Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
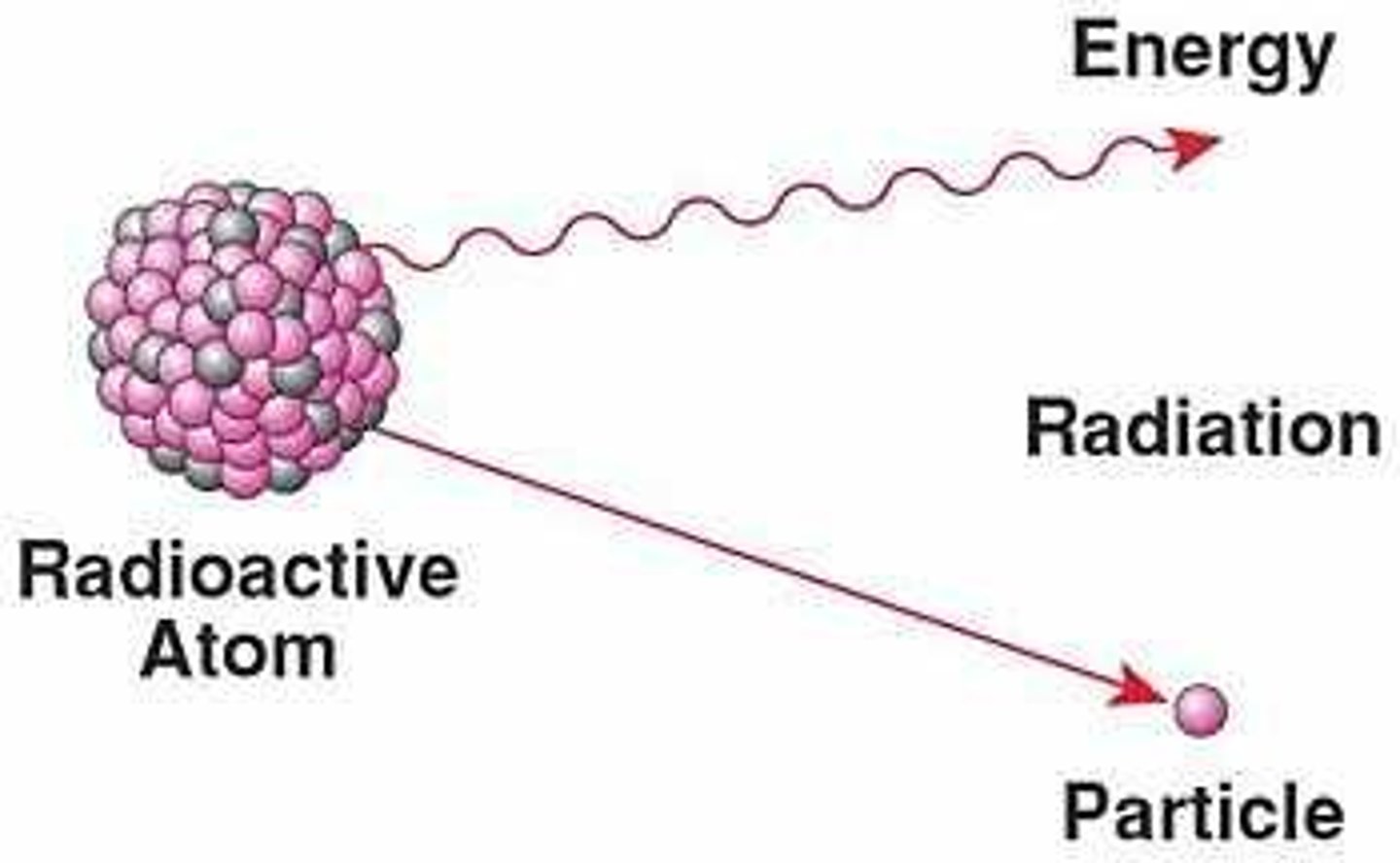
radioactivity
the process of an unstable nucleus emitting particles and energy to become more stable.
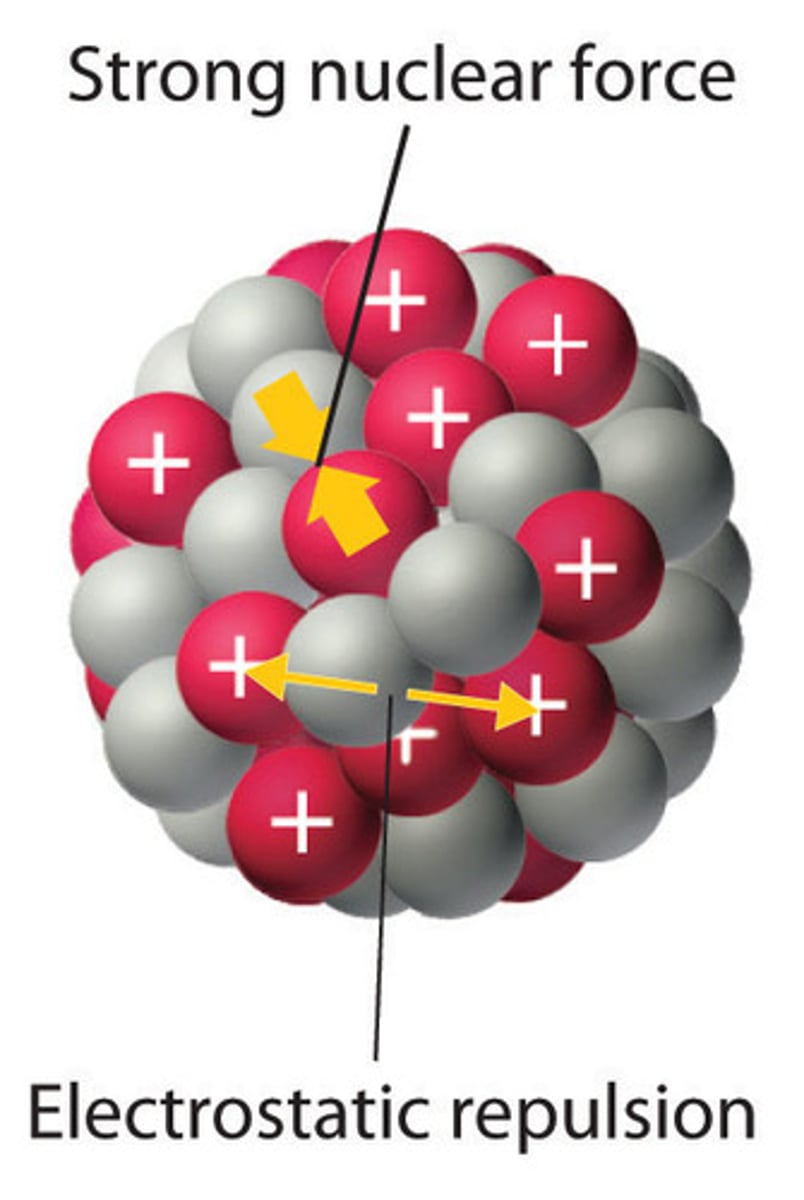
strong nuclear force
holds the nucleus together-attractive force between