CLAS 242 - The Julio-Claudian Period
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms

Identify and Analyze
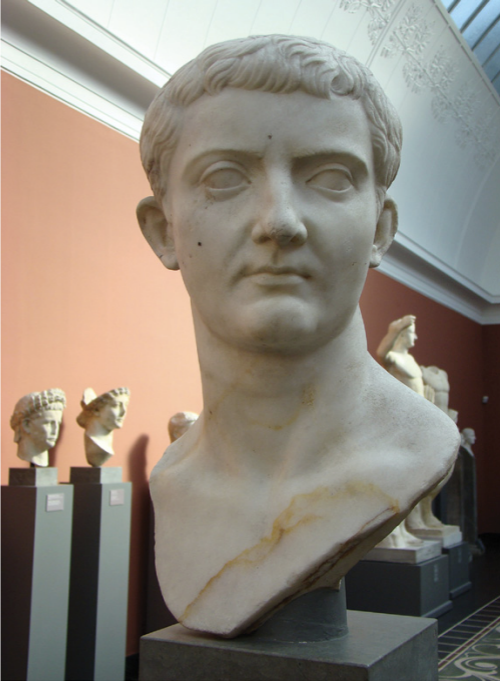
Portrait of Tiberius, from the Fayum in Egypt
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Next Emperor
adopted son of Augustus, Livia’s biological son from her previous marriage
by being deemed an heir, created the dynastic succession of the Julio-Claudians
Julio - Augustus’ household, from Julius Caesar’s family
Claudians - from Livia’s household and family
essentially a creation of a monarchy without calling it that
all art of this period represents the dynasty as a way to get the public used to this new concept
Good General and Strategist
won almost all the wars he was in charge of
End of Life
suffered from a skin condition
moved to an area that was well known for its salt baths which presumably helped relieve his suffering
14 years old at the time of this portrait
Augustan Classicism
hair + lobster claw
Tiberius relying heavily on trends established by Augustus
idea of him sharing qualities with his predecessor
Individual characteristics
high forehead
large eyes
long nose
small mouth with a notably protruding lower lip

Identify and Analyze
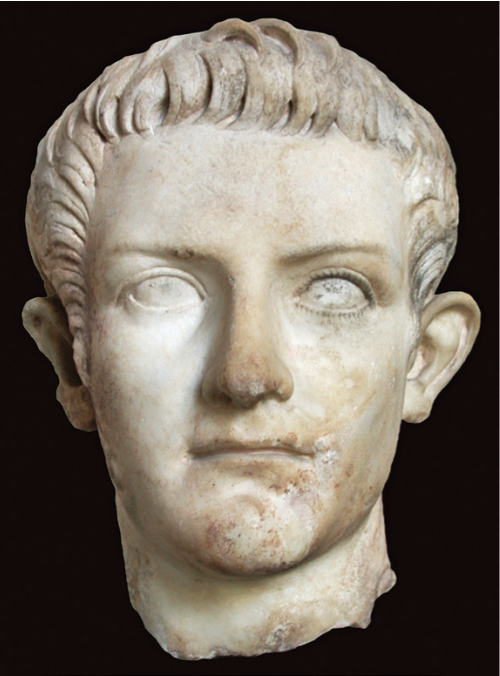
Portrait of Caligula, from Asia Minor
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Next Emperor
adopted son of Tiberius, his nephew and son of Germanicus
4 year reign before being assassinated
“Caligula”
means “little boots”
as a child, would mimic his father, a war general, by wearing his boots which were too big for the boy
the troops then started calling him “little boots” and it stuck
Insanity
a notable reputation for being crazy
a bit of preserved paint on the proper left eye
distinct pupil, iris, and lashes, which give an imbalanced look
reinforces this reputation
Various stories of his insanity
believed he was the reincarnation of Zeus
tried to elect his horse as a senator
sexual relations with all of his sisters
married one of them too
declared war on Poseidon
had his army go and stab at the sea
True stories?
good emperors were often represented by good stories, though bad emperors were later depicted as being alcoholics who cheated on their wife and etc
stories could have just been later writers changing certain stories to seem worse
“You guys suck. My horse could be a better senator than you.”
“Look how powerful and how such good of a commander I am, I can make my army do whatever I want. Hey army, go fight the sea.”
Augustan Classicism
Unique pieces of individualism
Protruding ears
deeper, closer set eyes
Protruding upper lip
Portraits not images, just messages for propaganda
Julio-Claudian Hair + Lobster Claw

Identify and Analyze
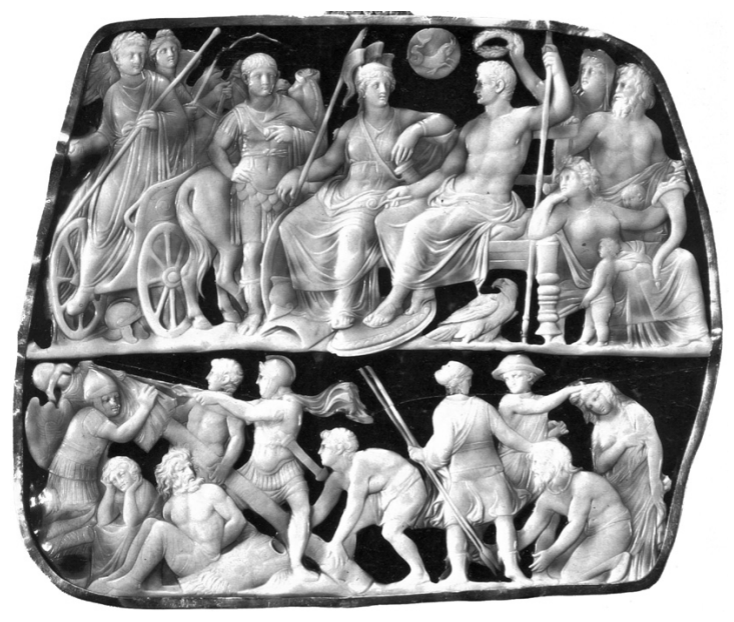
Gemma Augustea
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Gem Carving
elite gifts within royal circle
could be to family or just a gift to the king of a province
Cameo Carving
this style needed a stone with two differently coloured veins
agate, carnelian, and sardonyx
the images were then carved into one set of veins, with the other being used as the background colour
Bottom Register
Military Victory by Romans
spears and helmets
Tropeion
a trophy being erected where they have won
used to display the enemy’s armour to show that they were defeated
like a military scarecrow
Series of Captives
Men
Barbaric representations
beards and long hair
neither of which are Roman attributes
Torq
cultural necklace
Tunics
rather than togas
possibly showing Tiberius’ most famous victory
in Germany over the Celts
story exists that Celts didn’t wear armour into battle
Shield - Scorpion - Scorpio - Tiberius’
Upper Register
complicated
differing opinions on what is happening
Middle Figure
Augustus in afterlife, on throne,
represented like Jupiter - eagle and staff of office
crowned in victory of eternity
Right Figures
Roma and Tellus
Cornucopia representing the abundance of Rome
Two Babies
possibly Romulus and Remus
possibly Gaius and Lucius, Tiberius’ sons, not twins but were very close in age together
River God - Tiber personification
however, if Tellus is there, it could be a representation of Oceanus
“all the land and all the waters
Left Figures
Germanicus and Tiberius
together: German triumphs by Tiberius?
Tiber in Chariot
driven by Victory
implies triumph in military
incoming of his reign following Augustus' death
Upper Middle
Zodiac Figure - Goat of Capricorn
Augustus’ birth sign
Romans were super into astrology
Tiberius to the point it bordered on superstition
Time period where there was no difference between astronomy and astrology
Slight Hierarchy of Scale
Gods on top are bigger than figures below
could be completely unintentional

