Science final definitions
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Motion
A change in position of all checked overtime
Vector quantity
A equality that involves both magnitude and direction
Scalar quantity
A quantity that involves only magnitude but not direction
Position
An objects location relative to a starting point. position is a vector quantity
Distance
The amount of space between all objects or points. Distance is a scaler quantity.
Displacement
The distance travelled relative to a starting point. Displacement is a vector quantity.
Uniform motion
An object that is moving in a specific direction at a constant speed
1. constant speed
2. constant direction
Non uniform motion
An object travels an unequal distance in asserted amount of time and or is changing direction
Delta
Means change in
Velocity
The displacement of an object over a certain amount of time
Acceleration
An object whose velocity is changing (whether it’s speed is increasing or decreasing, or direction is changing)
Weight
Is the force of gravity, pulling down on an object
Mass
The measure of the amount of weight in an object
Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist change in motion
Physical property
Characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured
Chemical property
How a substance reacts with other substances
Physical change
Change in a state without change in chemical components
Chemical change
Produces a new substance
Chemistry
The science in which substances are examined
Products
Substances that exist after reaction has occurred
Reactants
Substance that exists before reaction occurred
Exothermic
Chemical reaction in which energy is given to make product feel warmer
Endothermic
Chemical reaction in which energy is taken to make product feel colder
Period
