Gene expression - Factors affecting expression of genes
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What factors can affect expression of genes?
- The genes may not be trancripted into mRNA
- The mRNA may not be translated into a protein
What protein helps with the transcription of DNA to RNA?
RNA polymerase
What are transcription factors?
Proteins that bind to specific sites on the DNA sequence that control the rate of transcription
What specifically do transcription factors control?
Whether mRNA for a particular gene is synthesised
Where do transcription factors bind?
Promoter regions
What are promoters?
A sequence of DNA located near the start of a gene
What are the different kinds of transcription factors?
- Activators
- Repressors
What are activators?
A type of transcription factor that increases the rate of transcription. They do this by helping RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter to initiate transcription
What are repressors?
They reduce the rate of transcription. They block the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter so transcription is slowed or stopped
What is the transcription factor we cover?
Oestrogen
How does oestrogen affect transcription factors?
It binds to the transcription factor oestrogen receptor to form an oestrogen/oestrogen receptor complex. This complex then binds to specific promotor regions and initiates transcription (complex acts as activator)
Give the steps of how oestrogen can influence transcription factors.
1. Oestrogen diffuses into the cell through the cell membrane.
2. Oestrogen binds to the oestrogen receptor, forming an oestrogen-oestrogen receptor complex.
3. The complex enters the nucleus, where it binds to specific sites on the DNA.
4. Genes are transcribed and translated into proteins, which alter the structure and function of the cell
Once mRNA has been made by transcription, what can still influence gene expression?
- RNAi is a factor that affects the expression of genes by affecting mRNA (before proteins are made)
- The transcription factors can also be blocked from reaching the DNA sequence by acetylation or methylation
What are the different kinds of RNAi?
- siRNA
- miRNA
What does RNAi stand for?
RNA interference
What are epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the study of changes to the phenotype that do not involve changes to the DNA base sequence. How environmental factors can alter the genetic inheritance of an organisms offspring
What is epigenetic control?
The control of whether a gene is switched on or off so thus influences whether a gene is expressed
What broad factors can effect the epigenome?
- Factors involved in in-utero development
- Environmental factors such as food, stress and presence of toxins
- Our hormones
How is epigenetic control determined?
Epigenetic control is determined by the presence or absence of chemical compounds, referred to as epigenetic marks
How do factors affect the epigenome?
As the epigenome surrounds DNA-histone complex, environmental factors can influence the compactness of the wrapping of DNA around histones which leads to DNA being read or not
What is epigenetic silencing?
Where the DNA-histone complex is kept in a tightly packed arrangement so genes cannot be read and are switched off
What are some different types of epigenetic control?
- RNAi
- DNA methylation
- Histone acetylation
Describe the process environmental factors go through in order to impact expression of genes.
1. Environmental factors stimulate proteins to carry their message into cells
2. The message is passed into the nucleus
3. Here the message passes to a specific protein which can be attached to a specific sequence of DNA bases
4. This leads to acetylation or methylation
OR
2. The message can passed on to RNAi
What is the epigenome?
It is made up of chemicals called tags that cover the DNA-histone complex. They determine the shape of the DNA-histone complex
How is the epigenome heritable?
DNA base sequence is inherited and some epigenetic marks persist through these generations
Describe RNAi.
- Only present in eukaryotic cells
- Short, double stranded sequences of RNA
What are the two types of RNAi?
siRNA and miRNA
What does RNAi do?
It prevents mRNA from being translated into a protein
What does siRNA stand for?
Small interfering RNA
Describe siRNA.
