Vasculature of the Brain
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
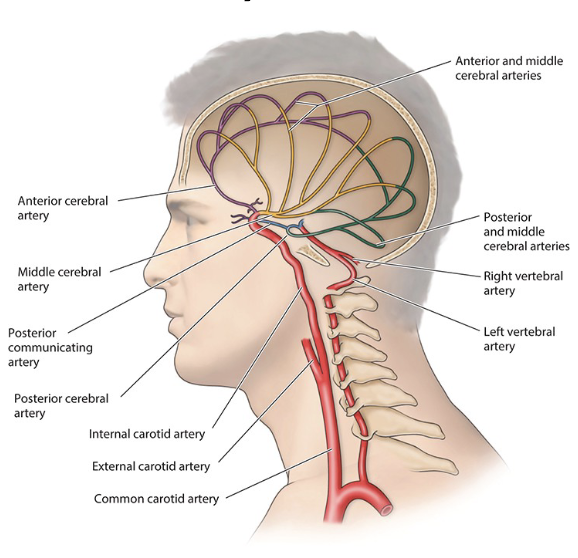
Why Brain Blood Supply Matters
• The brain represents only 2% of body weight but consumes about 20% of the body's energy, primarily in the form of oxygen and glucose.
• Proper blood supply is critical to prevent neurological deficits, ischemia, or stroke
Overview of Presentation:
• - Major arteries (ICA and vertebrobasilar systems)
• - Circle of Willis
• - Clinical significance (stroke, TIAs, etc.)
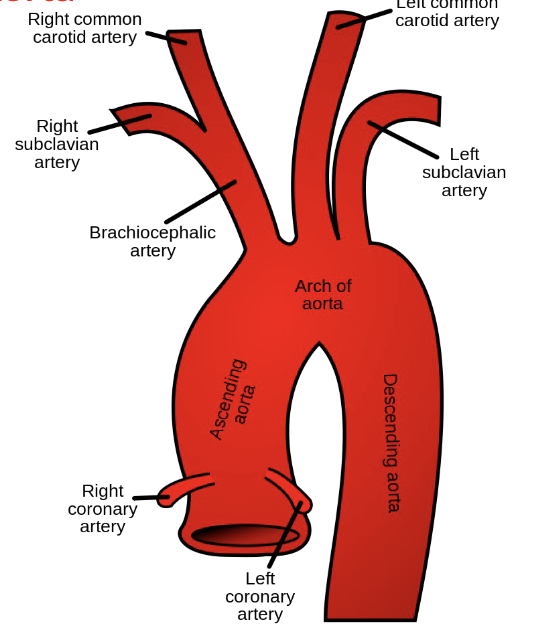
Systemic Circuit: Branches of the Aorta
L & R coronary arteries
Brachiocephalic trunk
left common carotid artery
left subclavian artery
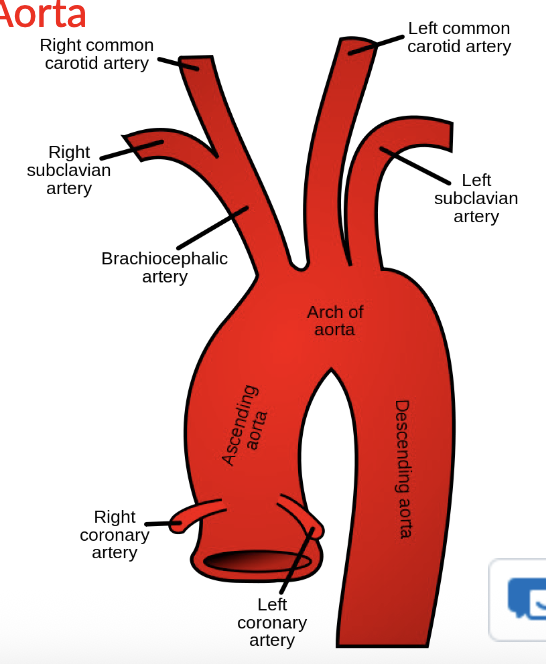
what comes off of Brachiocephalic trunk?
