Adrenal gland and steroid hormones
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Types of peptide hormones (6)
TRH
ADH
insulin
GH
FSH
TSH
hormones - amine derived from tyrosine/tryptophan
thyroxine
catecholamines - adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine
Lipid derived hormones
eicosanoids - prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes
testosterone
cortisol
calcitrol
aldosterone
Embryological origin of the outer cortex of adrenal gland
developed from mesoderm (coelomic mesoderm)
produce steroid hormones
controlled by pituitary
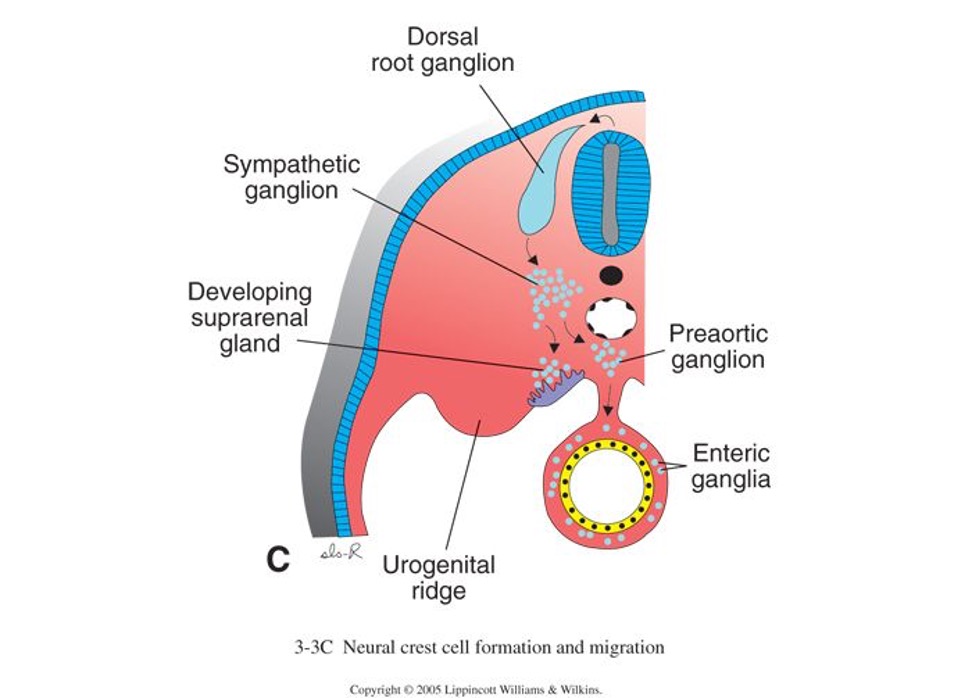
Embryological origin or the inner medulla of the adrenal gland
