4.1.8.8 government intervention in markets
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the reasons for government intervention in markets?
Reduce negative externalities
Increase or maximise positive externalities
Increase the supply of merit goods
Reduce the supply of demerit goods
Supply public goods undersupplied by the market
Why is it important to reduce inequalities in the distribution of income and wealth?
Unequal distribution lead to poverty
Tensions in society created
A breakdown in society can cause further market failure
Why do Governments intervene in order to support UK industry?
Full employment is a government target
Certain industries are more important than others as they employ large amounts of labour
Infrastructure is essential if business are to provide quality services
What do Governments influence the allocation of resources through?
Public expenditure:
government spending to pay for the needs of society such as health, education, infrastructure etc.
Taxation and subsidies:
making it more expensive for products that cause high negative externalities and cheaper for those that cause positive externalities
Regulation:
protecting consumers from exploitation of monopoly power that would lead to higher prices, supernormal profits and allocative inefficiency
creating an environment that will encourage firms to strive for productive efficiency through reduced costs
How is economic growth like as a key objective?
▪ Job creation
▪ Rising incomes
▪ Improved standards of living
▪ Improved international competitiveness of UK economy
▪ Improved confidence of consumers to spend
▪ Improved confidence of business to invest
▪ Lower government spending on job seekers allowance and associated
benefits
▪ Tax revenues are likely to increase allowing the government to re-invest
in infrastructure or spend on public services
How is Reducing Unemployment as a key objective?
• Higher demand
• Higher incomes
• Improved standards of living
• Higher tax revenue for government
• Lower government spending on unemployment related welfare
• Improved productivity of UK economy
• Reduced poverty
• Social benefits (reduced crime, improved wellbeing)
• Increased spending might impact on merit goods as it will probably
directed at the NHS and education
How is Inflation as a key objective?
• Inflation is important because it affects the value of money in your pocket, workers wage demands and consumer confidence
• High, or rising inflation, damages the real value of money and erodes spending power
• An inflation target of 2% has been set by the government
• Reducing demand will impact on inflation but might lead to less spending on merit goods
There are a number of ways in which governments can intervene
to correct market failure
These include:
Indirect taxation
Subsidies
Price controls
State provision
Regulation
What is taxation?
charge imposed on products, individuals and businesses
What is an indirect tax?
What is a direct tax?
What is the incidence of tax?
An indirect tax is a tax on a good or a service.
A direct tax is a tax on an individual or an organisation.
amount that the consumer (or producer) will pay for the tax.
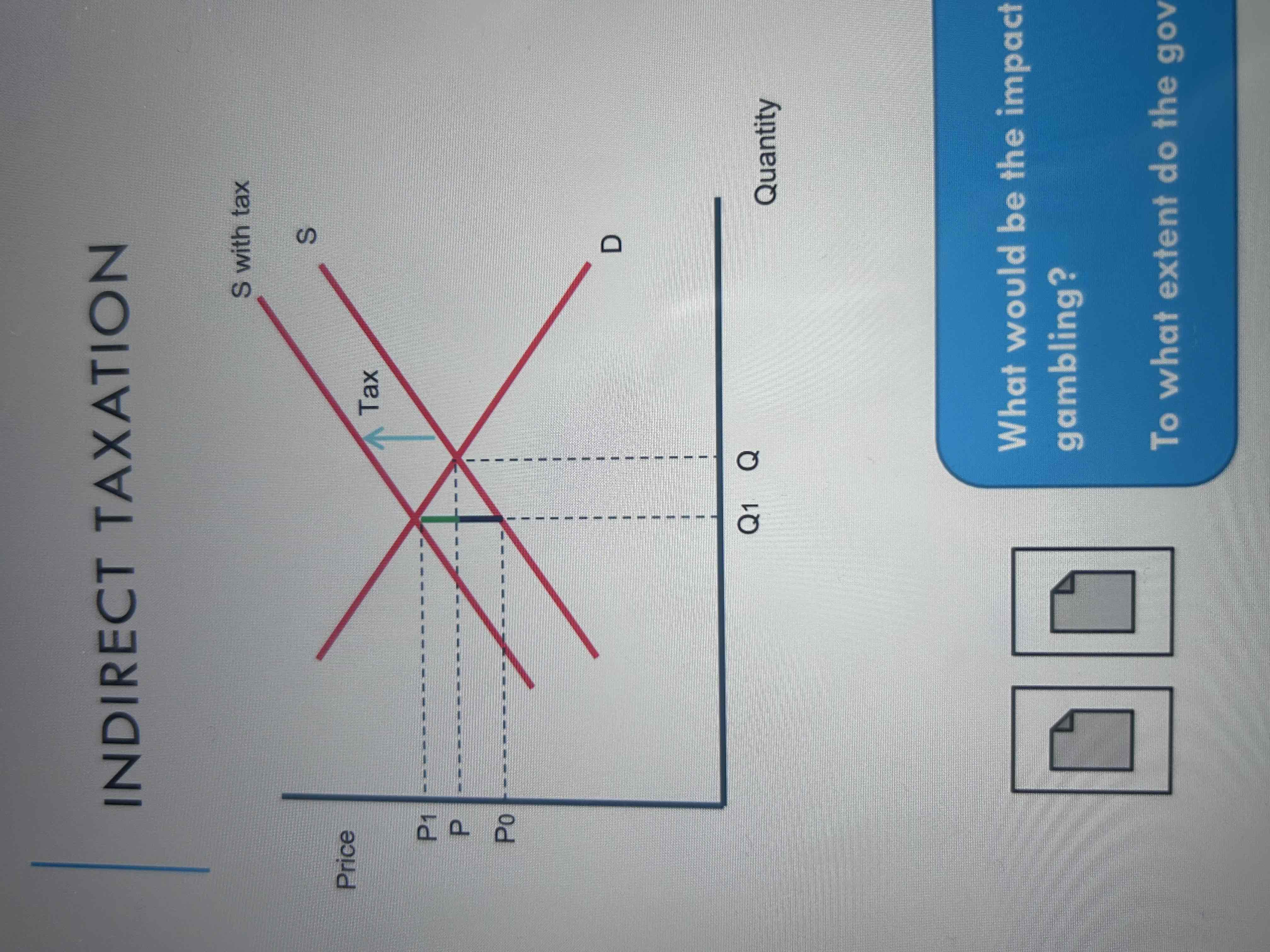
Show indirect taxation on a AD/AS diagram
The imposition of an indirect tax will lead to an increase in the cost of supply for a firm.
