Peri-anesthesia Monitoring and Complications III
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Make sure we are maintaining good O2 delivery throughout anesthesia period - practical
Why to we monitor BP?
MAP (Mean arterial pressure)
What value is most important when monitoring BP?
greater or equal to 60mmHg - small
greater or equal to 70mmHg - large
What is the ideal MAP in small animals? What is it in large animals?
Oscullometric
Doppler
What are two indirect ways of monitoring BP indirectly/non-invasively?
Less accurate and reliable
Non-continuous
What are cons of non-invasive BP?
Arrythmias
Hypo/hypertension
Movement
When is NIBP less accurate and reliable?
Hemorrhage
Infection
Phlebitis
Pain
Thrombosis
What are complications of invasive BP?
High pressure occludes atrial blood flow and w/ gradual cuff deflation
How does a oscillometric work?
Most accurate
Least accurate
MAP is ___ accurate and Diasotolic pressure is ___ accurate in oscillometric mechanisms?
Width should be 30-40% of circumference of leg/ attachment sight
What should cuff size for an oscillometric mechanism be?
Falsely low
Falsely high
If an oscillometric cuff is too big it will read ___ and too small will read ___?
Same level as base of heart.
Where should a oscillometric cuff be placed?
Shoulder joint
What are land marks for if a patient is standing, sternal or dorsal of where the cuff should be placed?
Sternum
Where are landmarks of if a patient is lateral that a cuff should be placed?
Erroneously high
Erroneously low
If a cuff is lower we will get a ___ reading and if its higher we will get ___ readings?
Joint
Metatarsal
You shouldn't place the cuff on a ___ unless its a pig then place it on the ____?
Snuggly - too loose = wrong readings
The cuff should fit ___?
The artery should aline here
What does this mark dictate?
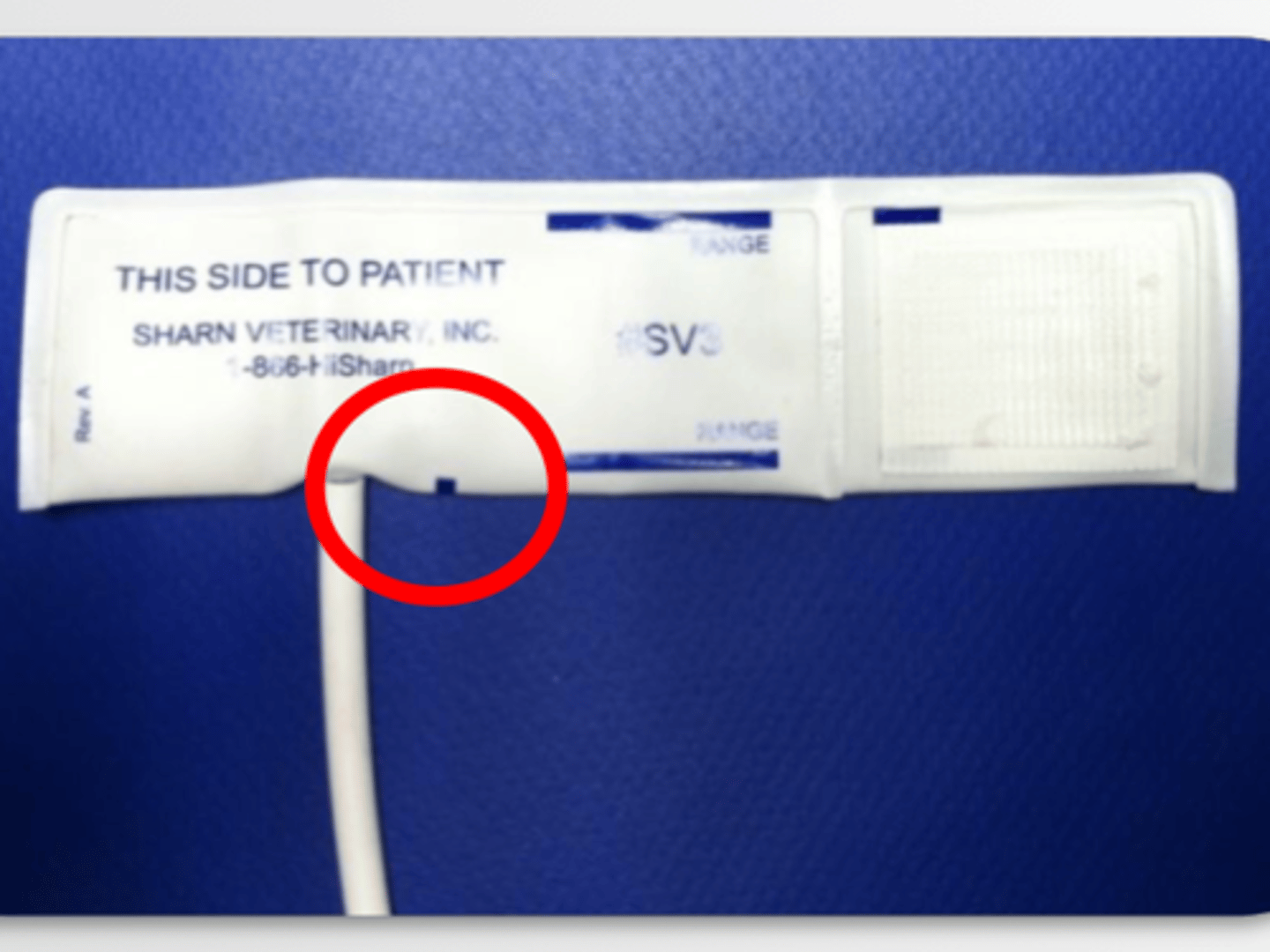
Movement
What should you avoid when the oscillometeric is running?
Does the pulse rate match - if yes the reliable
How do you access the accuracy of the NIBP machine?
Check again - dont tx anything based on only one reading
If readings show a sudden change what should be done?
Systolic pressure
The doppler method will only measure what?
Critical/ high risk patients
Routine for horses under inhalent anesthesia
When should invasive BP be used?
Dorsal pedal artery