derived from neural crest (neuroectoderm)
consists of cells secreting catecholamines (chromaffin)
under nervous control
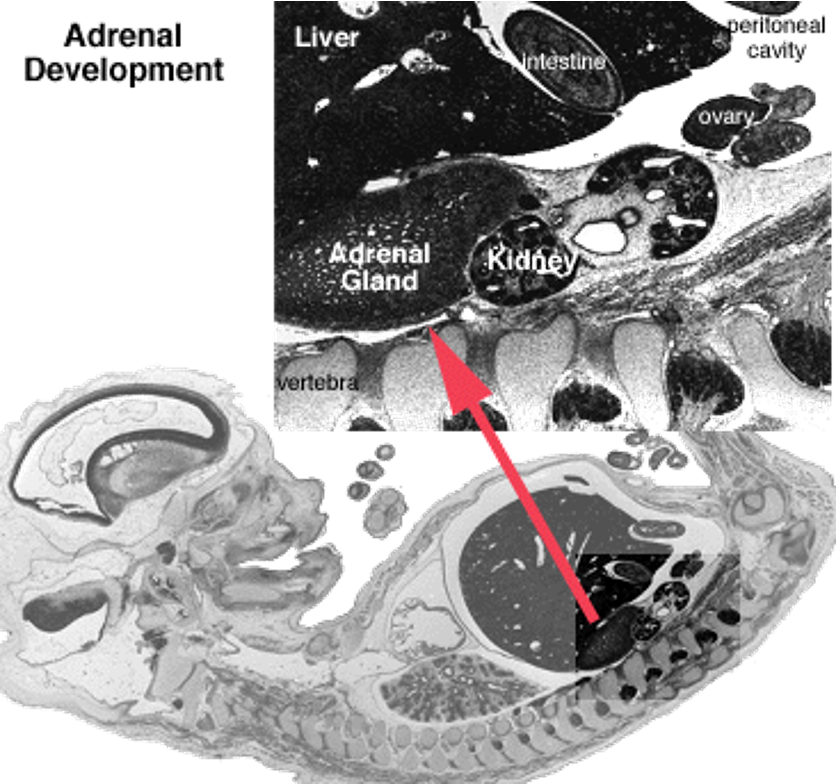
Adrenals in the foetal cortex - wk 20
adrenals (mostly cortex) larger than kidney
responsive to ACTH
adrenal hormones involved with maturation of lung and other systems
e.g. gut closure (IgG transport) under influence of corticosteroids
What does the neural crest cell form? (11)
adrenal medulla
ganglia - sensory, autonomic
melanocytes
Schwann cells
meninges - pia, arachnoid
pharyngeal arch cartilage
odontoblasts
parafollicular C cells
aorticopulmonary system
endocardial cushions
facial skeleton