Identify and Analyze
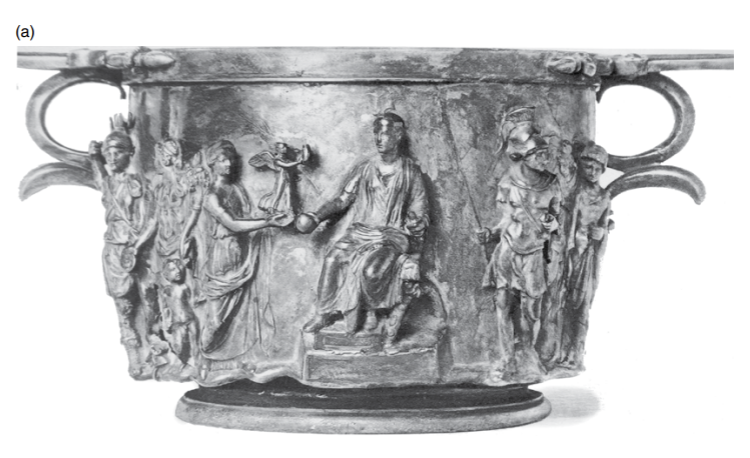
Boscoreale cups A and B, Boscoreale
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
found in a big villa just outside of Pompeii, covered from Vesuvius
a far away, big, rich family - could be Julian-Claudian offshoots
probably given as gifts under Tiberius
set of silver decorative cups
small scale copies of large public reliefs in Rome
do not survive
Cup A
Chasing
hammering in details from the front of the piece, opposite of repoussé
two scenes devided by the handles
Augustus on Magistrate Chair
Deified
a repeated image to be engrained in society’s mind
Patera
religious context given
could also be a globe for representing the expansion of the Roman Empire under Augustus
Right Figures
Mars, God of War, dressed in full armour
leads a series of captives
representations of barbarians/people of the provinces
Roman power that has taken over all the places
Left Figures
Venus Genetrix handing over Victoria
little baby cupid with her to show it;s Genetrix - head of Julio-Claudian line
crowning Augustus as a victor for all eternity
Virtus
personification of male military achievement
Honos
personification of male civic achievement
holds a cornucopia showing Roman prosperity under Augustus
Honos + Virtus together
virtues of Rome that has fed the military and expanded/kept Rome safe
Ethos of Rome
military expansion + Julio-Claudians wre the ones to bring that about
Jupiter’s famous promise to Romans from Vergil’s Aeneid: imperium sine fine - “empire [power] without end”
Cup B
Front Side
Tiberius in Victory Procession
Triumphal Quadriga - Victory Procession
Slave holds victory crown over his head
Victorious soldiers of Tiberius follow him
Individuals in front
leading cattle to sacrifice to the Gods
Back Side
altar and temple
Tiberius standing between, presiding over bull sacrifice
Building
Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus
where victory processions ended in Rome
Cups, although separate, were meant to be seen and understood together
Reinforce themes of the Gemma Augustea
divinity of Augustus
terrestrial military triumps of Tiberius
![<p>Boscoreale cups A and B, Boscoreale</p><p>The Julio-Claudian Period</p><p>14 CE - 68 CE</p><ul><li><p>found in a big villa just outside of Pompeii, covered from Vesuvius</p><ul><li><p>a far away, big, rich family - could be Julian-Claudian offshoots</p></li><li><p>probably given as gifts under Tiberius</p></li></ul></li><li><p>set of silver decorative cups</p><ul><li><p>small scale copies of large public reliefs in Rome</p><ul><li><p>do not survive</p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Cup A</p><ul><li><p>Chasing</p><ul><li><p>hammering in details from the front of the piece, opposite of repoussé</p></li></ul></li><li><p>two scenes devided by the handles</p></li><li><p>Augustus on Magistrate Chair</p><ul><li><p>Deified</p></li><li><p>a repeated image to be engrained in society’s mind</p></li><li><p>Patera</p><ul><li><p>religious context given</p></li><li><p>could also be a globe for representing the expansion of the Roman Empire under Augustus</p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Right Figures</p><ul><li><p>Mars, God of War, dressed in full armour</p><ul><li><p>leads a series of captives</p><ul><li><p>representations of barbarians/people of the provinces</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Roman power that has taken over all the places</p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Left Figures</p><ul><li><p>Venus Genetrix handing over Victoria</p><ul><li><p>little baby cupid with her to show it;s Genetrix - head of Julio-Claudian line</p></li><li><p>crowning Augustus as a victor for all eternity</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Virtus</p><ul><li><p>personification of male military achievement</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Honos</p><ul><li><p>personification of male civic achievement</p></li><li><p>holds a cornucopia showing Roman prosperity under Augustus</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Honos + Virtus together</p><ul><li><p>virtues of Rome that has fed the military and expanded/kept Rome safe</p></li><li><p>Ethos of Rome</p><ul><li><p>military expansion + Julio-Claudians wre the ones to bring that about</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Jupiter’s famous promise to Romans from Vergil’s Aeneid: imperium sine fine - “empire [power] without end”</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Cup B</p><ul><li><p>Front Side</p><ul><li><p>Tiberius in Victory Procession</p><ul><li><p>Triumphal Quadriga - Victory Procession</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Slave holds victory crown over his head</p></li><li><p>Victorious soldiers of Tiberius follow him</p></li><li><p>Individuals in front</p><ul><li><p>leading cattle to sacrifice to the Gods</p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Back Side</p><ul><li><p>altar and temple</p></li><li><p>Tiberius standing between, presiding over bull sacrifice</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Building</p><ul><li><p>Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus</p><ul><li><p>where victory processions ended in Rome</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Cups, although separate, were meant to be seen and understood together</p><ul><li><p>Reinforce themes of the Gemma Augustea</p><ul><li><p>divinity of Augustus</p></li><li><p>terrestrial military triumps of Tiberius</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b8b3b268-d1e8-4fa3-a708-deb1148ce5aa.png)
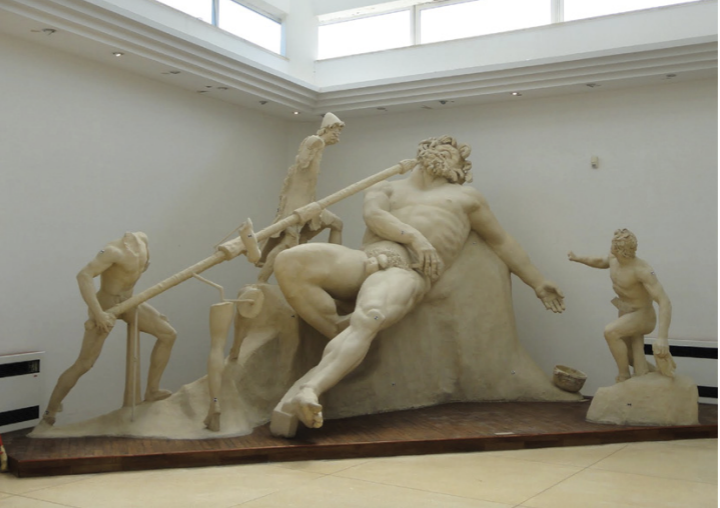