right subclavian artery
to right arm
right common carotid artery
to right side of head and brain
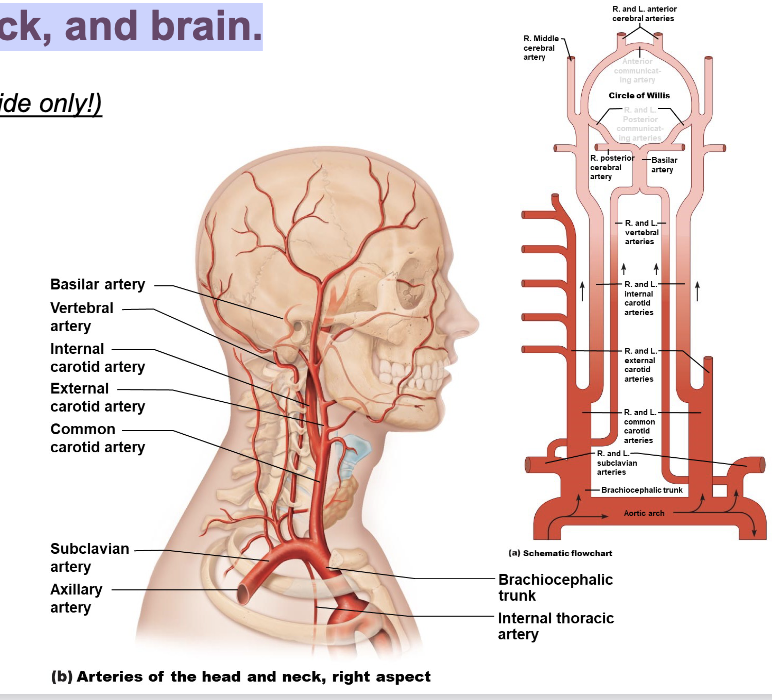
Arteries of the head, neck, and brain
aortic arch
brachiocephalic artery (right side only)
left common carotid
subclavian
what is apart of internal carotid (comes off L & R common carotid)?
middle cerebral
circle of willis
anterior cerebral artery
what comes of subclavian?
vertebral
basilar
posterior cerebral artries
circle of willis
what is Carotid System (Anterior Circulation) origin?
common carotid arteries
what is main branches Carotid System (Anterior Circulation)?
Internal Carotid Arteries (ICA)
what is the origin of Vertebrobasilar System (Posterior Circulation) ?
Vertebral arteries
• which merge to form the Basilar artery
what is supplies of Vertebrobasilar System (Posterior Circulation)?
Brainstem, cerebellum, occipital lobes
what is the course of the ICA?
Travels through the carotid canal in the skull, entering the brain to supply anterior circulation
what are key branches internal carotid artery system?
• Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA): Medial surfaces of the frontal and parietal lobes.
• Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA): Largest branch, lateral surfaces of the brain
where is the anterior cerebral artery (ACA)?
Medial surfaces of the frontal and parietal lobes
where is Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)?
Largest branch, lateral surfaces of the brain
what are other branches internal carotid artery system?
anterior choroidal artery
posterior communicating artery
what are the arteries for the Vertebrobasilar System (Posterior Circulation)?
vertebral arteries
basilar artery
branches
posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)
where does the vertebral arteries originate?
from the subclavian arteries
where does the vertebral arteries ascend?
ascend through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae
what forms the basilar artery?
Formed by the union of the two vertebral arteries.
what does the basilar artery supply?
Supplies the brainstem and cerebellum.
what are the branches of the Vertebrobasilar System (Posterior Circulation)?
posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) P1-P5
anterior Inferior Cerebellar artery (AICA)
Superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
Posterior Cerebral arteries (PCA)
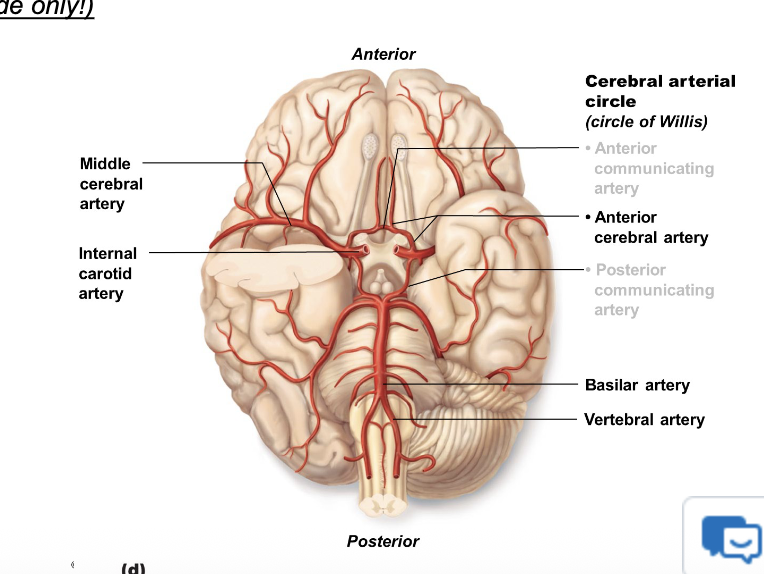
the circle of willis definition
A circular network of arteries\ located at the base of the brain, linking the anterior and posterior circulations.
what is the importance of the circle of willis?
provides collateral circulation in case of arterial blockage
anterior components of the circle of willis
The Anterior Cerebral Artery and Posterior Communicating arteries branch off the Internal Carotid Artery
R&L Anterior Cerebral Arteries (ACA):
Anterior Communicating Artery (AComm)
connects the two ACAs
what is the posterior components of the circle of willis ?
R&L Posterior Cerebral Arteries (PCA): Arise from the basilar artery
Posterior Communicating Arteries (PComm)
connect the ICA to the PCA
Mapping Cerebral Arteries to Brain Lobes:
anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
Middle cerebral Artery (MCA)
posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
where is anterior cerebral artery (ACA) located?
Medial frontal and parietal lobes.
where is the middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Lateral frontal, temporal, parietal, and parts of the occipital lobes.
where is the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) located?
Occipital lobes, posterior temporal lobes, brainstem
what is course and anatomy of anterior cerebral artery (ACA)?
Travels along the longitudinal fissure, supplying the medial surfaces of the frontal and parietal lobes
what are the areas supplied by superficial cortical branches?
frontal lobe
medial motor cortex (contralateral lower limbs)
medial somatosensory cortex (contralateral lower limb sensation)
what is part of frontal lobe?
prefrontal cortex (decision-making, personality)
olfactory cortex (smell)
Areas Supplied by Deep Branches:
basal ganglia
hypothalamus
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) course and anatomy
Largest Cerebral Artery:
Extends laterally, running through the Sylvian fissure
Example of Deep Branch = Lenticostriate
Areas Supplied by Superficial Cortical Branches in the middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Lateral surfaces of the frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital lobes and Insula
primary motor and sensory areas for the face, arm, and trunk
Expressive (Broca’s) and Receptive (Wernicke’s) Aphasia
what is the clinical note for MCA?
MCA is the artery most often involved in ischemic strokes.
Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) course and anatomy
• Arises from the basilar artery
• supplies posterior regions of the brain
what areas does the PCA supply?
occipital lobes
hippocampus
midbrain
thalamus
what is the occipital lobe?
Visual deficits, e.g. Hemianopia
Calcarine Artery supplies Primary Visual Area
Parieto-occipital Artery supplies Sup. Occip. and Post. Parietal lobes
Visual Attention
what is hippocmapus?
in posterior & inferior temporal lobes
memory loss
where is the midbrain?
cerebral peduncles (CST & CBT)
what is the thalamus?
contralateral sensory loss
what is the clinical note for PCA?
Occlusion of the PCA can result in visual deficits (e.g., hemianopia).