This will lead to a shift in the supply curve up and to the left.
Quantity supplied will decrease by Q-Q1. P will increase from P to P1.
The increase in tax has caused the price to rise by the vertical distance between the supply curves.
The incidence (amount) of the tax paid for by the producer is shown by the blue line (equivalent to P-P0).
The incidence of the tax paid for by the consumer is shown by the green line (P1-P).
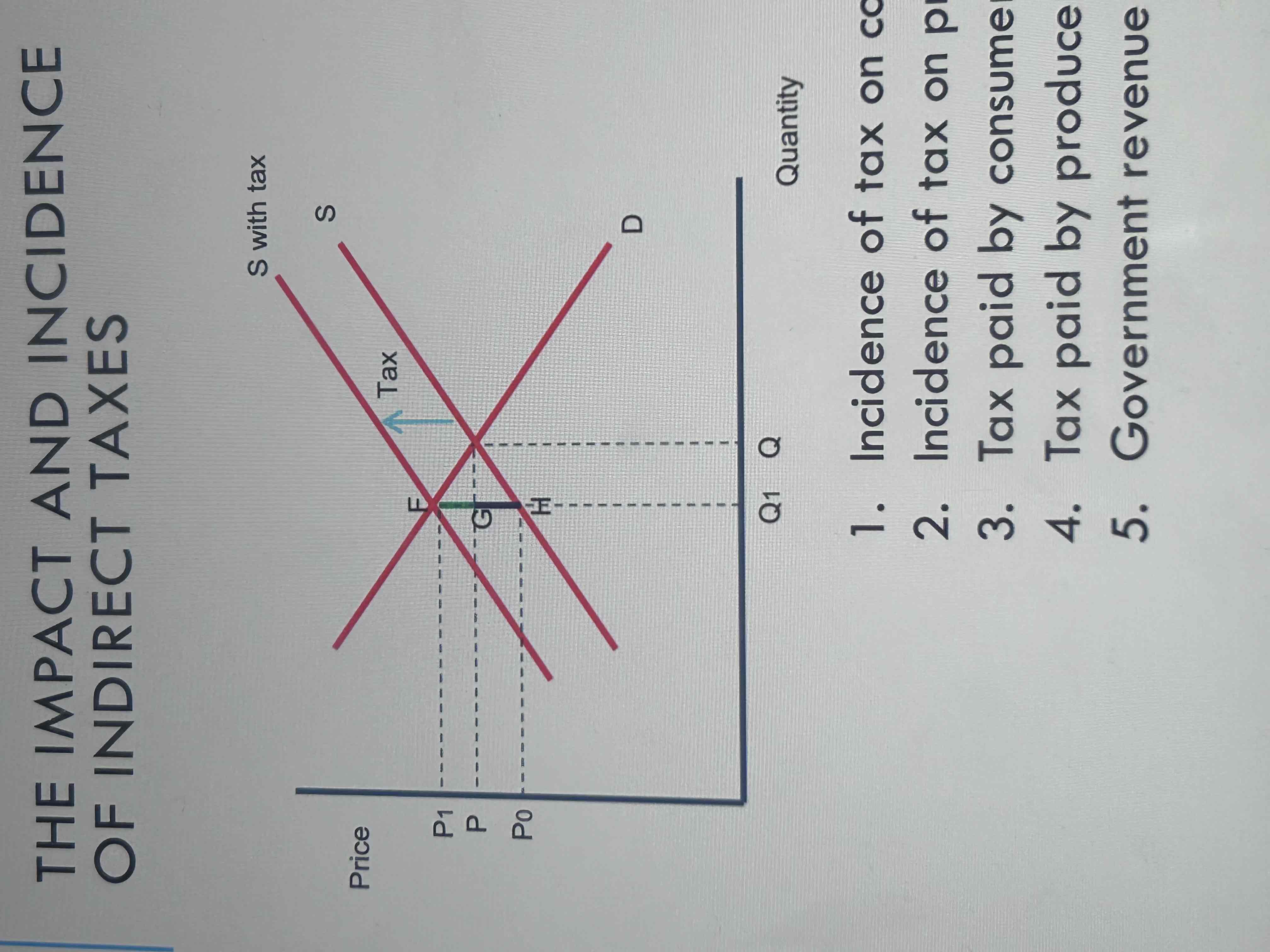
Label this diagram
1. Incidence of tax on consumers = 𝐹 𝐺
2. Incidence of tax on producers = 𝐺 𝐻
3. Tax paid by consumers = 𝑃 1 𝐹 𝐺 𝑃
4. Tax paid by producers = 𝐺 𝑃 𝑃0 𝐻
5. Government revenue from tax = 𝑃 1 𝐹 𝐻 𝑃0
How can you use the previous diagram to show govt revenue?
sum of tax paid by consumers and tax paid by producers
THE IMPACT AND INCIDENCE OF INDIRECT TAXES
If demand is price inelastic the incidence of the tax will be greater for the consumer.
