Nervous system
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
224 Terms
nervous system embryology
develops from Ectoderm (week 3-4)
Nerural tube → CNS
Neural crest → PNS
Alar plate = sensory neurones
Basal plate = motor neurones
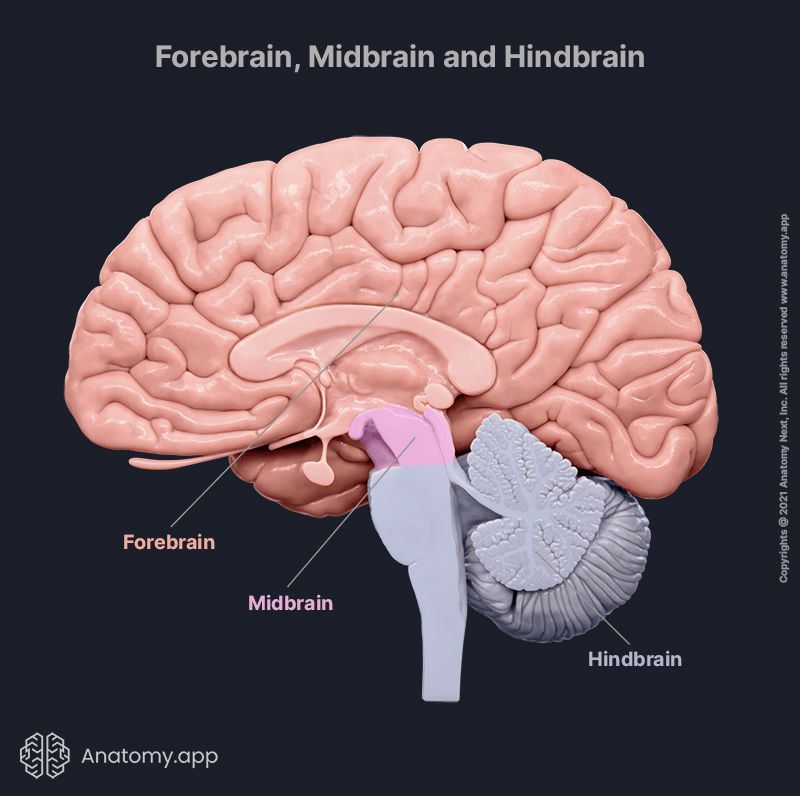
3 primary brain vesicles during embryonic development + further divisions
Prosencephalon (forebrain) → Cerebrum + diencephalon
Mesencephalon → Midbrain
Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain) → pons, cerebellum + medulla oblongata
Significance of Notochord
Arises from axial mesoderm day 16 (developed by w4)
determines orientation of vertebral column → via sonic hedgehog
evolves into nucleus pulposis
Stages of neurulation (development of neural tube)
1) ectoderm → thick neural plate
2) plate becomes long + narrow
3) neural plate → neural folds
4) fusion of neural folds (lateral apical surface) → neural tube
occurs week 3-4
What are Neural tube defects (NTDs) + risk factors
developmental defects of CNS → result of failed closure of the neural tube
folate deficiency
maternal obesity + diabetes
genetics
medications → sodium valproate, methotrexate
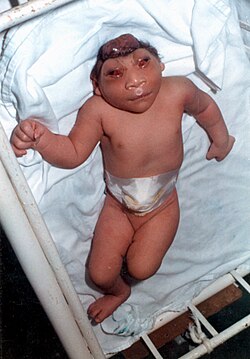
Anencephaly
Neural tube defect → failure of rostral neuropore to close
Infant born without most of brain, overlying skull + scalp, typically fatal
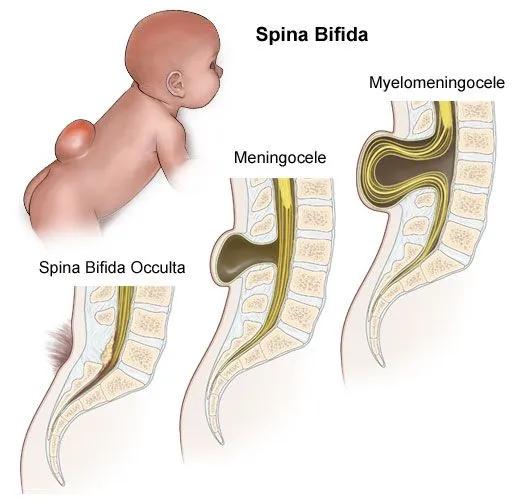
spina bifida pathology
most common NTD: failed caudal neuropore closure
abnormal vertebrae → meninges/spinal cord herniate through spinal canal
usually lumbosacral
3 classifications: occulta, meningocele, myelomeningocele (most severe)
spina bifida clinical presentations
lower limb weakness
deformities: hip dysplasia, club foot, scoliosis
Dysaesthesia
Incontinence
paralysis
spina bifida investigations + treatment
x-ray,CT, MRI
increased AFP in amniotic fluid (not in occulta)
surgery + physical therapy
Cerebral palsy pathophysiology
Neurodevelopmental disorder → non-progressive motor deficits (lesion to developing brain)
variation in severity + symptoms
Spastic (most common): damage to upper motor neurones = hypertonia + reduced function
Dyskinetic: damage to basal ganglia = involuntary movements
Ataxic: damage to cerebellum = incoordination
Mixed
Cerebral palsy causes
maternal infections - rubella, toxoplasmosis
Pre-term birth
IUGR
Meningitis
Severe neonatal jaundice
Clinical presentations of cerebral palsy
Failure to meet milestones
Hypo/hypertonia
Coordination, speech or walking problems
Learning difficulties
Difficulty feeding/swallowing
Cerebral palsy management
speech therapy
Occupational therapy
Physical therapy
Muscle relaxants/botulinum
Myasthenia Gravis pathophysiology
Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction → autoantibodies bind to nicotinic receptors
blocks Ach = no muscle contraction
classical complement pathway activated → inflammation = less Ach receptors
Clinical features of myasthenia gravis
muscle weakness
extraoptic → ptosis + diplopia
trouble breathing (resp acidois)
slurred speech
Myasthenia gravis investigations
Antibody tests: AchR, MuSK, LRP4
CT → thymoma
Electromyography
Edrophonium test: rapid onset cholinesterase inhibitor = prolonged Ach in neuromuscular junction
Myasthenia gravis management
cholinesterase inhibitors (pyridostigmine)
immunosuppressants (corticosteroids)
thymectomy
Multiple sclerosis pathophysiology
autoimmune demyelination of CNS → Type IV hypersensitivity
T cells break through blood brain barrier
Cytokines = inflammation + damage to oligodendrocytes
B cells + macrophage infiltration
Clinical features of MS
optical neuritis → unilateral reduced vision
Parasthesia
Ataxia
Lhermitte’s sign (electric shock travels down spine + limbs)
MS risk factors
EBV
Vitamin D deficiency
Smoking
Genetics
Obesity
MS investigations
CSF → oligoclonal bands
MRI → multiple hyperdense lesions/plaques
MS management
physical therapy
Corticosteroids
Interferon
