lec 6 - stem cell isolation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what are the uses of lineage tracing? what is the basic idea?

what are the 4 important properties of labeling tracers?
should not change the properties of the labeled cell, its progeny or neighboring cells
must be retained over time
must be passed onto all progeny of the founder cell
must never be transferred to unrelated neighboring cells
what is the goal for stem cell purity out of a heterogenous population?
need to achieve 95-100% purity
gives more accuacy
what is fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)
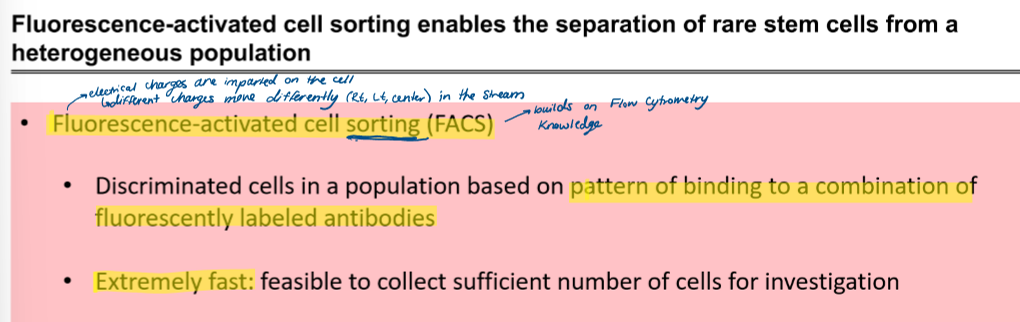
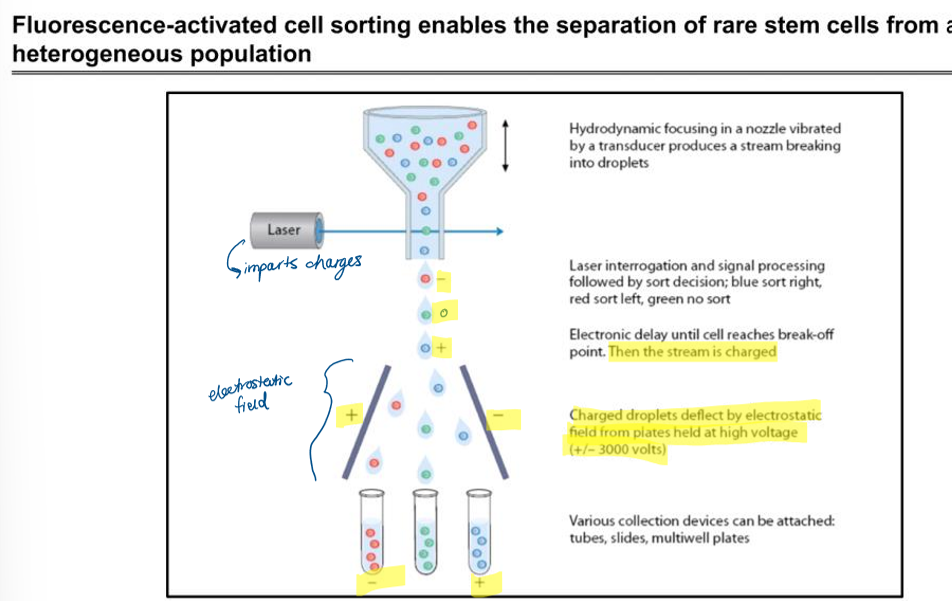
how does FACS work?
what are the benefits of Magnetic bead separation? when is this used?