Draw a diagram showing the incidence of tax with an inelastic demand curve
EF>FG
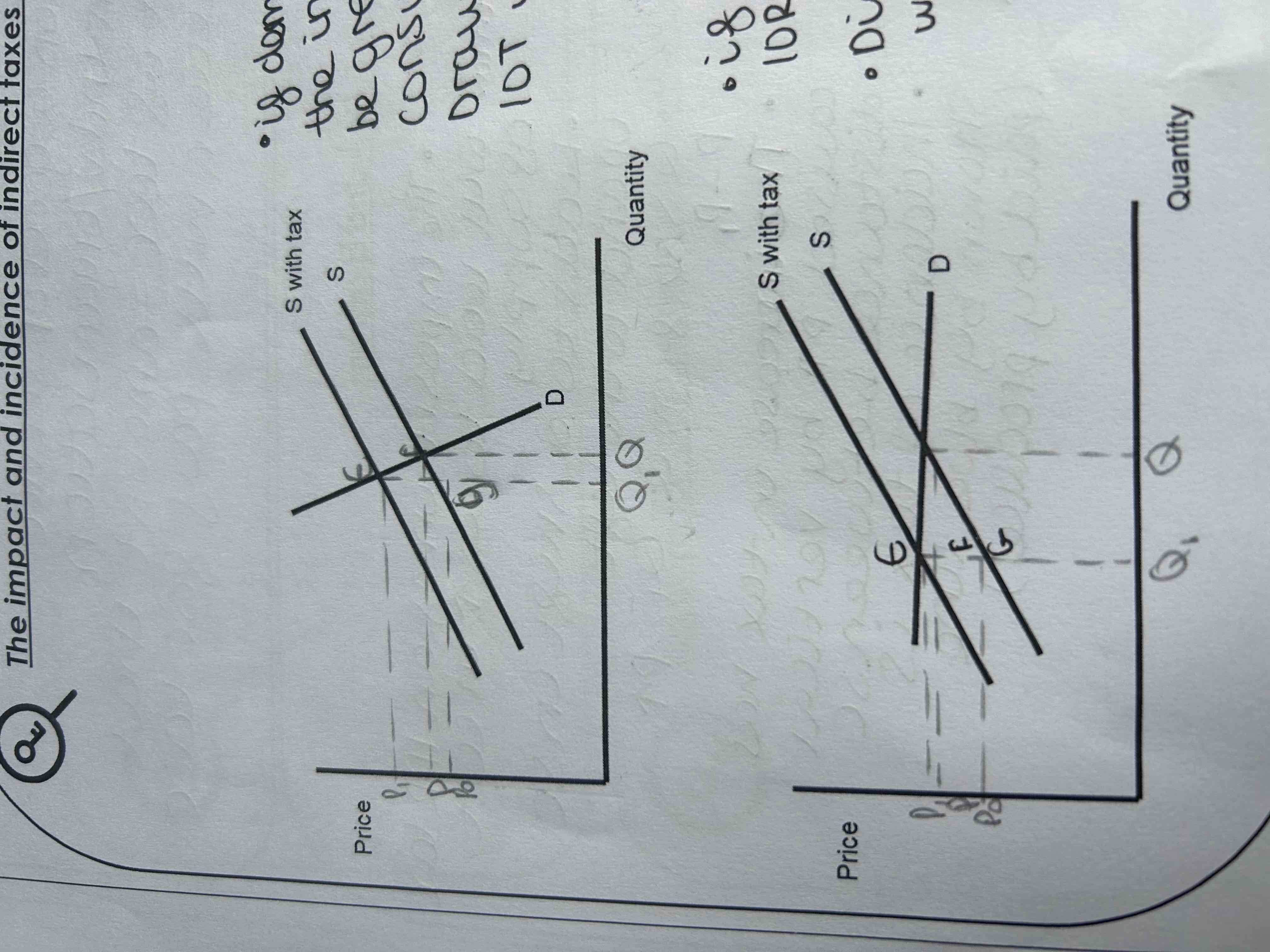
If demand is price elastic the incidence of the tax will be greater for the producer.
Draw a diagram showing the incidence of tax with an elastic demand curve.
FG>EF
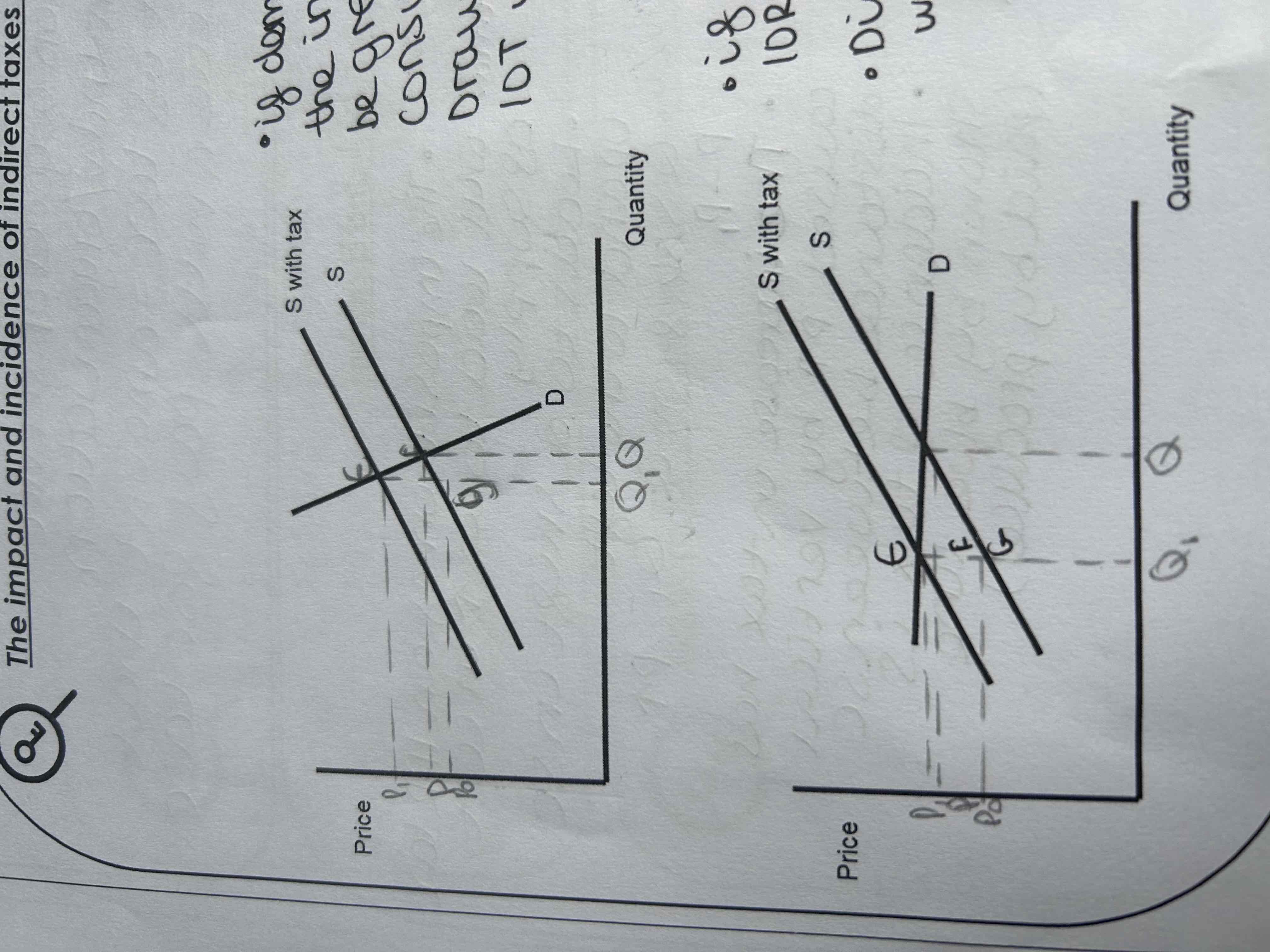
If supply is price inelastic the incidence of the tax will be greater for the producer.
