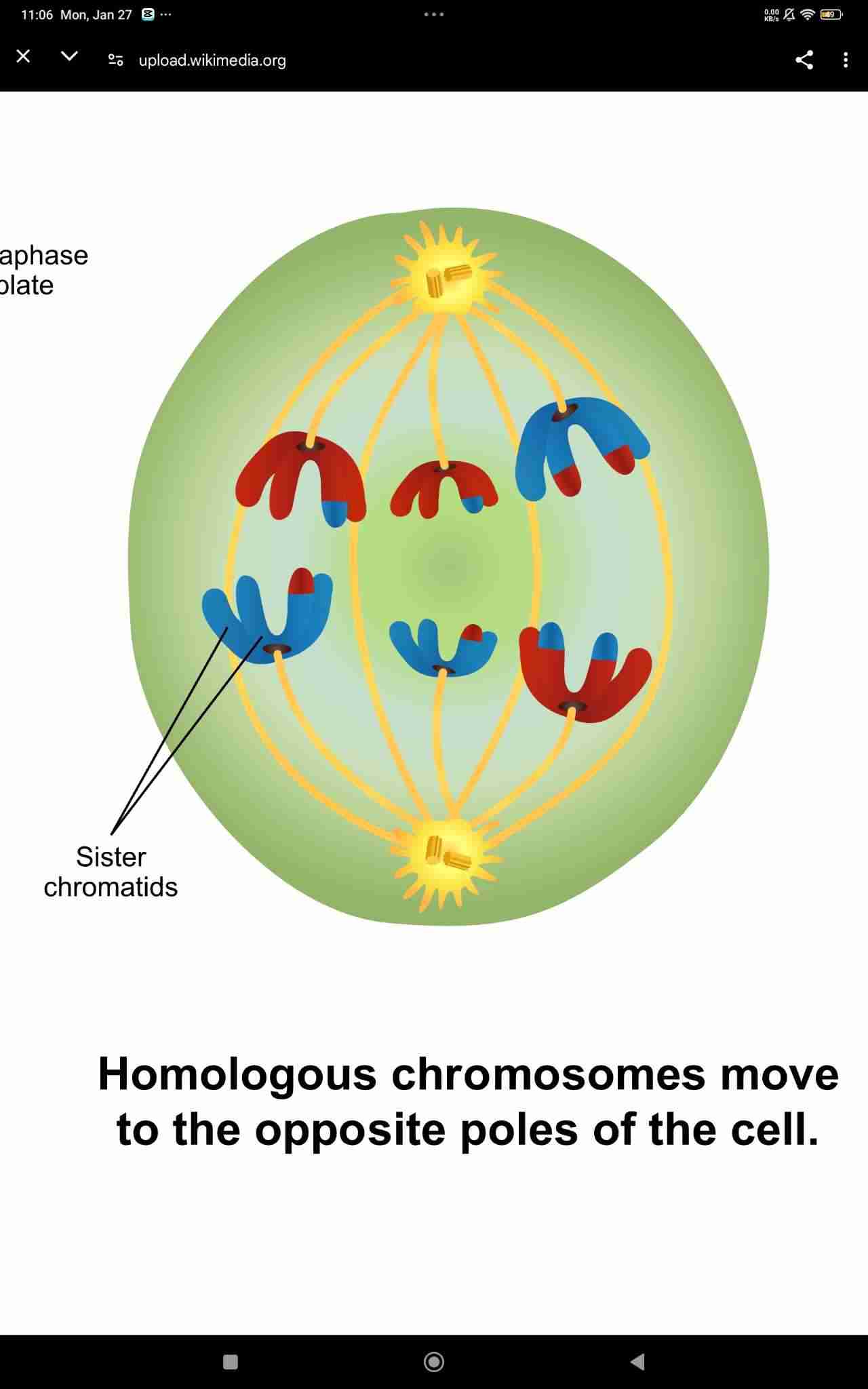
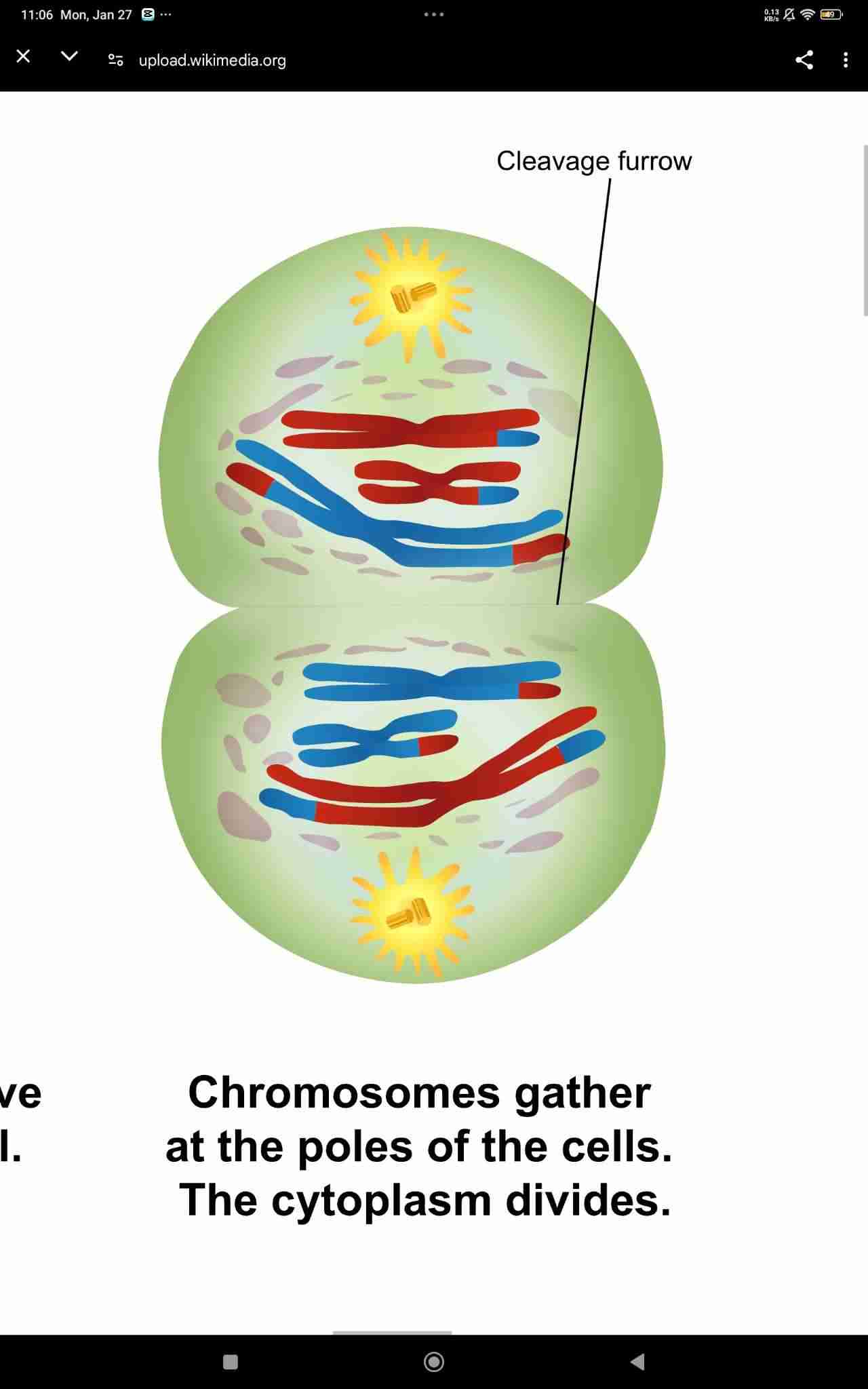
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
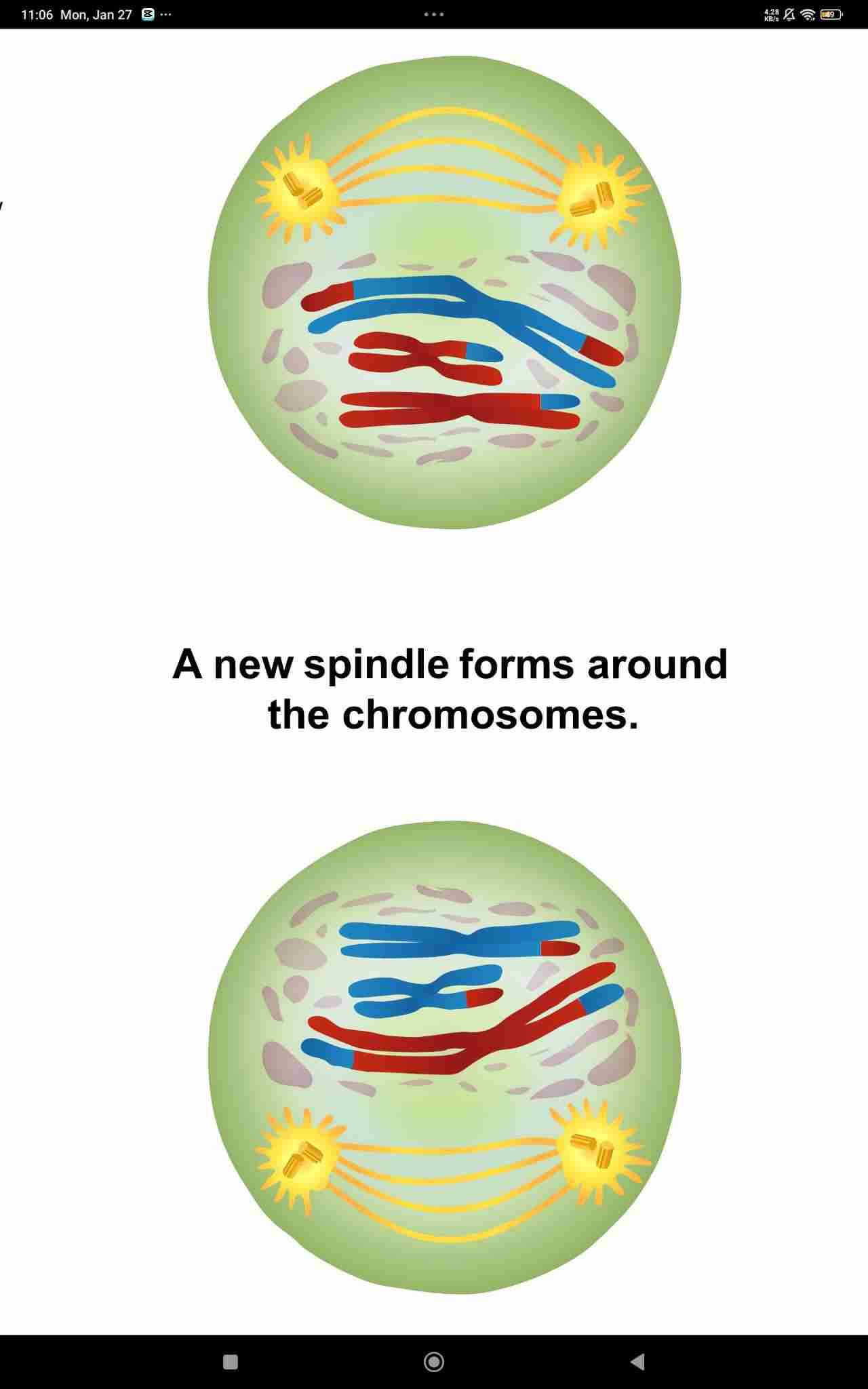
Prophase II