Blood supply of the adrenal gland
IVC, aorta, left renal artery
left renal vein
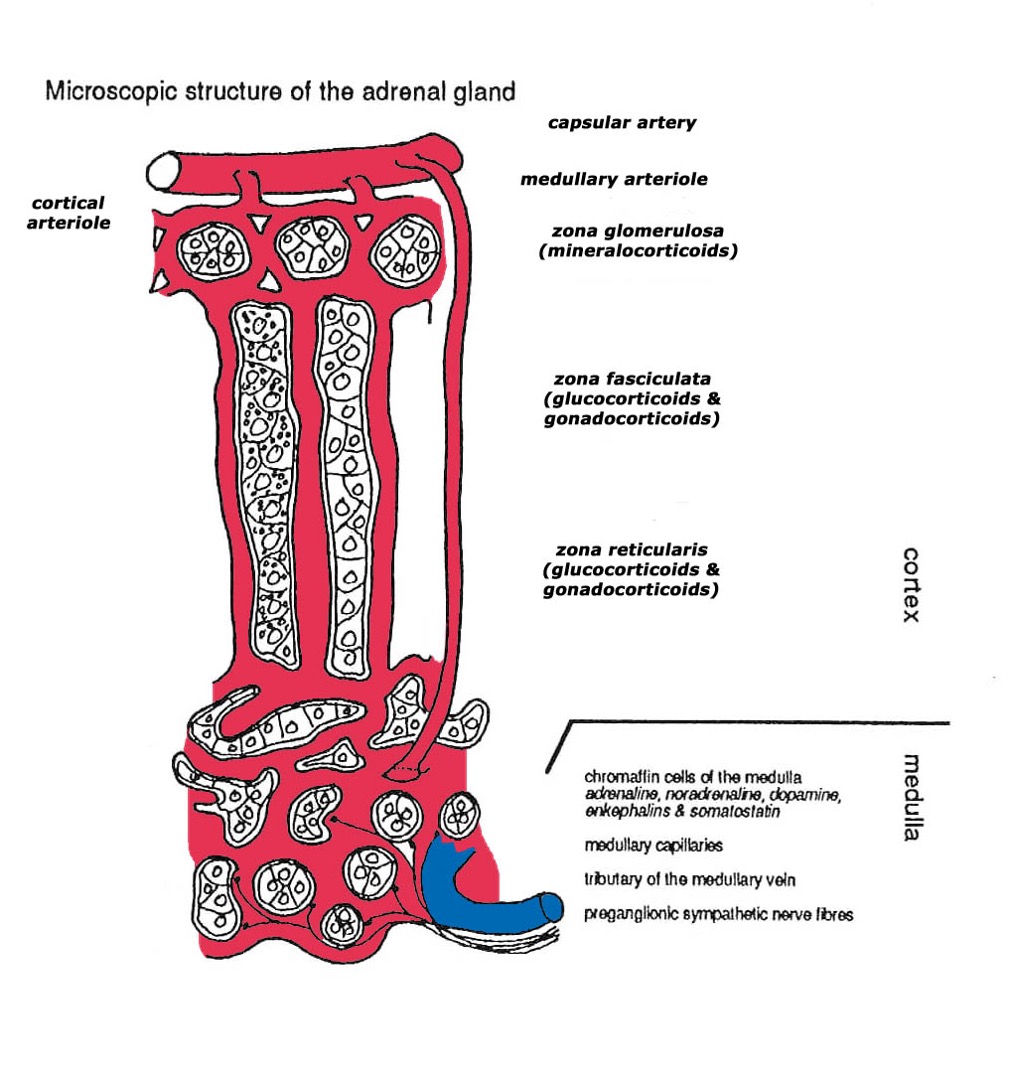
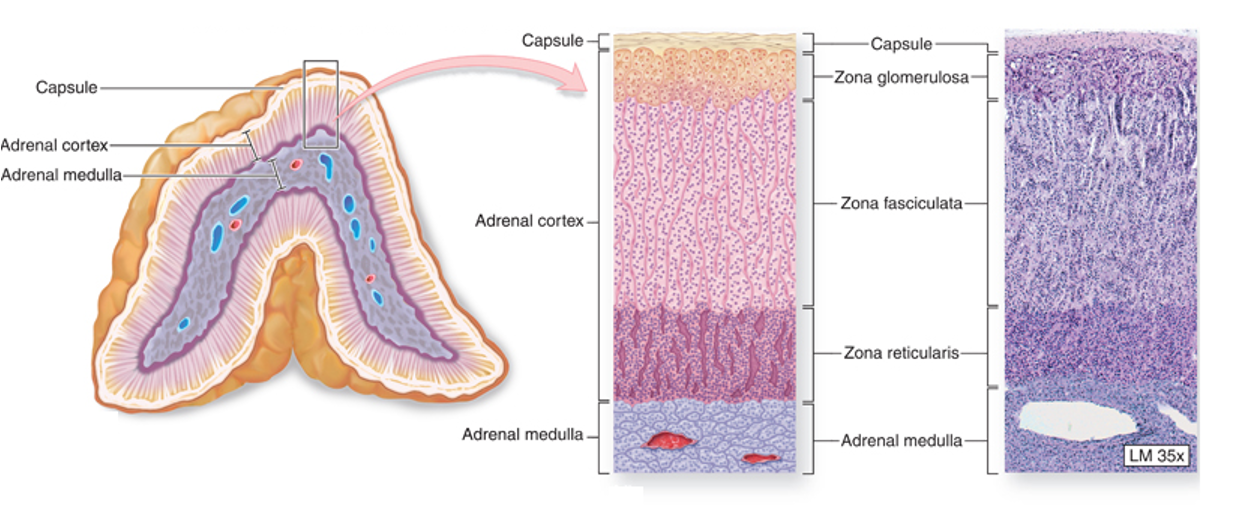
Adrenal cortex and medulla histology
Zona glomerulosa – mineralocorticoids, eg, aldosterone
columnar/ovoid cells
Zona fasciculata - glucocortocoids, eg, cortisol
sinusoids between columns of cells
Zona reticularis - gonadocorticoids, eg, androgens
cells arranged in cords seperated by sinusoids
Medulla – adrenaline, noradrenaline (chromaffin cells)
pale staining, cells arranged in groups - rich blood supply
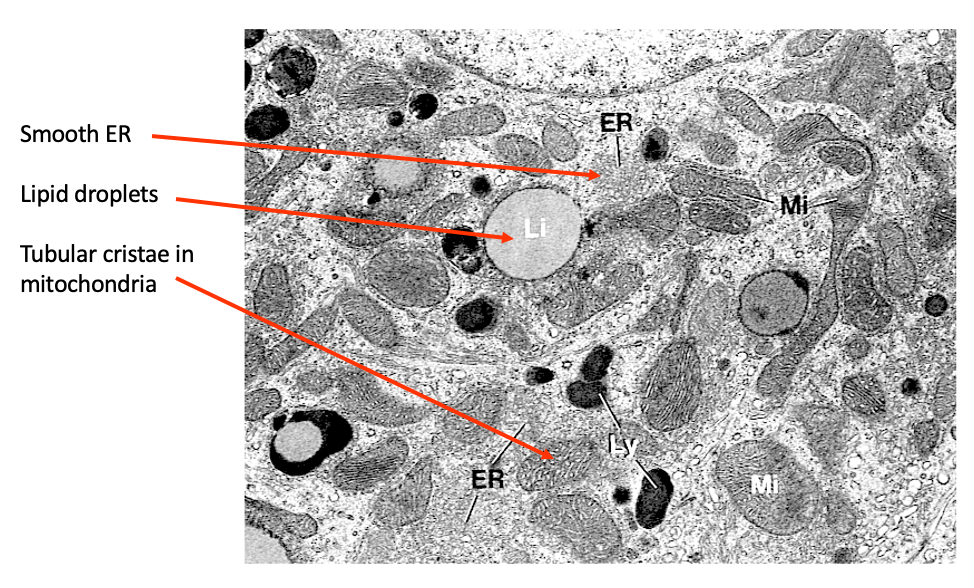
Ultrastructure - steroid secreting cell from cortex
Cholesterol stored in lipid droplets until used