Draw a diagram showing the incidence of tax with an inelastic supply curve.
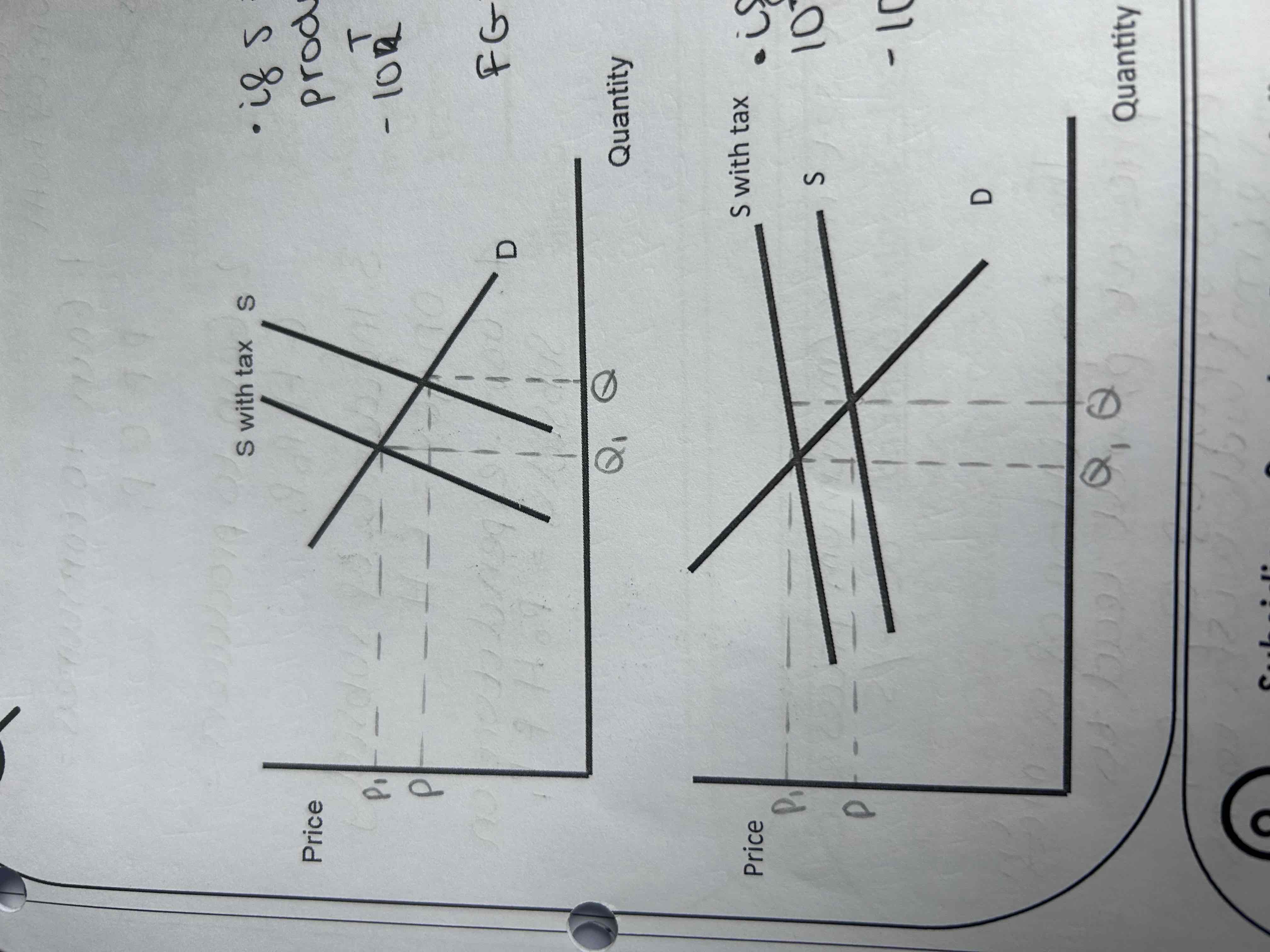
If supply is price elastic the incidence of the tax will be greater for the consumer.
Draw a diagram showing the incidence of tax with an elastic supply curve.
Demand is price elastic if…
a change in price leads to a bigger % change in demand.
Demand is price inelastic when…
a change in price causes a smaller % change in demand.
Supply is price elastic if…
a change in price leads to a bigger % change in demand.