- Type of RNAi so shares the same qualities
- Fully complimentary to mRNA target so only binds to this specific mRNA sequence
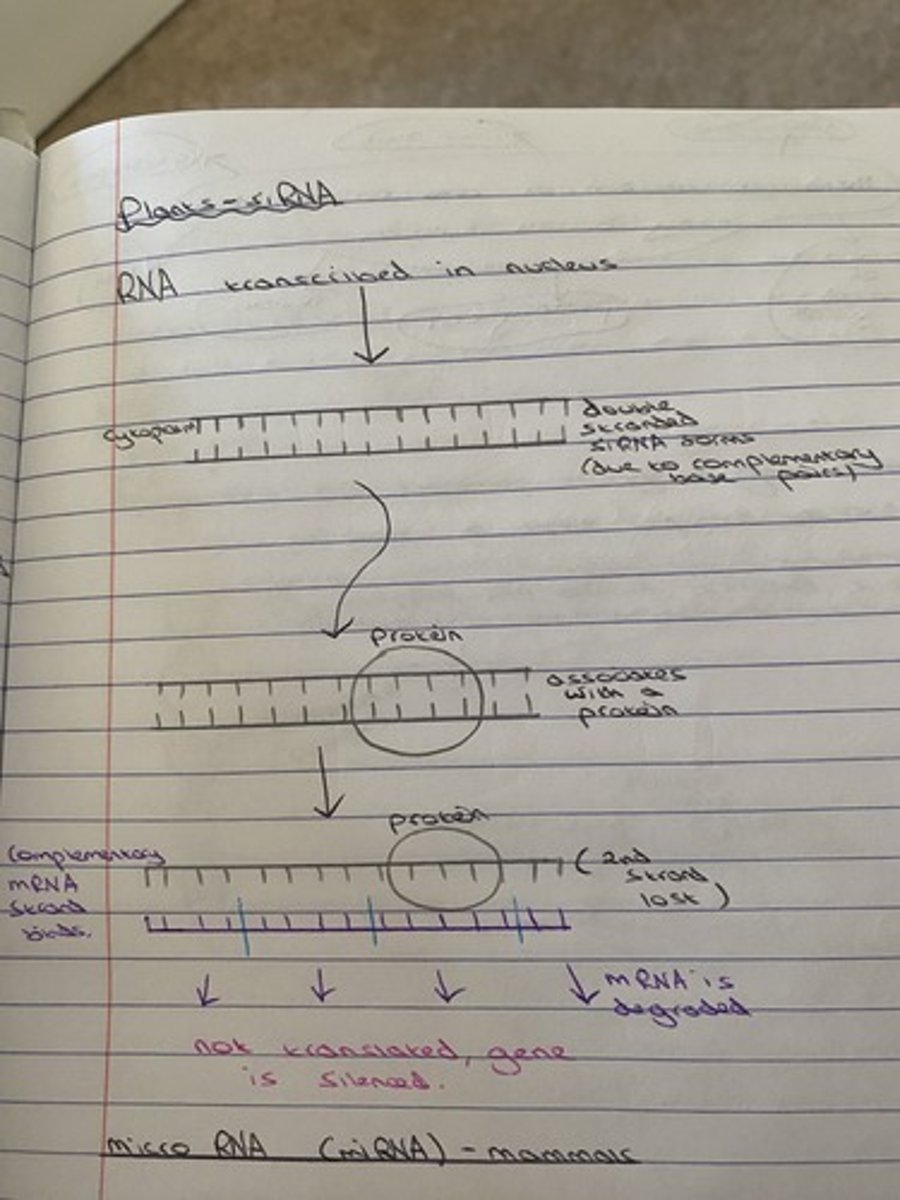
How does siRNA interfere with the expression of genes?
1. A gene is transcribed into mRNA.
2. This mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm.
3. At the same time a double stranded sequence of siRNA will unwind into 2 separate
strands
4. One of these strands will degrade, leaving single stranded siRNA.
5. The remaining strand of siRNA will bind to the complementary sequence of mRNA (hybridisation)
6. The siRNA/mRNA hybrid recruits a protein called RNA inducing silencing complex
(RISC).
7. RISC destroys the mRNA, preventing the translation of the associated gene
What is hybridisation in siRNA?
Where the remaining strand of siRNA binds to the complementary sequence of mRNA
Diagram to show how siRNA works.
What does miRNA stand for?
Micro interfering RNA
Describe miRNA.
- Type of iRNA so shares these qualities
- It is partially complimentary to its mRNA target so can bind to lots of different sequences
How does miRNA interfere with the expression of genes?