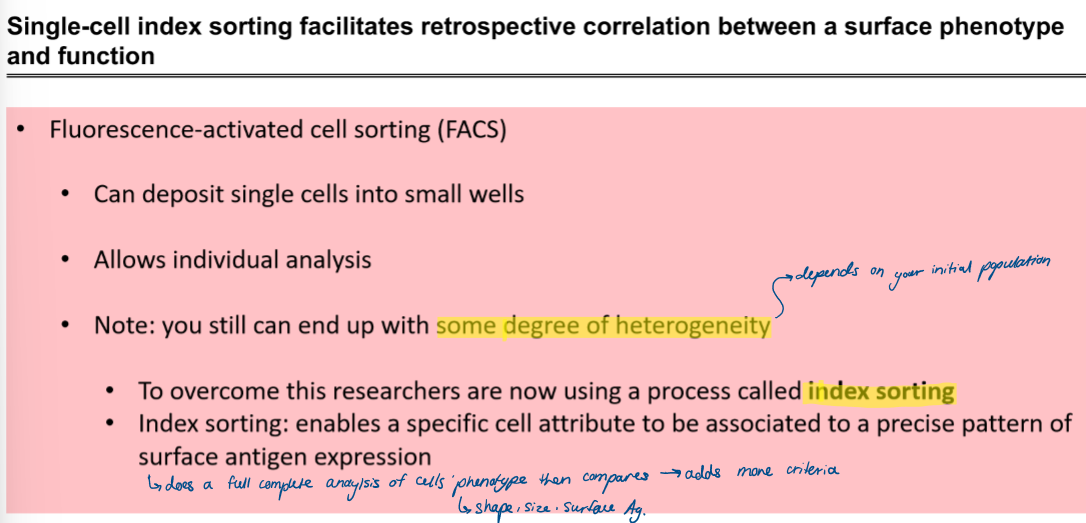
what is the next step after FACS if there is still heterheneity?
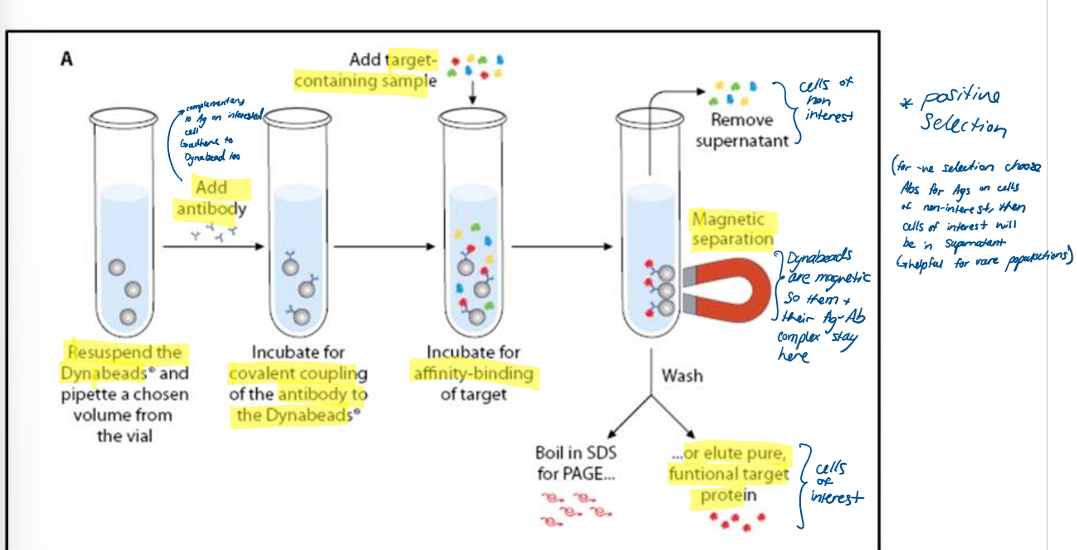
what is magnetic cell separation? used on rare/common cells?

what are the 2 magnetic cell separation methods?

explain how Dynabeads can be used for positive or negative selection
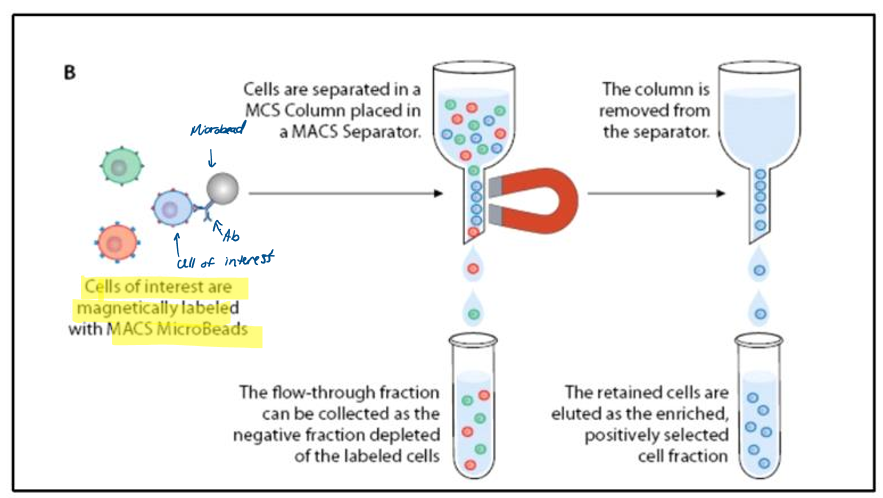
explain how MACS Microbeads can be used
what are the three methods for stem cell characterization/measuring stemness?