Supply is price inelastic when…
a change in price causes a smaller % change in demand
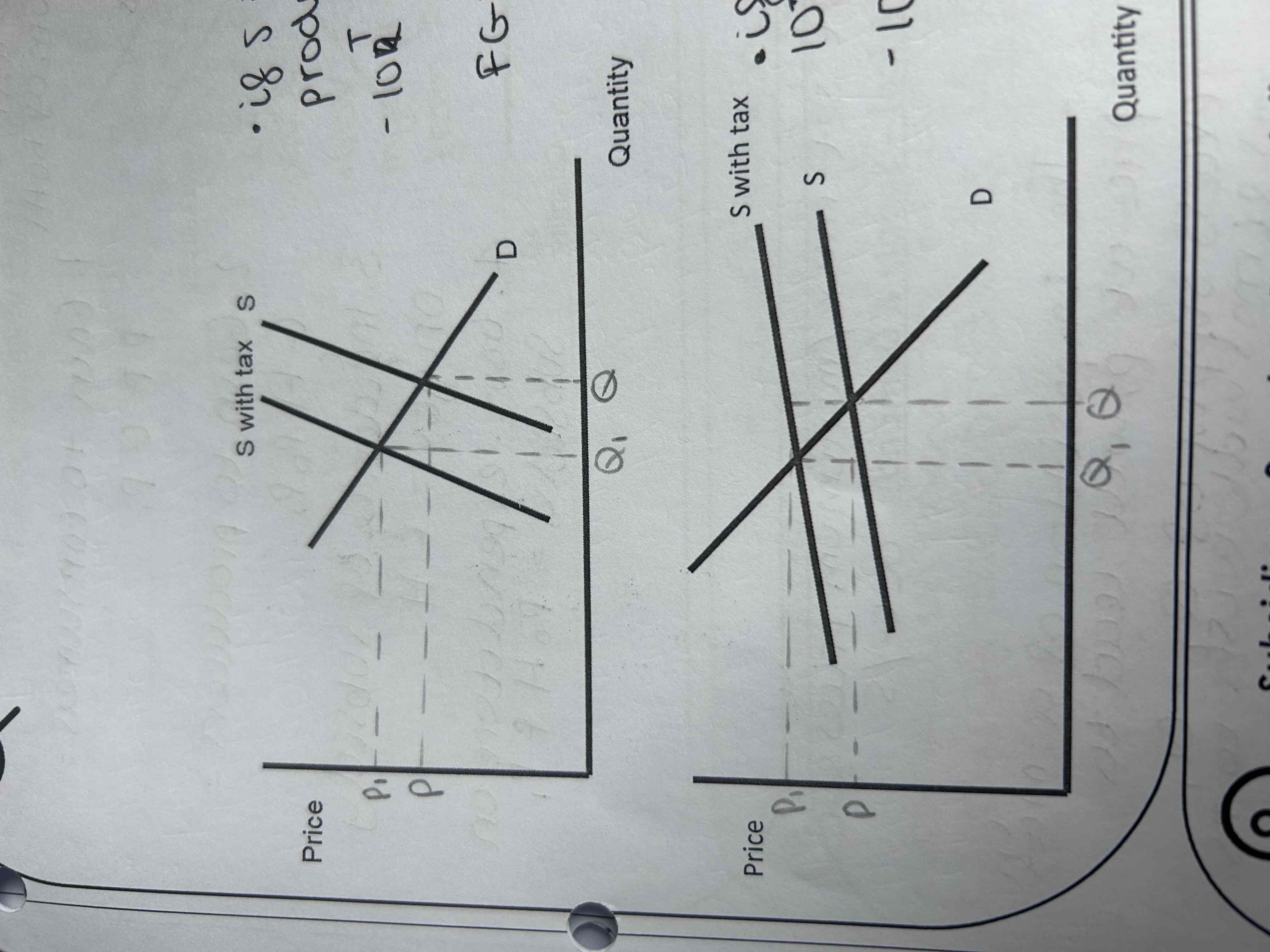
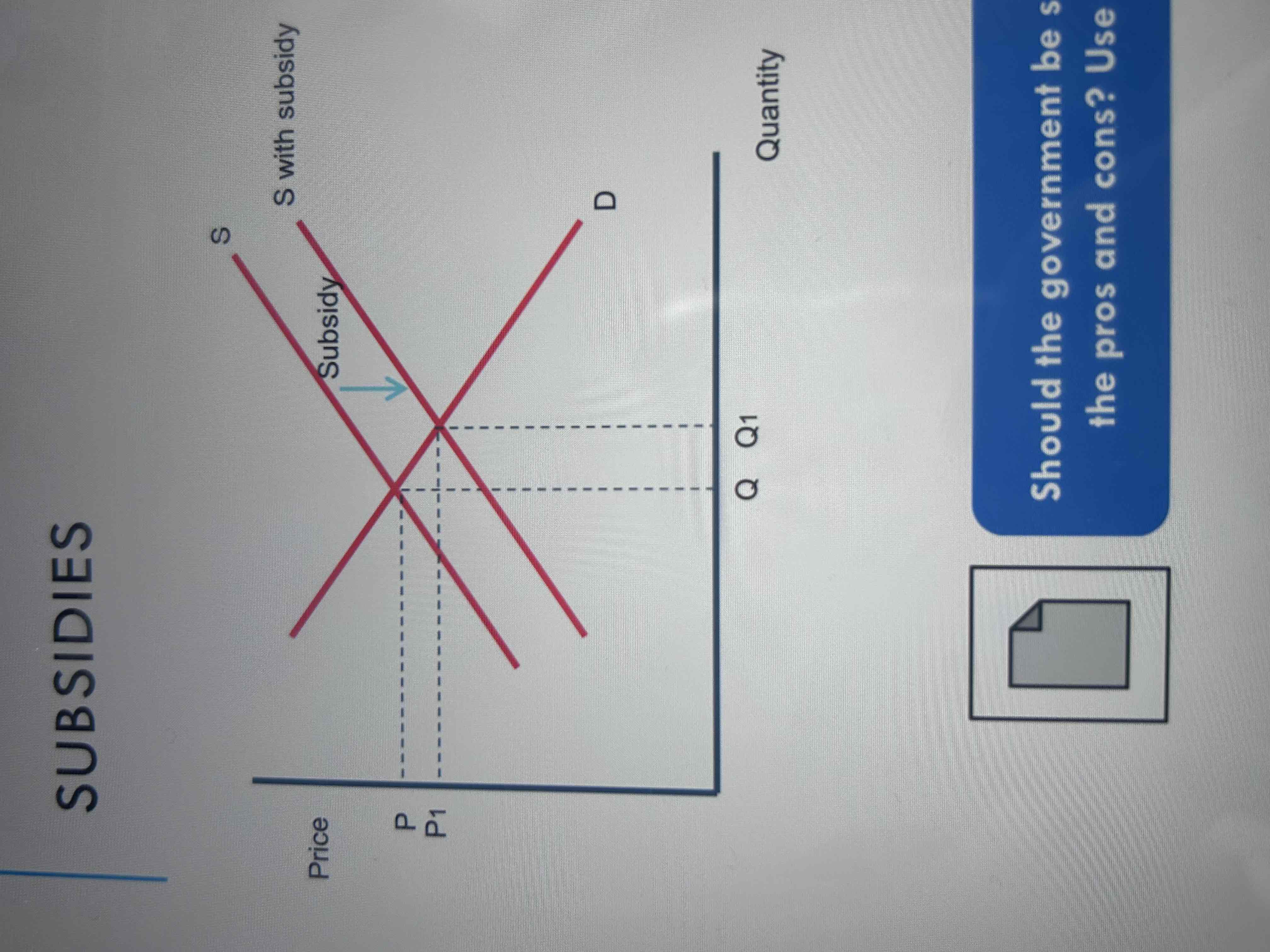
Draw a subsidy diagram
• The imposition of a subsidy will lead to a decrease in the cost of supply for a firm.