protons and neutrons. becomes very weak as nucleus gets bigger
radiation
energy and particles given off during nuclear decay
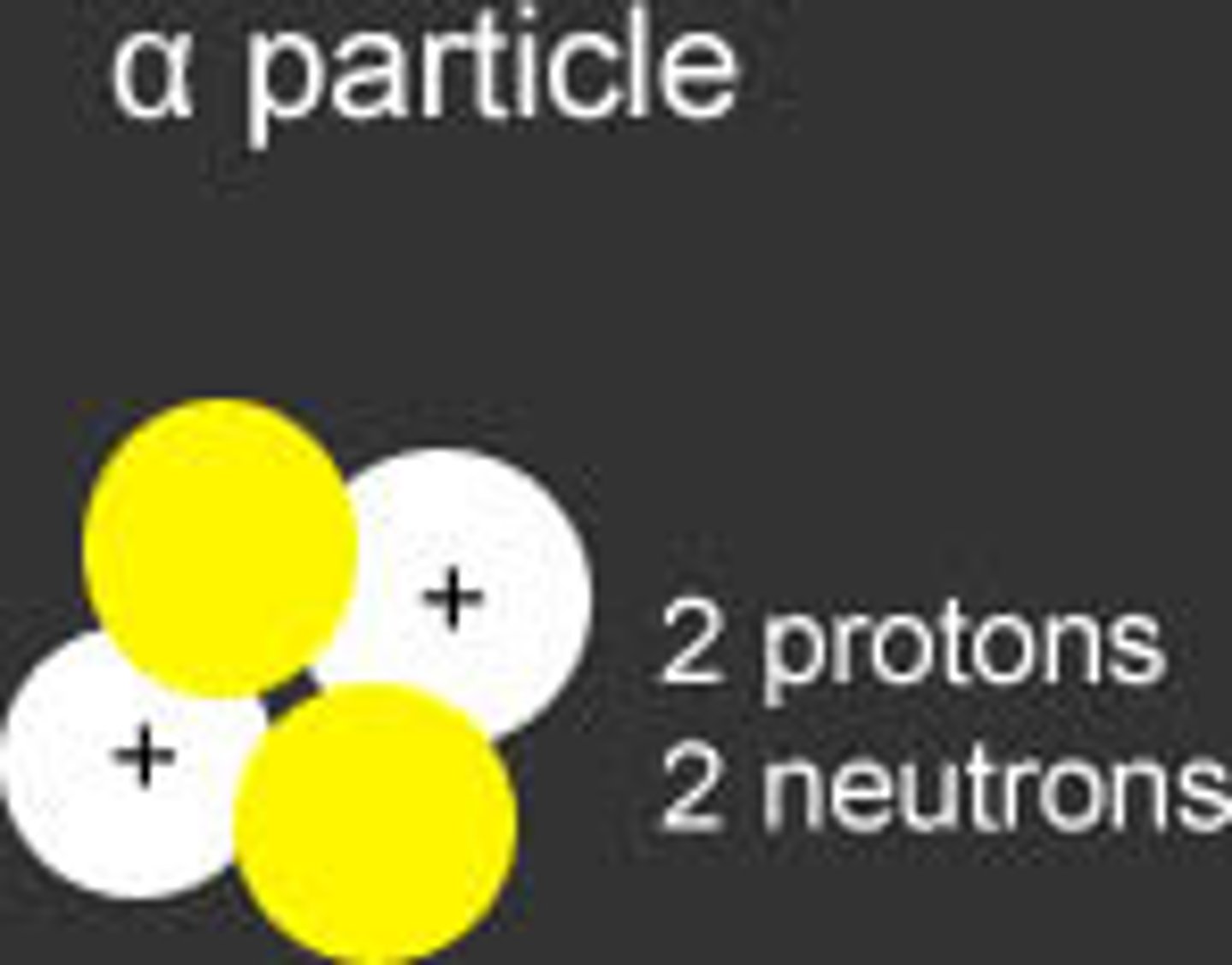
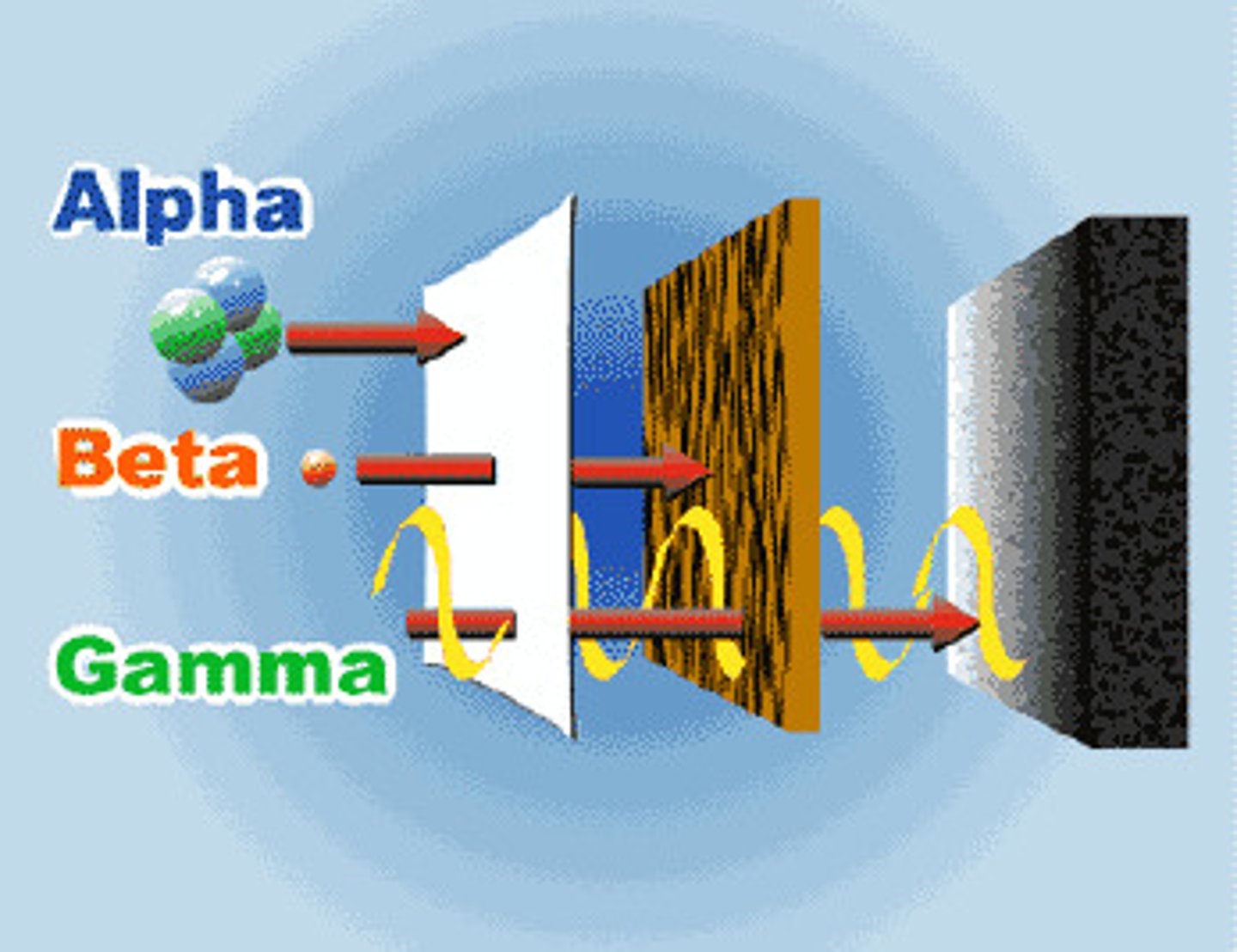
alpha particles
made of 2 protons & 2 neutrons (same as helium nucleus) least penetrating. can be stopped by paper
