structure and function of the Body
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
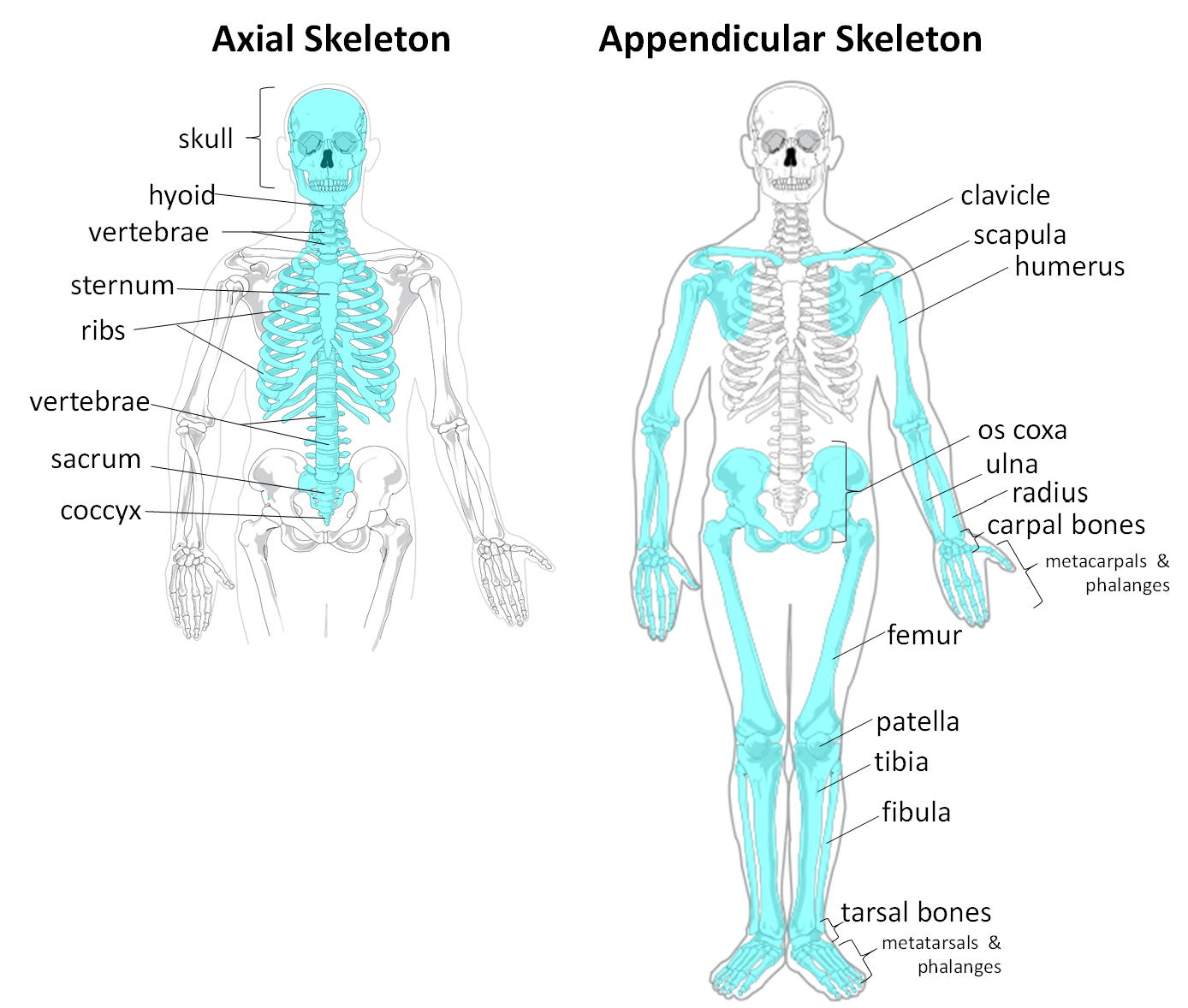
The skeletal system is divided into what two systems?
the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
Fibrous Joints
are a type of joint that connects bones with dense connective tissue without allowing movement. also known as Synarthroses.