Identify and Analyze
Sculpture group of Polyphemus, grotto dining room of Tiberius, villa at Sperlonga
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Villa at Sperlonga
private garden/grotto for Emperor Tiberius
dining area inside with Mediterranean around the outside
fish to scoop up and eat
Sculpture
Book 9 of Homer’s Odyssey, the blinding of Polyphemus by Odysseus and his men
represents anticipatory moment in the narrative
Hellenistic
after Alexander the Great became way bigger
freaked everyone out when found because they had been expecting Augustan Classicism
Bodies
insane detail
Polyphemus Groin
flaccid penis and curly pubes showing intricacies of marble sculpture
Possibly stolen?
blew apart stylistic chronologies which used to be very strict
or Tiberius just liked the style and commissioned it
Identify and Analyze
Wine skin bearer, grotto dining room of Tiberius, villa at Sperlonga
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 Ce - 68 CE
Wine bearer - the one who got Polyphemus drunk
Furrowed Brow + Wild Hair
Use of bow drill
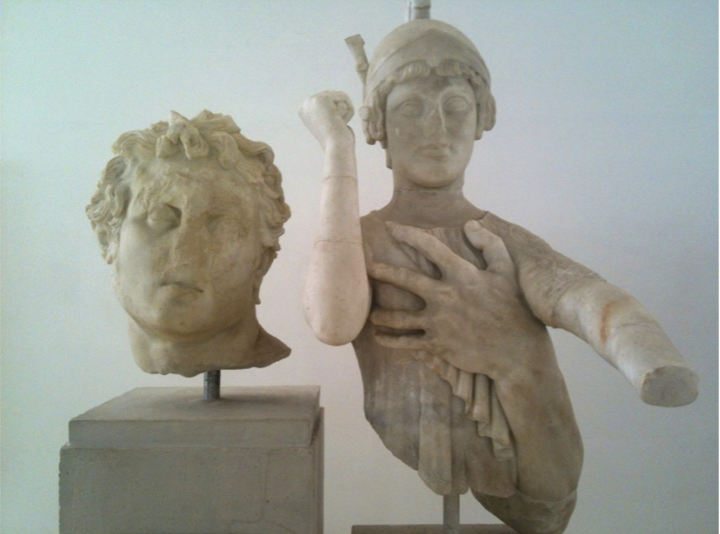

Identify and Analyze
Odysseus, grotto dining room of Tiberius, villa at Sperlonga
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Figure Held
Archaic - ish?
more like Julio-Claudian Classicism of the time
Troy - Odysseus steals Palladium - representation of Minerva
Even though Minerva loves Odysseus, you just stole her statue so now she’s gonna curse you
plus he killed Polyphemus, the son of Poseidon, so now you’re double whammied
Metaphor for parallel acts in Tiberius’ life?
returned the Palladium to the temple of Vesta
also rebuilt it after a devastating fire
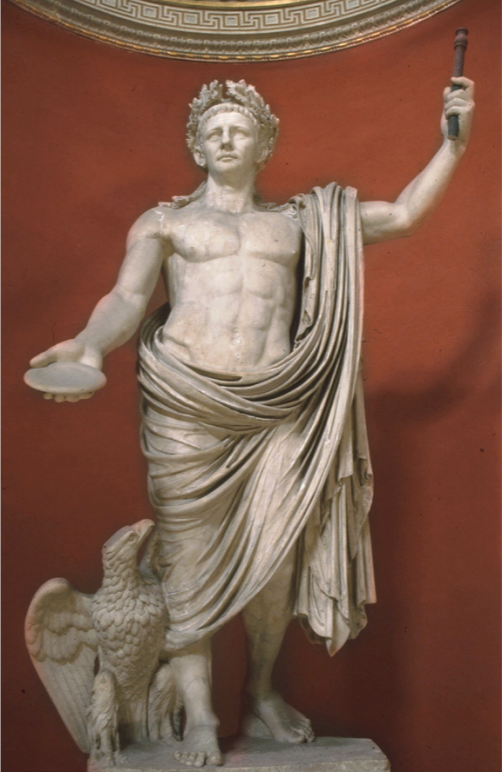

Identify and Analyze
Portrait of Claudius with attributes of Jupiter, Lanuvium, Italy
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Next Emperor
Caligula assassinated
hey maybe we should go back to the republic? last guy sucked
lots of panic
Praetorian Guard
almost exclusively from foreign mercenaries
bodyguard of the Roman emperors, formed by Augustus
guarded emperor, his palaces, and sometimes acted to remove or create emperors
knew they were out of a job with no heir from Caligula
found Tiberius Claudius Nero, Caligula’s uncle, hiding behind a curtain in the palace, fearing for his own assassination, and was then named emperor
Claudius
club foot - some birth defect that made him limp
facial twitch and stuttering - affected his speech
fairly bookish/nerdy
couldn’t serve in the military due to his leg
last person to be able to read/speak/write Etruscan
super into beast fights
didn’t like the blood of Gladiator fights
~50 years old when crowned
In Art
references to Julius + Old Republic
not to restart republic but because of his education
he had an appreciation
Verism + Idealism
Italic accents
because he’s older - showing his age
pronounced nasolabial grooves
creased forehead
bags under his eyes
later portraits - loose skin around his jaw and neck
Hellenistic ideal body
his own spin on previous emperors
Individual Traits
protruding ears
Late Republican Forms
Jupiter Attributes - Claudius acting as his representative
Eagle, laurels, staff of office, patera
portraying emperor/empire as having being given the divine right to rule forever by Jupiter
Claudius worshipped as a god during his lifetime in far provinces, deified after his death
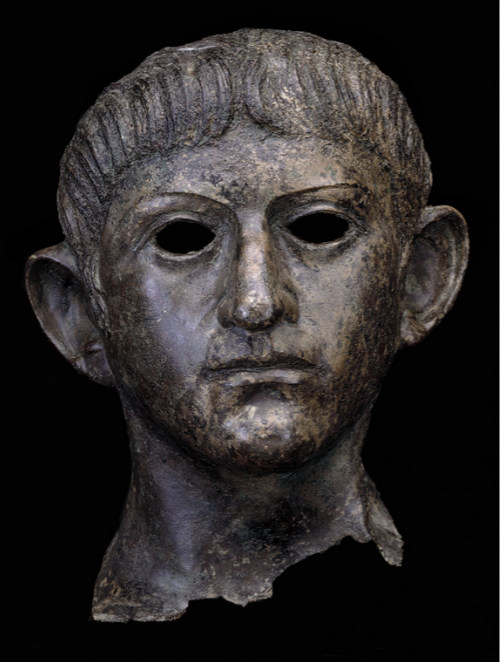