gamma rays
A very dangerous and can only be blocked by lead or very thick slabs of concrete.
transmutation
The process of one element changing into another element
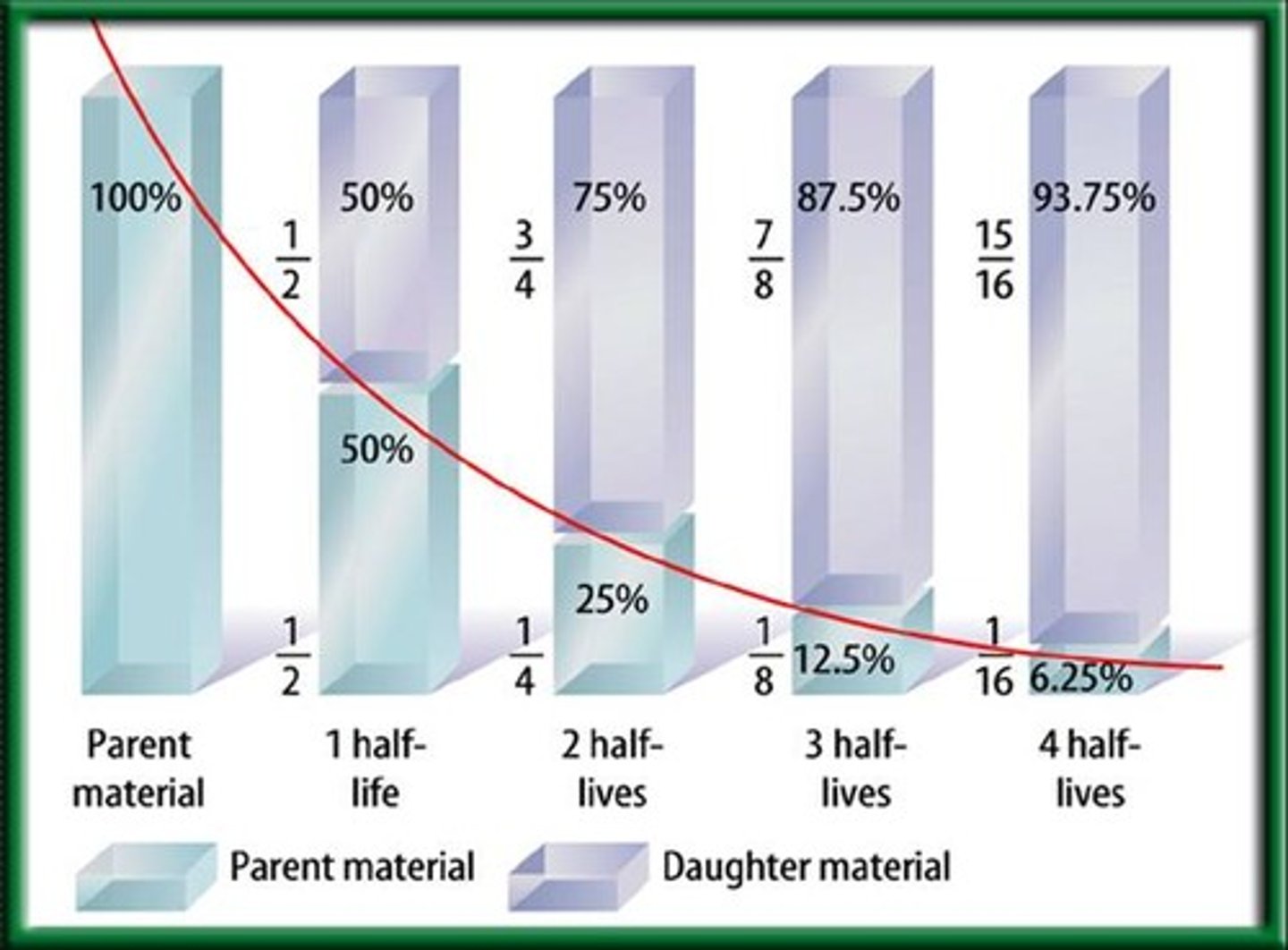
half-life
The amount of time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay.