• This will lead to a shift in the supply curve down and to the right.
• Quantity supplied will increase by Q1-Q.P will decrease from P to P1.
• The subsidy has caused supply to rise by the vertical distance between the supply curves.
• The subsidy will be shared between the consumer and the producer.
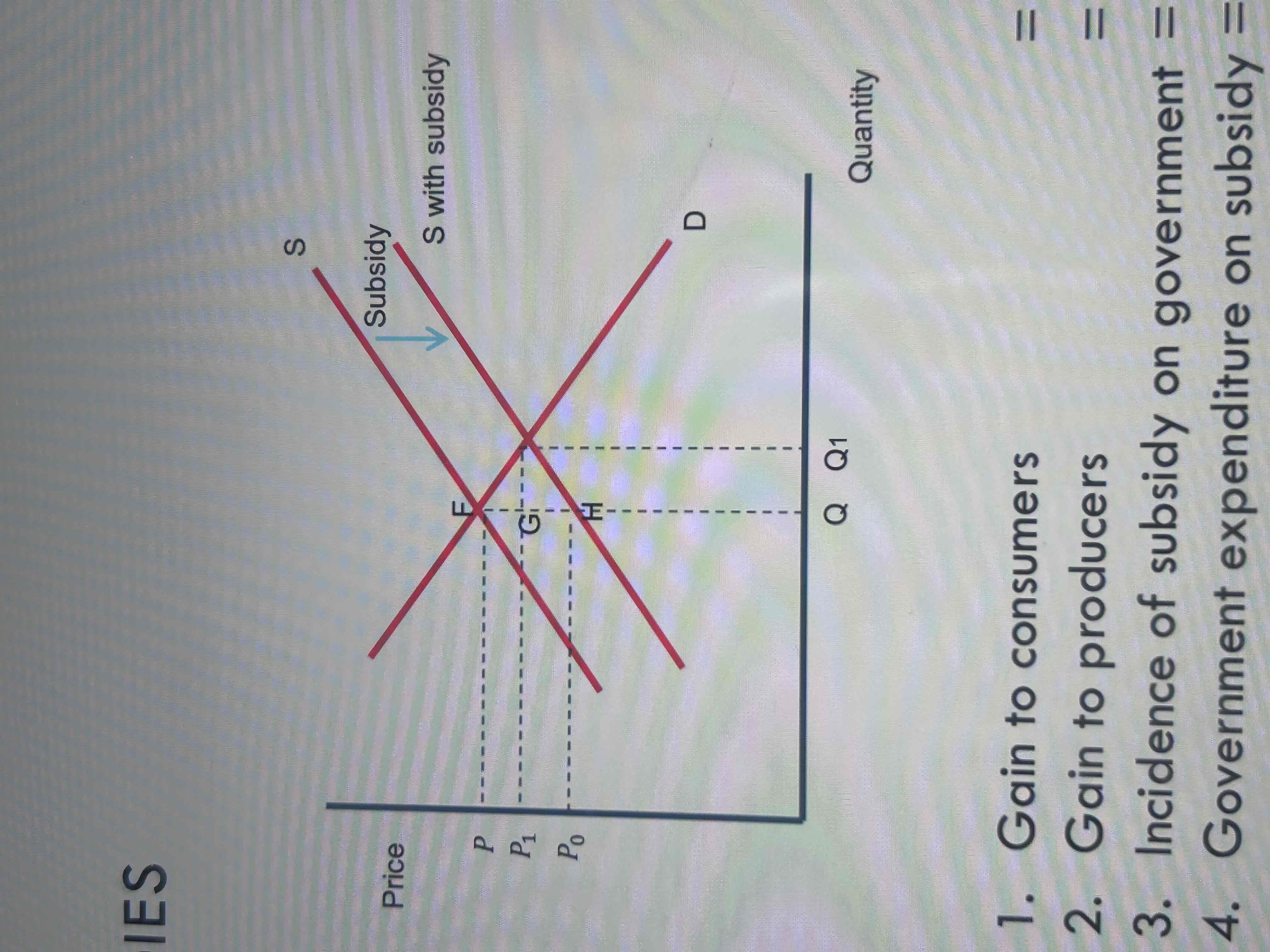
Label this diagram
1. Gain to consumers = 𝑃 𝐹 𝐺 𝑃 1
2. Gain to producers = 𝐺 𝐻 𝑃0 𝑃 1
3. Incidence of subsidy on government = 𝐹 𝐻
4. Government expenditure on subsidy = 𝑃0 𝐻 𝐹 𝑃 1
