PoB2 Week7 C13 History of Life and Paleobiology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Earth history
Earth formed ~4,550,000,000 years ago 4550 Mya 4.55 Bya 4550 Ma 4.55 Ga The age of the earth is ~4,550,000,000 years
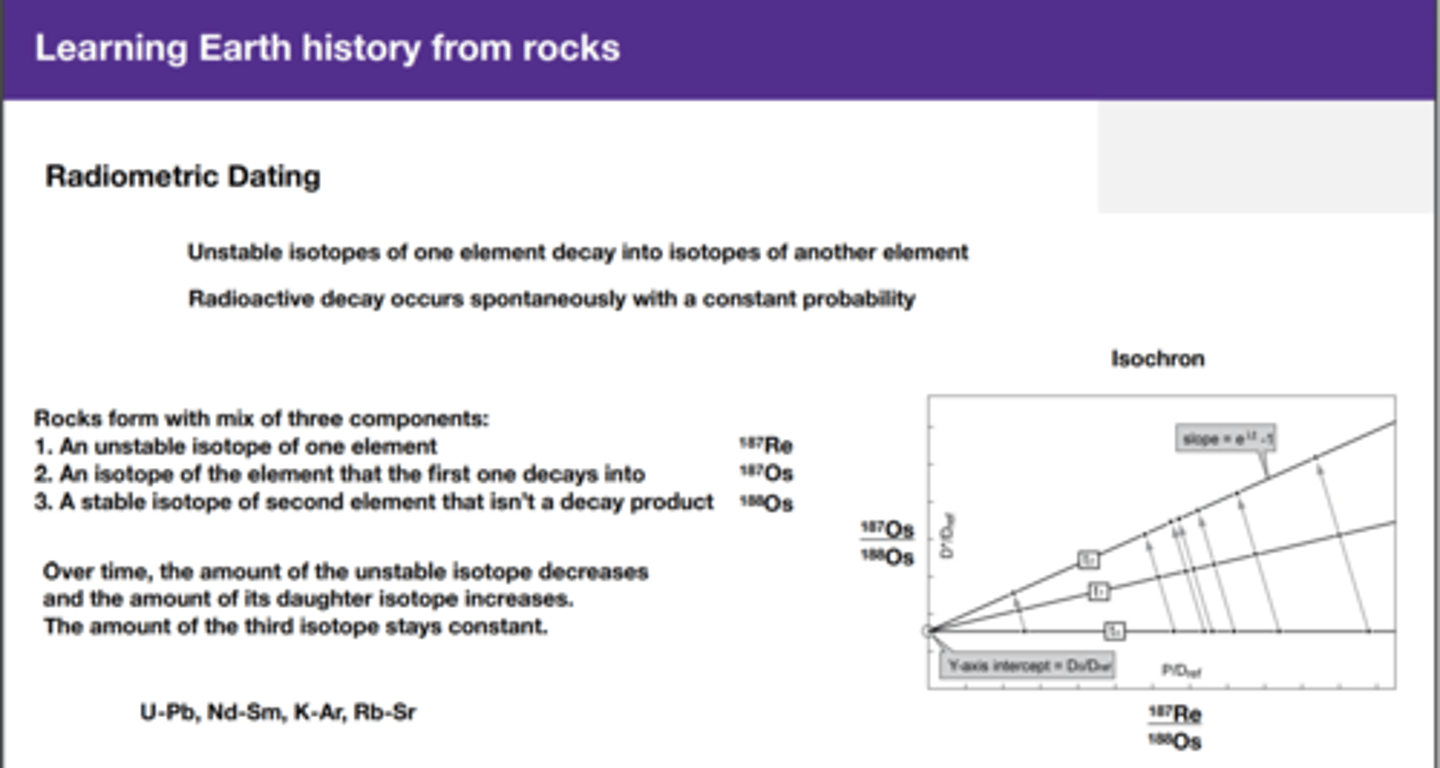
Radiometric Dating
Unstable isotopes of one element decay into isotopes of another element Radioactive decay occurs spontaneously with a constant probability
Rocks form with mix of three components: 1. An unstable isotope of one element 2. An isotope of the element that the first one decays into 3. A stable isotope of second element that isn't a decay product
Over time, the amount of the unstable isotope decreases and the amount of its daughter isotope increases. The amount of the third isotope stays constant.
U-Pb, Nd-Sm, K-Ar, Rb-Sr
The origins of life
Primordial Soup:
Organic molecules form readily from inorganic precursors
Nitrogen, CO2, methane, ammonia, hydrogen (lightening) => Amino acids, sugars, nitrogenous bases
Polymer synthesis on surfaces
Spontaneous formation of lipid vesicles
RNA World
Proteins, DNA
Microbial mats and Stromatolites
3500 Mya
Microbial mats: very thick biofilms
-built by phototrophic and/ or chemolithotrophic bacteria
Stromatolites: Oldest known fossils formed from many layers of bacteria and sediment.
