Ecology Part 2 ( Cycles of Matter)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Biogeochemical Cycles
Matter can neither be created or destroyed
Cycle of transferring nutrients from the environment, to an organism, and back to the environment
Remember - Energy Pathways
Energy enters an ecosystem in the form of sunlight
Eventually all energy is lost as heat
Biosphere requires a continual flow of new energy
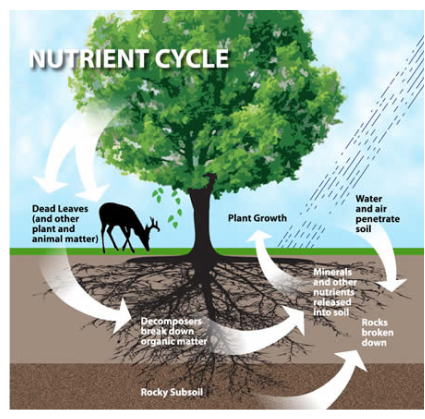
Nutrient Cycling
On Earth there is finite supply of nutrients
To maintain balance, matter is recycled
Main elements that are recycled: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
The Cycles
Hydrologic Cycle or Water Cycle
Carbon/Oxygen Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle
Phosphorus Cycle
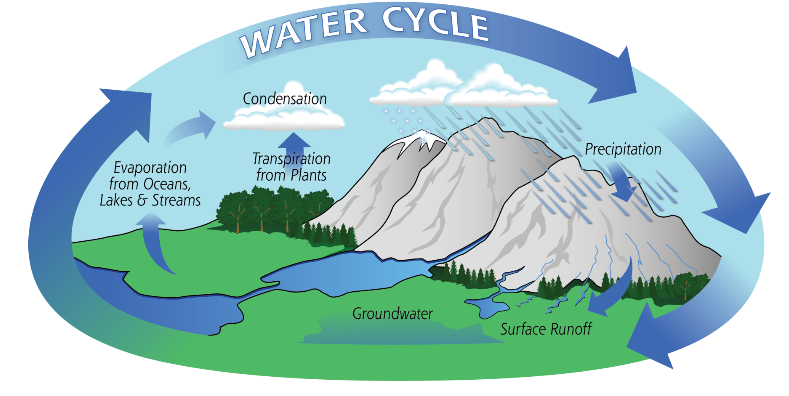
Hydrologic Cycle/Water Cycle
path of water through the environment
The Water Molecule
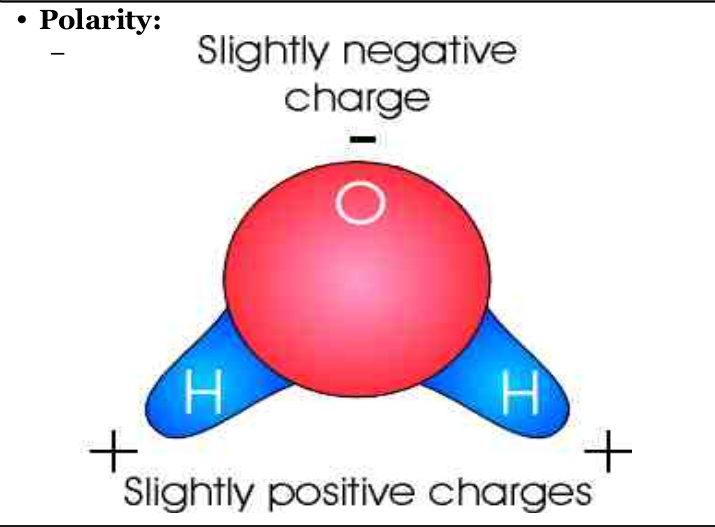
Polarity:
The attraction of water molecules. One end of the molecule is positive, and otherend is negative.