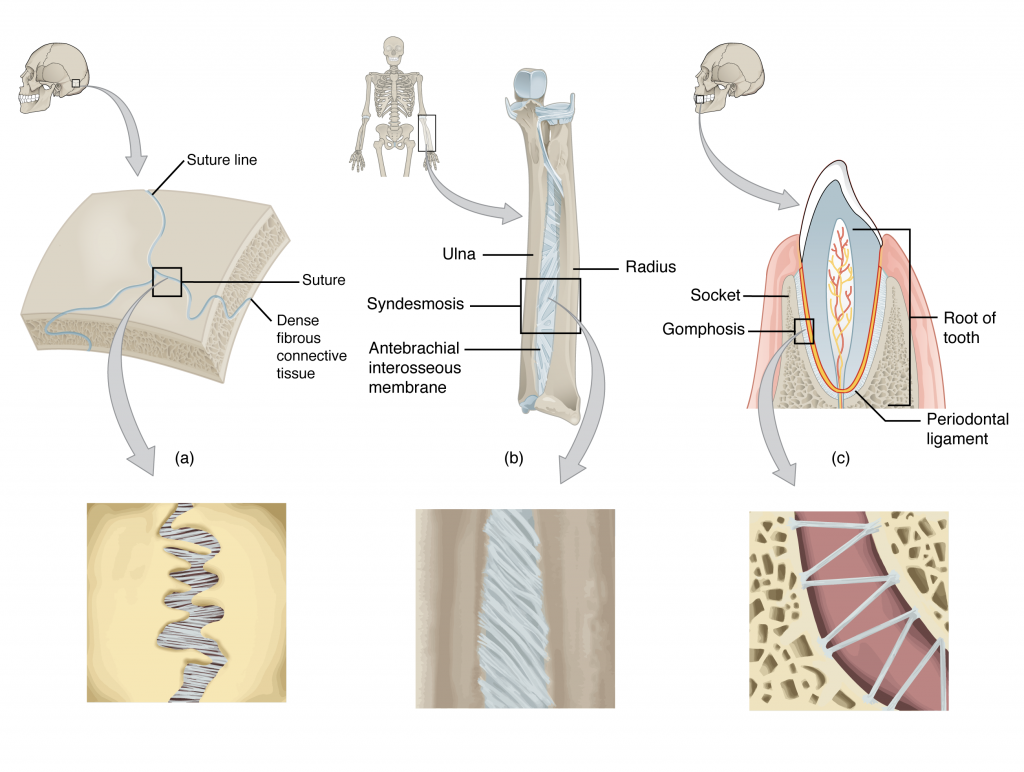
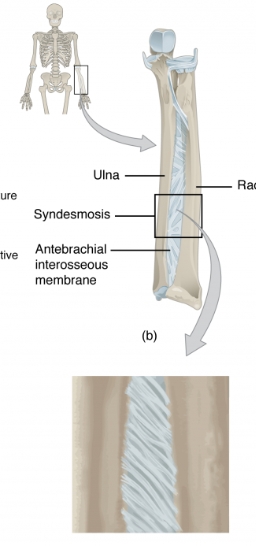
Syndesmosis
a type of fibrous joint in which two parallel bones are united to each other by fibrous connective tissue.
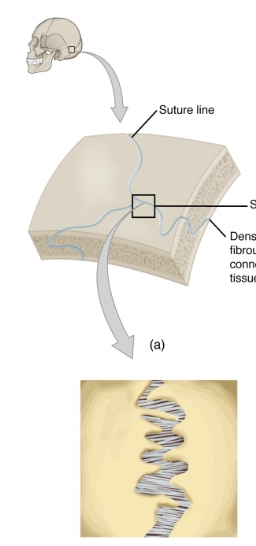
Suture
a type of fibrous joint found between the bones of the skull, allowing minimal movement and providing stability.