Where do you set a IBP in a dog?
Auricular a.
Where do you set a IBP in pigs / ruminants?
Facial a.
Transverse facial a.
Metatarsal a.
Where can you set an IBP in horses?
Turn down inhalant
What is the first step to tx hypotension?
BP= CO x SVR (vascular resistance)
How do you calculate BP?
(Pre-load x compliance x contactility)/SVR
How do you find SV?
Anesthetics
ACE
Shock
What causes a drop in SVR?
Decrease anesthetics
NE (Vasopressors)
How do you tx a decrease in SVR?
Vasodilation
A patient under anethesia has bright red mucus membranes what are we seeing?
Vasoconstriction (poss anemia)
A patient under anesthesia has pale pink mucus membranes what are we seeing?
Anti-cholinergics
Decreased anesthetics
How can we tx a drop in HR caused by anesthetic drugs?
Dehydration
Blood loss
SVR
What can cause preload to decrease?
Decrease anesthetics
Fluids
Vasopressors
How do you treat a decrease of preload?
Before
Dehydration should be corrected ___ anesthesia?
Giving a fluid bolus of 5ml/kg x 1-2 times to see if BP increases
What is the fluid challenge test?
5mL/kg/hr
What is the standard fluid rate for a dog?
3mL/kg/hr
What is the standard fluid rate for a cat?
Crystalloid
At 10% of blood loss what can you replace w/?
Colloid
At 10-20% blood loss what can you replace w?
Transfusion
At more than 20% blood loss what can you replace with?
8%
7%
Dogs blood volume is __% of their body weight
Cats blood volume is __% of their body weight?
37kg x 80ml/kg = 2960ml
900/2960= 30.4%
Transfusion
A 37 kg dog lost 900mls of blood what kind of fluid replacement should they get?
10kg x 70ml/kg = 700ml
69/700 = 9.8%
Crystalloid fluid replacement
A 10kg cat lost 69mls of blood. What kind of fluid replacement should they get?
Increase
Decrease
Vasoconstriction will ___ effective circulation.
Vasodilation will ___ effective circulation?
Decrease inhalent
Vasopressor
How can you fix preload?
Pericardial effusion
HCM
(Be aware of before)
What can cause decrease in compliance (Lusitrophy)?
Anesthetics and drugs
DCM
What can cause decrease in contractility (inotropy)?
Decrease anesthetics
Dobutamine
Dopamine
How do you increase contractility?
SpO2 - slope should be going up fast
What can you use to diagnose a decrease in contractility?
Diluted
Horses
Dobutamine and dopamine have to be _____ and ___ are very sensitive to it?