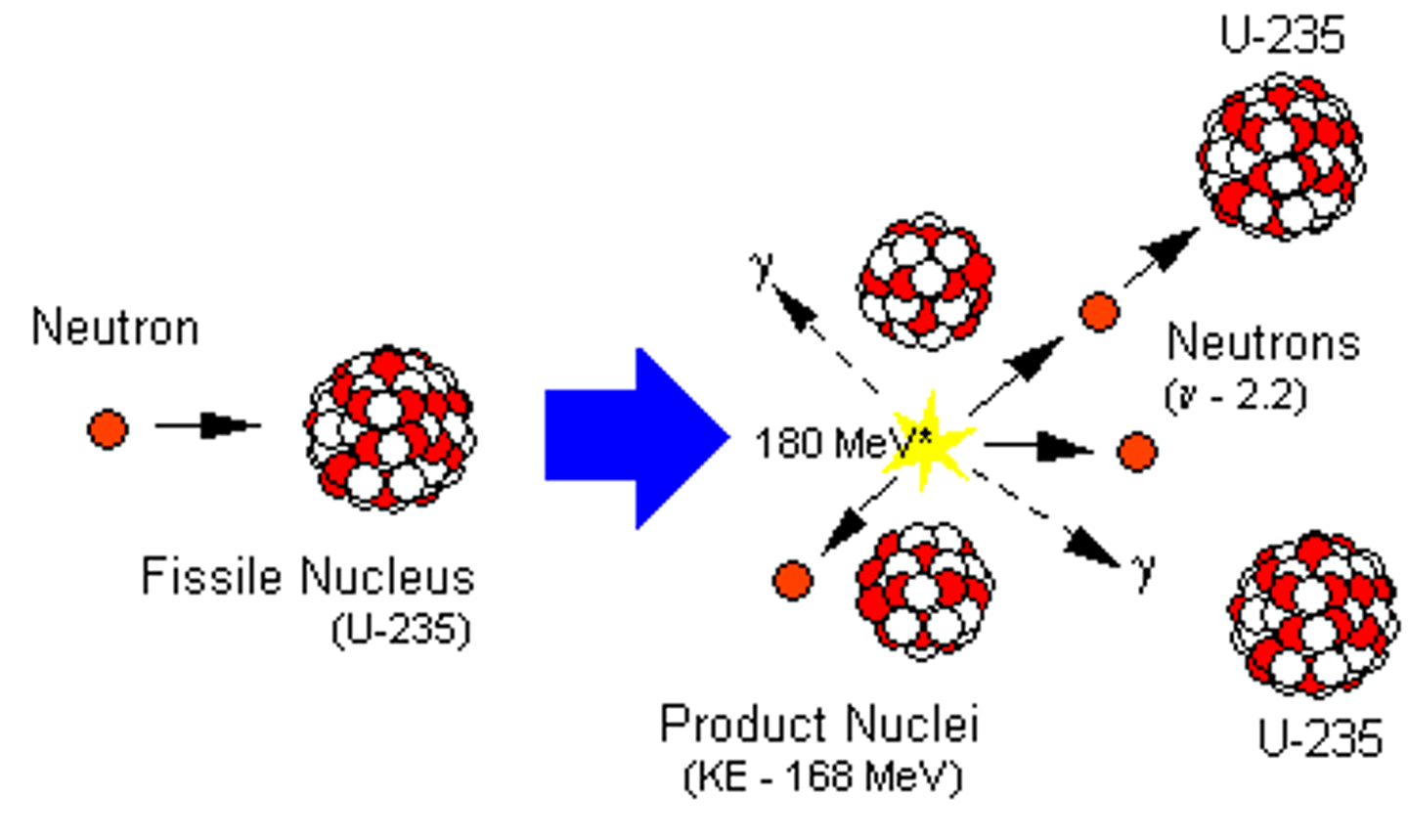
fission
The process of splitting a nucleus into smaller, less massive nuclei.
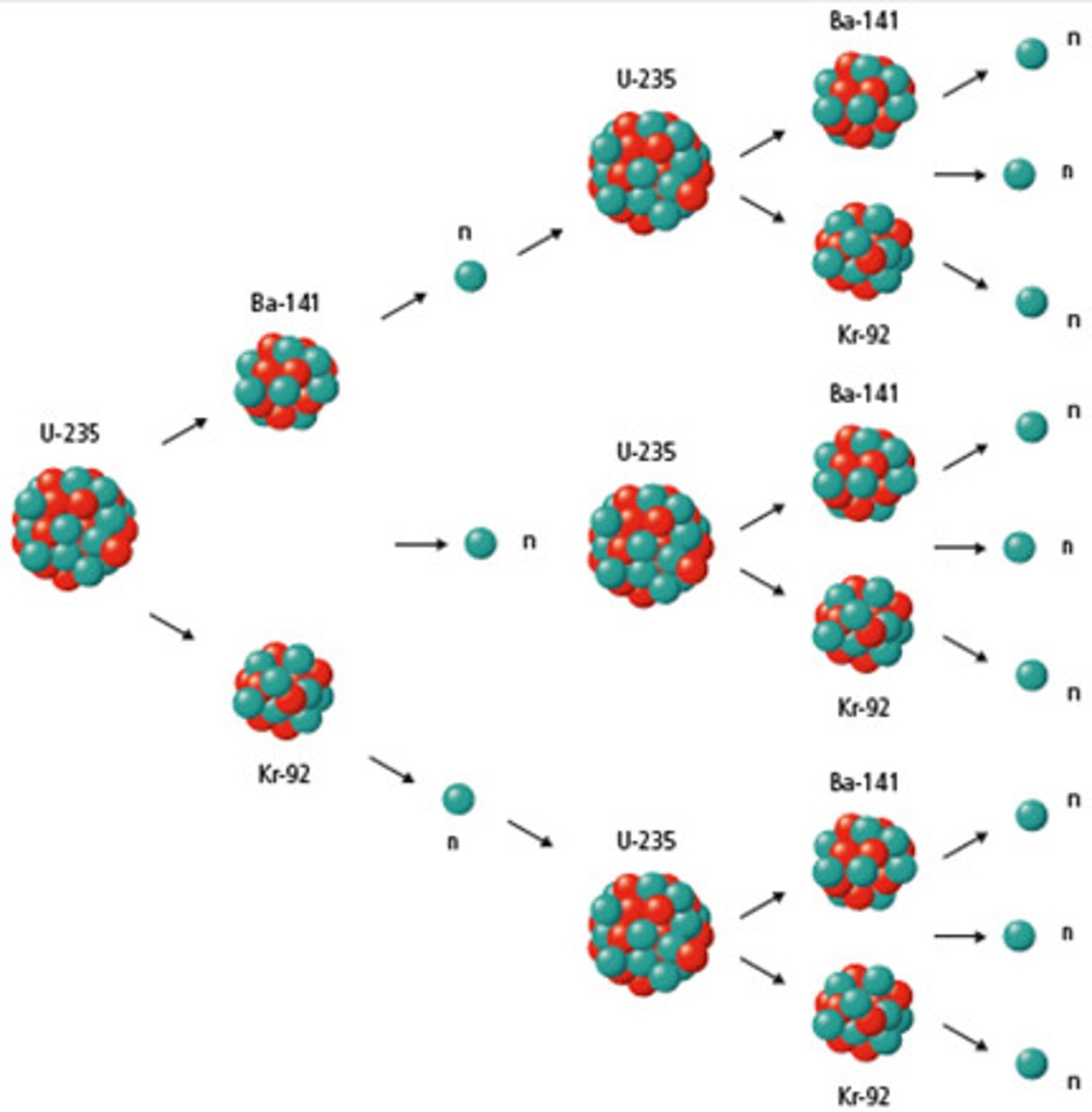
nuclear chain reaction
a series of fission reactions caused by neutrons being emitted and splitting other nuclei
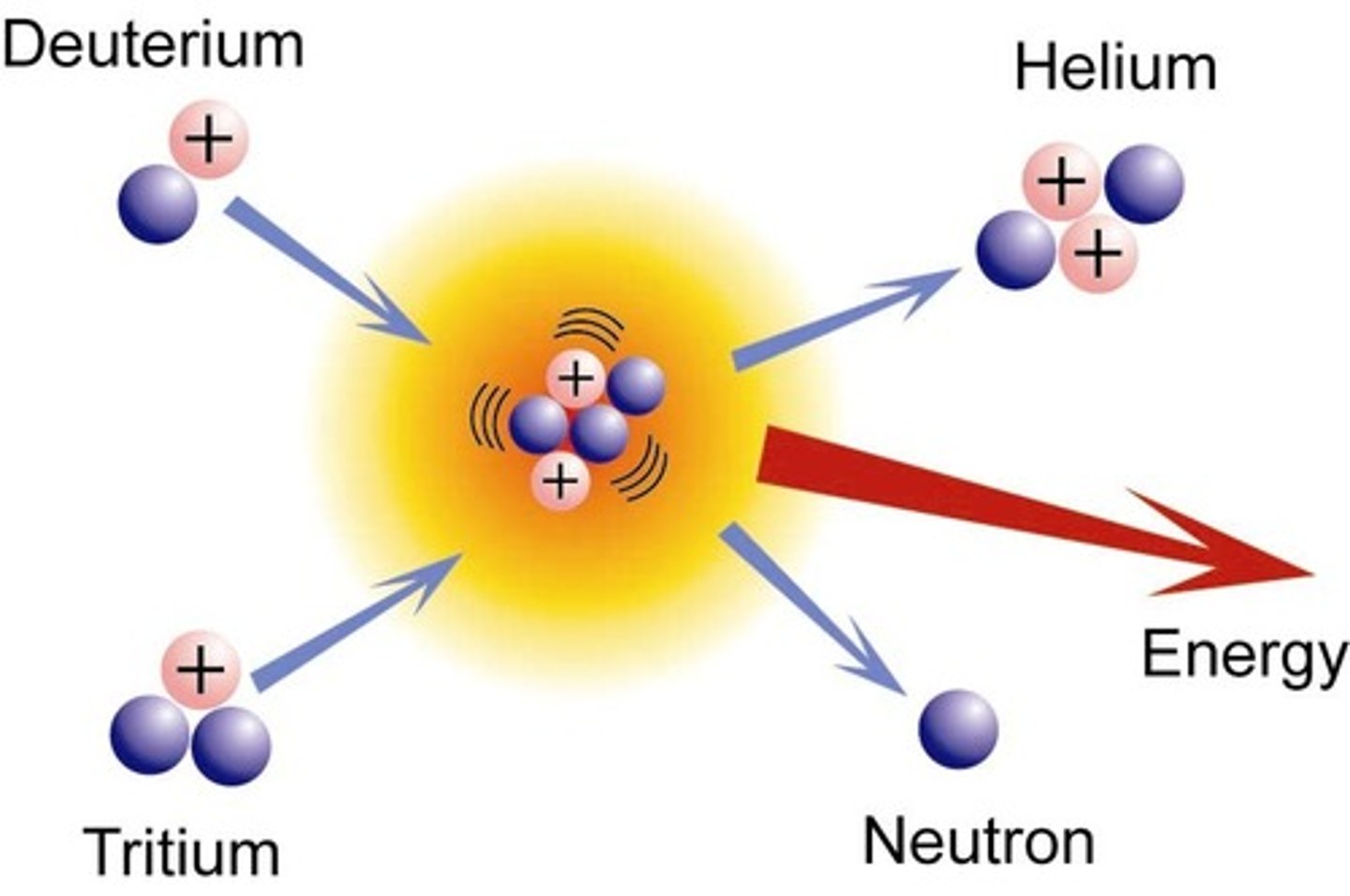
fusion
When two nuclei of smaller masses combine to form one larger, more massive nucleus.
daughter nucleus
The more stable nucleus AFTER an atom decays.
parent nucleus
