1.2.4-1.2.5
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Cells
They build up the tissue. Smalles living organism.
Tissues
Group of cells with structure that build up the organs.
Organs
A group of Organs will build up the organ systems.
Organ system
made up of organs and works to perform one or more functions.
Central Nervous system
Processes information and makes decisions by sendinfg signals back to the body. Contains the brain and Spinal Cord.
Peripheral Nervous System
Brings information in from the outside world and to the CNS for processing
Frontal lobe
Front of the brain. Controls emotions and behavior. Is also used for planning and using info.
Temporal Lobe
Side of the Brain. processes language and stores information
Porietal Lobe
Top of the brain. Crucial in integrating sensory and visible information.
Occipital Lobe
Recieves and processes sensory nerve impulses from the eyes
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Blunt force to the head causing trauma in the brain.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
A progressive degeneratoion of the brain causing it to die off eventually.
Epithelial Tissues
it is tissue composed of epithelial cells aligned in sheets. Connected to one another.
Connective tissue
it is tissue that supports and connects the tissue in the body along with attatching muscle to the bone
Nervous Tissue
It makes up nerves the spinal cord and brain.
Muscle tissue
It makes up the muscles in the body. Can be smooth, striated, or cardiac.
Atrium
The Upper Chammber of the heart.
Ventricle
Lower Chambers of the heart.
Valve
Seperates the ventricles and moderates them from spilling straight into the veins
Tricuspid valve
The valve splitting the Right ventricle and Right atrium
Mitral valve
The valve splitting the left ventricle and left atrium
Aortic valve
The valve splitting the opening to the aorta
Pulmonary Valve
The valve slpitting the opening to the pulmonary artery
Arteries
Consistes of the Pulmonary artery and Aorta. These pool into their respective areas. Aorta- Body Pulmonary- Lungs
Pulmonary Artery
Delivers unoxygenated blood to the lungs
Aorta
Delivers oxygenated blood to the body
Veins
The veins deliver the blood they have just recieved from the body or lung to the apropriate atrium. Superior/ inferior vena cava- RA Pulmonary Vein- LA
Superior vena cava
Carries deoxygenated blood to the Right atrium
Pulmonary Vein
