AQA GCSE: Physics - Space
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Supernova
A gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space
How elements heavier than iron were formed
Protostar
A contracting cloud of gas and dust; the earliest stage of a star's life
Nebula
A large cloud of dust and gas in space

Main Sequence Star
A normal star that is undergoing nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium.
Black Hole
An object in space whose gravity is so strong not even light can escape.

Red Giant
A star that expands and cools once it runs out of hydrogen fuel
Red Supergiant
Same as red giant, but original star was much more massive

Neutron Star
The small, dense remains of a high-mass star after a supernova

White Dwarf
A small, hot, dim star that is the leftover center of an old star

Black Dwarf
A white dwarf that has burnt out completely.

Solar System
The sun with the celestial bodies that revolve around it in its gravitational field
Comet
Frozen rocks that move around the sun in elliptical orbits

Unstable star
When a star has no more hydrogen nuclei to use in fusion
Meteor
Small bits of rock that burn up upon entering the atmosphere

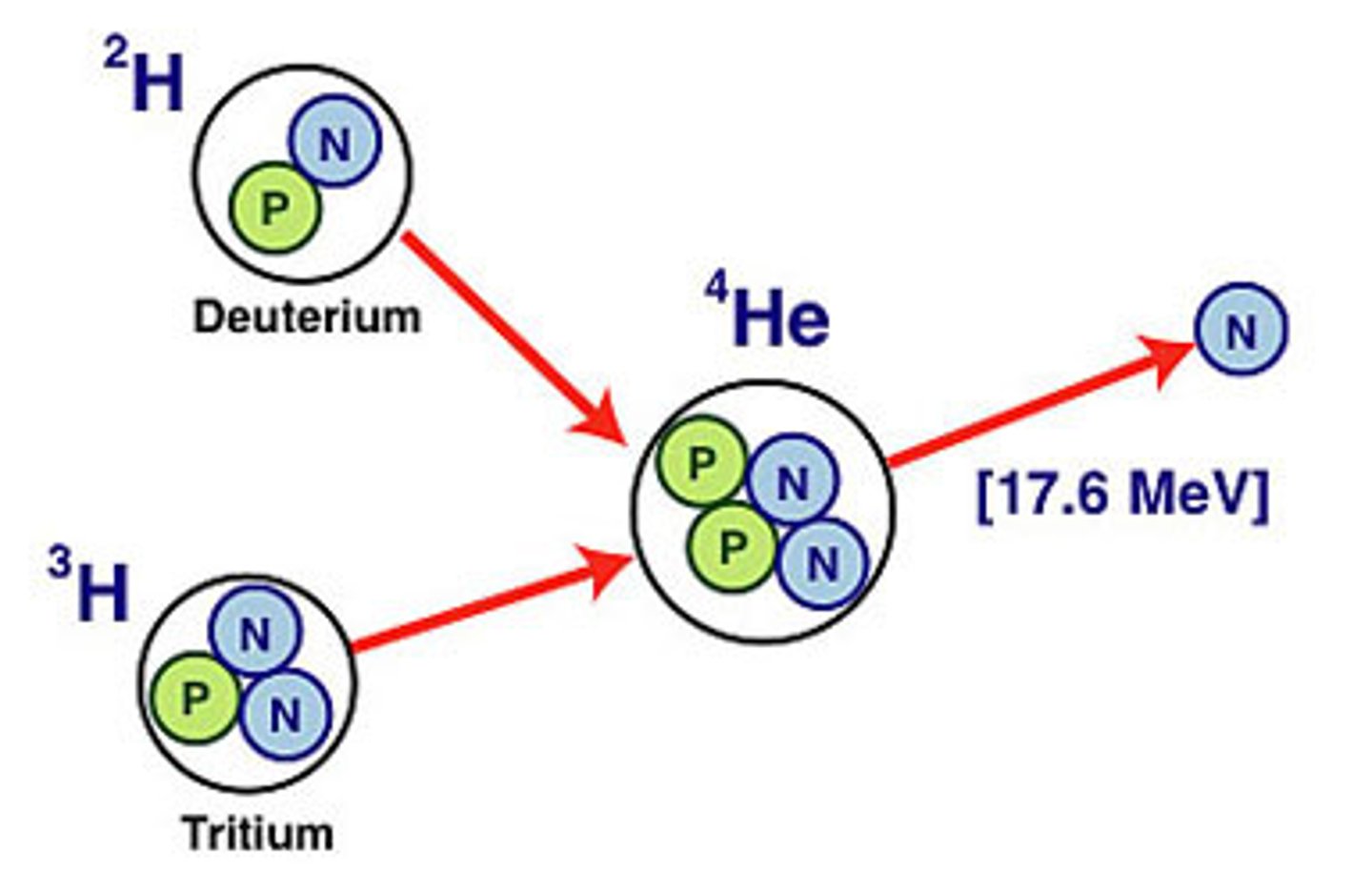
Fusion
Creation of energy by joining the nuclei of two hydrogen atoms to form helium.
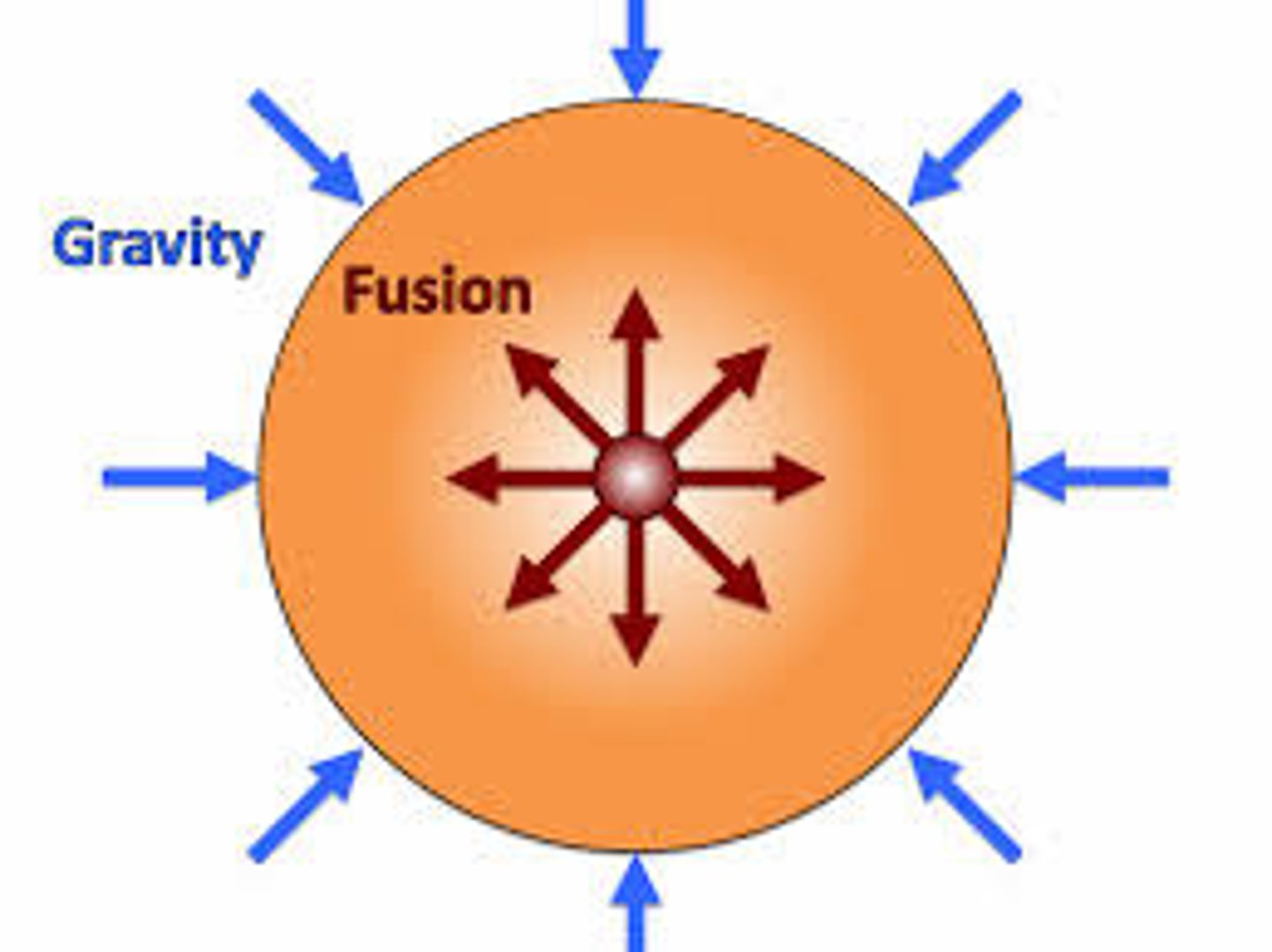
Stable Star
The forces of gravity condensing the star and the force of the radiation expanding the star are balanced
Uranium
Heaviest known natural element
Orbit
The path of an object as it revolves around another object in space
Centripetal Force
A force acting towards the center of an object
36000 km
Height of Communication Satellites
Red Shift
The change in the wavelength of light (towards the red end of the spectrum) due to an Star/Galaxy moving away from the observer.
The larger the change, the faster the Star/Galaxy is moving away
The Big Bang
The theory that the universe began as an infinitesimally small and dense region that exploded suddenly
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
CMBR
High energy gamma radiation created just after the Big Bang that, due to the universe expanding, has been stretched to the wavelength of microwave radiation
Dark Matter
Matter that does not give off electromagnetic radiation