The radioactive nucleus BEFORE it decays and releases radiation.
Electrostatic Force
attraction or repulsion of particles or objects due to their electric charge.
Isotope
An element with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons.
Beta Decay
Occurs when a neutron becomes a proton and an electron is emitted from the nucleus.
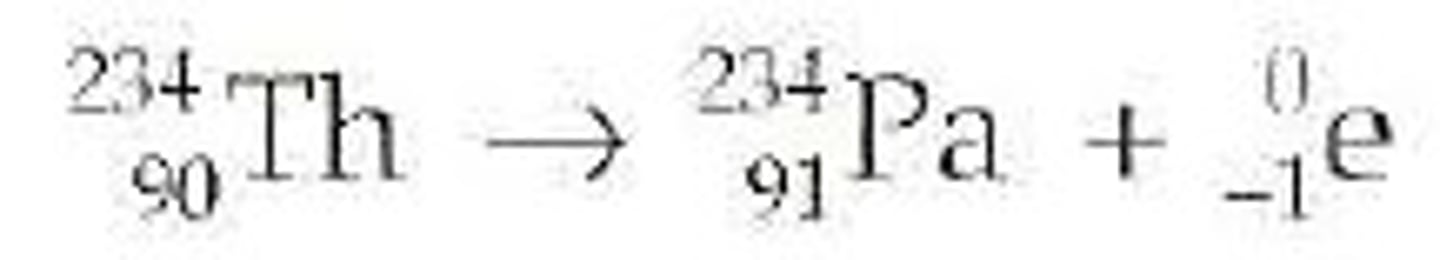
Empty Space
Most of the atom is this
Helium Nucleus
This is what is released during alpha decay.