Monoclonal antibodies
Guillain-Barre syndrome pathophysiology
Acute, post infection polyneuropathy → autoimmune demyelination of PNS (molecular mimicry)
myelin autoantigen presented to T helper cells
Production of cytokines → activate B cells + macrophages
Attack myelin sheath = affects nerve conduction velocity
Infections associated with guillain-barre syndrome
Campylobacter jejuni
EBV
Cytomegalovirus
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Clinical features of Guillain-Barre syndrome
reduced reflexes (areflexia)
Paraesthesia
Muscle weakness
Postural hypotension
Symmetrical ascending paralysis
Guillain-barre syndrome investigations
Brighton criteria:
nerve conduction studies
CSF → raised proteins
Guillain-barre syndrome management
supportive care
VTE prophylaxis (PE risk)
IV immunoglobulins
Plasmapheresis
Motor neurone disease (MND) + most common types
Group of degenerative disorders → progressive muscle weakness + disability
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Progressive bulbar palsy
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) pathophysiology
affects upper + lower motor neurones (sensory spared)
Superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) mutation = increased free radicals → neurone injury + death
C9orf72 mutation (40% cases)
Risk factors associated with MND
smoking
Heavy metal exposure
Pesticides
Genetics (5-10% cases)
Clinical presentations of ALS/MND
asymmetrical limb weakness
Mix of lower + upper motor neurone lesion signs
Wasting of hand muscles
Eye movements spared
MND investigations
History
Neurological exam
Muscle biopsy
Electromyography
ALS management
riluzole (slows progression)
Benzodiazepines
Antimuscarinics + antispasmodics (baclofen)
Non-invasive ventilation
Palliative care
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease pathophysiology
Autosomal dominant motor + sensory neuropathy
Genetic mutation = defective functioning proteins in myelin sheath/axon (PNS)
onset 10-30 y/o
Clinical presentations of Charcot-marie-tooth disease
muscle atrophy
Distal muscle weakness
Reduced reflexes (areflexia)
Foot abnormalities → pes cavus, foot drop
High stepping gait
Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome management
physical/occupational therapy
Analgesia
Orthotics
orthopaedic surgery
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease investigations
nerve conduction study
Genetic testing
Botulism pathology
clostridium botulinum → neurotoxin A,B,E + F
BoNT blocks Ach neurotransmitter signalling in peripheral alpha motor neurones
Clinical presentations of botulism
muscle weakness leading to paralysis
effects on ANS
dry mouth
postural hypotension
respiratory failure (severe)
Botulism management
botulinum antitoxin - A,B,E antibodies
supportive care
respiratory monitoring/ventilation
surgical treatment
What types of cells make up the nervous system
neurones (10%): react to stimuli, impulse conduction + emit chemical regulators
Neuroglia (90%): maintain ionic state, scaffolding + aid recovery/restructure + nourish neurones
What cells myelinate neurones in PNS + CNS
CNS → oligodendrocytes
PNS → schwann cells
Examples of neuroglia
astrocytes (CNS): maintain electrochemical environment
Microglia (CNS): form immune system of brain
Satellite (PNS): astrocyte equivalent
Where is CSF produced + reabsorbed
Ependymal cells → choroid plexus (3-500mls/day)
Reabsorbed via venous sinuses in arachnoid granulations
CSF functions
cushioning
Immune function
Nutrition
Homeostasis
Removes waste metabolites
Examples of excitatory neurotransmitters
Ach
Glutamate
Catecholamines
Serotonin (5-HT)
Histamine
ATP
Examples of inhibitory neurotransmitters
GABA
Glycine
Examples of both inhibitory + excitatory neurotransmitters
nitric oxide
Endocannabinoids
Neuropeptides
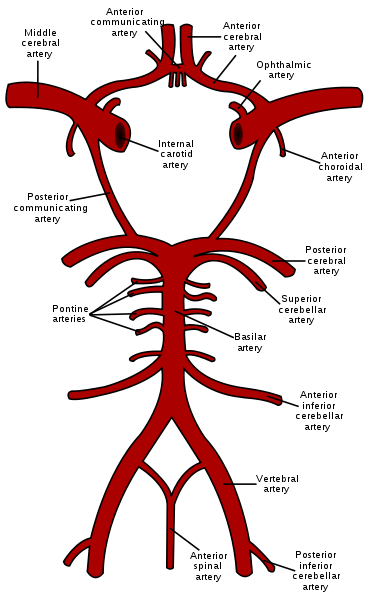
What arteries make up cerebral circulation
internal carotid (x2) → anterior circ.