describe in vivo assays

what are the perquisites for an in vivo assay?

how can immune system rejection be avoided in in vivo assays?

how are NOD mice tested to ensure they have Type 1 diabetes? what is type 1 diabetes?

how can human ESC be studied in mice?
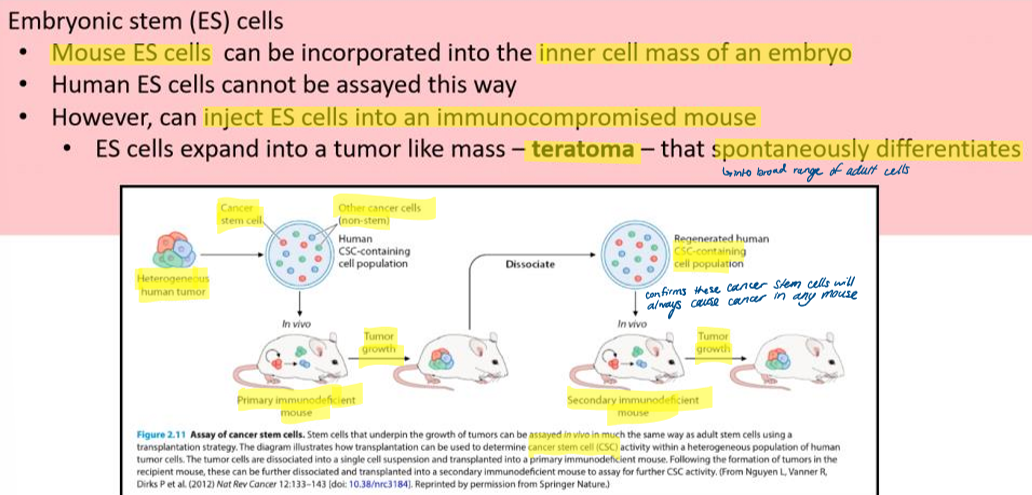
what is xenotransplantation and how is it used in stem cell research? what are the factors to consider

what is the need to image stem cells in living organisms?
to understand mobilization, homing and engraftment
images are based on sensitivity and resolution (both need to be optimal)
researchers often take a multimodal approach
how is intravital microscopy (IVM) used to study stem cells?
e.g. brain is easier to see bc on top layer, bone marrow is harder bc too deep

what is non-invasive tracking of stem cells? what are some examples?
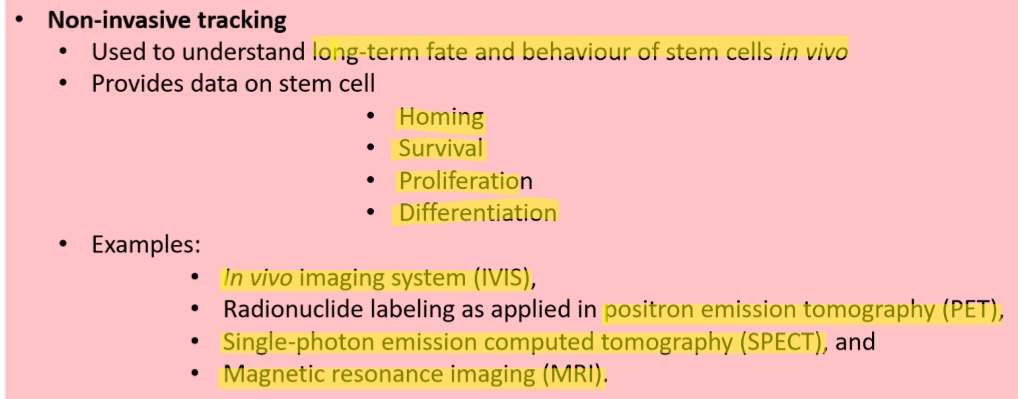
explain how in vivo imaging system (IVIS) works, its advantage and limitations

explain how radionuclide imaging works, its advantage and limitations

explain how MRI imaging works, its advantage and limitations

what are in vitro studies? what does it assess? what are requirements?