Horizontal rows
Group/family
Vertical rows
Metals
Left of ladder
Non-metals
Right of ladder
Metaliods
Along the staircase
Atom
Small units that maintain its chemical properties
Proton
Positive charged atom
Neutron
No charge
Election
Negative charged atom
Ion
Charged atom
Cation
Atom with a positive charge
Ionic bond
When metals bond with non-metals
Polyatomic ion
Grouped atoms hold an ionic charge
Covalent bond
2 non-metals bond together
Isotope
Different form of the same element
Valance electrons
Election in the outer most shell
Multivalent ions
When ions formed have more than one possible charge
Alkali metals
In group one
Are malleable, soft, and can be cut easily
Alkaline earth metals
Somewhat reactive
Group 2
Halogens
Group 17
Very reactive, non-metals
Noble gases
Group 18
Gasses, colourless
Biodiversity
The diversity of living things
Invasive species
Species that expand their range and out compete when opportunity arises
Abiotic
Non living chemical and physical parts of an environment
Autotroph
Organisms that can make their own food from basic nutrients and sunlight
Photosynthesis
Process which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in sugar form
Carrying capacity
Size of a population that can be supported indefinitely by the resources of given ecosystem
Heterotroph
Organisms which east of feed off others
Food web
Food chains which interlock with each other to form a feeding relationship
Ecosystem
All the interacting parts of a biological community and it’s environment
Limiting factors
Factors that limit growth, distribution, or amount of population in an ecosystem
Weather
Physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific time and place
Biomagnification
Concentration of toxins increase as you move up a food chain
Sustainability