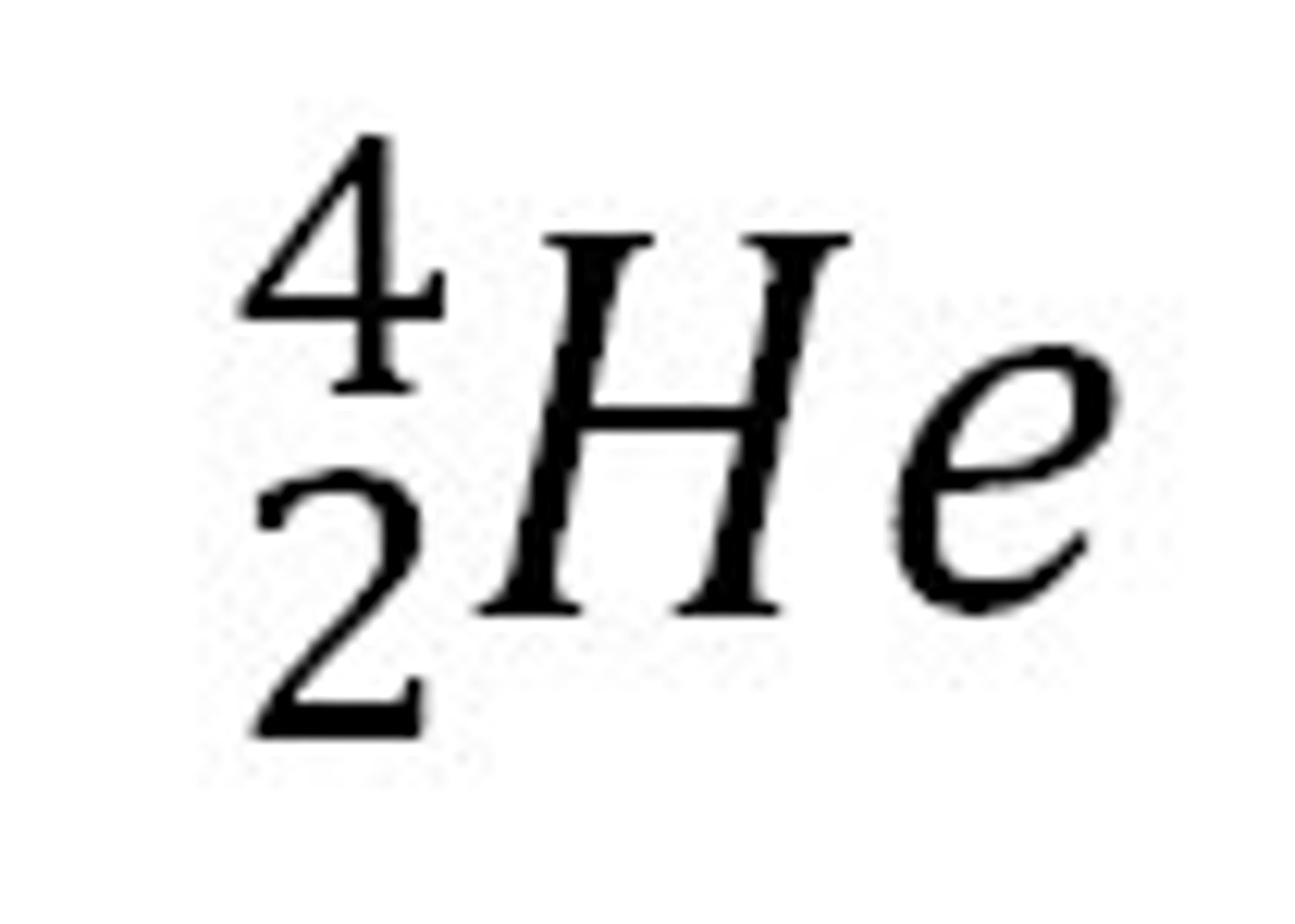
Electron
This is what is released during beta decay
Protons and Neutrons
The nucleus is packed tight with these two particles.
Nucleus
This is was changes during Nuclear decay.
Geiger counter
Radiation detector that produces a click or a flash of light when a charged particle is detected.