The vein that carries oxygenated blood to the Left Atrium
Systemic Circulation
circulation that supplies blood to all the body and then back to the heart
Pulmonary Circulation
flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
Angina
The coronary artery is partially occluded. Causes heart pain because of the reduced blood flow.
Atherosclerosis with thrombus
Disease causing build up of plaque in the inner artery walls. Damages inner walls too.
Myocardial infarction (Heart attack)
Blood flow is reduced causing the Heart to slowly die off.
Aortic Valve stenosis
When the aortic valve narrows and partially blocks the blood flow to the heart.
Patent Foramen Ovale
Birth defect where there is a hole bresent between the two upper chambers (atrium)
Congestive Heart failure
Right ventricle wall is weak and the blood will stay within the ventricles. The left ventricle wall becomes to ineffective to pump blood.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
The walls of the left ventricle become thick and stiff so the heart cannot take in or pump out enough blood to supply body
Ventricular Septal Defect
It is an unusual hole in the wall between the two ventricles
Bacterial Endocarditis
It's when clumps of bacteria and other cells begin to form on the heart's valves.
Annas Heart
Ventricle Septum defect. Hole in the middle of the two ventricles. Could have lead to the deoxygenated and oxygenated blood mixing causing her death.
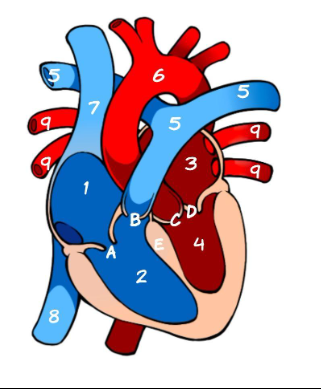
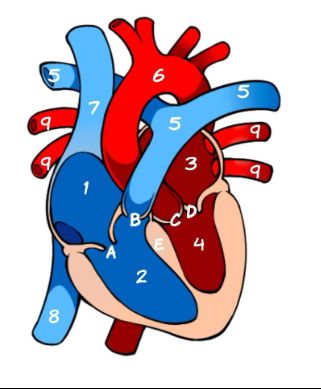
What is 1
Right Atrium (pic)
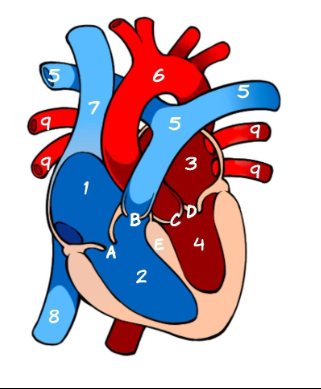
What is 2
Left Atrium (pic)
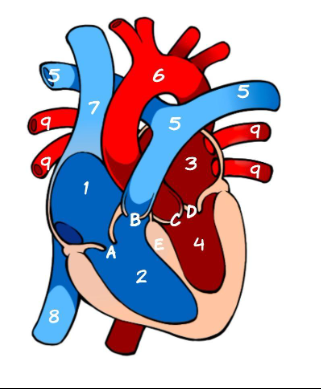
What is 3
Right ventricle (pic)
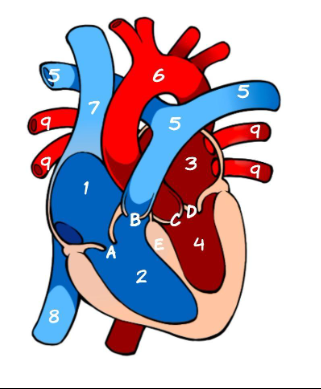
What is 4
Left ventricle (pic)
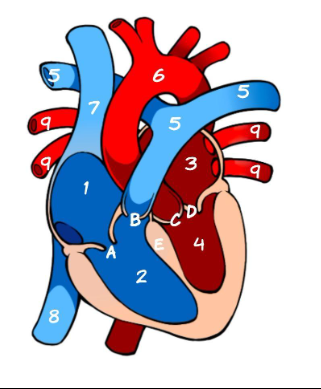
What is 5
Pulmonary Artery (pic)
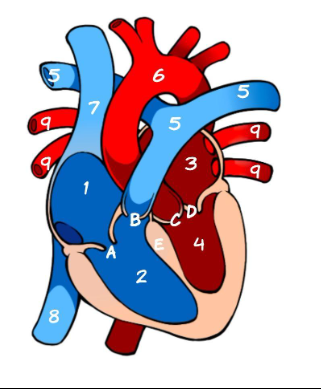
What is 6
Aorta (pic)
What is 7
Superior Vena Cava (pic)
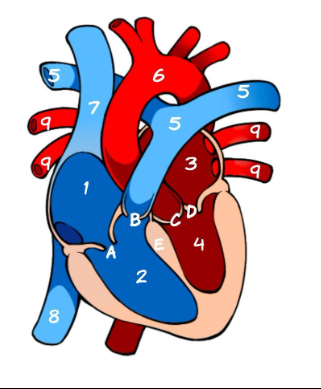
What is 8
Inferior Vena Cava (pic)
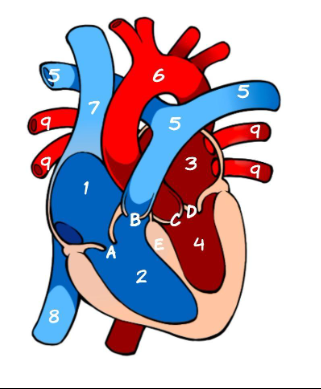
What is 9
Pulmonary vein (pic)
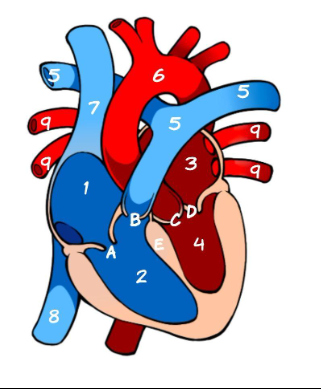
What is A
Tricuspid (pic)
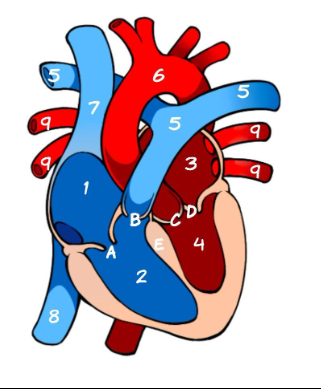
What is B
Pulmonary valve
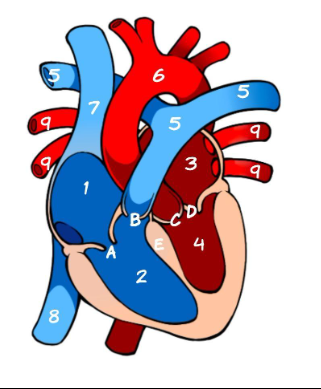
What is C
Aortic Valve
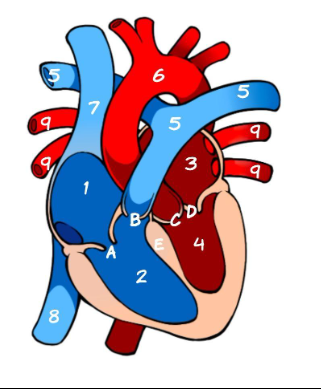
What is D
Mitral Valve
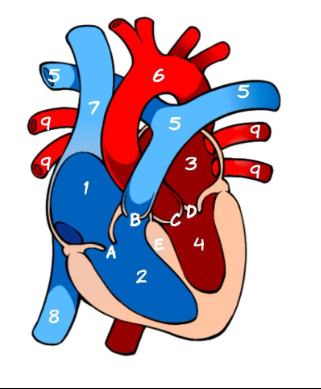
What is E
Septum