Earths services/resources in ways and at levels that can continue forever
Decomposition
The process where dead plants and animal material break down and are converted into simpler organic form
Biotic
Living components of an environment
Climate
How weather behaves over a long period of time
Exponential growth
The unrestricted growth of a population of organisms occurring when resources in habitat are unlimited
10% rule
When energy is passed from one trophic level to the next only ten percent of energy is passed on
Carnivores
Only eat meat
Herbivores
Only eats places
Omnivore
Eats both plants and meat
Primary consumer
Feeds on products and is the first to eat
Secondary consumer
Feeds on primary consumer and is second to eat
Tertiary consumer
Feeds on secondary and third to eat
Quaternary consumer
Feeds on tertiary and fourth to eat
Producer
Only organisms in an ecosystem that can make its own energy
Density independent factors
Fire, tornado, floods, earthquake, tsunami, hurricane
Density dependent factors
Food supply, water quality, space/shelter, territory, disease, sunlight
Sustainability
Ability to maintain or improve quality of life for current and future generations by balance
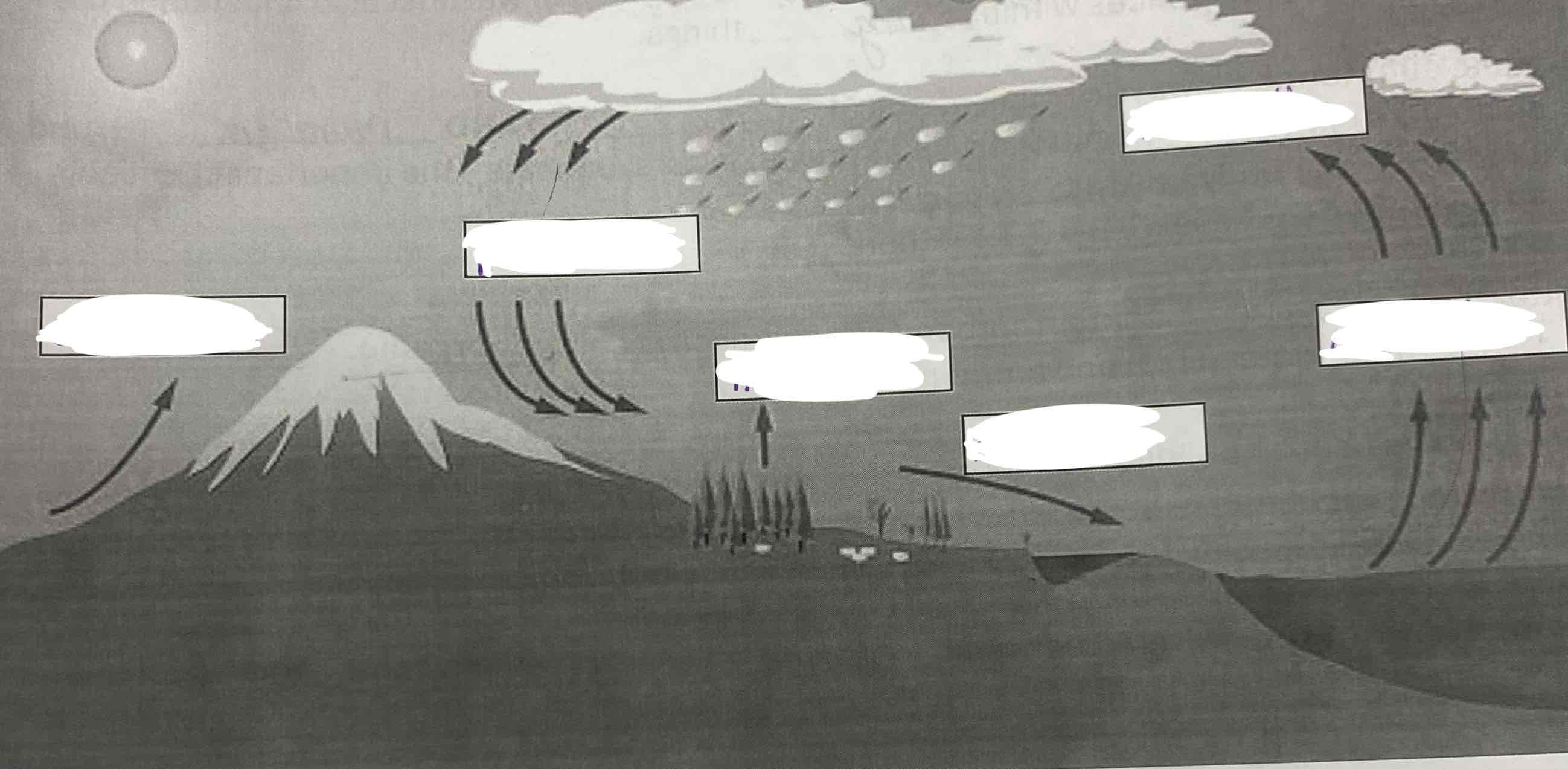

Condensation, evaporation, precipitation, transpiration, run off
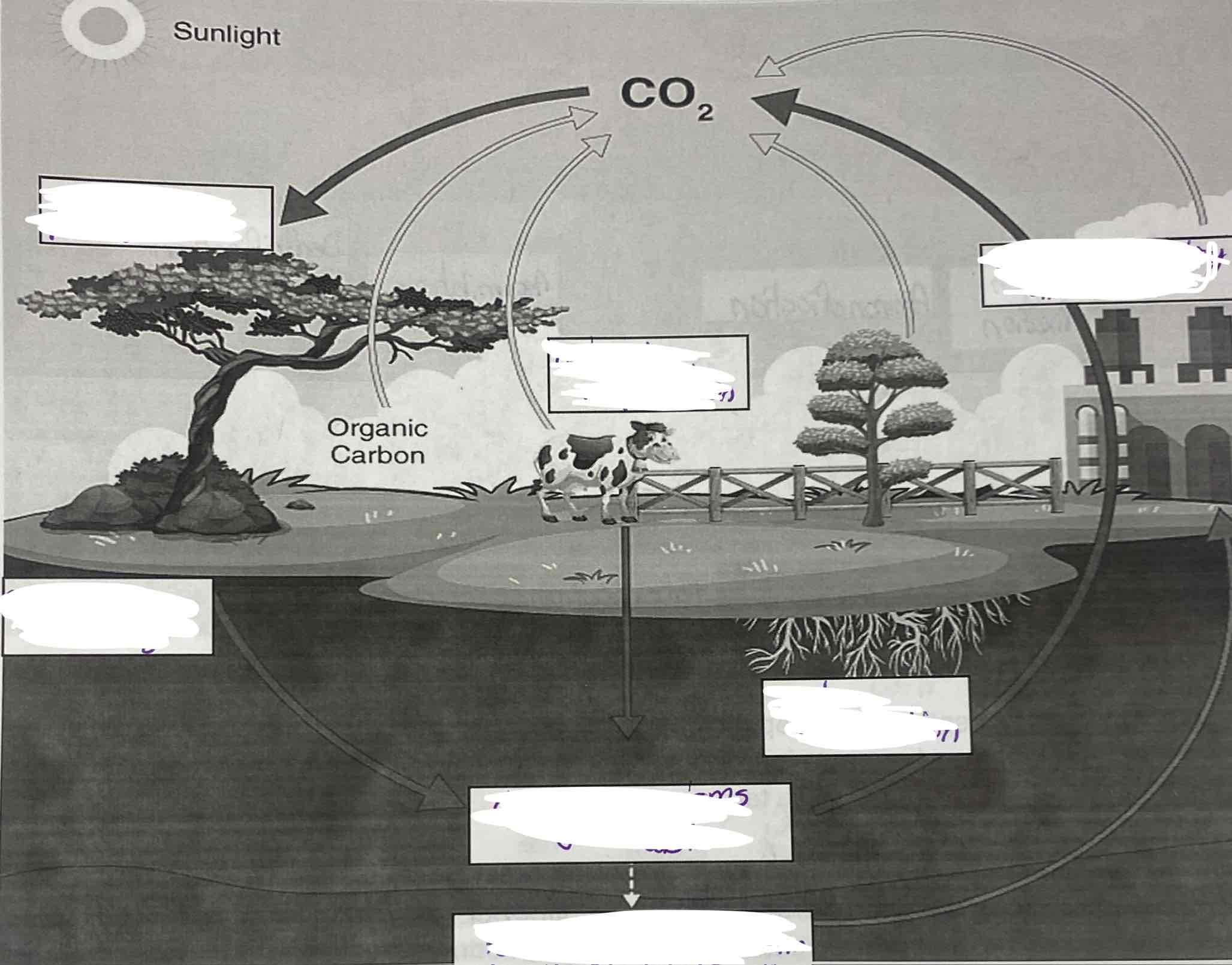
Photosynthesis, organisms decay, fossil fuels form, animal respiration, root restoration, dead organisms and waste, vehicle and factory emissions
Water cycle
One of the forms of matter that is continually recycled through biosphere
Carbon cycle
Cycles between all living things and non living things
Nitrogen cycle
Cycles between living and non living worlds. Used to make proteins and DNA
Phosphorus cycle
When rocks erode phosphite goes into waterways