Vertebral (x2) → posterior circ.
Anastamosis of terminal branches = circle of Willis
Receives 17% of total CO
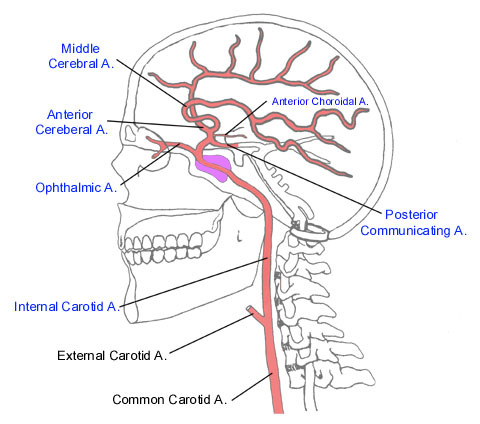
Internal cerebral artery entry + branches
ICA enters skull via carotid canal
Divides into anterior + middle cerebral arteries
Occurs after exiting cavernous sinus
What nerves are the ICAs in close proximity to
abducens
Ocularmotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal → ophthalmic + maxillary
Vertebral artery branches + entry
Arise from subclavian a. + pass up via transverse foramen
enters skull via foramen magnum
Divide → posterior inferior cerebellar + anterior spinal a.
VAs merge at ponto-medullar junction = basilar a.
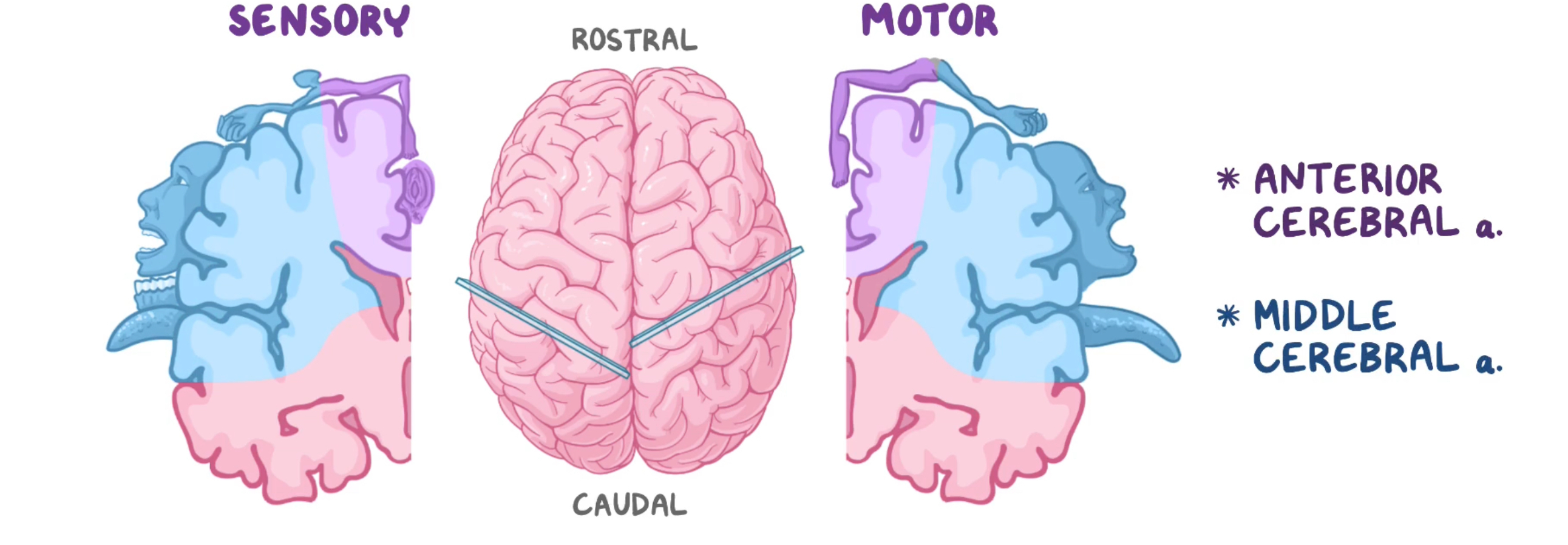
Cortical homunculus
visually portrays neurone distribution perceived within the brain → helps explain symptoms in stroke pts
motor: frontal lobe
Sensory: parietal lobe
How do cerebral veins differ
No valves → bidirectional blood flow possible
No muscular layer
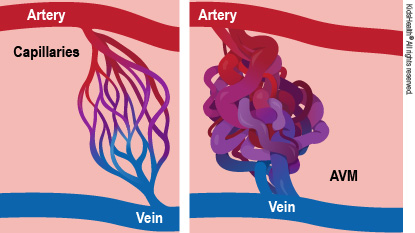
Arteriovenous malformation pathology
abnormal formation between artery + vein → no capillary bed
Arteriovenous fistula + nidus (tangled vessels)
Cont. high pressure = fibrosis of vessels
AVM expands + compressed surrounding tissue → reduced blood flow → ischaemia
Clinical presentations of AVM
Bruits on auscultation
Neurological deficits
Seizures/epilepsy
Severe headaches (indicates subarchnoid haemorrhage)
AVM investigations
angiography
CT/MRI
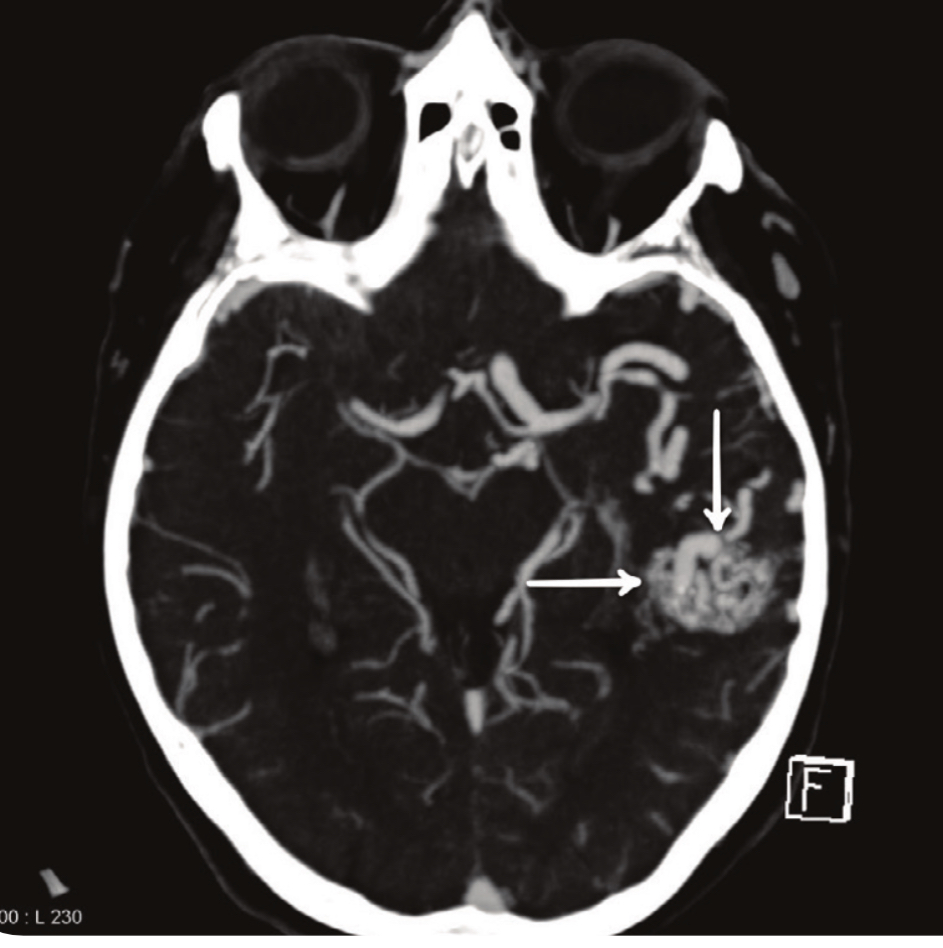
AVM treatment
radiosurgery
Endovascular embolization