1. A gene is transcribed into mRNA.
2. This mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm.
3. At the same time a double stranded sequence of miRNA will unwind into 2 separate
strands.
4. One of these strands will degrade, leaving single stranded miRNA.
5. miRNA will bind to a complementary region on the mRNA strand.
6. The miRNA and the mRNA are only partially complementary to each other.
7. The miRNA/mRNA hybrid associates with a protein complex.
8. The hybrid is then moved to a processing body.
9. Here it may be destroyed or stored so the mRNA may be translated at a later time.
What is methylation?
It is the addition of a methyl group (CH3)
Briefly explain what increased and decreased methylation does.
- Increased = less transcription - gene off
- Decreased = more transcription - gene on
Where do methyl groups attach in DNA?
They attach to cytosine bases of DNA
Explain what increased methylation does.
- It makes it harder for DNA polymerase and transcription factors to bind to the DNA so transcription does not take place
- It also attracts proteins that condense the DNA-histone complex
What does increased methylation of DNA lead to?
The chromatin is more condensed so there is reduced gene expression. It is said that the gene is switched off
What is acetylation?
Addition of an acetyl group to a molecule (COCH3)
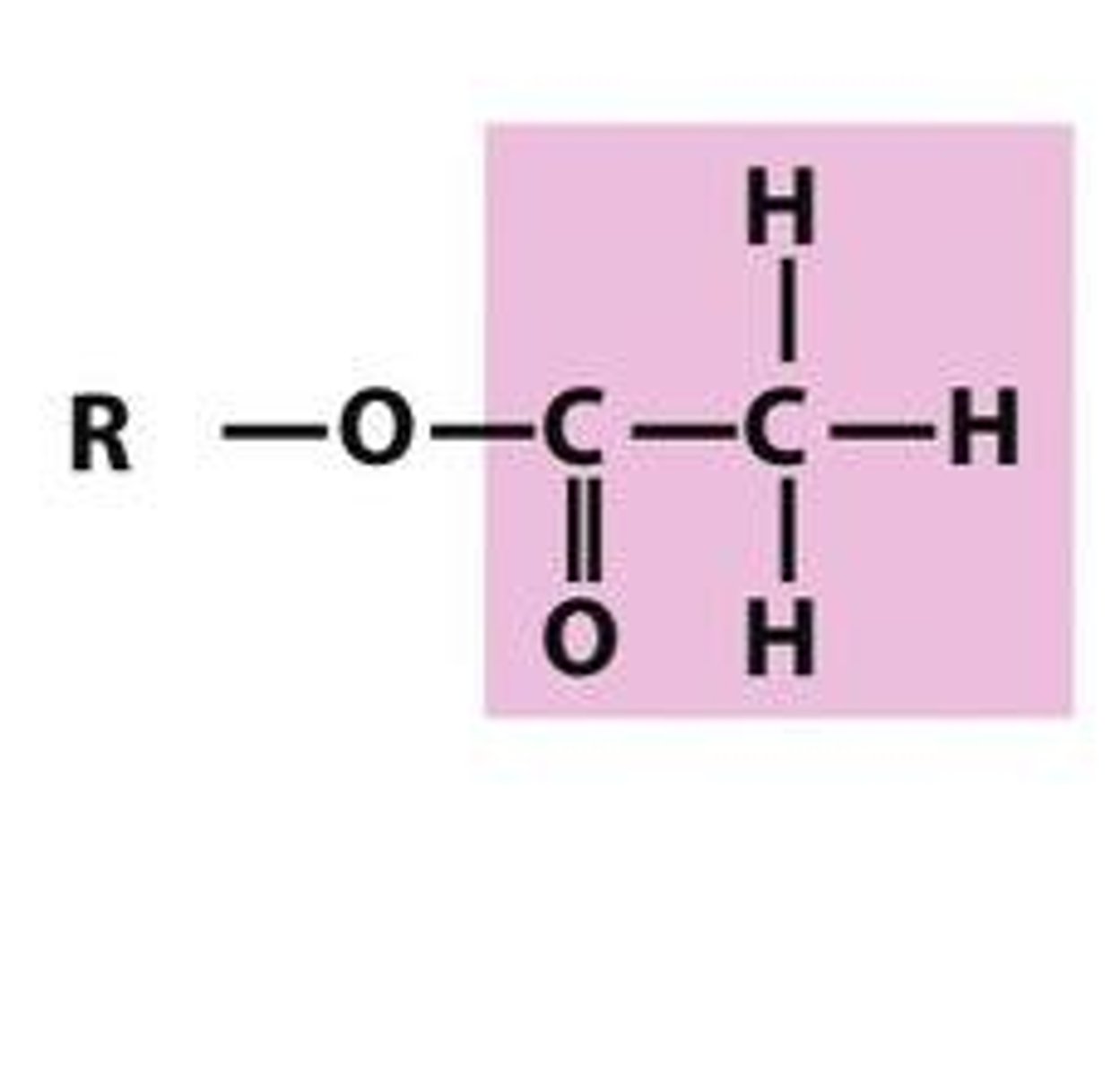
Where does the acetyl group come from?