Small branches off the ICA supplyblood locally to
some deep brain areas and cranial nerves
what are the Small branches off the ICA supplyblood locally to some deep brain areas and cranial nerves:
Internal Capsule
CNs II, III, IV, V1 and V2
• Motor Eye
• Sensory face + vision
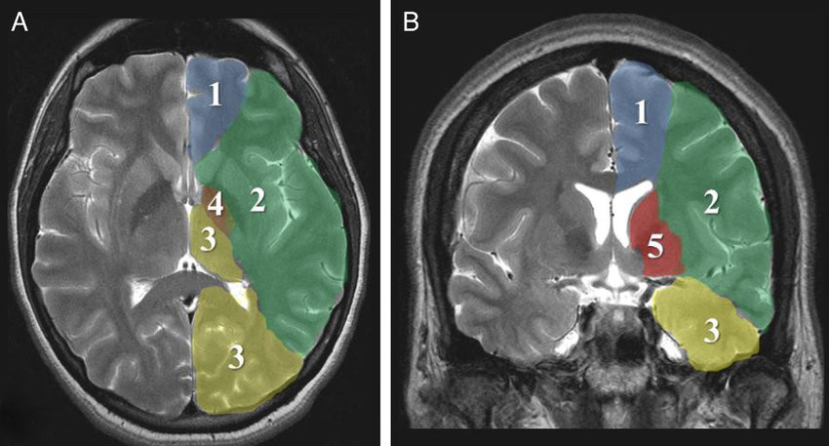
Supply areas of the cerebral arteries. A: axial slice; B: coronal slice. (1) Anterior cerebral artery, (2) middle cerebral artery, (3) posterior cerebral artery, (4) anterior choroidal artery, (5) lenticulostriate arteries.
what Branches off the ICA?
anterior choroidal artery
posterior communicating artery
what does the anterior choroidal artery supply?
internal capsule
basal ganglia
optic tract
what does the internal capsule control?
sensory and motor deficits
what is the basal ganglia also supplied by?
Also supplied by deep branches of the ACA and MCA
what does the PCA supply?
hypothalamus
optic chiasm
what is the Branches off the Basilar Artery?
posterior inferior cerebellar
pontine
superior cerebellar
posterior communicating artery
what are the Branches off the Vertebral/Basilar Artery
posterior inferior cerebellar (P1)
anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA)
pontine
superior cerebellar
posterior spinal arteries
anterior spinal artery
spinal arteries
also connected to the systemic circulation
what is the posterior inferior cerebellar (P1) ?
Off the vertebral artery
Supplies lower cerebellum
Lateral Caudal Medulla
Motor & Cardiovascular problems
Dizzy, Headache, Vomiting, Balance
Wallenberg Syndrome
Horner’s Syndrome
what are symptoms of posterior inferior cerebellar (P1)?
dizzy, headache, vomiting, balance
what syndromes are associated with posterior inferior cerebellar (P1)?
wallenberg syndrome
horner’s syndrome
what is anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA)?
• Posterior & Lateral Pons
• Lateral Pontine Syndrome:
• Vestibular Nuclei – dizziness
• Cochlear Nucleus – deafness
• Trigeminal Nucleus – sensory face & motor mastication
what is lateral pontine syndrome?
Vestibular Nuclei – dizziness
Cochlear Nucleus – deafness
Trigeminal Nucleus – sensory face & motor mastication
what is pontine?
anterior pons
what does superior cerebellar supply?
supplies upper cerebellum
ataxia, balance, dizziness
what are the posterior spinal arteries?
posterior medulla
cun. + grac. Nuclei
dorsal SPC
dorsal columns
what are the anterior spinal artery?
anterior medulla
pyramidal decussation
anterior SPC
motor deficits
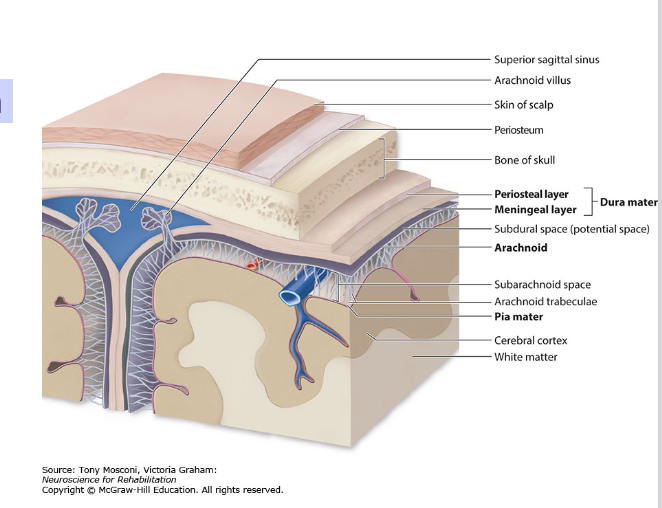
what is part of venous drainage?
superficial venous drainage
deep venous drainage
all eventually exits through internal jugular vein
what is superfiical venous drainage ?