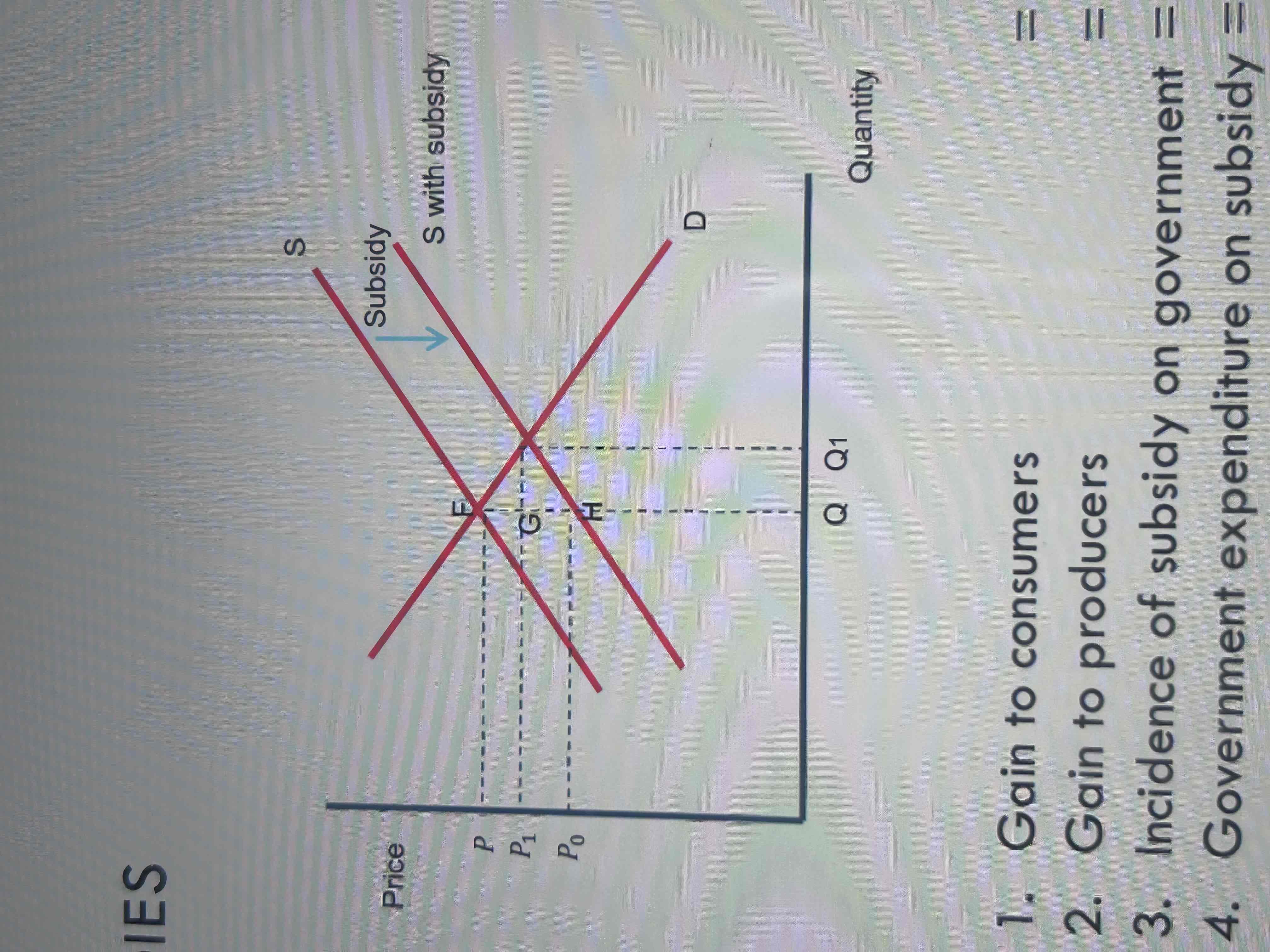
Using the previous diagram, how can we measure govt loss?
Sum of gain to consumers and producers
What is a price control?
maximum or minimum prices for a good or service.
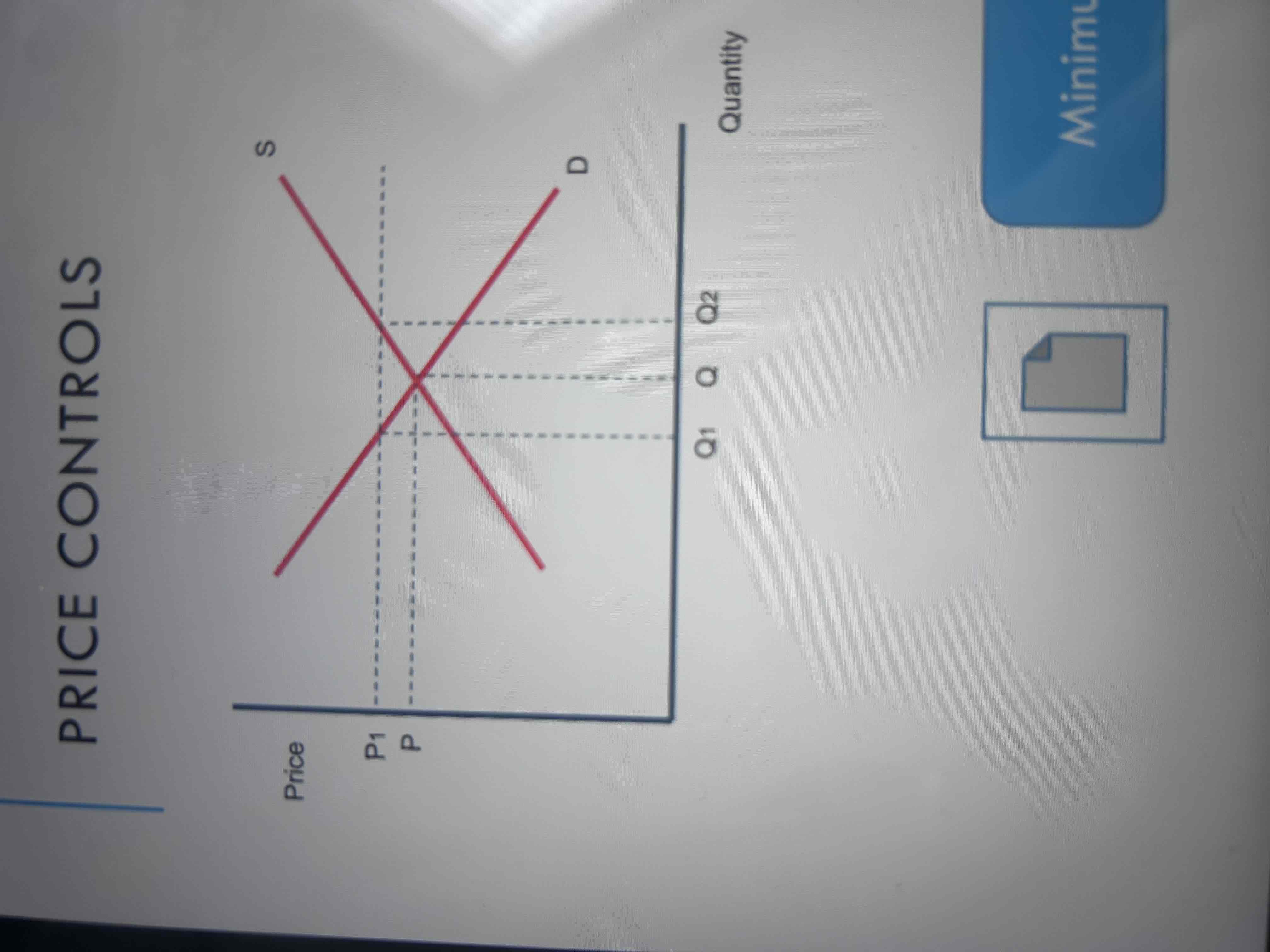
Diagram for price control (minimum price)
The imposition of a minimum price at 𝑃 1 will lead to excess supply of 𝑄2− 𝑄1 as firms will wish to supply more at a higher price
suggested that the demand for workers would be lower than the equilibrium level and there would be an excess supply of labour.