Identify and Analyze
Bronze head of Claudius, Rendham, Suffolk, perhaps originally from Colchester
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
England conquered under Claudius
mostly everywhere else of Europe was already conquered
Region Portrait Variation
Julio-Claudian classicism style
Protruding ears + Hair combined with smoother face

Identify and Analyze
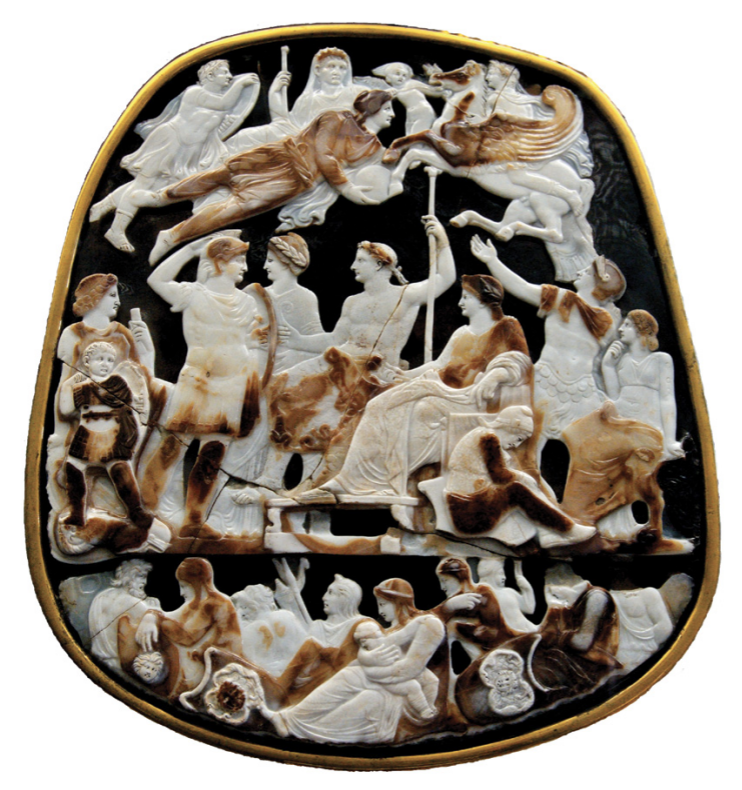
Grand Camée
The Julio-Claudian Period
14CE - 68 CE
bigger than Gemma Augustae
Name - ended up in a French museum
Bottom Register
defeated enemies - men, women, and children
Left - traditional Eastern/Northern barbarian style
Upper Register
who are all these people? - 2 debates
1. Tiberius, deceased, with Germanicus and Livia (Tiberius’ wife) or Roma
2. Claudius as Jupiter with wife, Agrippina, Nero as next Emperor
Nero is adopted son, Agrippina’s son from her previous marriage
Problem with Julio-Claudian Art - everyone looks the same
Claudius after Nero
has to pull out the whole dynasty thing
as he’s not apart of the direct line so he had to remind people how he was related
also wasn’t publicly selected by Caligula

Identify and Analyze
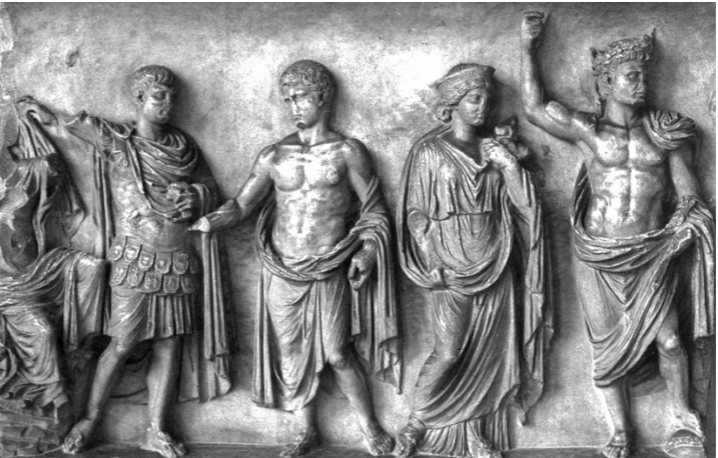
Relief of the Julio‐Claudian dynasty, Ravenna
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Almost entirely classical
contrapposto
Far Right
Augustus
corona civica - crown - head of empire
thunderbolt - power of jupiter
globe under foot - the entirety of the world (the far reaches of the Roman empire) under Rome’s rule
imperium sine fine
Middle Right
Livia
dressed like Venus Genetrix
founder of the dynasty
Middle Left
Julius Caesar - Divus Julius
small star in his hair - deified
shooting star that passed over during his funeral games
his soul ascending to be with the gods
Far Left
Drusus and Antonia
Claudius’ parents
All Together
all of our family/ the dynasty
Claudius associating himself with direct Julio-Claudian line
Julius - father of the house
Augustus/Livia - parents of the dynasty
Drusus/Antonia - parents of Claudius/current emperor
Representartion of holiness in figures from front
subtleness of body facing full forwards
becomes more standard from here on
Bare Feet - divinity/deified after death (maybe, debated)

Identify and Analyze
Relief from the Altar of the Vicomagistri, Rome
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Vicomagistri
magistri (priests) vico (neighbourhoods)
ministers in charge of the neighbourhood’s religious happenings to make sure they went right
worshipped at shrines erected at the boundaries of their districts, usually at significant crossroads
Sacrificial scene
bulls being led off
characters with veils
Non-Classical Elements
increase in front-ality in a couple figures on the left
different heights/levels of heads
people in behind are taller to be able to see their faces
Classical Elements
bodies and faces
Composition
breaks “Greek” rules with Italic composition

Identify and Analyze
Sebasteion at Aphrodisias, Turkey
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
major sculpting centre in Greece
marble mines nearby
Augustus labished all kinds of money into this
town was named after Venus (Aphrodite)
Sebastos - Greek name from Caesar
name for place meaning “Emperor’s/Caesar’s palace”
Probably built under Nero, but was started under Claudius
very famous picture of Claudius resides here
3 stories
all covered in reliefs
mostly mythological
also some of emperors

Identify and Analyze
Relief of Claudius conquering Britannia, Sebasteion at Aphrodisias
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Claudius
as a supreme Greek hero figure
we know it’s him because his name is written underneath
and facial features
in line with other myths on the building
cloak common in representations of Greek heroes
under his helmet - Julio-Claudian hair lobster claw
Britannia
personification of Britain
Greek pleading/begging for mercy
laying on ground with one hand in the air
Amazon
one breast exposed
word comes from “no breast”
myth that they mostly used bows so they would cut off one breast for better usage of it
Amazons being subdued by heroes
common depiction
Greek subduing enemies - Amazons were apparently enemies
Claudius’ conquer of England
metaphorical rape as a new variation of triumph imagery in Roman art