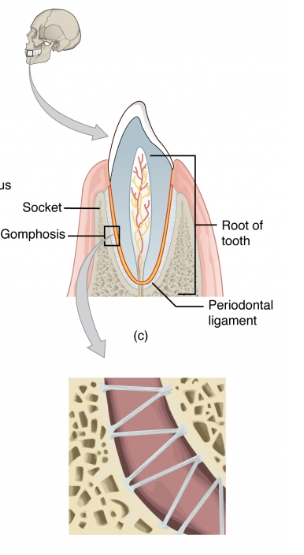
Gomphosis
a type of fibrous joint that anchors teeth to their sockets in the jawbone, allowing no movement.
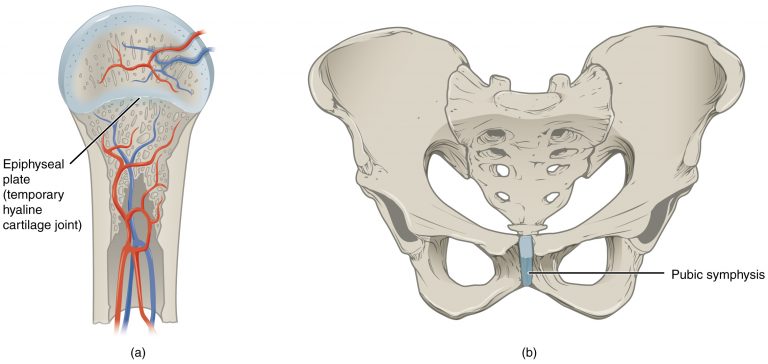
Cartilaginous Joints
types of joints where bones are connected by cartilage, allowing limited movement.
synovial Joints
allow free movement between the articulating bones.
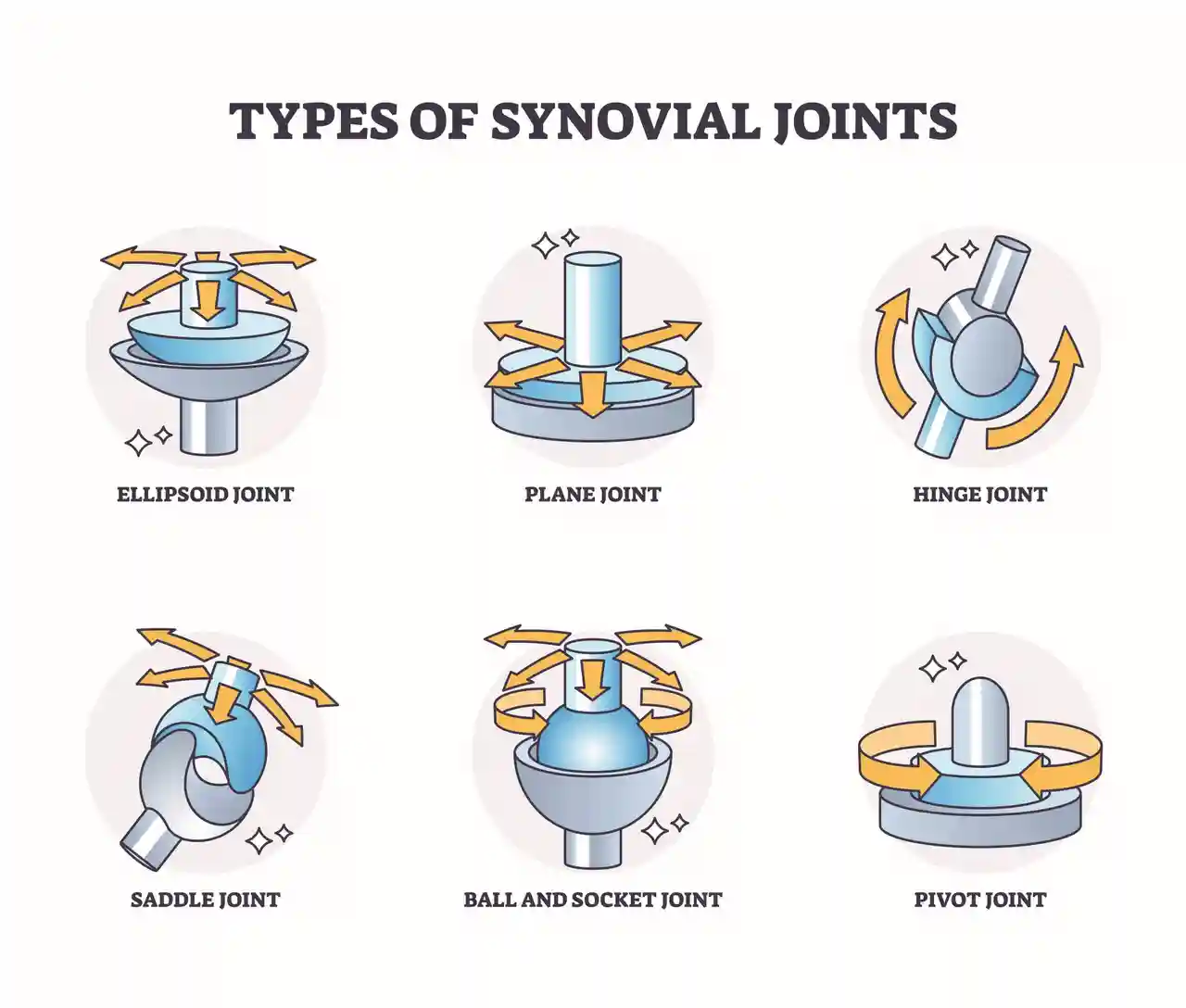