describe the two ways in vitro assays are carried out?

what makes a successful in vitro assay? is this better for ESC or adult SC?

what are the ways stem cell molecular make up is studies?
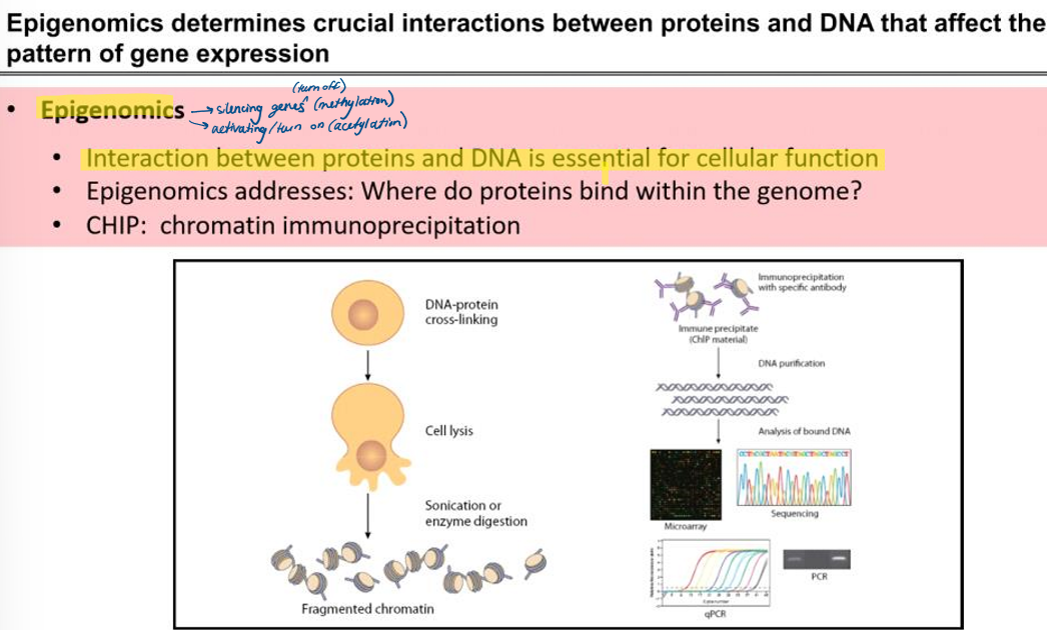
genomics/epigenomics
transcriptomics/proteomics
metabolomics
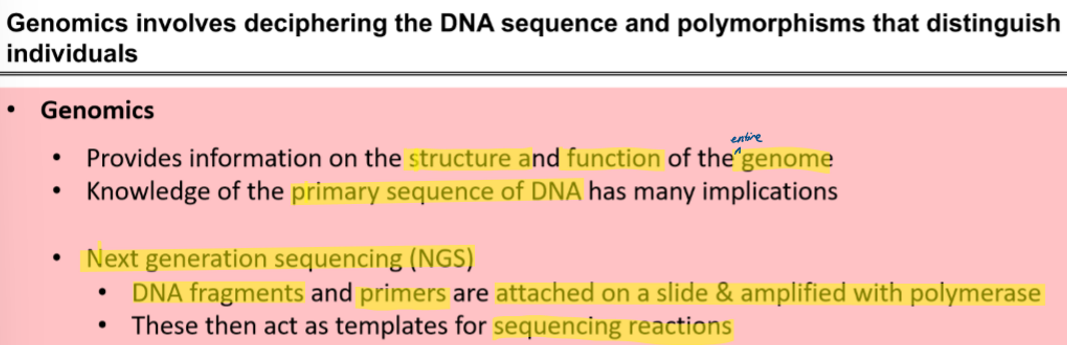
describe genomics and a Next generation sequencing
describe epigenomics and a chromatin immunoprecipitation
what is transcriptomics

what is proteomics

what is metabolomics