Acetyl CoA
Where to acetyl groups attach in DNA?
They attach to the histones which are proteins that provide structural support to chromosomes by condensing DNA strands to chromatin
Briefly explain what increased and decreased acetylation does.
- Increased = more transcription - gene on
- Decreased = less transcription - gene off
Explain what decreased acetylation of histones does.
It increases the +ve charge on histones therefore increasing their attraction to the DNA -ve phosphate groups. Therefore the chromatin condenses which prevents transcription factors and enzymes such as RNA polymerase from binding to the DNA - gene switched off
Explain what increased histone acetylation does.
Acetyl group removed, attraction of histones to DNA decreases so chromatin decondenses. Leads to increased transcription of a gene - it is said that the gene is switched on
How are acetyl groups removed?
By histone deacetylases (HDACs)
How do histone deacetylases work?
They cause the strands of DNA to recondense into chromatin which makes it harder for the transcriptional enzymes to access the DNA (switching the gene off)
How can epigenetic controls increase the risk of cancer?
Increased methylation of tumour suppressor genes can reduce their expression, leading to the growth of a cancerous tumour
How can the epigenome influence diseases other than cancer?
A duplication mutation in a gene called FMR1 on the X chromosome leads to a disease called Fragile X syndrome (FXS)
Describe FXS.
Sufferers of FXS have many more copies of the DNA sequence CGG than normal. CGG is a sequence containing a CpG site. An increased number of CpG sites leads to increased methylation of the DNA.
This switches the FMR1 gene off - the FMR protein is not produced.
Lack of the FMR protein leads to a wide range of learning and behavioural difficulties.
What is good about medical conditions caused by epigenetics?
They are reversible because the chemical compounds can be added or removed
How can we treat poor epigenetic control?
- Reducing the rate of methylation at CpG sites
- Reducing the rate of deacetylation at histones
How can the rate of methylation at CpG sites be slowed/prevented?
There is a chemotherapy drug that prevents the methylation of tumour suppressor genes. This reactivates the tumour suppressor genes, slowing the rate of tumour growth
How can the deacetylation of histones be prevented or slowed?
HDAC inhibitors are drugs that prevent HDACs from removing acetyl groups from histones
List examples of some diseases which have genetic and environmental factors.
- Autism
- Breast cancer
- Parkinson's disease
Describe how autism is affected by the environment and genetics.
Research has suggested that exposure to air pollution or pesticides contribute to an increased risk of autism in those who are already genetically susceptible
Describe how breast cancer is affected by the environment and genetics.
Research has shown that breast cancer is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental risk factors. Exposure to hormone therapies and increased alcohol intake have both been shown to increase the risk of breast cancer
Describe how parkinsons disease is affected by the environment and genetics.
Poor nutrition and nicotine consumption both have a stronger impact in those who are
genetically susceptible
What group is research into the effects of genotype and environment performed on and why?
Identical twins because they have identical genotypes so any changes to the phenotype must be a result of the environment