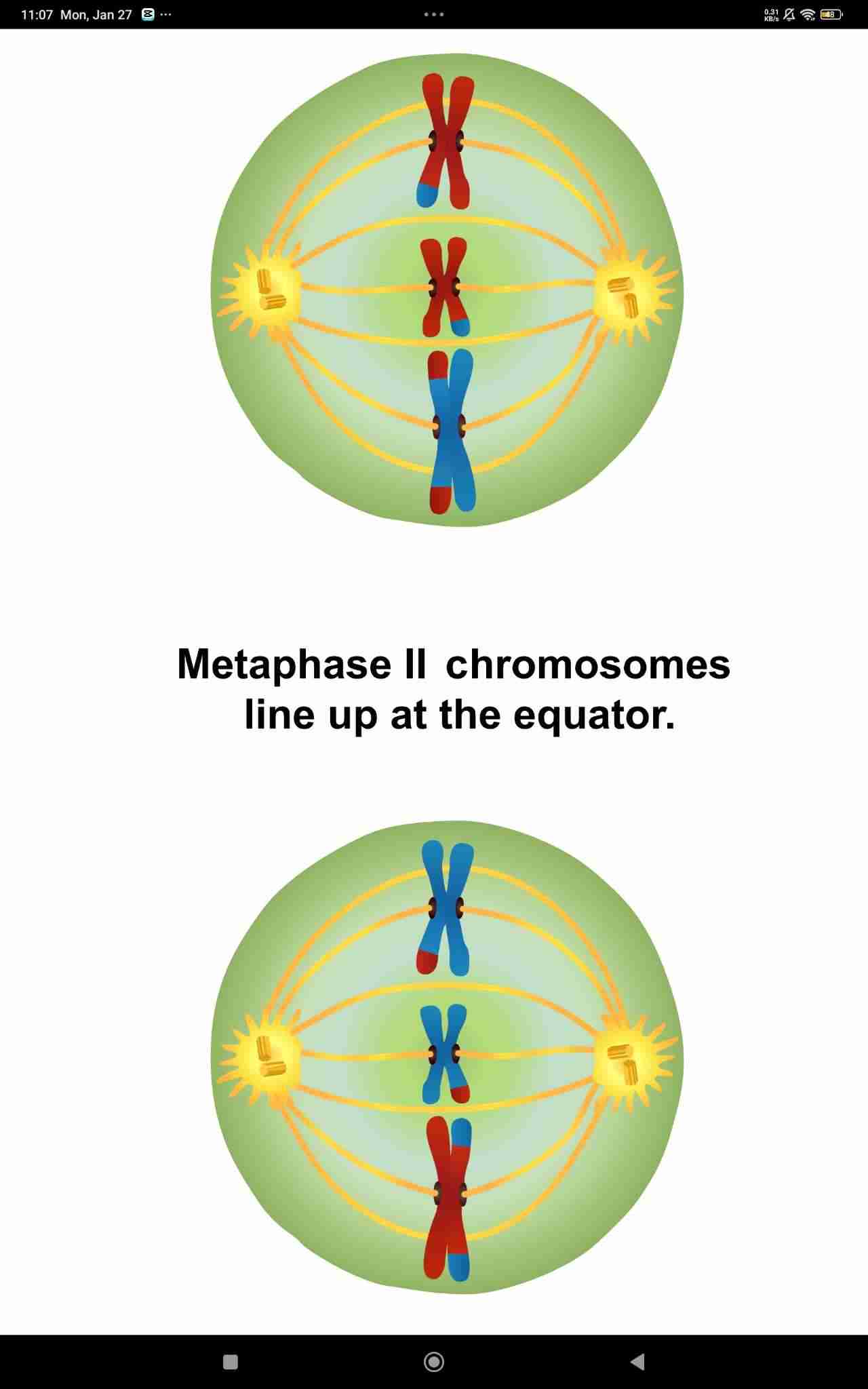
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
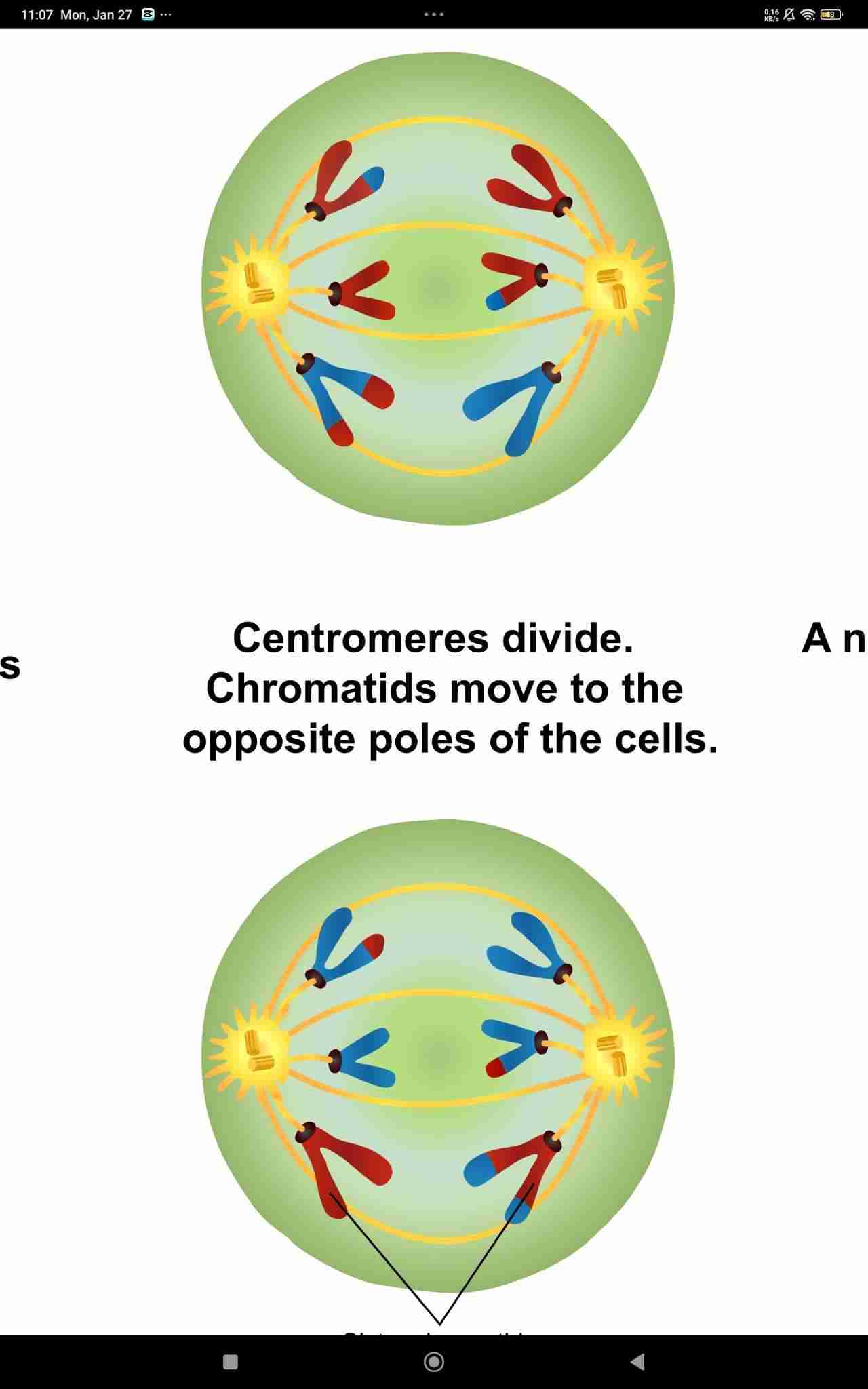
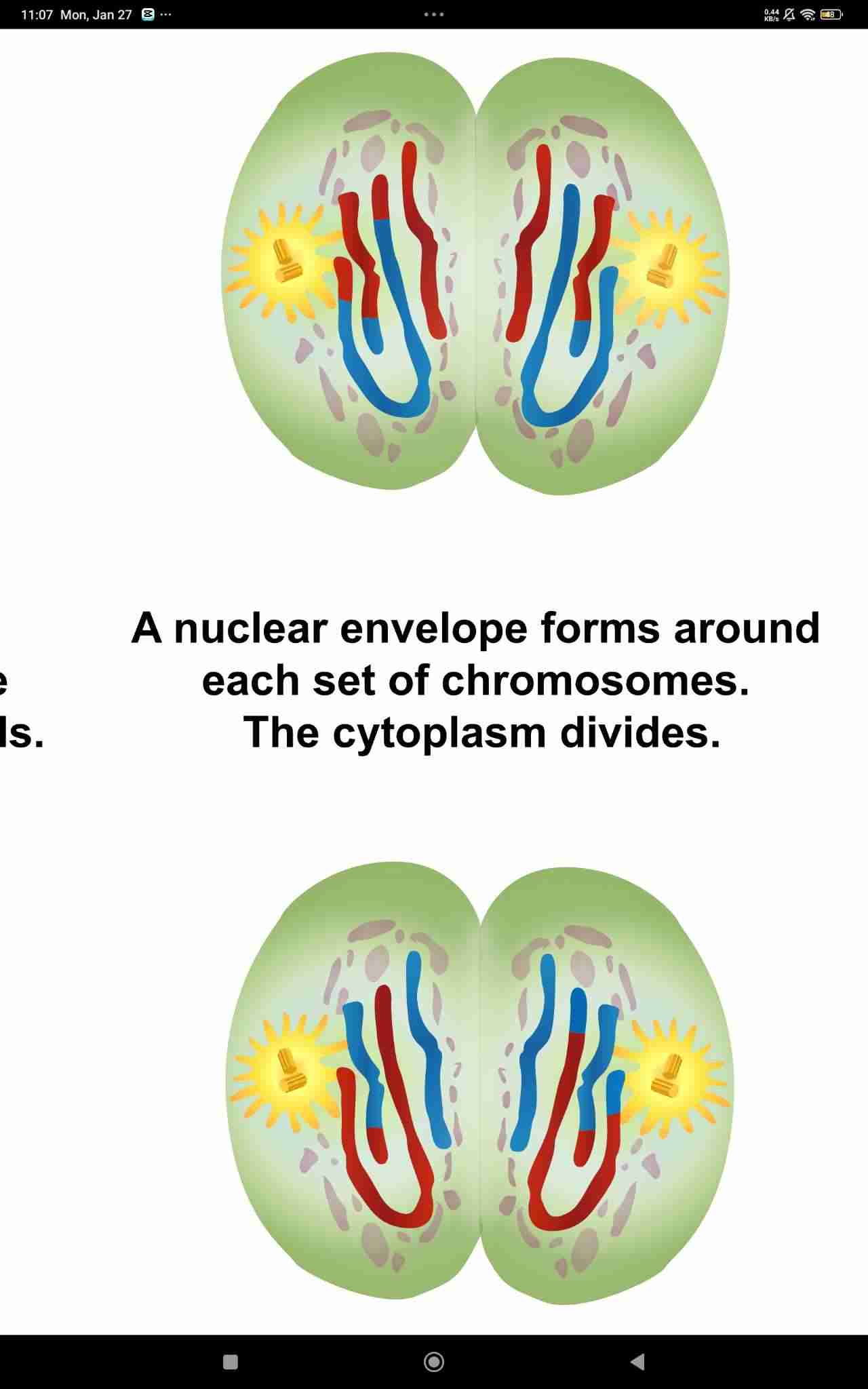
Telophase II and Cytokinesis
Meiosis
(Reduction Division)
•Only produces gametes.
•Begins with a diploid cell.
•Has two cell division stages. Meiosis I and II
Gametes
Sex cells:
Male = Sperm Cells | Female = Egg Cells
Meiosis I
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Produces two haploid cells each containing one chromosome from the homologous pairs.
Meiosis II
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Separates sister chromatids to produce four haploid cells.
Tetrad
Group of four sister chromatids in paired homologous chromosomes.
Alleles
Different versions of the same gene on each chromosome.
Crossing over
Also called as Recombination. Chromatids from each homologous chromosomes exchange segments of alleles.