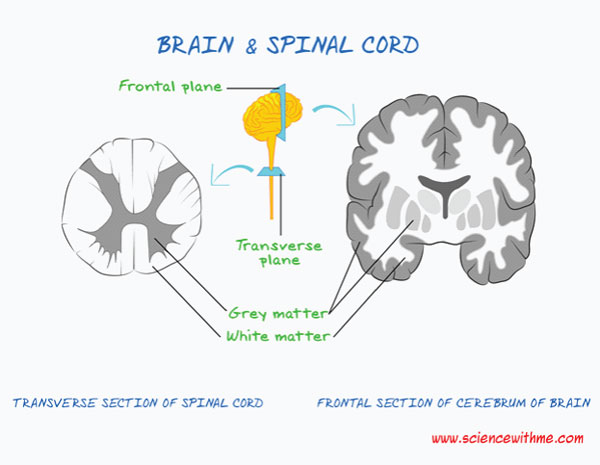
Grey vs white matter
grey: neurone rich region
White: myelinated axons
Meningeal layers (deep to superficial)
pia matter
Subarachnoid space
Arachnoid space
Dura matter
Types of sensory receptors
mechanoreceptors
Thermoreceptors
Nociceptors (pain)
Chemoreceptors
Photoreceptors
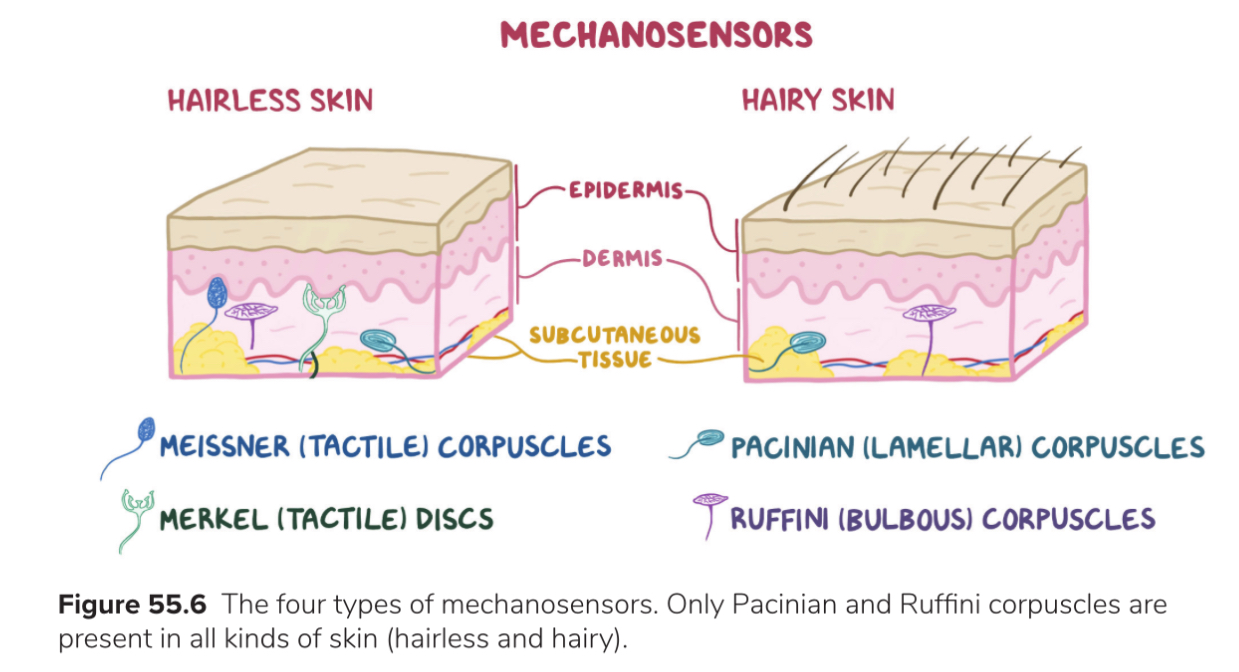
Types of mechanoreceptors: function + location
Meissner’s corpuscle: hairless dermis→ light touch (fingertips, lips, soles, palms)
Merkel’s discs: hairless epidermis → distinguish shapes + textures, pressure
Pacinian corpuscle: deep dermis, ligaments, joints → vibration
Ruffini’s corpuscle: dermis + joints → proprioception, stretching
Types of somatosensory fibres
A alpha: large myelinated = fastest → proprioception
A beta: large myelinated → vibration, fine touch
A delta: small myelinated = fast → sharp pain, gross touch, cold temp
C: unmyelinated= slowest → hot temp, gross touch
Adaptation of sensory receptors
Fewer signals sent in response to a continuous stimulus over time
fast/phasic: high sensitivity → firing stops quickly
Slow/tonic: constant sensitivity
What is lateral inhibition
1st order neurone releases inhibitory internurones = prevents multiple neurones firing
Thermoreceptors
detect changes in skin temp
TRP ion channels → heat transduction = TRPV, cold transduction= TRPM8
At extreme temps channels become inactive
Ascending somatosensory pathways + functions
dorsal column- medial lemniscal: conscious fine touch + proprioception
Spinothalamic: conscious crude touch + pressure (anterior), Sharp pain + temp (lateral)