The Oxygen Revolution
2400 Mya
the accumulation of oxygen released by cyanobacteria beginning 2.6 billion years ago
oxygen precipitates iron out of the ocean
Fossil Evidence of Eukaryotes
1800 Mya
The Cryogenian Period
geologic period (850-630 million years ago) characterized by a very cold global climate
Snowball Earth
Glacial dropstone in tropical marine sediments
The Ediacaran
time period on the geological time scale when complex life forms were developing
Abundant, globally distributed macroscopic organisms
The Ediacaran Biota: Kimberella
Maybe some evidence for familiar animal lineages
The Phanerozoic
visible life
541 Ma ago to present
The Cambrian explosion of animal diversity
Why leave more fossils:
- Hard Parts
- Predation
- Mobility
Animals diversified much earlier but left little record in the rocks: - molecular clocks - chemical biomarkers
Biostratigraphy
a relative dating technique based on the regular changes seen in evolving groups of animals as well as the presence or absence of particular species
index fossil: a fossil known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found
Pollen and Spores for land;
unicellular eukaryotes with shells diatoms, radiolarians, coccolithophores for ocean animals
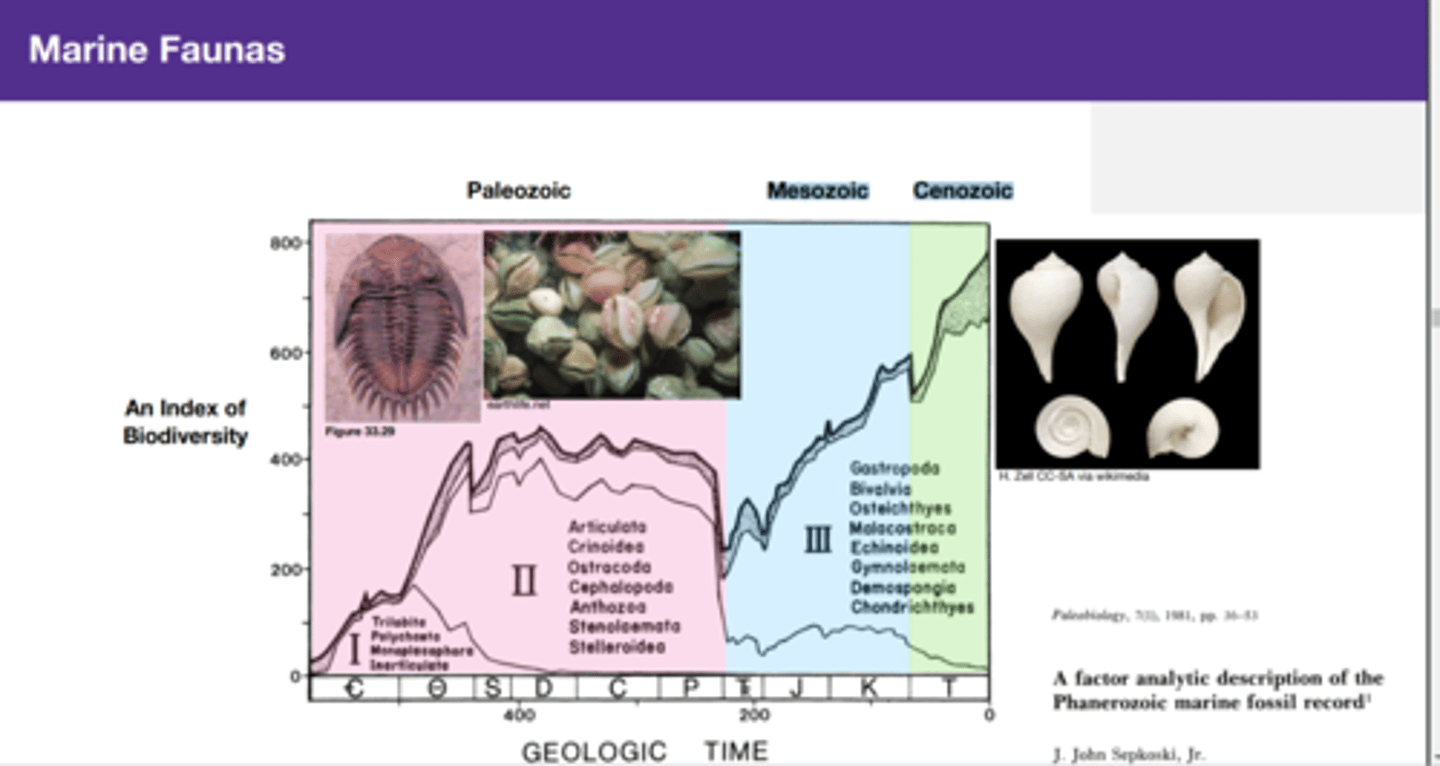
Marine Faunas
Three stages: biodiversity changes mark the different stages
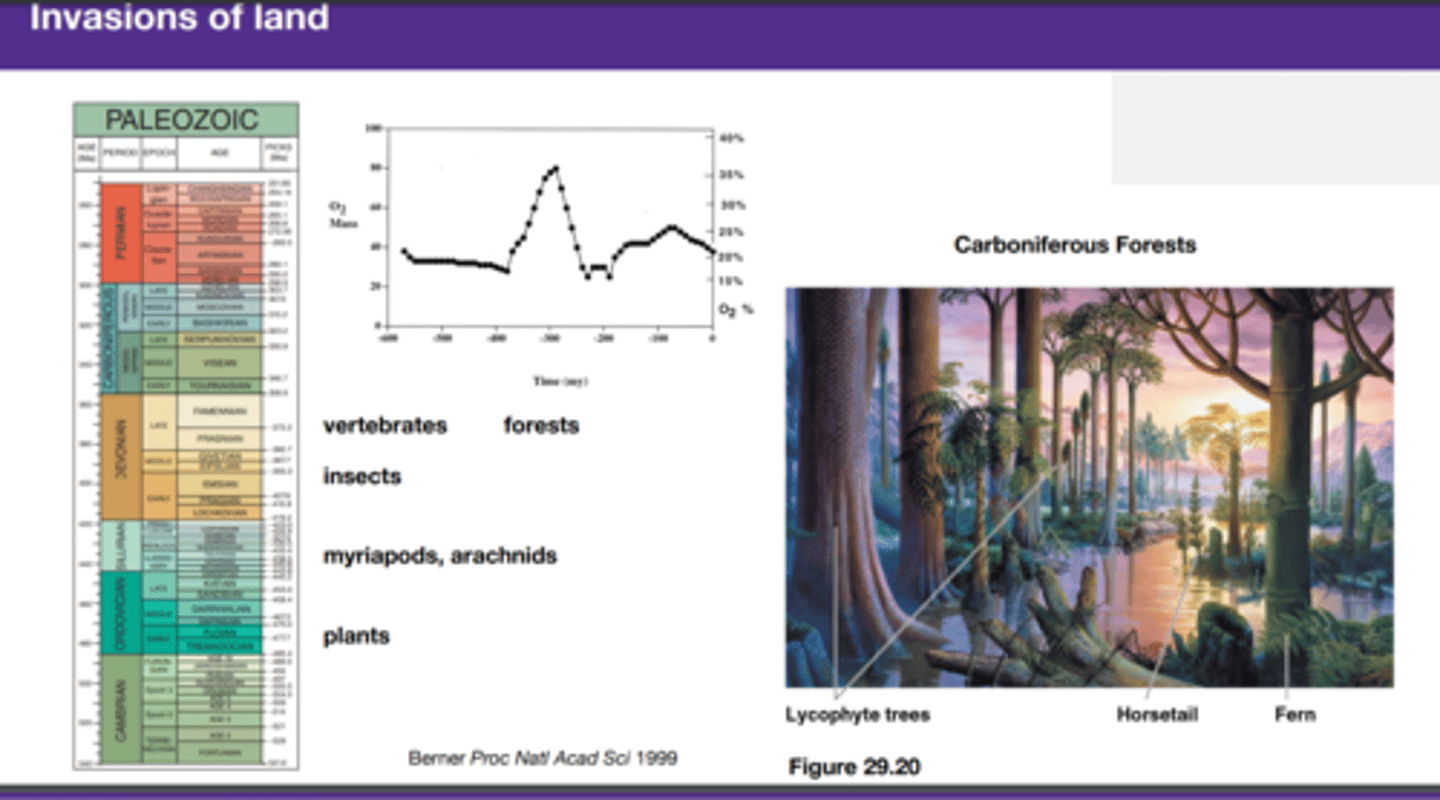
Invasions of land
PALEOZOIC
O2 up, CO2 down;
Cannot break down died forest
Mesozoic
Age of reptiles; flowering plants
Cenozoic Era
Age of mammals
MESSINIAN salinity crisis: The Mediterranean dried up
The great American interchange:
The biotic event triggered by the docking of North and South America in the Pliocene
The last glacial period: All of Canada was covered with ice 18,000 years ago (except for Northern Yukon). Lower sea levels at that time exposed the Bering land bridge
Radioactive decay fuels
convection cells in the earth
Three boundaries
convergent, divergent, transform
Two types of crust
continental and oceanic
continental: thick, buoyant; oceanic: think, dense
Plate movements explain biogeographic patterns
Uniformitarianism
A principle that geologic processes that occurred in the past can be explained by current geologic processes
"An attempt to explain the former changes of the Earth's surface by reference to causes now in operation"
Catastrophism
A principle that states that geologic change occurs suddenly
Georges Cuvier, 1796
Death from above, 1980
Iridium abundance (parts per billion)
Geological evidence for the end-Cretaceous impact
"Big Five" Mass Extinctions
End-Permian Mass Extinction Estimated 96% of species go extinct Coincident with formation of the Siberian Traps, a huge domain of lava that may have altered climate