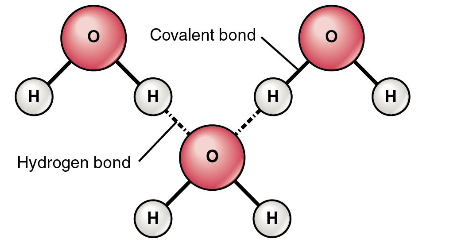
Polarity Results in Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen Bonding
Attraction between slightly negative O and slightly positive H
Hydrogen bonds require energy to break:
This is what allows water to gain and storelarge amounts of energy
This also gives water a high boiling and freezing points.
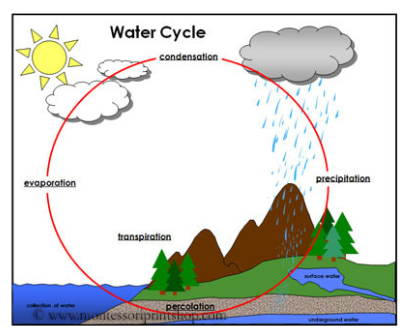
Hydrologic Cycle – Abiotic/Biotic Components
Abiotic: Precipitation, Groundwater, Evaporation, Condensation
Biotic: Cellular Respiration
The Cycling of Water
Moves from atmosphere to earth through precipitation. Surface runoff and groundwater flows to other bodies of water.
Water enters the atmosphere through transpiration and evaporation
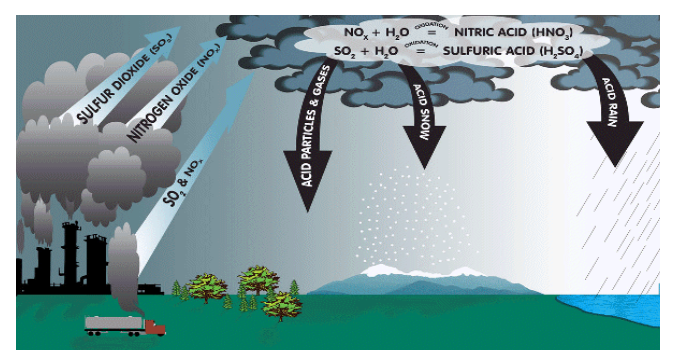
Acid Deposition
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides can condense with water vapor in the air to form tiny droplets of acid.
This is called acid rain.
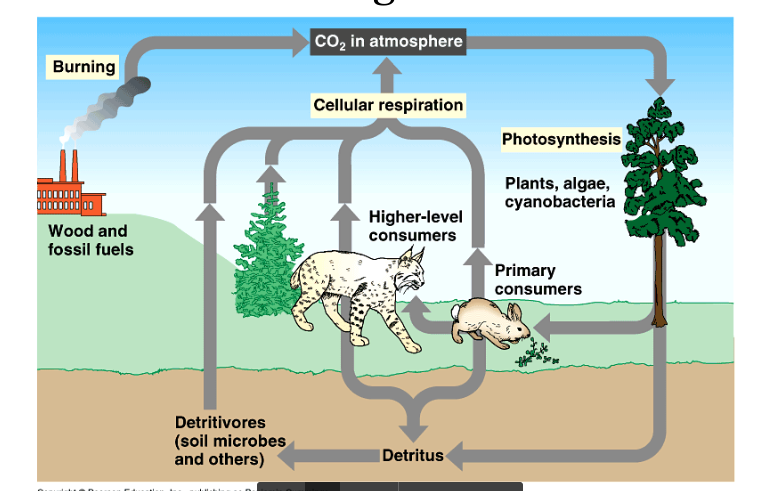
Carbon/Oxygen Cycle
The flow of CO2 through the biosphere.
The main part of this cycle involves the relation between respiration and photosynthesis.
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
CO2 in the atmosphere traps heat where it is re-emitted to the ground.