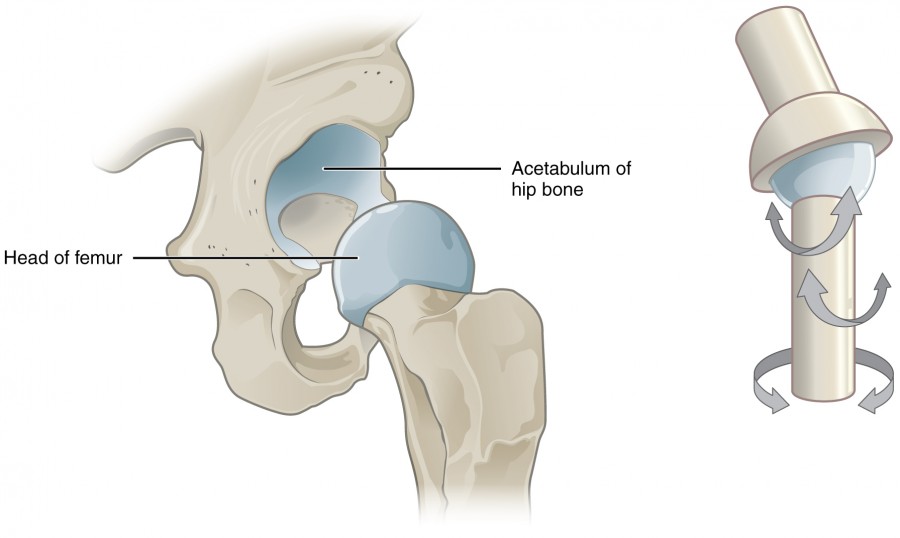
uniaxial Joints
a type of synovial joint that allows movement around only one axis, such as hinging or pivoting. examples include the elbow and knee.
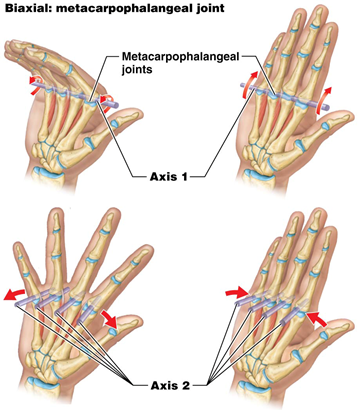
Biaxial Joints
a type of synovial joint that permits movement around two axes, allowing flexion and extension, as well as lateral movement. Examples include the wrist and knuckle joints.