Identify and Analyze
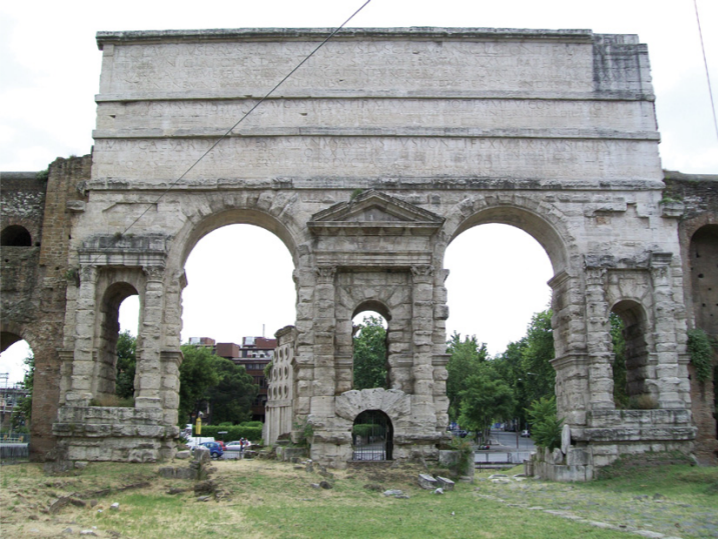
Porta Maggiore, Rome
The Julian-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
not much architectural things under Claudius
Beside Tomb of Breadmaker
Monumental gateway coming into the city
2 other purposes
1. superstructure on top
for aqueduct
2. city walls
for protection
made under Augsutus in 3rd century bce

Identify and Analyze
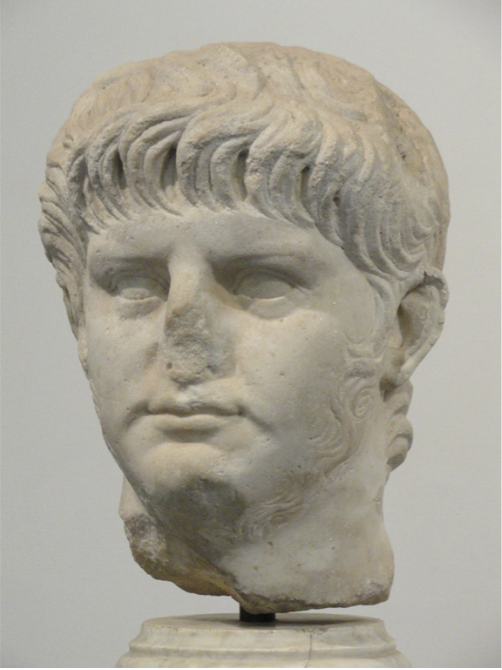
Portrait of Nero, Palatine Hill, Rome
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Next Emperor
adopted son of Tiberius, Agrippina’s son from her previous marriage
changed his name after adoption
became emperor at 17
Early Rule
good emperor
legislations, competent military
Civil servants/slaves
Seneca, Roman philosopher, Nero’s helper
Burrus, commander of the guard
later on, after Agrippina’s murder, they were all fired and everything went array
Artistry
thought of himself as an artist
competing in Olympics (came in all firsts)
music, arts, etc.
Famous Story of Nero
fiddling while Rome burned
thought that he may have started it in order to build himself a new palace
led to creation of volunteer firefighters/creating fire safety
Later Rule
lots of little revolts from officials
Nero was declared as a public enemy and commited suicide
Last Julio-Claudian Emperor
Individual Characteristics in Portraiture
mutton-chops/neck beard
emperors were meant to be clean shaven
represented with a huge neck
No Julio-Claudian Hair
instead - thick waves of hair and bangs that lie in parallel commas
may reflect his actual hairstyle as described in one of his biographies

Identify and Analyze
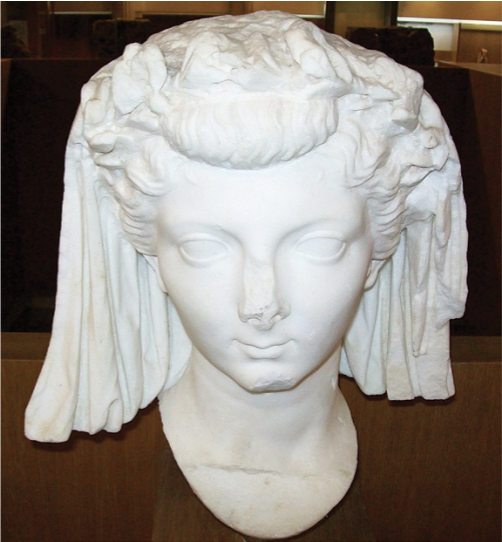
Portrait of Livia Augusta, mother of Tiberius, Paestum
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Rome as a patriarchy
not many representations of royal women outside of funeral contexts
Livia
Augustus’ wife
earliest imperial women granted public statues
Female Portraiture
meant to be face of female morality
seen not heard, no politics
maybe important in religion/household
always Classical
everyone looking the exact same - like Greek Goddesses
reflection of the ideology of imperial rule
Hair Vegetation
stylized grain
maybe in guise as Ceres, goddess of agriculture (Demeter)
establishing an imperial identity and bolstering regimes of her husband
elevates Livia above mortal women
Hair Veil
role as matron
wife of Augustus and mother of Tiberius

Identify and Analyze
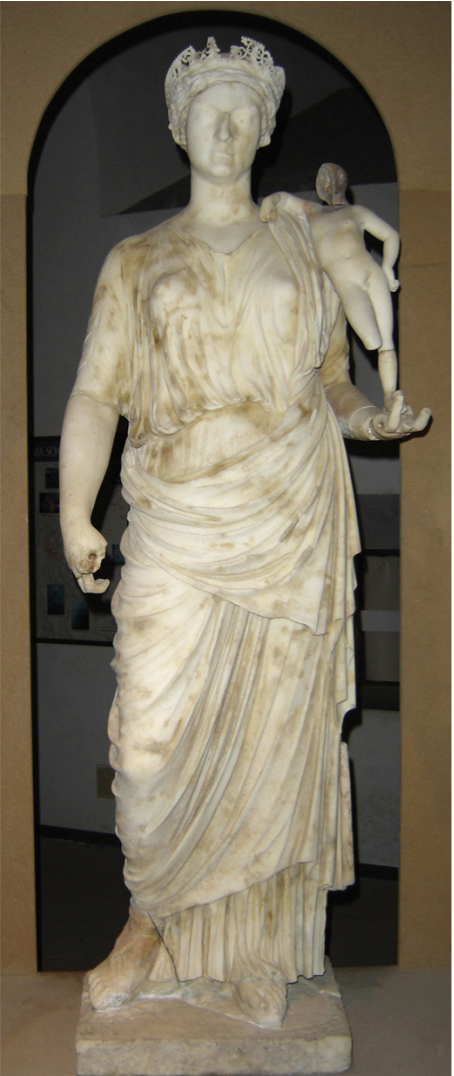
Antonia (Minor) Augusta, as Venus Genetrix statue, villa at Punta Epitaffio, Italy
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
“Minor” - younger, “Major” - older
Claudius’ mother
redirecting divine founder imagery from Livia to Antonia
Venus Genetrix
holding baby cupid
Antonia represented as head of household
consistency in use of divine imagery among Julio-Claudian imperial women
Crown idealized in Greek Classical

