Slideshow 1 (Regions of Body and Directional Terms) [BIOL2813]
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the levels of composition in the human body (in order)?
1. Atoms and ions
2. Molecules
3. Cells
4. Tissue
5. Organs
6. Systems
7. Whole body
What are the systems of the human body?
1. Integumentary
2. Skeletal
3. Musculature
4. Nervous
5. Endocrine
6. Cardiovascular
7. Lymphatic
8. Respiratory
9. Digestive
10. Urinary
11. Reproductive
What is homeostasis?
the tendency towards a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements (systems in the body)
What are the components of a homeostatic mechanism?
1. Sensor/Receptor (nervous tissue)
2. Control centre (brain or spinal cord)
3. Effector (a muscle or gland)
What does a sensor/receptor do in homeostasis?
detects an internal or external change
What does a control centre do in homeostasis?
integrates information from receptors and determines the appropriate response
What does an effector do in homeostasis?
carries out the decided response to the change
What is negative feedback?
a process which works to counteract a stimulus in order to return to homeostatic conditions
What is positive feedback?
a process which works to intensify a stimulus, moving further from homeostasis
Frontal/coronal plane
divides the body into front and back portions
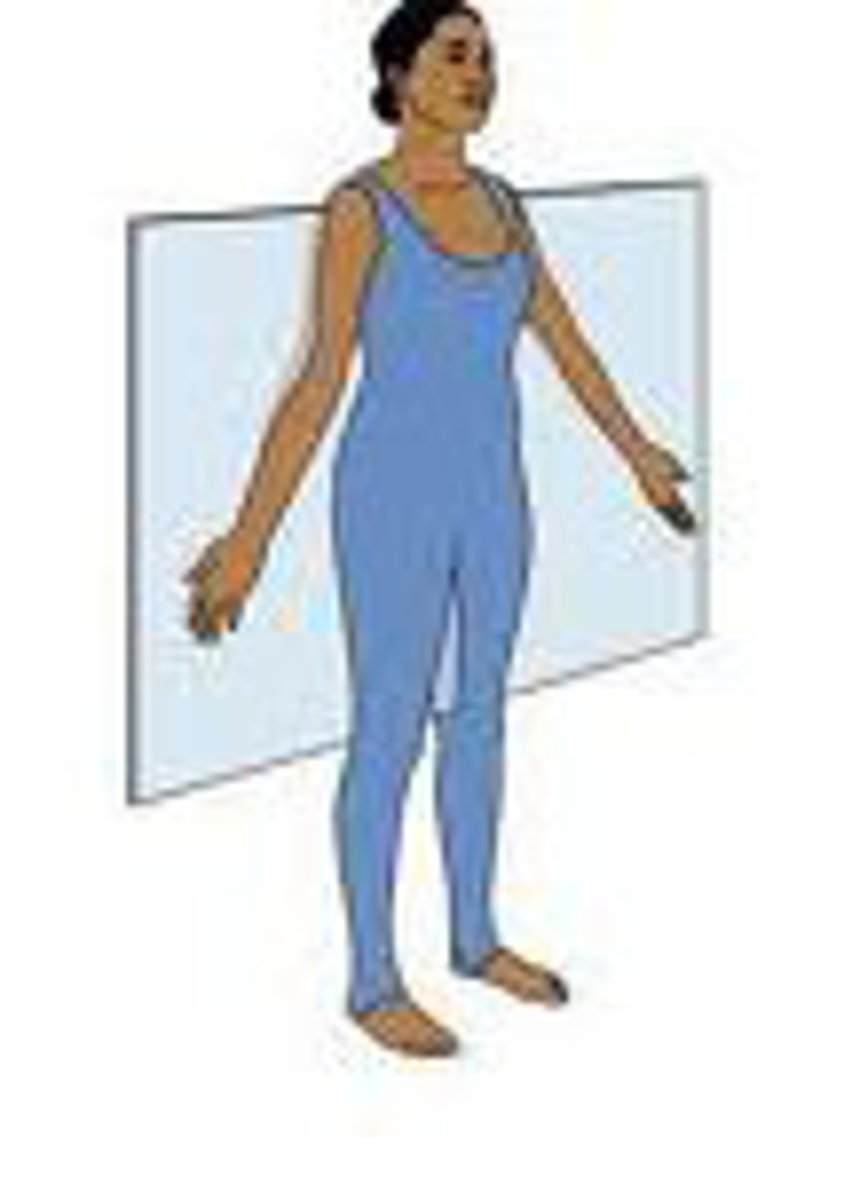

Sagittal plane
divides the body into left and right portions
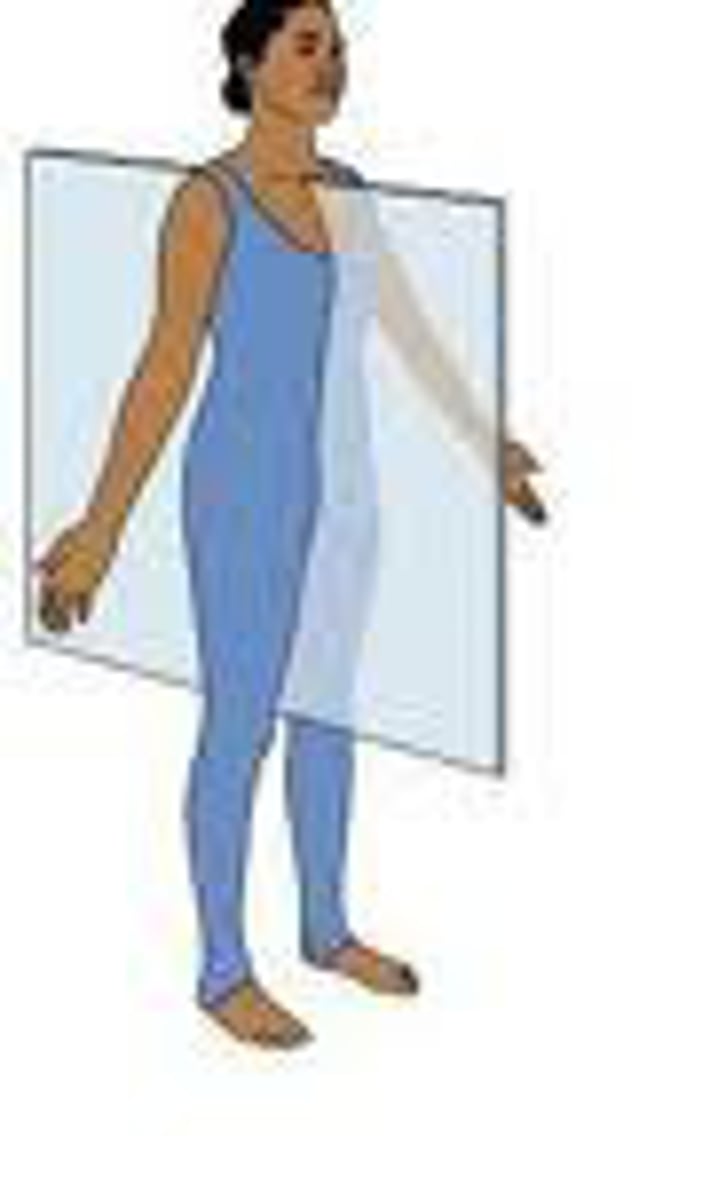
Transverse plane
divides the body into upper and lower portions
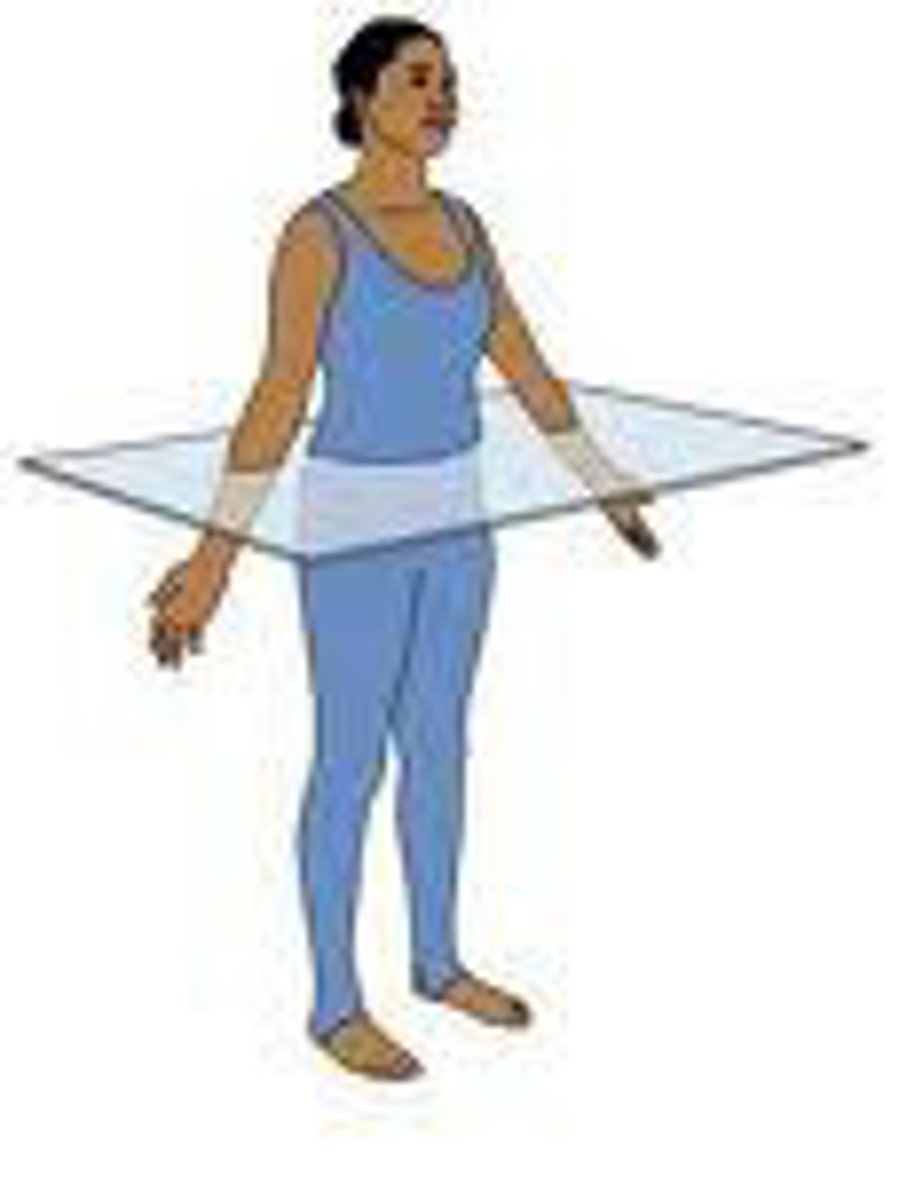
What is a body cavity?