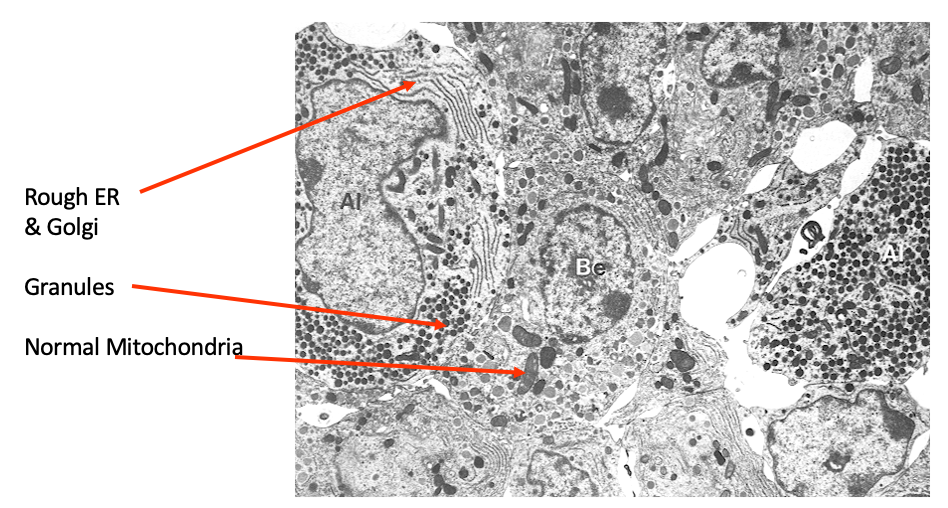
Ultrastructure - peptide secreting cell from medulla
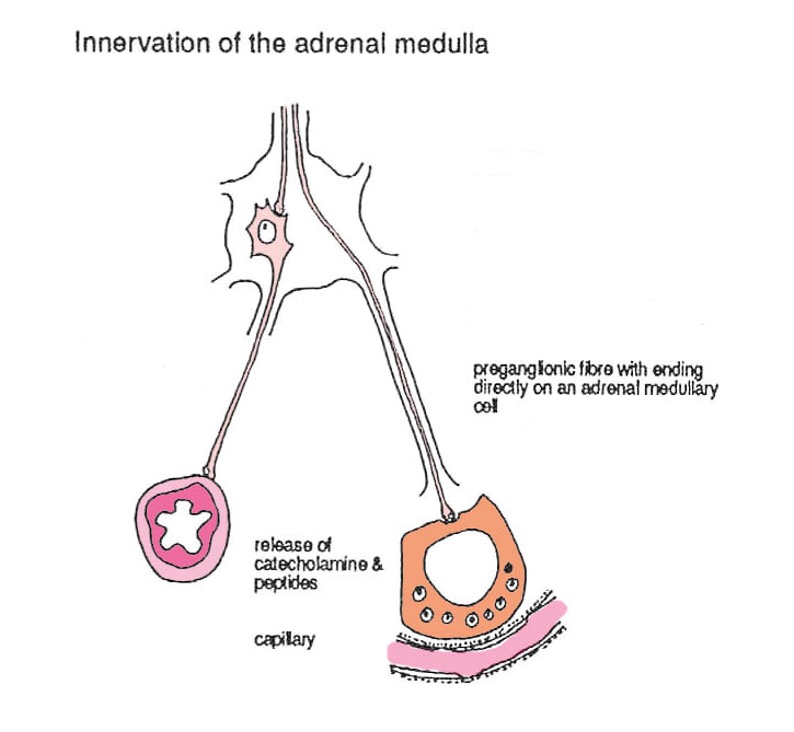
Innervation of the adrenal medulla
Preganglionic fibres cause the suprarenal medulla to pour forth adrenalin
Vasomotor supply to suprarenal gland reaches it by postganglionic fibres
How is cholesterol turned into adrenal steroid hormones? (steroidogenesis)
cholesterol obtained from blood as LDL or synthesised from acetyl- CoA
rate limiting step: transport of cholesterol from outer to inner mitochondrial membrane
cleavage of cholesterol side chain → pregnenolone
pregnenolone converted to:
aldosterone (zona glomerulosa)