Ionizing radiation
Radiation strong enough to rip the electrons off of atoms
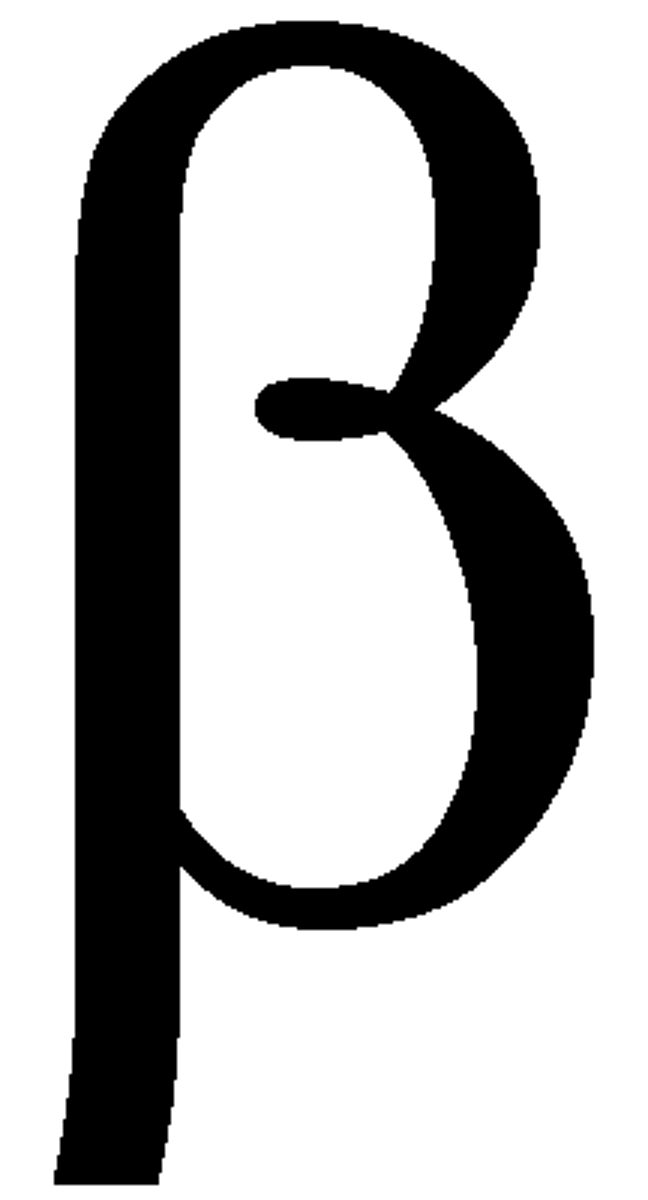
Beta symbol
β
Gamma symbol
V
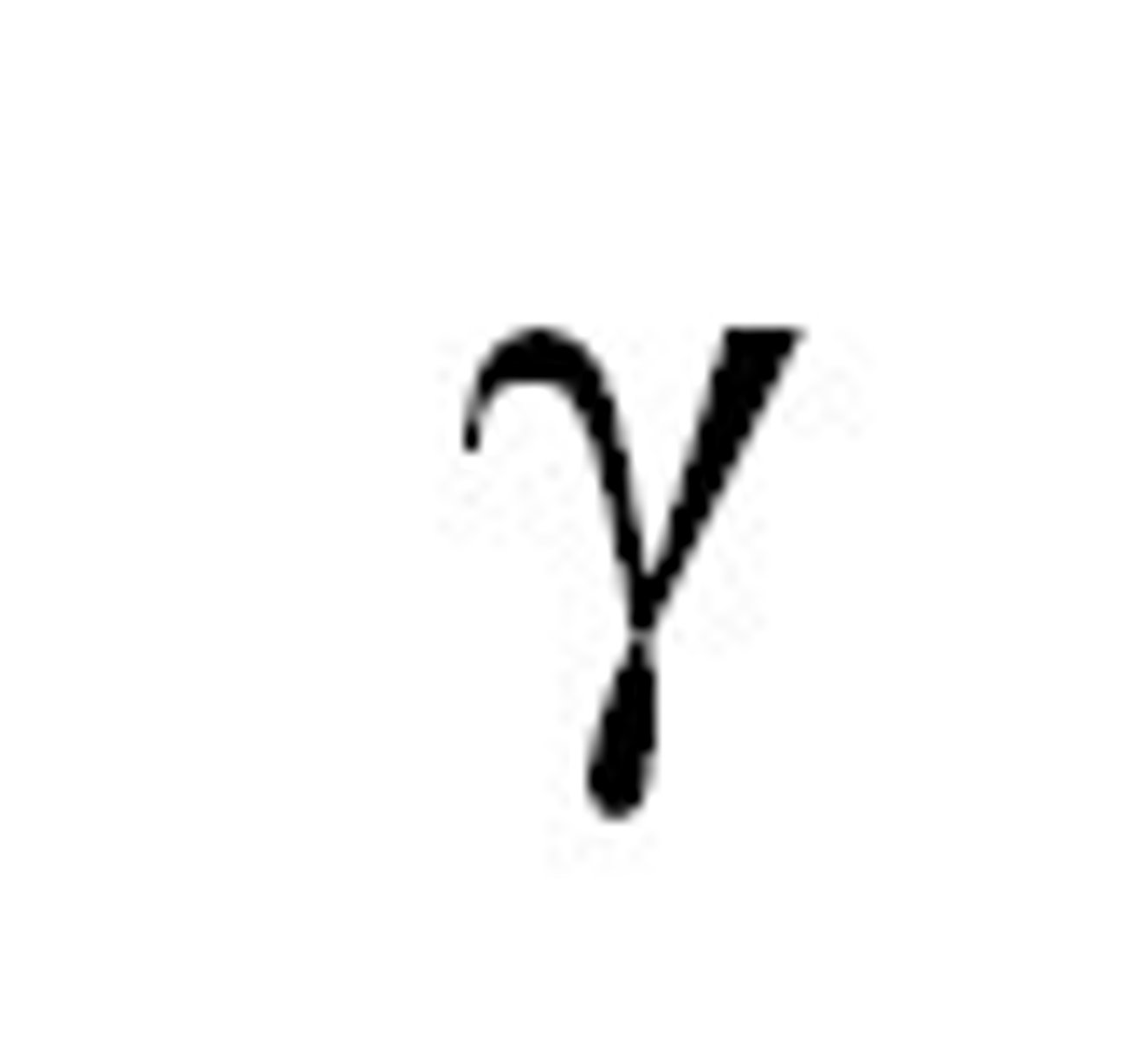
Alpha symbol
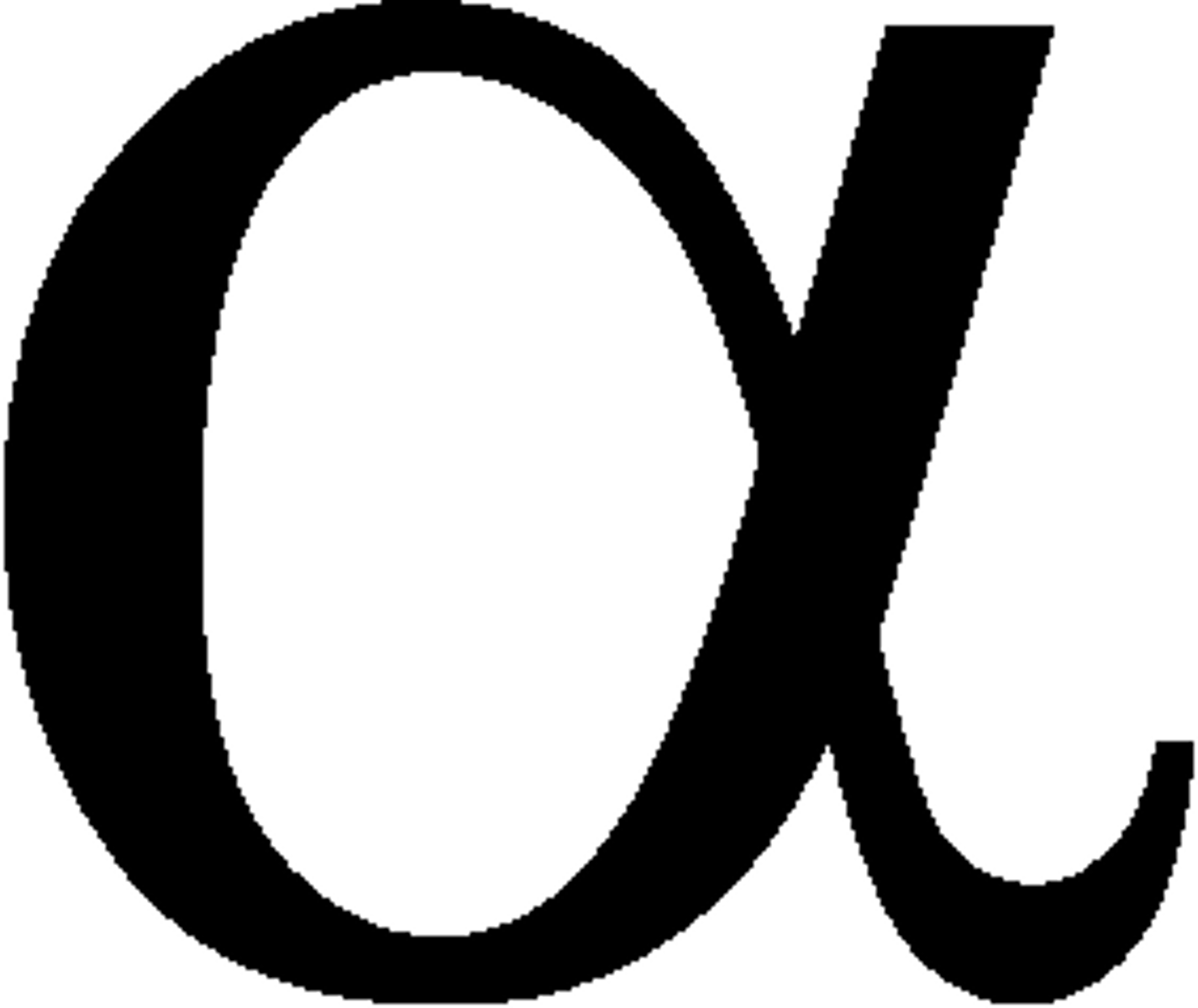
