NCM 103: Vital Signs
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Vital Signs
Important signs of our bodies wherein we can tell that there is something wrong, if it is not c/in normal range
Blood Pressure
The force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) with two values: systolic (when the heart beats) and diastolic (when the heart rests).
Arterial Blood Pressure
A measure of the pressure exerted by the blood as it flows through the arteries
Systolic Pressure
The pressure of the blood vessels as a result of the contraction of the ventricle
Diastolic Pressure
When the ventricles are at rest; present at all times c/in the arteries
Pulse Pressure
Difference bet. systolic and diastolic pressure
Mean Arterial Pressure
Equivalent to 2/3 DP + 1/3 SP
70 - 110 mmHg
Normal range of mean arterial pressure
Less blood is pumped (lower cardiac output); decreased BP
Weak pumping action indicates
More blood is pumped (higher cardiac output); increased BP
Strong pumping action indicates
Peripheral Vascular Resistance
The resistance in the blood vessels that the heart must overcome to push blood through the circulatory system.
Capacity of arterioles and capillaries
Compliance of the arteries
Viscosity of the blood
Factors of Peripheral Vascular Resistance
Blood Volume
The total amount of blood circulating in the body at a given time. It is crucial for maintaining blood pressure and delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
Decreased BP
Decreased blood volume is to…
Increased BP
Increased blood volume is to…
Increased BP
Highly viscous blood causes
age
exercise
stress
race
sex
medications
obesity
diurnal variations
hypertension
hypotension
Factors affecting BP
Normal
Elevated
Hypertension stage 1
Hypertension stage 2
Classifications of BP
SP = <120; DP = <80
Normal BP
SP = 120-129; DP = <80
Elevated BP
SP = 130-139; DP = 80-89
Hypertension stage 1
SP = >140; DP = >90
Hypertension stage 2
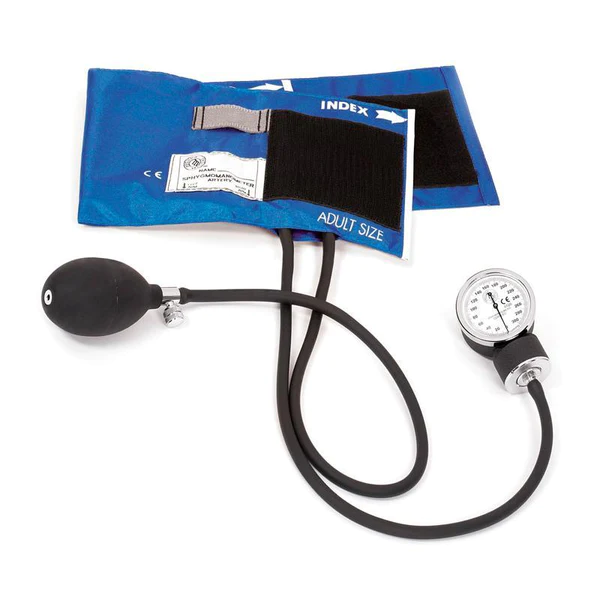
Inflation bulb
Air release valve
Pressure cuff
Index Marking
Aneroid Manometer
Artery position indicator label
Tube connectors
Parts of a sphygmomanometer
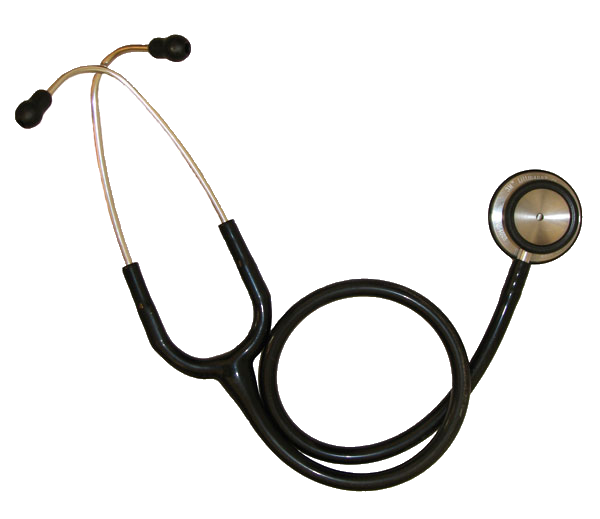
Binaural
tubing
Eartips
Binaural spring
Diaphragm
Bell
Drum
Parts of a stethoscope
BP reading will be artificially elevated
Blood Pressure Cuff is too small means
BP reading will be too low
Blood pressure cuff is too large
Upper arm (brachial artery)
Forearm (radial artery)
Thigh (popliteal artery)
Lower leg (posterior tibial artery)
Blood Pressure assessment sites
Auscultatory Gap
Temporary disappearance of sounds normally heard over the brachial artery when cuff pressure is high followed by reappearance of the sounds at a lower level
Instruct patient to avoid coffee, smoking, or any other unprescribed drug with sympathetic activity on the day of measurement
ensure equipment is intact and functioning
Remember the following for accuracy in readings
Sitting position
Arm and back are supported
Feet should be resting firmly on the floor
Feet not dangling
Position of patient when taking BP
Body Temperature
Reflects the balance between the heat produced and the heat lost from the body
Core Temperature
Temperature of the deep tissues; remains constant
Surface Temperature
Temperature of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and fat; rises and falls in response to the environment
basal metabolic rate