cortisol (zona fasciculata)
testosterone, oestrone, oestradiol, oestriol (zona reticulaire)
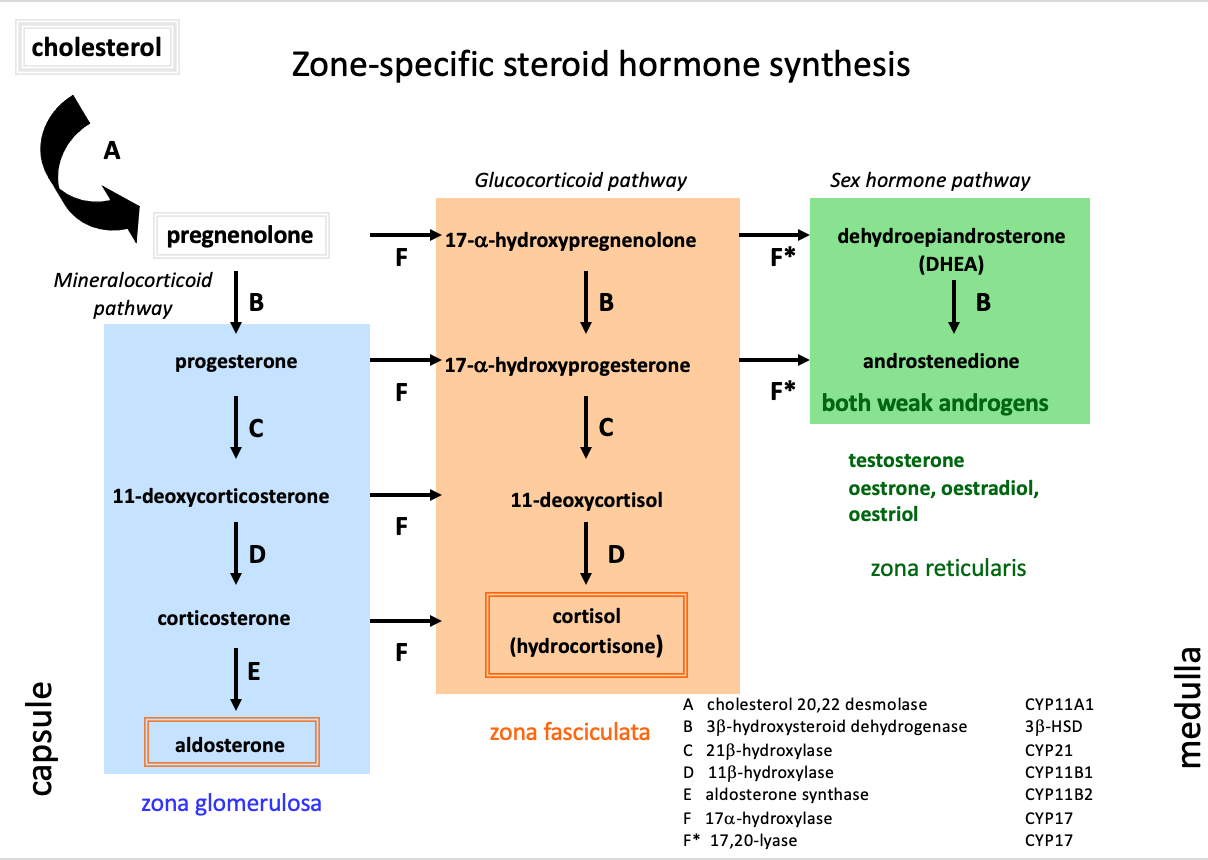
Mineralocorticoid pathway (zona glomerulosa)
pregnenolone
progesterone
1,1 deoxycorticosterone
corticosterone
aldosterone
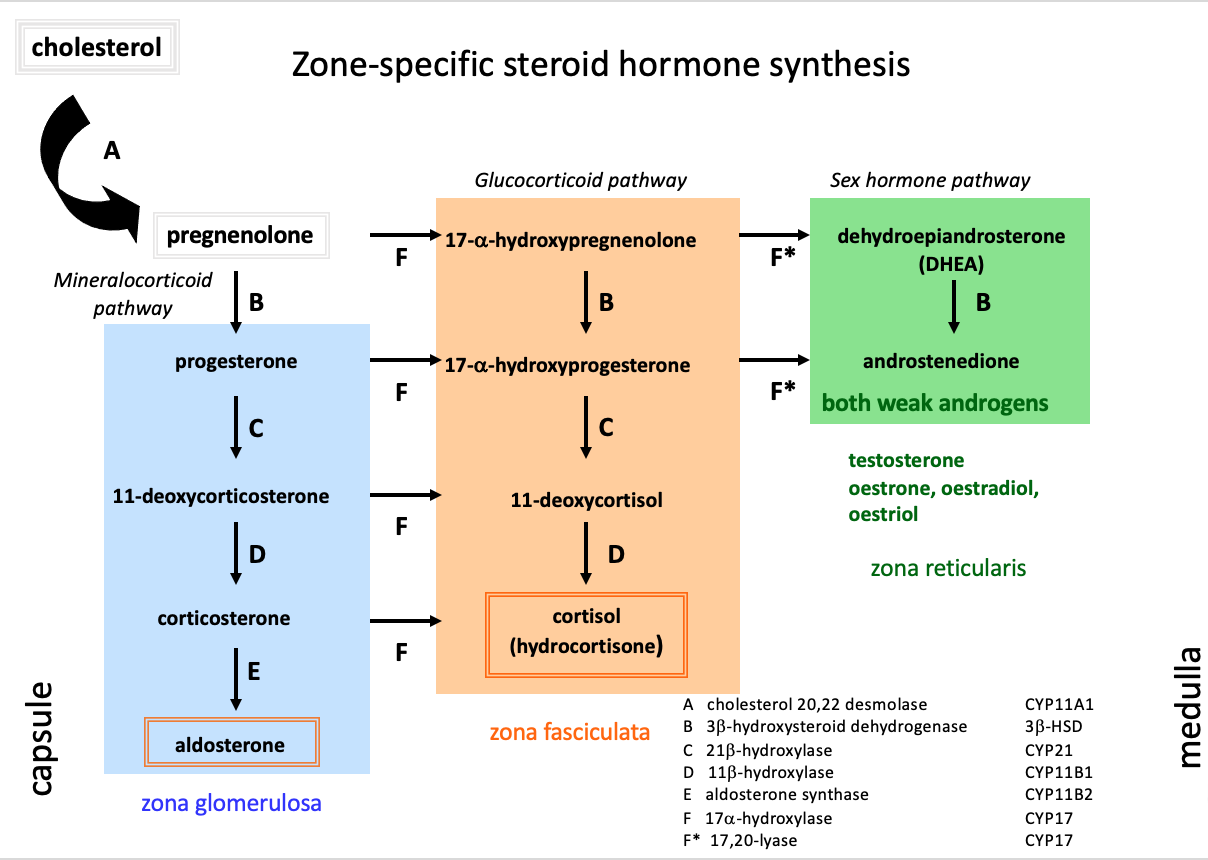
Glucocorticoid pathway (zona fasciulata)
pregnenolone
17-a-hydroxypregnenolone
17-a-hydroxyprogesterone
11-deoxycortisol
cortisol
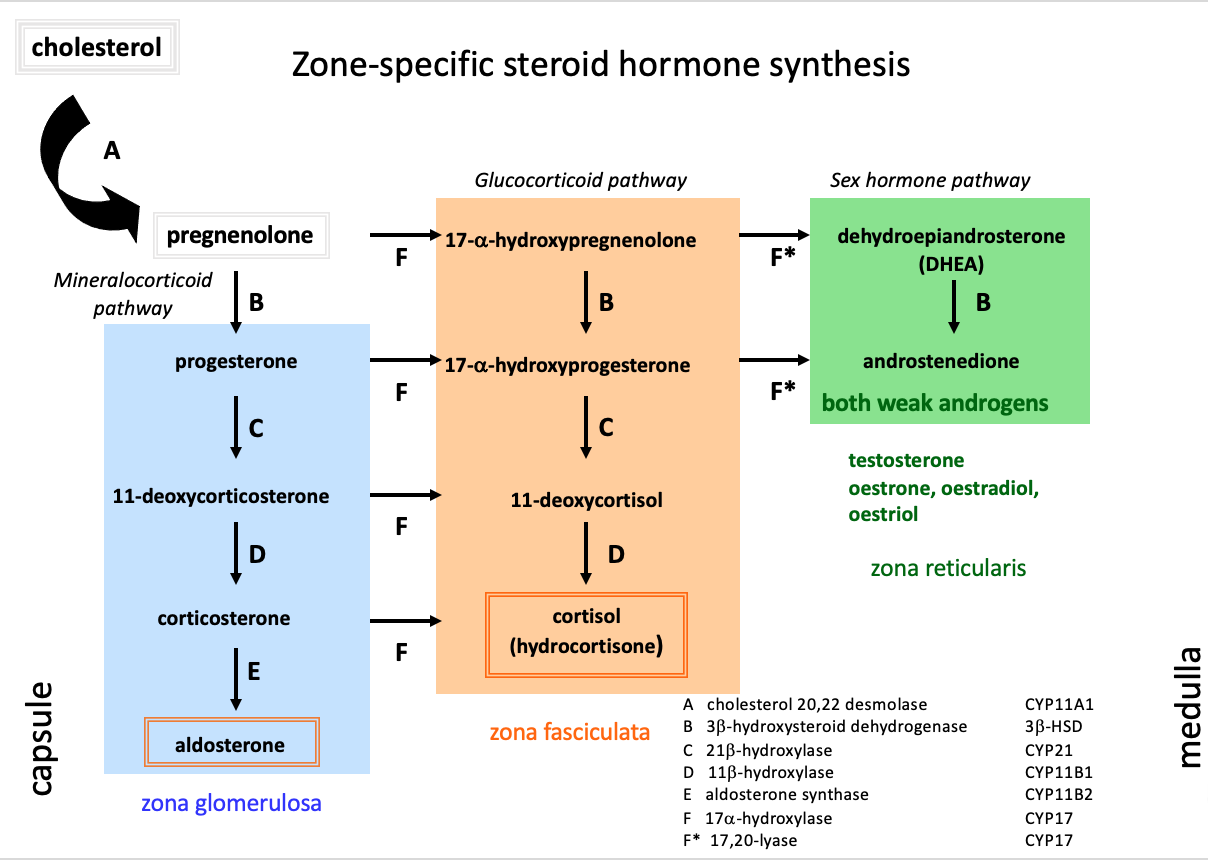
Sex hormone pathway (zona reticularis)
dehydroepiandrosterone
androstenedione
testosterone, oestrone, oestradiol, oestriol
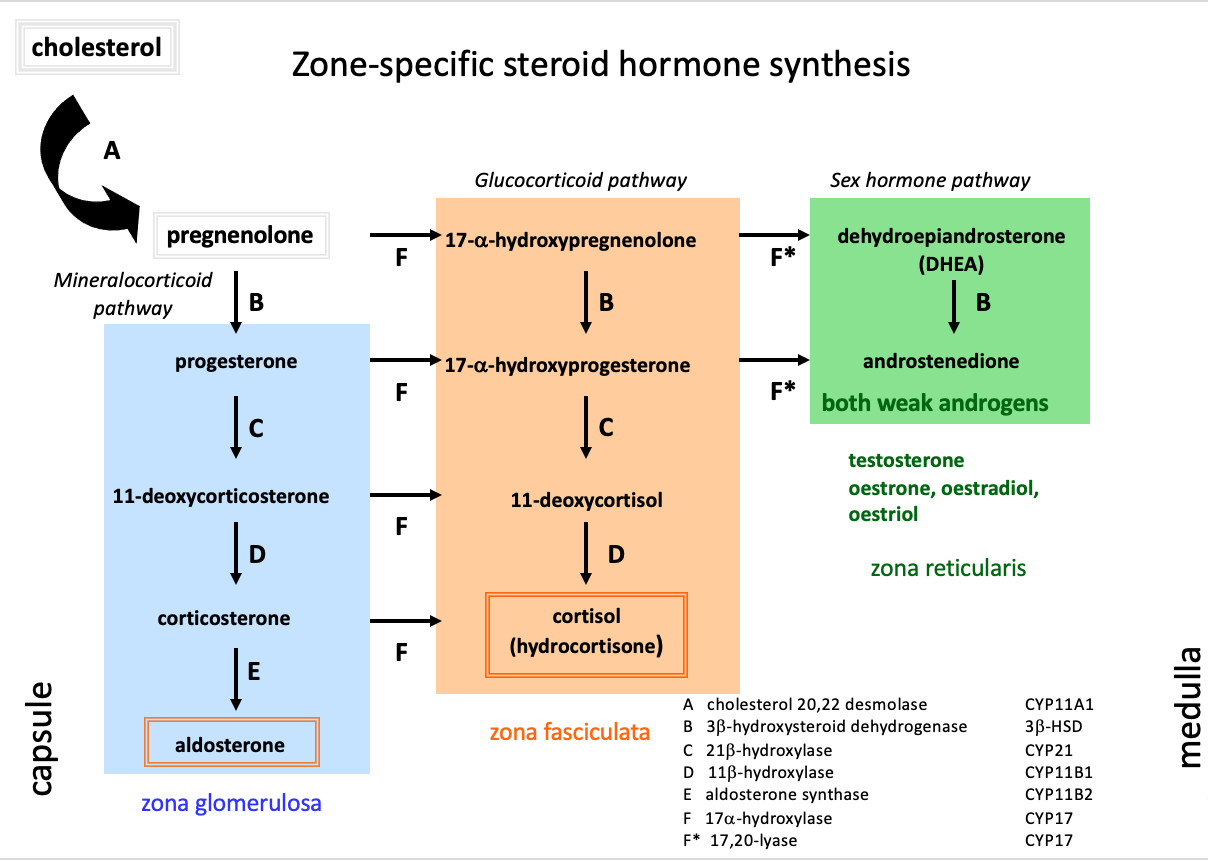
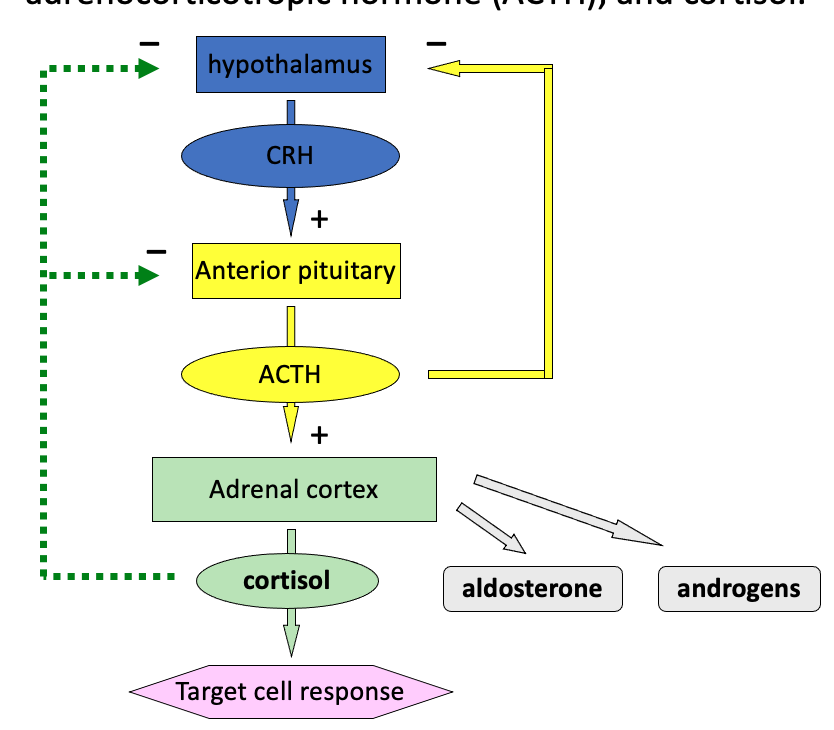
What is the HPA axis and what does it consist of?
Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis
Includes:
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
cortisol
What stimulates aldosterone secretion and what does it do?
Secretion stimulated by raised [K+], Ang II, and ACTH
helps your body retain salt and water and get rid of potassium. This helps control blood pressure and fluid balance.
What happens when there is a stress stimuli? (steroid feedback)
Stress stimulus activates hypothalamus.
Hypothalamus releases CRH (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone).
CRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone).
ACTH travels via the bloodstream to the adrenal glands, triggering the release of cortisol.
High cortisol levels provide negative feedback:
Suppress further release of CRH from the hypothalamus.
Suppress further release of ACTH from the anterior pituitary.
What is diurnal rhythm?
Biological clock, controlled by suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
e.g. cortisol levels peak in morning then decreases, low body temp in morning then increases
Where are steroid hormones synthesised and how are they transported?
Produced in endocrine, released by simple diffusion
Transported in the circulation bound to plasma proteins (carriers)
How do steroid hormones act at target cells?