Identify and Analyze
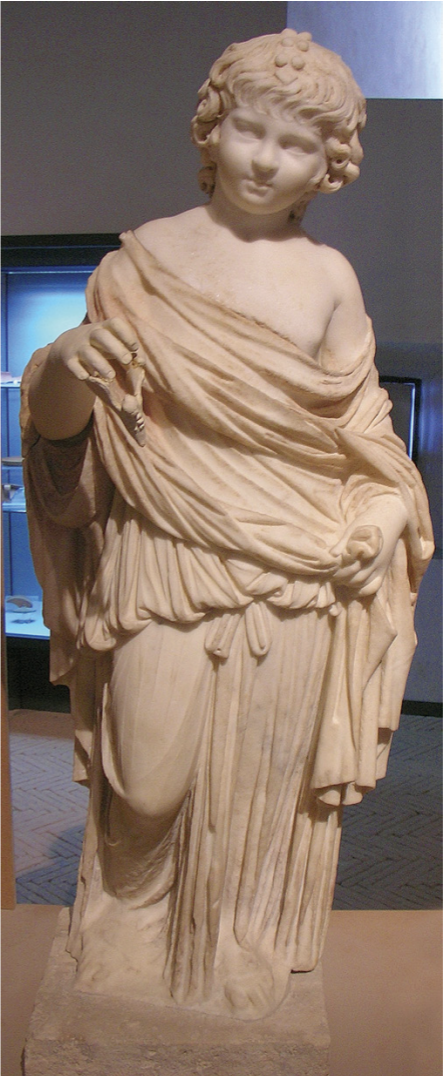
Claudia Augusta as Psyche statue, imperial villa at Punta Epitaffio, Italy
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
believed to be Claudia Augusta
Nero’s daughter who died at 3 years old
simply meant to represent a sense of a “young woman/girl”
body plump and pre-pubescent
Classical
clothes, face, hair, drapery, etc.
Right Hand - Butterfly
“Psyche” - Greek word for butterfly, also the same word for soul/spirit
Greek myth/famous poem of Psyche who fell in love with Eros/Cupid
was making its rounds/very popular at the time
representation of his daughter as Psyche
fulfulling that “innocent young love” as Psyche
Identify and Analyze
Plan of the Domus Transitoria, Rome
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
“Passageway Palace”
Nero famous for palace architecture
As an imperial palace, it was huge
mostly typical layout, just big
Original destroyed by fire
thought to be set by Nero so he could build a new palace for his magnificence as Roman Emperor
reported that when the new palace was finished, he stated “Now at last i can begin to live like a human being”
Post and Lintel Architecture
a building system with a horizontal feature (lintel) supported by two vertical features (posts or columns). to create open space such as rooms or doorways
utilized concrete to create barrel vaults
lifted the ceilings of rooms to allow more space and create windows to let in light
Interiors
designed with water features such as fountains and pools
added visual interest, light, and helped cool the rooms
decorated with cut marble floors
and wall paintings
large amounts of white backgrounds that emphasized the available light

Identify and Analyze
Ceiling painting from the Domus Transitoria, Rome
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
wall painting on a ceiling now
4th style Wall Paining
combination of all 3 styles
from 1st - faux imported stones, now relegated largely to the dado
from 2nd - illusion of space and architecture
from 3rd. - faux framed panel paintings
founded under Nero
more eclectic and complex
brighter colours
help emphasize the light coming in through the bigger windows
Identify and Analyze (two images)
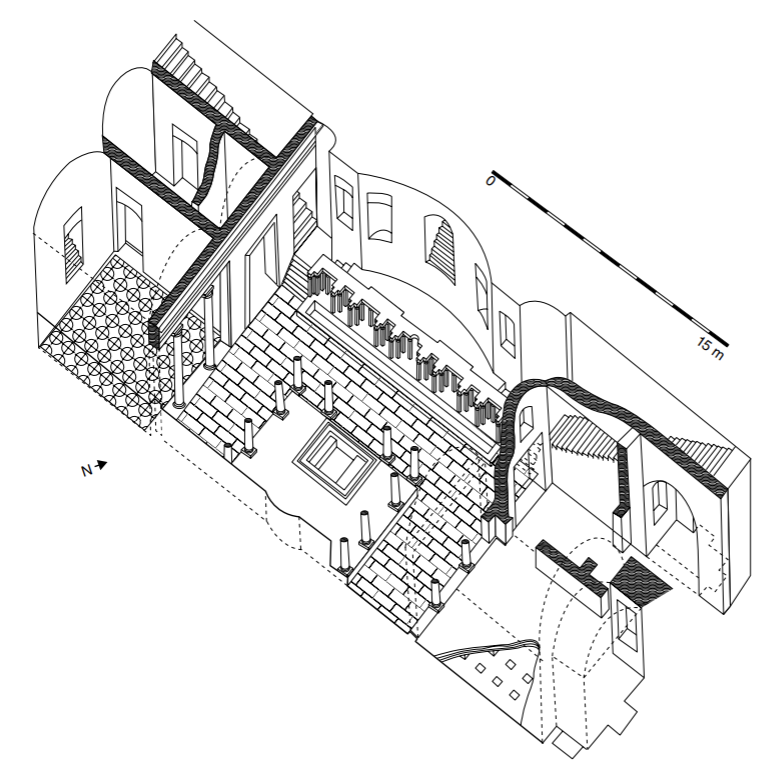
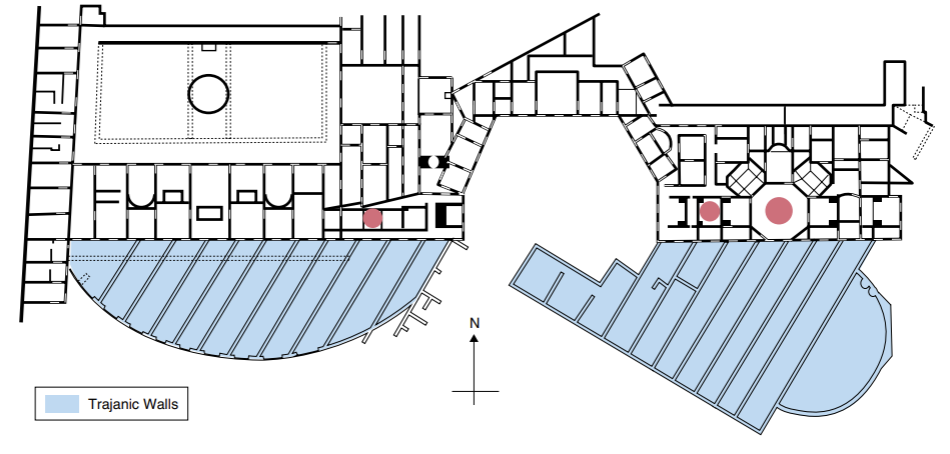
Plan and map, Domus Aurea, Rome
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
“Golden House”
overlooked Forum from atop Palatine Hill
covered around 300 acres
dominated four of the fourteen neighbours of Rome
front portico a mile long
many rooms with many different purposes
no more atriums
busier than previous architecture
first imperial building in Rome done entirely in concrete
most ambitious and innovative use of concrete yet
built after Domus Transitoria burnt down in the great fire of 64 CE
many believed that Nero set the fire as a desire to build a new palace for himself
upon completion he is reported to have said “Now at last I can begin to live like a human being”
Vaults
arches, but now done with concrete
create wooden form, pour concrete, let it dry, bada bing bada boom you’ve got a vault
Four Kinds - see vault deck for pictures/to practice
Barrel Vault
arches extended to create corridor
Groin Vault
4 way cross
top connects to create larger area
like a crossroads
Fenestrated Sequence of a Groin Vault
extended groin vault with a series of windows on top
Hemispherical dome
an arch, spun on 360 degree axis to create a dome