muscle activity
thyroxine output
epinephrine, norepinephrine, and sympathetic ns simulation
fever
Factor's affecting body heat production
Radiation
Conduction
Convection
Evaporation
Heat is lost through…
Conduction
Transfer of heat with contact to two other objects with lower temperature
Radiation
Transfer of heat without contact between two objects
Convection
Transfer of heat by air currents
Evaporation
Continuous vaporization of moisture from the respiratory tract and from the mucosa of teh mouth and from the skin
sensors in the periphery and core
integrators in the hypothalamus
effector system that adjusts the production and loss of heat
Factors regulating Body temperature
age
diurnal variation
exercise
hormones
stress
environment
Factors affecting body temperature
Pyrexia
Body temperature above normal
Hyperpyrexia
When temperature is over 41 deg C
Pulse
Palpable bounding of blood flow in the peripheral artery
Peripheral Pulse
Pulses away from the heart
Apical Pulse
Central pulse; heartbeat
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood pumped into the arteries by the heart and equal the result of the stroke volume times the heart rate per minutes
age
sex
exercise
fever
medications
stress
position
pathology
Factors affecting pulse rate
130 (80-190)
Newborn pulse average
120 (80-140)
1 y/o pulse average
100 (75-120)
5-8 y/o pulse average
70 (50-90)
10 y/o pulse average
75 (50-90)
Teen pulse average
80 (60-100)
Adult pulse average
70 (60-100)
Older adult pulse average
temporal
carotid
apical
brachial
radial
femoral
posterior tibial
dorsalis pedis
Pulse sites
Tachycardia
Excessively fast heart rate
Bradycardia
Less than 60bpm in adults
Costal Breathing
Aka thoracic beathing; involves external intercostals and other accessory muscles; observed by chest movement
Diaphragmatic Breathing
Aka abdominal breathing; involves the contraction of the diaphragm; observed by movement of abdomen
Eupnea
Normal breathing
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath; difficulty breathing
Bradypnea
Abnormally slow respirations
Tachypnea
Abnormally fast respirations
Apnea
Absence of breathing
exercise
stress
environment
medications
pathology
Factors affecting respiration
Hyperventilation
Very deep rapid respirations
Hypoventilation
Very shallow rapid respirations
Respiratory rhythm
Refers to the regularity of expirations and inspirations
FALSE
True or False, inform your pt, that you will be taking their RR
Biot’s Respiration
Respirations that are abnormally shallow for 2 or 3 breaths; followed by an irregular period of apnea
Cheyne-stokes breathing
Rate and depth are irregular; characterized by periods of apnea and hyperventilation
Stridor
Stertor
Wheeze
Bubbling
Breath sounds
Intercostal retraction
Substernal retraction
Suprasternal retraction
Chest Movements
Pulse Oximeter
Noninvasive device that estimates a client’s bood oxygen saturation by means of a sensor attached to the client’s finger, toe, nose, earlobe, or forehead
Hypoxemia
Low O2 Sat.
95% - 100%
Normal range of O2 Sat
90%
Level at which O2 Sat should be evaluated
70%
Level at which O2 Sat is lfe threatening
2 light emitting diodes (LEDS)
Photodetector placed directly opposite to the LEDs
Parts of an oximeter
hemoglobin
circulation
activity
carbon monoxide poisoning
disease
virulence
communicable disease
pathogenicity
opportunistic pathogen
Factors affecting o2 saturation