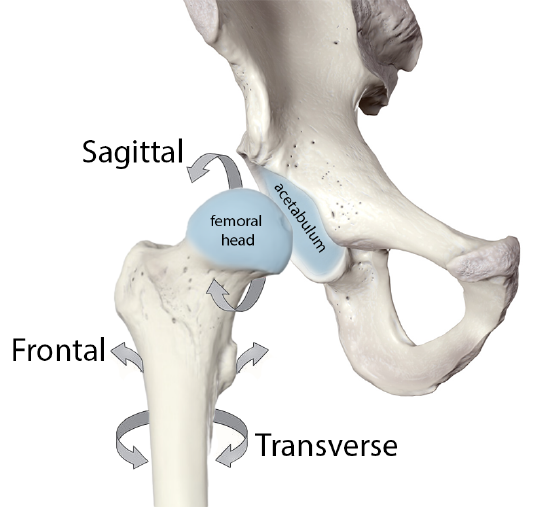
Multiaxial joints
type of synovial joint that permits movement in three anatomical planes (sagittal, frontal, and horizontal)
vertebral column
Cervical vertebrae
Thoracic Vertebrae
Lumbar Vertebrae
Sacral Vertebrae
Coccygeal vertebrae
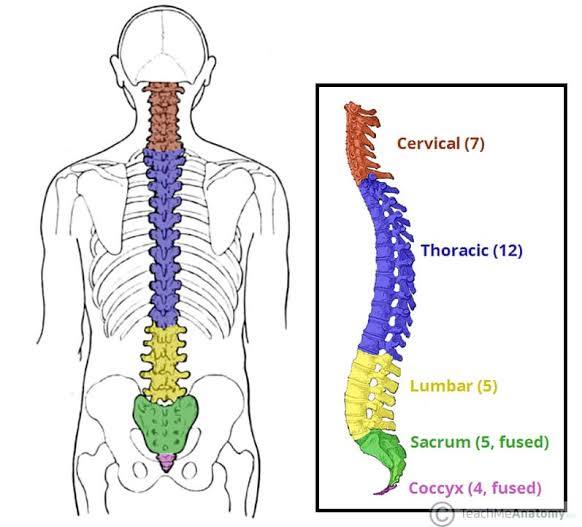
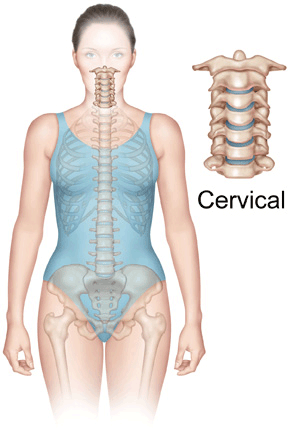
Cervical Vertebrae (neck Region)
the seven bones (C1-C7) that make up the neck region of the spine, starting below the skull and supporting the head and allowing neck motion
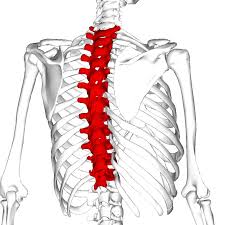
Thoracic Vertebrae
The thoracic spine consists of 12 vertebrae, labeled T1 through T12.