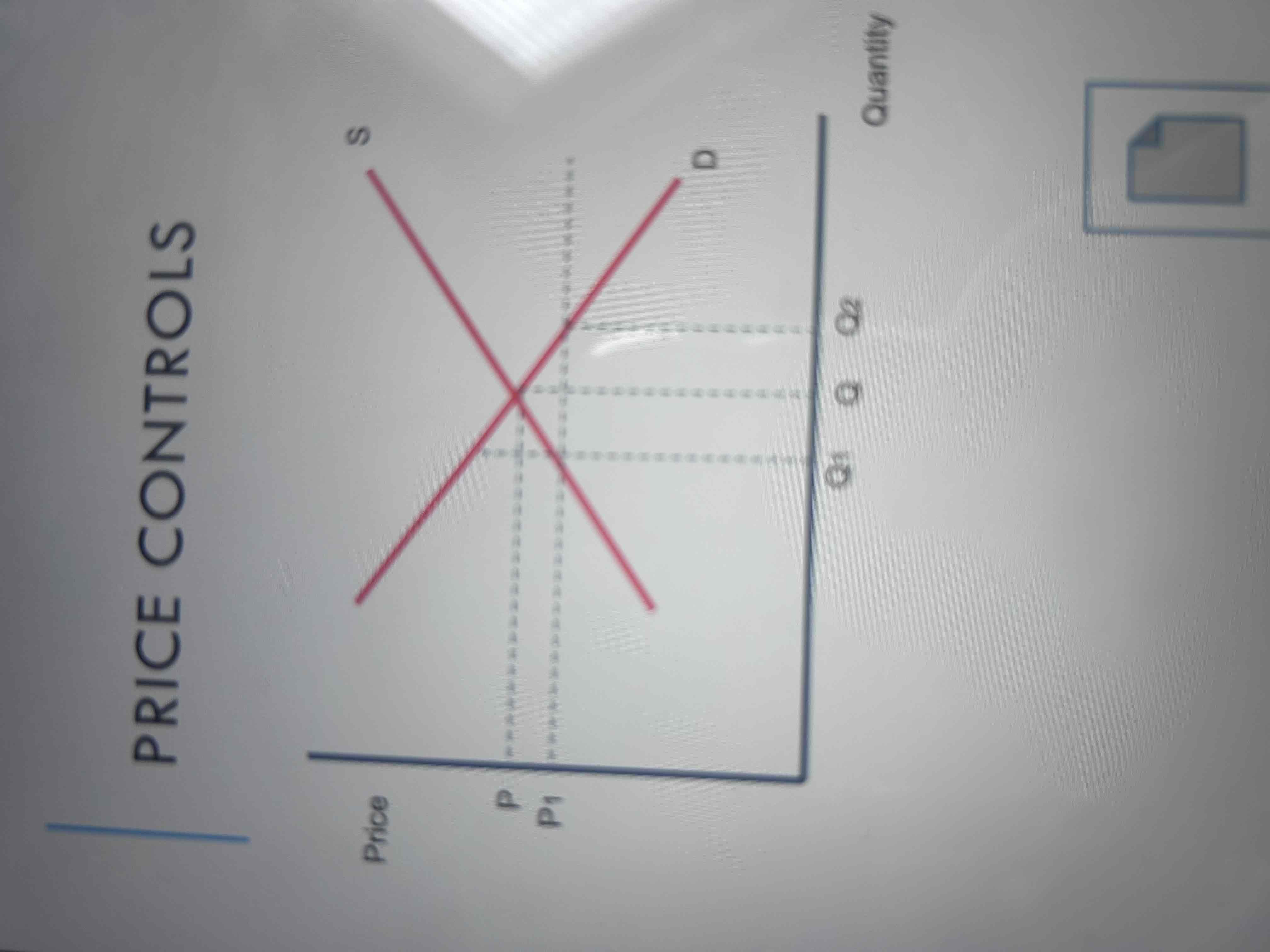
Digram for price control (maximum price)
The imposition of a maximum price at 𝑃 1 will lead to excess demand of 𝑄2− 𝑄1 as consumers will wish to demand more at a lower price.
impose a maximum price to prevent the consumer from being exploited.
What is state provision?
government intervenes in the market in order to supply a good or a service.
ensure that an adequate supply of these products is available to the market.
When will state provision occur?
This will occur if the government believes that the product is:
A merit good
The government supplies goods and services such as state education and health e.g. NHS as society believes that these are under provided by the market mechanism
A public good
The government supplies goods and services such as defence and infrastructure e.g. roads as these would be under provided by the public sector due to the free rider problem
What is regulation, why does it take place?
undertaken by government to create competitive market
government believes that this will protect the interests of consumers so that they are not exploited by firms
reason for regulation is to create conditions for continued investment in infrastructure in important areas of the economy