Spinocerebellar: unconscious proprioception from muscles to cerebellum
Brown-Sequard syndrome pathophysiology
spinal cord hemisection
DCML → ipsilateral loss of fine touch + proprioception (decussates in medulla)
spinothalamic → contralateral loss of temp + pain (decussates in spinal cord)
Cauda Equina syndrome + causes
Compression/irritation of lumbosacral nerves below L2 (cauda equina)
disc herniation (most common)
spinal stenosis
spondylolisthesis
trauma
tumours
Cauda Equina syndrome clinical presentations
severe back pain
incontinence (reduced sphincter tone)
sexual dysfunction
lower limb weakness
saddle anaesthesia
Cauda Equina investigations + management
neurological exam + MRI
surgical decompression (w/in 48hrs)
NSAIDs + corticosteroids
Blood brain barrier
selective barrier → CNS homeostasis
nutrient passage, controlled fluid movement, toxin protection
permeability may change due to inflammation, tumours, irradiation
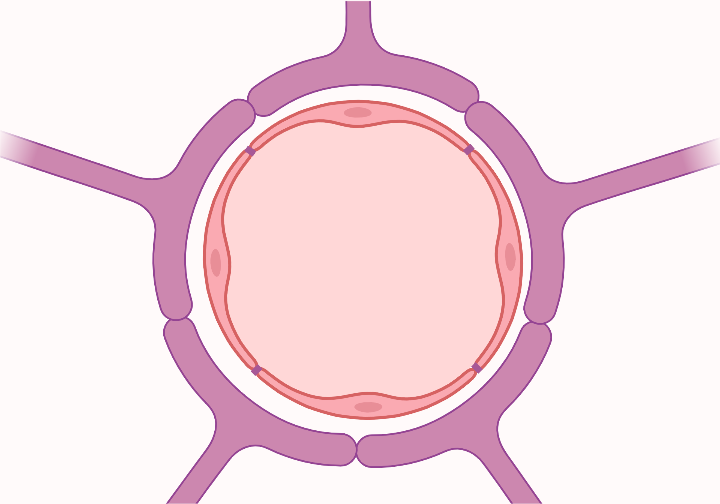
Blood brain barrier structure
tight junctions: between capillary endothelial cells
basement membrane
astrocytes: supporting structure
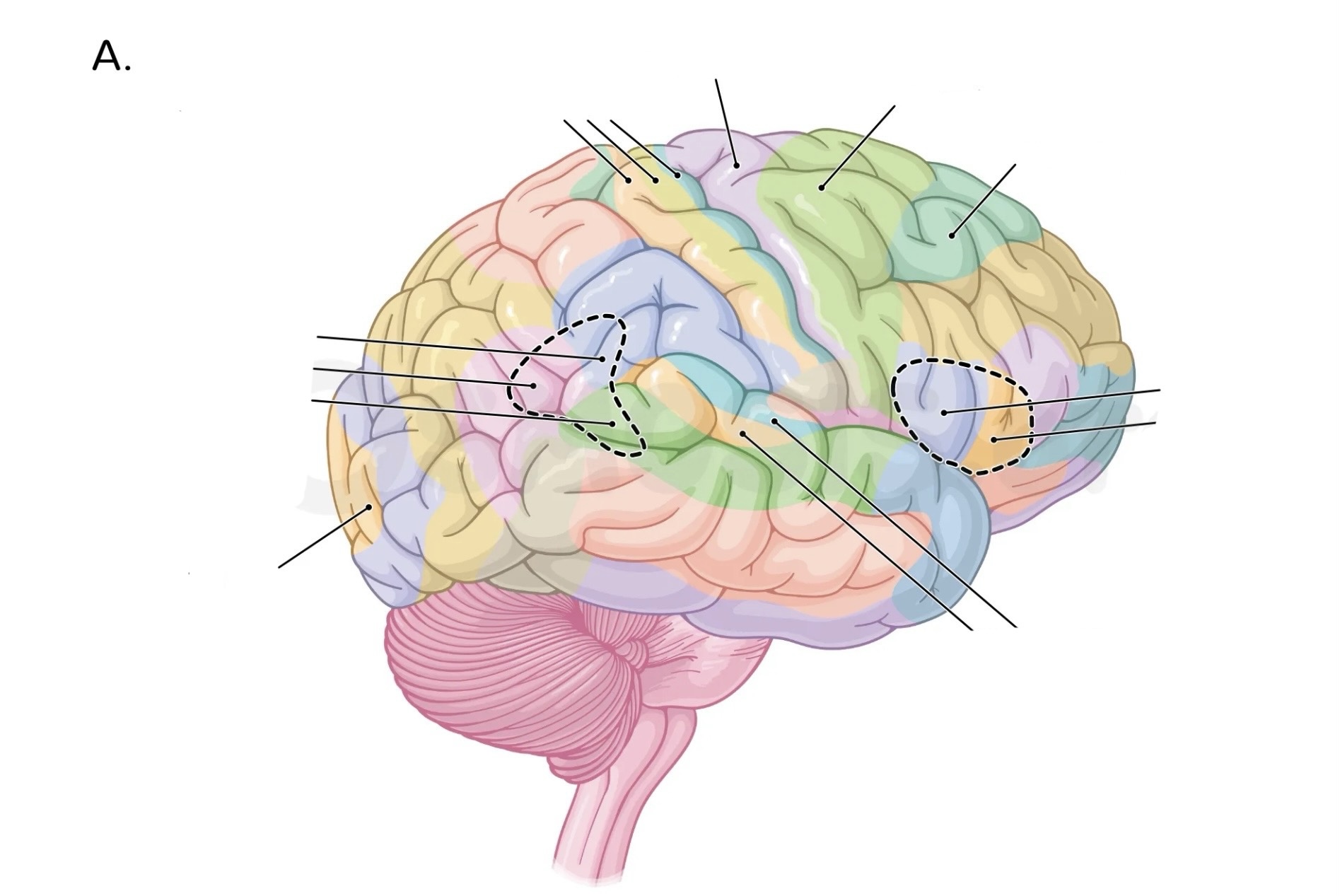
Brodmann’s areas
areas of brain that are histologically similar → neurones arranged in same pattern
Syringomyelia pathophysiology
CSF filled cyst around spinal cord central canal
Accumulated fluid = increased pressure
Causes damage to spinothalamic tract
Syringomyelia clinical presentations
loss of pain + temp
Loss of crude touch
Muscle atrophy
Weakness/paralysis
Dysethetic pain
Syringomyelia causes