Identify and Analyze
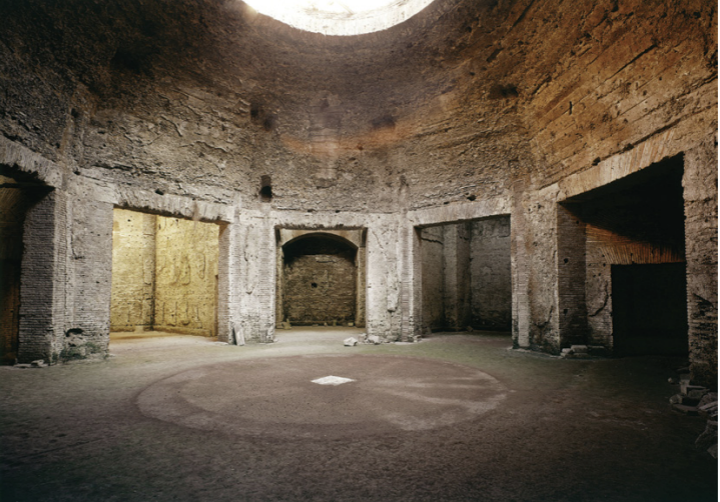
“Dining room” in the Domus Aurea, Rome
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Resembles a dome, but is not perfect
sits on an 8 sided wall to mimic a circular shape
poured concrete + faced brick to add to illusion
segmented dome
Oculus
“eye”
opening at top for light/air
Theatrics Inside
beneath dome ceiling, a secondary dome with a space between the two to hide things
trap doors could be opened to reveal things
rose petals to fall on guests, perfumes, etc.

Identify and Analyze
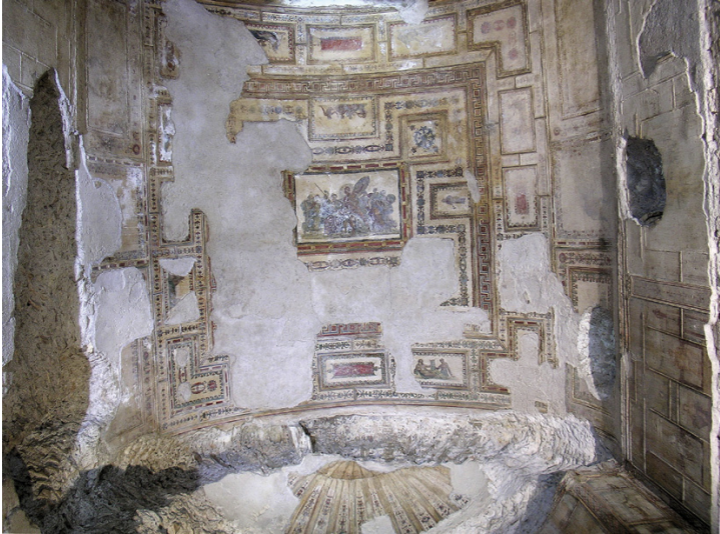
Ceiling painting of Achilles on Scyros, Room 119, Domus Aurea, Rome
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Achilles on Scyros myth
sent there by his mother to avoid being drafted into the war
an island of women, Achilles dressed up in disguise as a women
Odysseus went there, saw him and went “wow what a masucline man”
threw armour on the ground and while all the other women were disinterested, Achilles ran up thinking “wow how cool”
Odysseus said “ha gotcha you’re coming to fight for me now demi boy”
4th Style Wall Painting
like domus transitoria - subjects almost exclusively related to the Trojan War
Hellenistic Greek painting conventions
skin tones, dramatic diagonals, and atmospheric perspective
based on battle scenes

Identify and Analyze
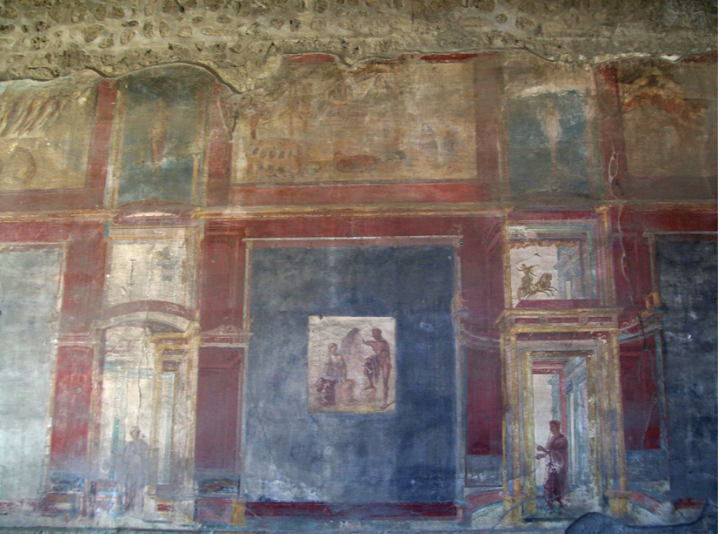
Painting of amphitheater riot, from house 1.3.23, Pompeii
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Historical paintings were rarely made
Famous Riot
59 CE at Pompeii in amphitheatre
gladiator fights
fans of opposing teams fight
any kind of spectacle had different teams for each town/city
Pompeii vs Nuceria (Their Rival City)
Fist fights, fires set off, etc

Identify and Analyze
Wall paintings of still life and mythological scene, macellum, Pompeii
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Macellum - “food market”
Northeast corner of the foru at Pompeii
Tripartite zones
both horizontal/vertical
Perspectival architecture
human figures
Upper zones
still life paintings
poultry, fish, bread, fruit, and flowers laid out no counters
echoes actual products available at stalls and shops in market
Centre
mythological panels
Odysseus and Penelope in one panel
Jupiter and Io with guardian Argus
Theme is possibly female virtue?
largely female audience doing their marketing would be confronted with the large panels
positive Penelope rewarded, negative Io is punished
Scaenae frons
creates illusonistic spaces