Other greenhouse gasses:
Water vapour (H2O)
Methane (CH4)
Nitrous oxides
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) ,
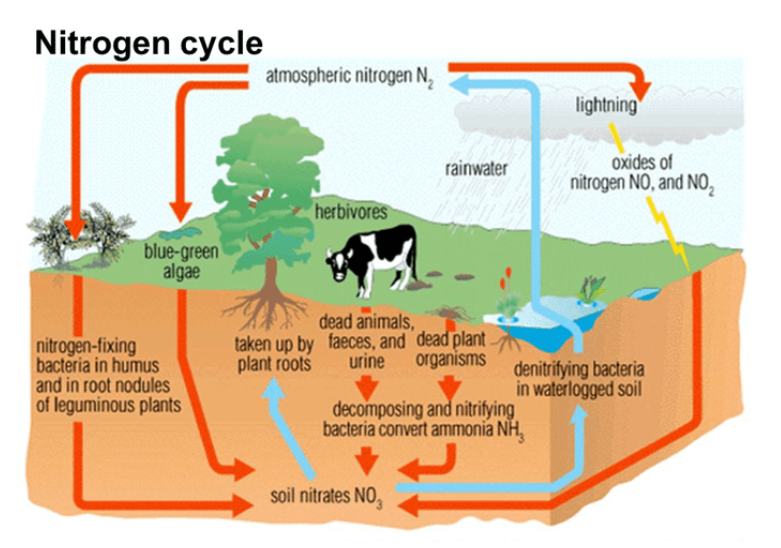
Nitrogen Cycle
The complex cycling of nitrogen between organisms and the environment.
Nitrogen in the atmosphere is N2 gas. Organisms need nitrogen in the form of nitrates or nitrites to grow.
Nitrogen Use
There are 2 main ways atmospheric nitrogen can be converted into useful forms.
Lightning: Lightning can force nitrogen and oxygen together to form nitrates then plants turn it into proteins
Legumes: Legumes have nitrogen fixing nodules on their roots that can convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates. Called Nitrogen Fixation or nitrification.
Ammonification
After an organism dies, it decays. Decaying matter which contains nitrogen produces ammonia. Ammonia will degrade into nitrites then will turn into nitrates then those will re enter the cycle

Denitrification
Some bacteria convert the nitrates back into atmospheric nitrogen.
Denitrifying bacteria. NO3- 🡪 NO2- 🡪 N2
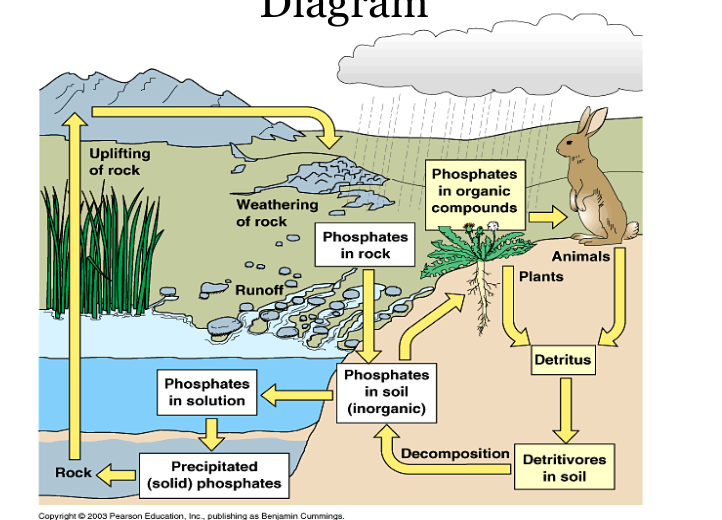
Phosphorous Cycle
Phosphorus is a nutrient required by all living things.
Long term cycle: Phosphorous in rocks dissolved in water and carried from land to the ocean then turned into sediments that may be thrusted upwards once again to form new land
Short term cycle: phospahates in water enter food chain through plants. Plants are eaten by animals. Decomposition of dead organisms put phosphates back into the soil