chiari malformations (most common)
Spinal tumour
Spinal cord trauma
Spinal cord abscess
Primary headaches
Not assoc. with underlying condition → common, chronic/recurrent
tension
Cluster
Migraine
Secondary headaches
precipitated by a condition/disorder → acute
subarachnoid haemorrhage
Intracranial mass
Giant cell arteritis
Meningitis
Sinusitis
Tension headache clinical presentations + triggers
bilateral tightness → band like
Slowly progressive → 30min to 1 week
Stress, dehydration
Migraine clinical presentations
severe unilateral
Pulsating pain
Photophobia/phonophobia
+/- nausea + vomiting
+/- aura
4-72hrs
Cluster headache clinical presentations
Unilateral excruciating stabbing pain behind eye
15min-3hr
Autonomic symptoms on affected side → ptosis, miosis, lacrimation, nasal congestion
Red flag headache symptoms
New/sudden onset
Worsening severity
Increased frequency
Systemic symptoms → weight loss, fever
Neurological symptoms → weakness, vision loss
Hx trauma
Saccular/berry aneurysm pathology
Haemodynamic stress overtime = gradual ballooning of vessel wall
Thickening of intima + adventitia
Present at bifurication of arteries → anterior communicating most common
Rupture = subarachnoid haemorrhage
Allodynia pathology
pain in response to typically non-painful stimuli (eg light touch)
Central sensitisation: CNS amplifies signals → hypersensitivity
Persistent transmission of nociception = cortical reorganisation in sensory + motor regions of brain
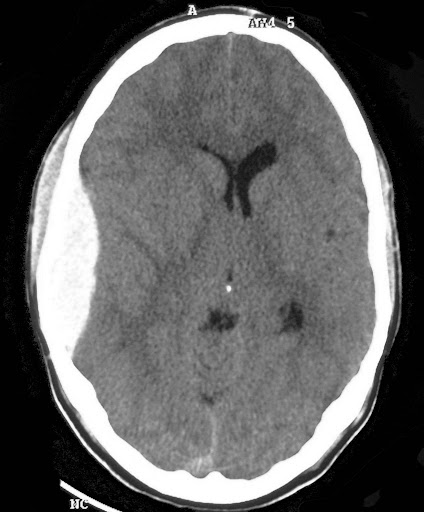
Extradural haematoma pathology
damaged blood vessel (middle meningeal a.)