Steroid hormones diffuse though cell membrane
Hormone binds to intracellular receptors in cell
Hormone-receptor complex becomes active and binds to DNA sequence
Gene expression is modulated
New proteins/biological effects
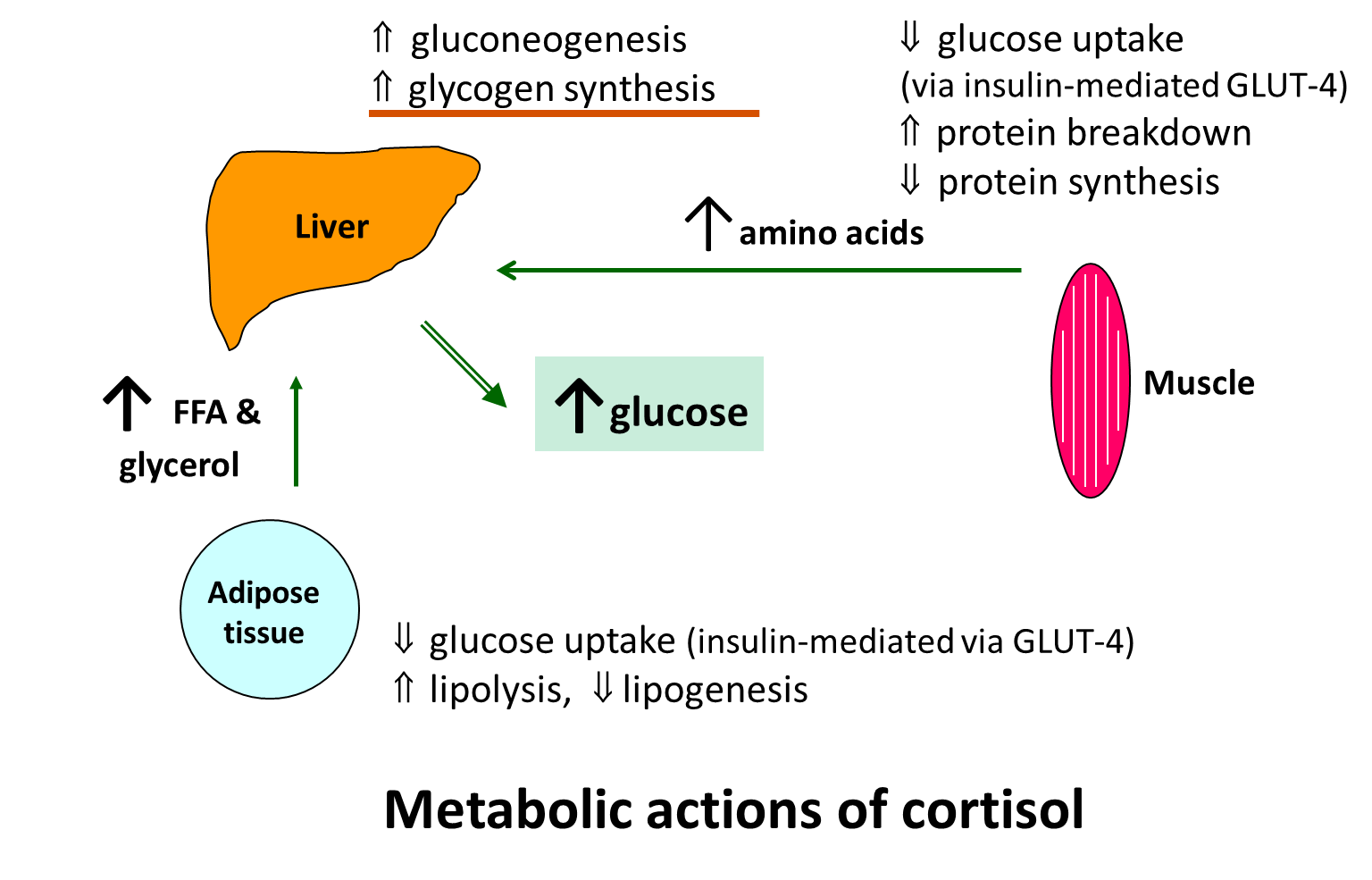
Actions of cortisol
metabolic
muscle and adipose - catabolic
liver - stimulate gluconeogenesis and glycogen storage
overall - elevate plasma glucose levels
anti inflammatory/ immunosuppressive effects
role in adaptation to stress
What are the anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive effects of cortisol? (5)
stimulate production of lipocortin 1 (annexin1) - inhibits PLA2 (generates arachidonic acid), precursor for prostanoids & leukotrienes
Decrease number and activation of T-lymphocytes
Decrease production of cytokines (interleukins, TNF-a that recruit other inflammatory cells)
Stabilises lysosomes (reduces neutrophil bacterial killing processes)
Decrease NO production (reduce vasodilation)
Anti-inflammatory examples of use of glucocorticoid analogues
Asthma, COPD
Ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease
Rheumatoid arthritis
Skin conditions, e.g. eczema, psoriasis
Others, inc. rhinitis, conjunctivitis, local injections (joints/ soft tissue)….
Dexamethasone in ARDS
immunosuppression/replacement therapy examples of use of glucocorticoid analogues
Immunosuppression - organ transplantation
Replacement - Addison’s disease