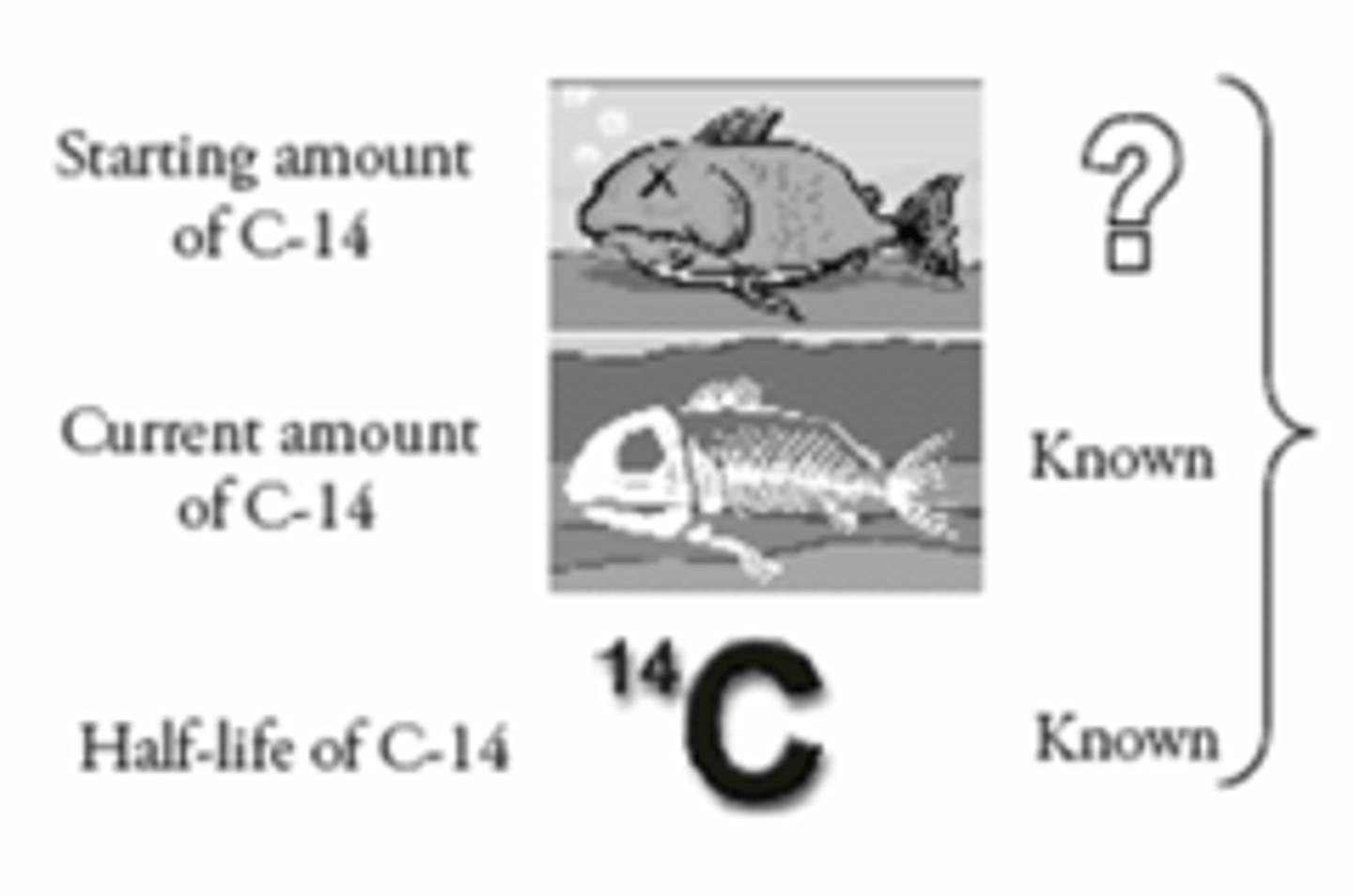
Carbon Dating
Tells us how old organic materials are. It can tell us up to 60,000 years.
Background Radiation
The nuclear radiation that arises naturally from cosmic rays and from radioactive isotopes in the soil and air.