Blood accumulates between skull + dura matter
Skull limits expansion = increased intercranial pressure
Slow accumulation → lucid interval
Biconvex shape on CT (doesn’t cross sutures)
Extradural haematoma clinical presentations
loss/decreased consciousness
Lucid state
Headache
Nausea/vomiting
Cushing’s triad → bradycardia, hypertension, irregular breathing
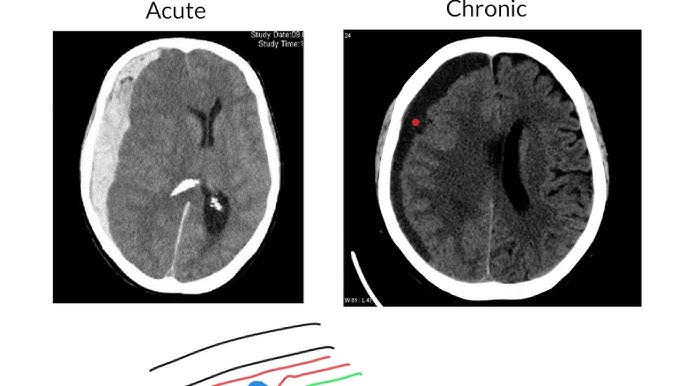
Subdural haemorrhage pathology
blood accumulates between dura + arachnoid matter
Ruptured bridging veins in subdural space → pooling (haematoma)
Acute = symptoms within 3 days, chronic = after 21 days
Crescent shaped on CT (can cross sutures)
Intracranial bleed investigations
CT
Angiography
Bloods→ FBC, U+Es, LFTs, coagulation, group + save
Lumbar puncture → blood/xanthochromia (subarachnoid haemorrhage)
Intracranial bleed management
craniotomy
Burr hole
Reverse anticoagulant (vitamin K)
Antihypertensives
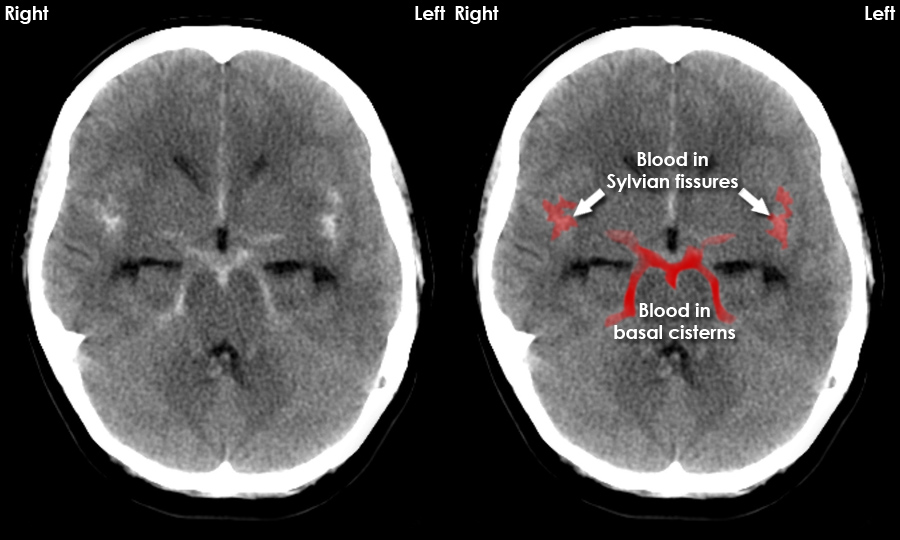
Subarachnoid haemorrhage pathology
bleeding in subarachnoid space
Blood released into CSF = increased intercranial pressure
Compresses surrounding blood vessels → less o2 delivered to brain
Subarachnoid haemorrhage clinical presentations
thunderclap headache (occiptial)
Altered mental status/consciousness
Nuchal rigidity
Seizures