fluid-filled spaces within the body that serve to protect, separate, and support internal organs
What are the largest cavities in the body?
the dorsal (posterior) and ventral (anterior) cavities
What sub-cavities are in the dorsal cavity?
1. cranial
2. vertebral (spinal)
What sub-cavities are in the ventral cavity above the diaphragm?
1. thoracic (contains pleural and pericardial cavities)
What sub-cavities are in the ventral cavity below the diaphragm?
1. abdominal (peritoneum)
2. pelvic
What are membranes?
sheets of epithelial tissue supported by connective tissue
What do mucous membranes do? Where are they found?
absorb (digestive), filter (respiratory), or lubricate (reproductive). Found in passageways that open to the exterior of the body (respiratory, digestive, reproductive, and urinary)
What do serous membranes do? Where are they found?
line cavities and excrete fluid to lubricate organs. Found in pericardial, pleural, and peritoneum cavities.
What do synovial membranes do? Where are they found?
secrete fluid for lubrication. Found in freely moving joints
What do cutaneous membranes do? Where are they found?
provide a relatively thick, waterproof layer for protection. Is found surrounding the entire body (skin)
What are the regional names for:
1. the head
2. the skull
3. the face
4. the neck
5. the forehead
1. cephalic
2. cranial
3. facial
4. cervical
5. frontal
What are the regional names for:
1. the temple
2. the eye
3. the ear
4. the cheek
5. the nose
1. temporal
2. orbital/ocular
3. otic
4. buccal
5. nasal
What are the regional names for:
1. the mouth
2. the chin
3. the breastbone
4. the armpit
5. the breast
6. the shoulder
1. oral
2. mental
3. sternal
4. axillary
5. mammary
6. acromial
What are the regional names for these parts of the Trunk:
1. chest
2. abdomen
3. pelvis
1. thoracic
2. abdominal
3. pelvic
What are the regional names for:
1. the (upper) arm
2. the back of the elbow
3. the forearm
4. the wrist
5. the palm
6. the fingers
7. the hand
8. the thumb
1. brachial
2. antecubital
3. antebrachial
4. carpal
5. palmar/volar
6. digital/phalangeal
7. manual
8. pollex
What are the regional names for:
1. the navel
2. the hip
3. the groin
4. the pubis
1. umbilical
2. coxal
3. inguinal
4. pubic
What are the regional names for:
1. the thigh
2. the anterior surface of the knee
3. the (lower) leg
1. femoral
2. patellar
3. crural
What are the regional names for:
1. the foot
2. the ankle
3. the toes
4. the top of the foot
5. the big (great) toe
1. pedal
2. tarsal
3. digital/phalangeal
4. dorsum
5. hallux
What are the regional names for:
1. the base of the skull
2. the shoulder blade
3. the spinal column
4. the back
5. the loin
6. the space between the hips (at the top of the butt)
7. the buttock
8. the region of the anus and external genitals
1. occipital
2. scapular
3. vertebral
4. dorsal
5. lumbar
6. sacral
7. gluteal
8. perineal
What are the regional names for:
1. the hollow behind the knee
2. the calf
3. the sole of the foot
4. the heel of the foot
5. the back of the elbow
6. the back of the hand
1. popliteal
2. sural
3. plantar
4. calcaneal
5. dorsum
What are the directional terms for:
1. upper (non-extremity)
2. lower (non-extremity)
1. superior/cephalic/cranial
2. inferior/caudal
What are the directional terms for:
1. upper (extremity)
2. lower (extremity)
1. proximal
2. distal
What are the directional terms for:
1. towards the front of the body (usually non-extremity)
2. towards the back of the body (usually non-extremity)
1. anterior (ventral)
2. posterior (dorsal)
What are the directional terms for:
1. towards the left or right side of the body
2. towards the middle of the body
1. lateral
2. medial
What are the directional terms for:
1. towards the surface of the body
2. towards the inside of the body
1. superficial (external)
2. deep (internal)
What are the directional terms for:
1. on the same side
2. on the opposite side
1. ipsilateral
2. contralateral
What is the directional term for:
1. between
1. intermediate