• The superficial veins of the brain drain the cortex and empty into dural venous sinuses, particularly the superior sagittal sinus.
• Other major sinuses include the transverse sinus and sigmoid sinus
what is deep venous drainage?
Drain structures within the brain, such as the basal ganglia and the thalamus
what are major structures of the deep venous drainage?
• great cerebral vein (of Galen)
• straight sinus
• inferior sagittal sinus
what is blood brain barrier?
• Highly selective permeability barrier that separates circulating blood from the brain's extracellular fluid
• It protects the brain from harmful substances but also complicates drug delivery to the CNS
what are components of the blood brain barrier?
Tight junctions between endothelial cells restrict passage of substances.
Astrocyte foot processes surround the capillaries, contributing to the barrier’s strength.
Only small, lipid-soluble molecules, and certain transportable substances can pass through
what is circumventricular organs (CVOs) for the blood brain barrier ?
Eight brain structures that lack a blood-brain barrier and are located near the midline, associated with the ventricular system
These organs detect blood-borne compounds or secrete neurosecretory products into the blood to regulate the internal environment
what is an example of CVOs?
Area postrema triggers vomiting in response to blood-borne chemicals
what is Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
fills the ventricles and subarachnoid space, bathing the brain's external surface
what is CSF production?
Produced by choroid plexus
Removed through Arachnoid Villi
Protrusions into the dural sinuses