Nausea/vomiting
intracranial bleed causes/risk factors
head trauma
Ruptured aneurysm (berry, cerebral)
Arteriovenous malformations
Alcohol abuse
Elderly
Coagulopathies
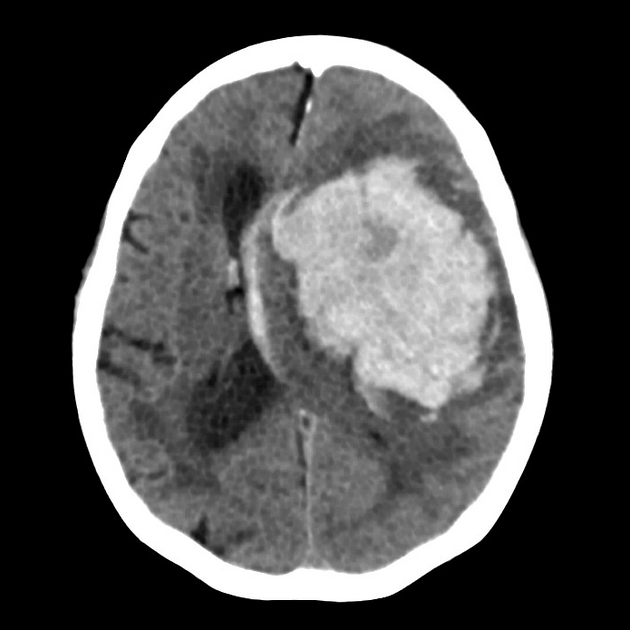
Intracerebral haemorrhage pathology
ruptured blood vessel w/ in cerebrum
Intraparenchymal accumulation (only in brain tissue) or intraventricular
Herniation on CT
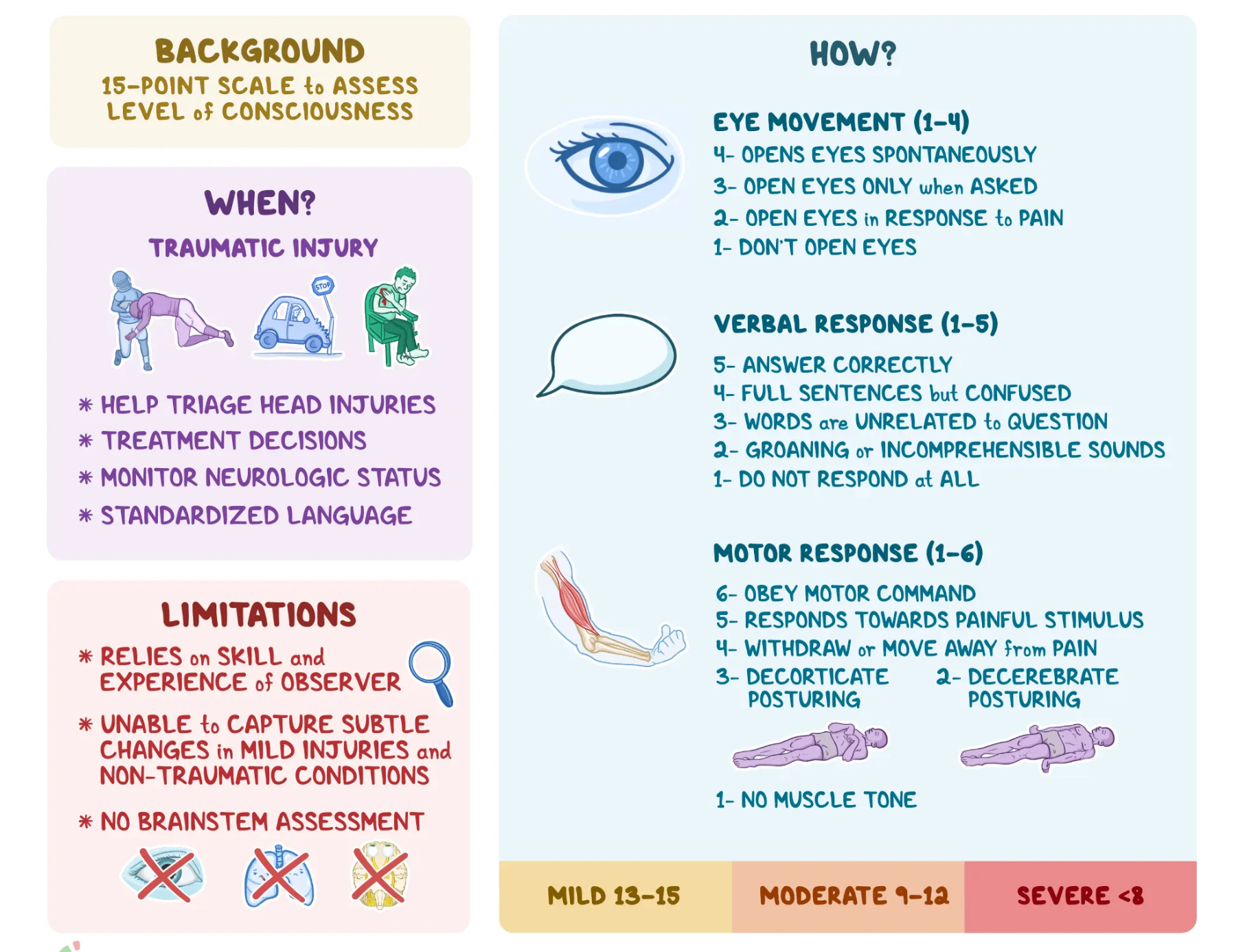
Glasgow coma scale (GCS)
Neurological assessment determines conscious level after brain injury (3-15)
eye movement
Verbal response
Motor response
Transient Ischaemic attack (TIA)
temporary neurological dysfunction (<24hrs) due to focal ischaemia without infarction
Blood vessel occlusion/stenosis = reduced blood flow
Crescendo: 2+ TIAs within a week
Stroke pathology
ischaemic: acute + complete artery occlusion → endothelial cell dysfunction/atherosclerosis or embolism/thromboembolism
Haemorrhagic (less common)
Decreased blood flow = hypoxia + infarction
Stoke risk factors/causes
atrial fibrillation
Smoking
Hypertension
Hyperlipidaemia
Diabetes
Carotid artery stenosis
Stoke clinical presentations (FAST)
facial drooping
Arm/limb weakness
Speech disturbances (dysphasia)
Visual field defects
Sensory loss
Stroke investigations
CT/diffusion weighted MRI
Angiography
ECG