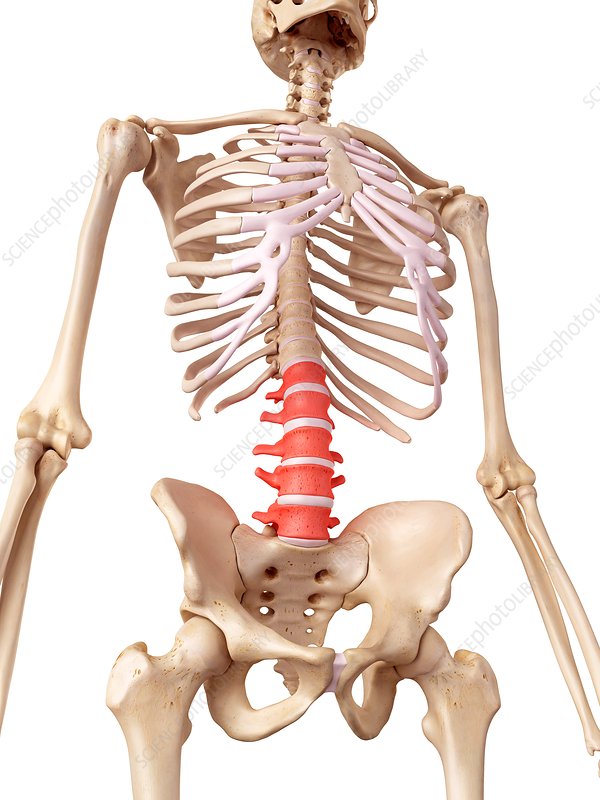
Lumbar Vertebrae
the five large bones that form the lower part of the human spine, numbered L1 through L5
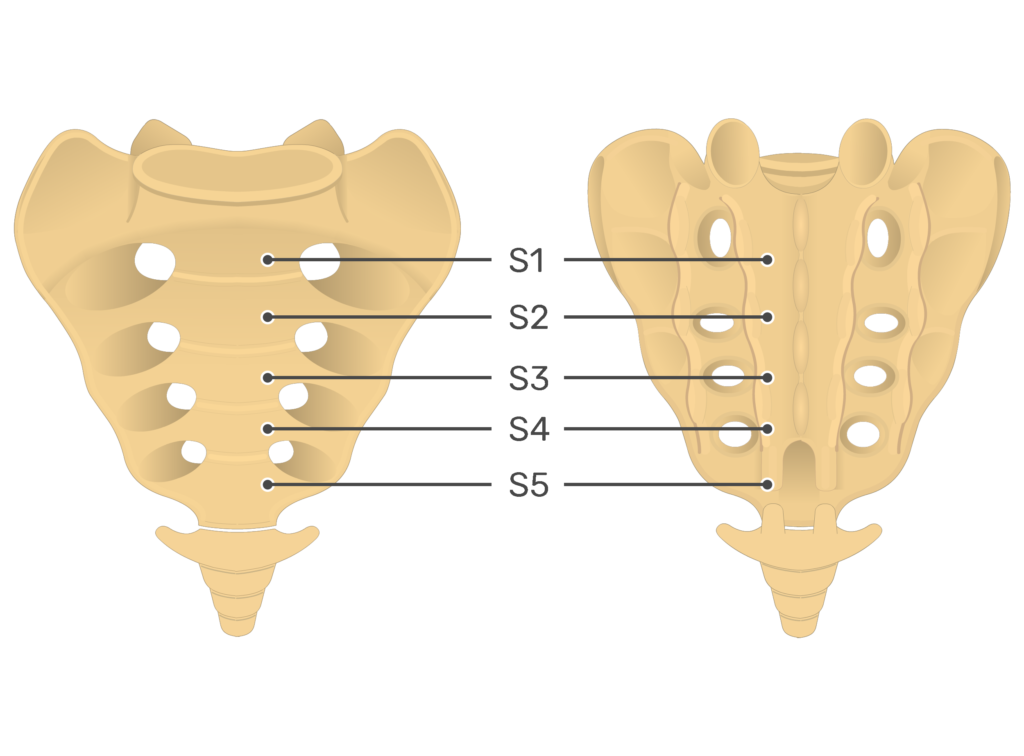
Sacral Vertebrae
five individual vertebrae in the human spine that fuse together after puberty to form a single, triangular bone
Coccygeal Vertebrae
The 3 to 5 fused segments at the very end of the human vertebral column provide attachment points for pelvic muscles and ligaments and supporting the body in a seated position.