Approximately 500 mL per day; excess fluid is eliminated through venous drainage in dural sinuses
what does the choroid plexus produce?
CSF production
what removes CSF production?
arachnoid villi
what is functions of Ventricular System & CSF?
buoyancy
excretion
chemical communication
what is buoyancy?
Cushions the brain, reducing pressure on delicate tissues and protecting against physical shocks
what is excretion?
Removes waste and regulates the CNS chemical environment since the brain lacks a lymphatic system.
CSF aids in waste and excess neurotransmitter removal via the blood–CSF barrier in the choroid plexus
what is chemical communication?
CSF allows neurochemicals released by neurons to spread and influence adjacent neural tissue
what are the 2 types of stroke?
ischemic stroke
hemorrhagic stroke
what causes ischemic stroke?
Caused by a blockage (e.g., thrombus or embolism)
• MCA, ACA, PCA & Basilar
what causes Hemorrhagic stroke?
Caused by bleeding (e.g., aneurysm rupture or trauma)
• Circle of Willis and Deep Arteries
Importance of Understanding Arteries:
• Each artery supplies specific brain areas
• Symptoms vary based on the affected artery
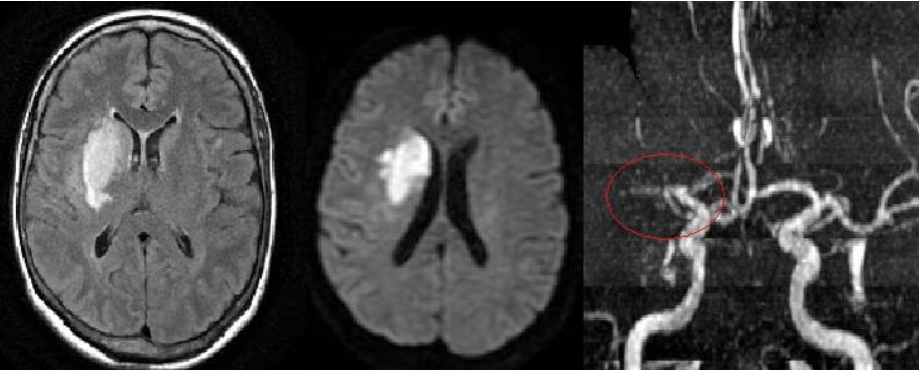
Basal Ganglia Stroke
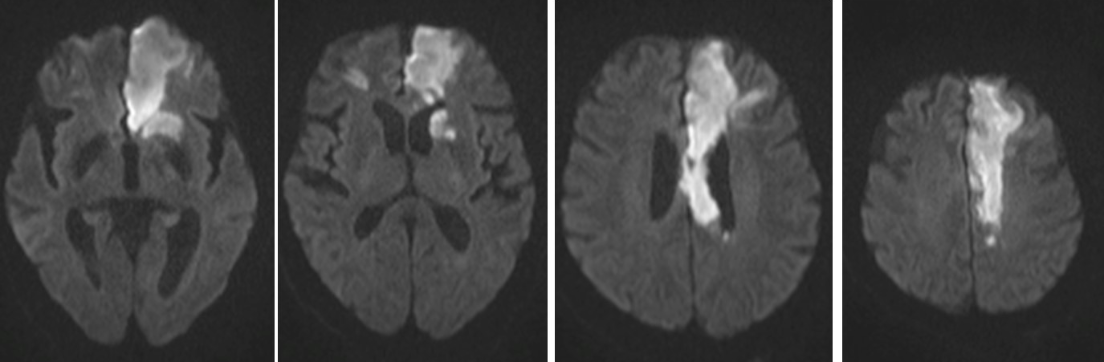
ACA Stroke
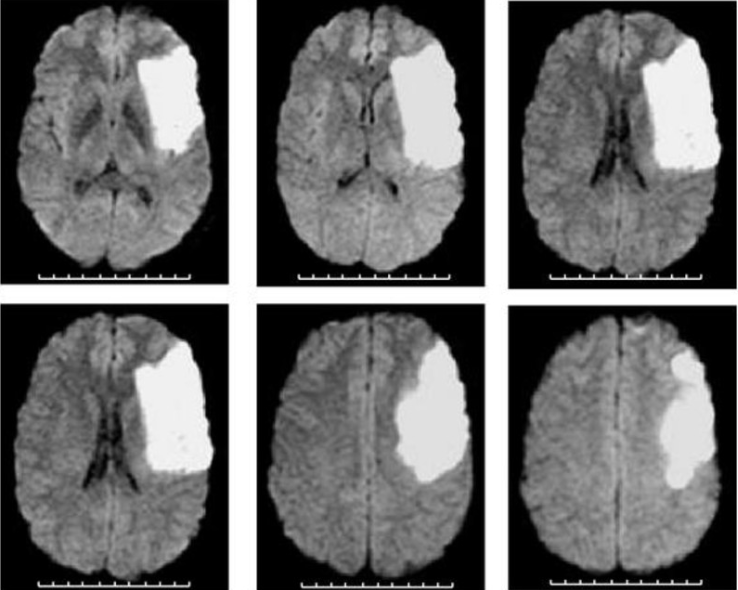
MCA Stroke
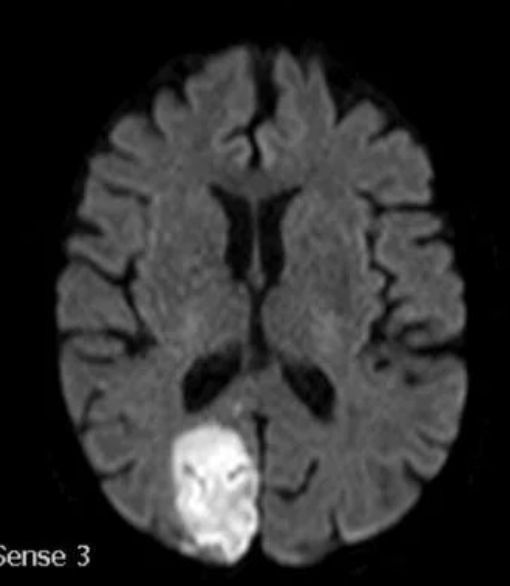
PCA Stroke
• Different strokes affect distinct brain areas depending on the artery involved.
• Early recognition of symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
• Understanding the arteries helps predict outcomes and guide treatment.
Conclusion