Identify and Analyze (two images)
Stucco wall treatment, Stabian Baths, Pompei
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
“Stabian” Baths - right besides gates leading to nearby city
organized around a palaestra
a large open area serving as an exercise ground
porticoes on three sides to provide shade (walking/lounging)
Stucco
architecturally moulded
no longer painted, now it’s 3D
4th style wall
Scaenae frons
creates illusonistic spaces
orignally painted with red black blue and yellow
reminiscent of the corridor at the Domus Aurea
Gods represented in some panels, recognizable
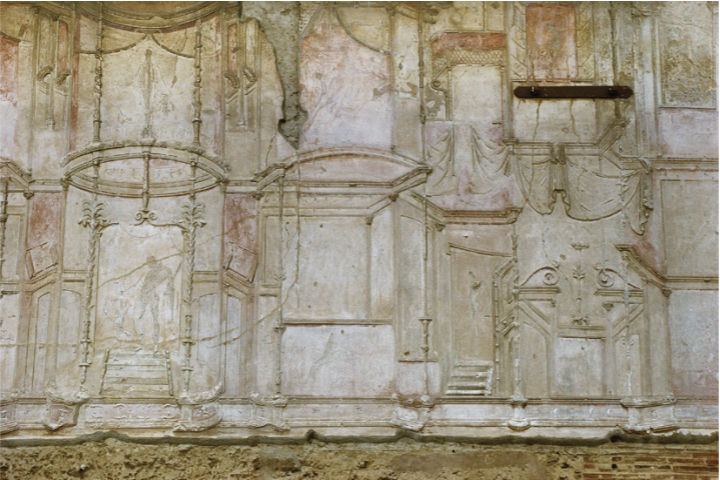


Identify and Analyze
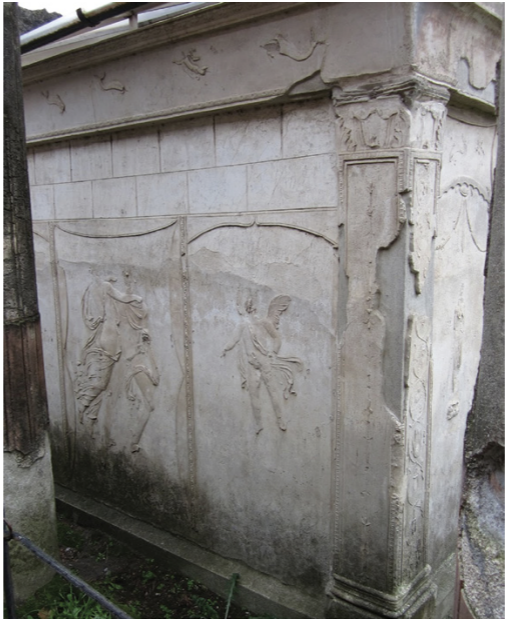
Sanctuary of Isis, Pompeii, exterior of baptistery
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
best preserved example of a cult site to foreign deity
After Augustus + Cleopatra
Egyptian craxe sweep throughout Rome
Cult of Isis
biggest import of this craze
Mystery Religion
related to eternal life
myth - Isis brings her husband Osiris back to life
Big 3 Mystery Religions at the Time
Isis. Vs Mythras Vs. Christianity
Isis most popular at the time
Aspects of Altar survive
Greco-Roman style
some imagery related directly to Isis
some relating to Dionysus and Ariadne
Dionysus myth of him deifying Ariadne after her death (maybe, double check)
there’s also a Maenad
Built in Brick
originally coated with stucco to creat image of a grander complex of cut stone masonry
Small southeast corner building
Arcuated Pediment
aka Syrian pediment
combines the standard triangular pediment with a semi circular arch which usually fills the centre of the pediment
Tank inside
believed to hold the Nile water
improtant to rites of Isis
believed to be a baptistery

Identify and Analyze
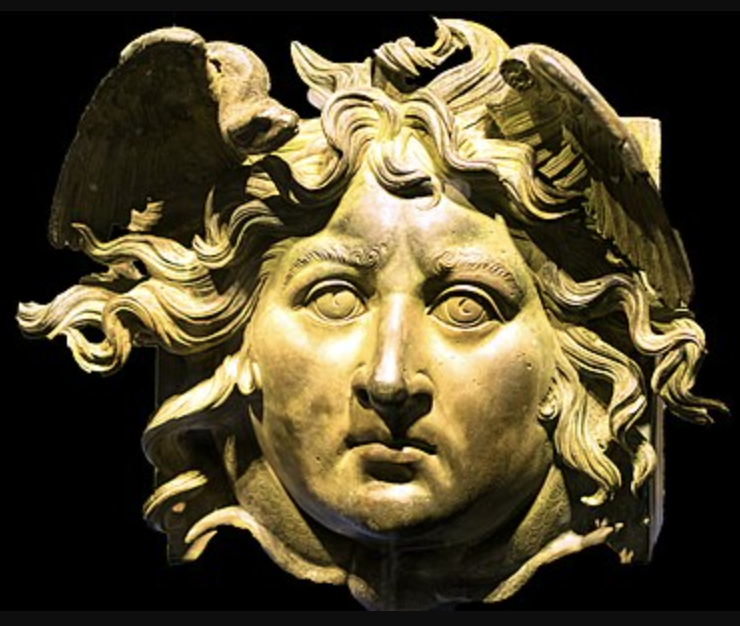
Medusa head from Caligula’s floating palace, Nemi, Italy
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
Floating Palace
aka Caligula’s pleasure boats
two shipwrecks found in Italy that are thought to be these
head from it
Apotropeic
Lost Wax Method of Bronze Casting
Medusa
snake hair is only a modern adaptation/way of thinking
in Antiquity - shown with flowing hair with wings inside

Identify and Analyze
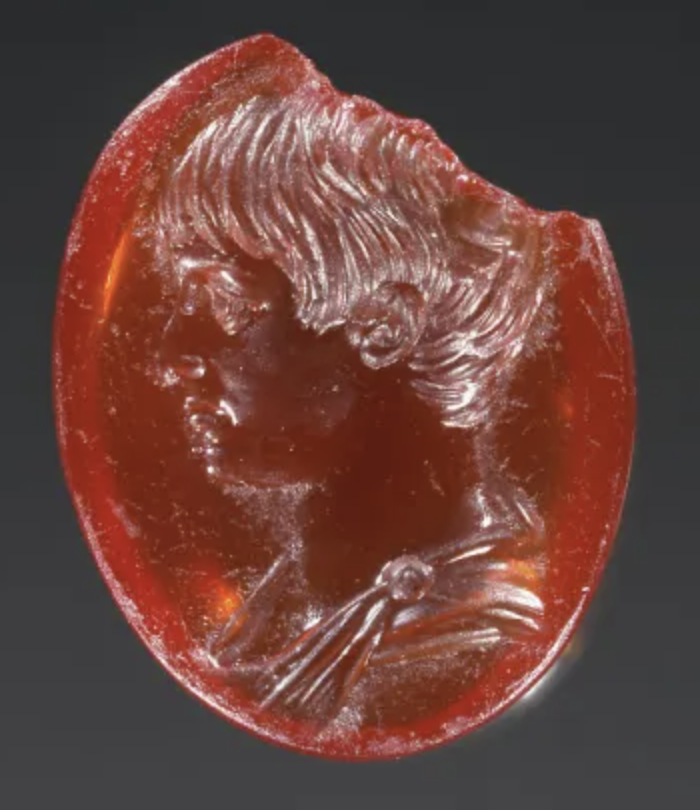
Engraved gem with profile portrait of Julio‐Claudian youth
The Julio-Claudian Period
14 CE - 68 CE
thought to be Caligula
mostly just some youth of the family
Identify and Analyze
Mosaic glass bowl