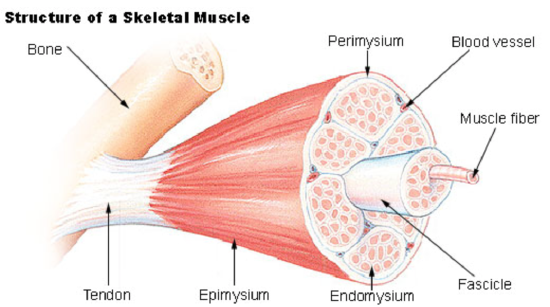
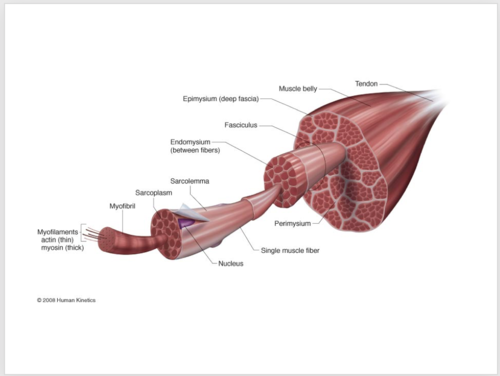
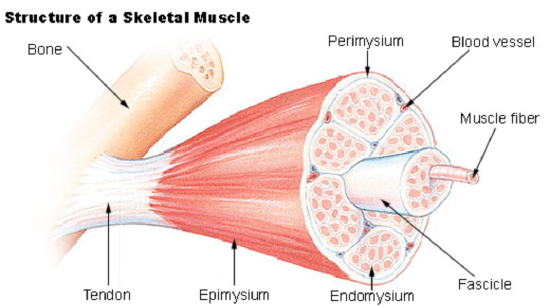
muscular system
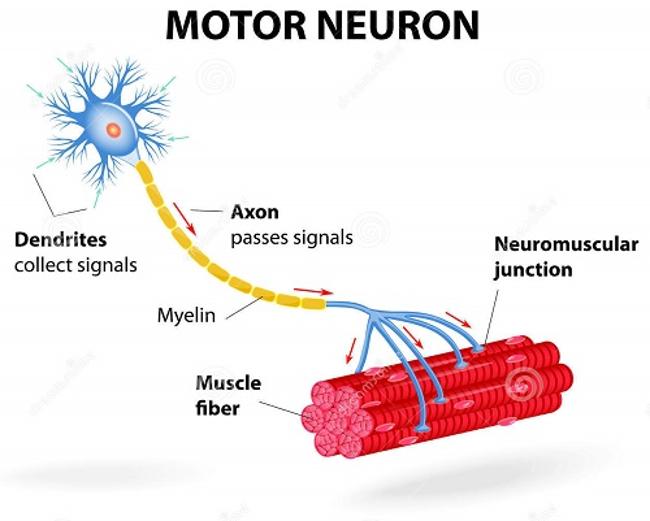
motor unit
the functional unit of a muscle, consisting of a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates
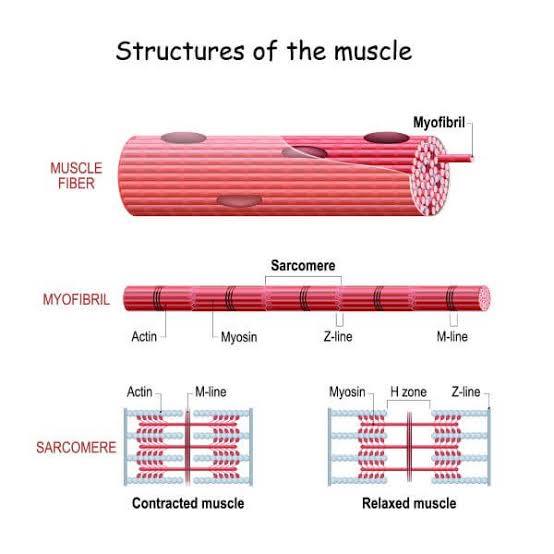
muscle Fiber
a single, long, cylindrical cell that is the fundamental contractile unit of skeletal muscle
Myosin and actin
two key protein filaments crucial for cell movement and muscle contraction