IPS1- Metabolic Pathway Concepts p2
1/64
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
R–CO–R → R₂CHOH
How are polyhydric alcohols formed from ketones?
A. R–CO–R → R₂CHOH
B. R–CO–R → R–CH₂OH
C. R–CO–R → R–COOH
D. R–CO–R → R–O–R
Monosaccharides
[CARBOHYRDATE CLASSIFICATION]
They are synthesized by reduction of the monosaccharides for use in the manufacture of foods for weight reduction and for diabetics
Monosaccharides
[CARBOHYRDATE CLASSIFICATION]
They are poorly absorbed and they have about half the energy yield of sugars.
B. They are poorly absorbed and yield about half the energy of sugars
Why are sugar alcohols used in foods for diabetics and weight reduction?
A. They are sweeter than glucose
B. They are poorly absorbed and yield about half the energy of sugars
C. They provide more calories than sugars
D. They cannot be metabolized
Disaccharides
[CARBOHYRDATE CLASSIFICATION]
These are condensation products of two monosaccharide units
Glucose + galactose
What two sugars make up lactose?
A. Glucose + fructose
B. Glucose + galactose
C. Glucose + glucose
D. Fructose + galactose
Glucose + glucose, α(1→4)
What two sugars make up maltose, and what bond connects them?
A. Glucose + fructose, α(1→4)
B. Glucose + glucose, α(1→4)
C. Glucose + glucose, α(1→6)
D. Glucose + galactose, β(1→4)
Glucose + glucose, α(1→6)
What two sugars make up isomaltose, and what bond connects them?
A. Glucose + glucose, α(1→6)
B. Glucose + glucose, α(1→4)
C. Glucose + fructose, α(1→2)
D. Glucose + galactose, β(1→4)
Glucose + fructose
What two sugars make up sucrose?
A. Glucose + galactose
B. Glucose + glucose
C. Glucose + fructose
D. Fructose + galactose
Glucose + glucose, α(1→1)
What two sugars make up trehalose, and what bond connects them?
A. Glucose + glucose, α(1→1)
B. Glucose + glucose, α(1→4)
C. Glucose + fructose, α(1→2)
D. Glucose + galactose, β(1→4)
Oligosaccharides
[CARBOHYRDATE CLASSIFICATION]
Condensation products of 3–10 monosaccharides
No, most are not digested
Are most oligosaccharides digested by human enzymes?
A. Yes, completely
B. No, most are not digested
C. Only in infants
D. Only when combined with proteins
Carbohydrates
_____- are aldehyde or ketone derivatives of polyhydric alcohols.
Polysaccharides
[CARBOHYRDATE CLASSIFICATION]
Are made by linking more than ten sugar units (monosaccharides) together.
starches
dextrins
Example of Polysaccharide
Either straight (linear) or branched
Polysaccharides can be:
A. Only linear
B. Only branched
C. Either linear or branched
D. Neither
Polysaccharides made of 6-carbon sugars
What are hexosans?
A. Polysaccharides made of 5-carbon sugars
B. Polysaccharides made of 6-carbon sugars
C. Monosaccharides with six carbons
D. Polysaccharides with mixed sugars
Polysaccharides made of 5-carbon sugars
What are pentosans?
A. Polysaccharides made of 5-carbon sugars
B. Polysaccharides made of 6-carbon sugars
C. Disaccharides with pentoses
D. Fiber polysaccharides
six-carbon sugars
starches and dextrins are made of ____ carbon sugar
True
[T/F] Foods also have many nonstarch polysaccharides
Nonstarch polysaccharides
Which polysaccharides are indigestible by human enzymes and make up most dietary fiber?
A. Starches
B. Dextrins
C. Nonstarch polysaccharides
D. Maltose
Cellulose
Inulin
Example of Nonstarch polysaccharides [2]
Cellulose
[NON STARCH POLYSACCHARIDE]
____ - from plant cell walls, made of glucose
Inulin
[NON STARCH POLYSACCHARIDE]
____ - a storage carbohydrate in some plants, made of fructose
Fructose
What is inulin made of?
A. Glucose
B. Fructose
C. Galactose
D. Ribose
Glucose
What is cellulose made of?
A. Glucose
B. Fructose
C. Galactose
D. Ribose
Glucose
Biomedically, which monosaccharide is the most important?
A. Galactose
B. Ribose
C. Glucose
D. Fructose
The straight-chain form shows glucose as a simple open chain (called an aldohexose).
But glucose mostly forms a ring (cyclic) structure by the aldehyde group reacting with a hydroxyl group.
This ring form is more stable and it explains many of glucose’s properties.
Glucose has three ways to show its structure such as ____
Aldohexose
Glucose is chemically classified as what type of sugar?
A. Aldohexose
B. Ketohexose
C. Pentose
D. Aldopentose
Straight-chain form
Which structural form of glucose shows it as a simple open chain?
A. Cyclic form
B. Straight-chain form
C. Disaccharide form
D. Branched form
The aldehyde group reacts with a hydroxyl group
What causes glucose to form a cyclic (ring) structure?
A. Oxidation of glucose
B. The aldehyde group reacts with a hydroxyl group
C. Polymerization
D. Loss of a hydrogen atom
Ring (cyclic) form
Which form of glucose is more stable and explains many of its properties?
A. Open-chain form
B. Ring (cyclic) form
C. Ketone form
D. Oxidized form
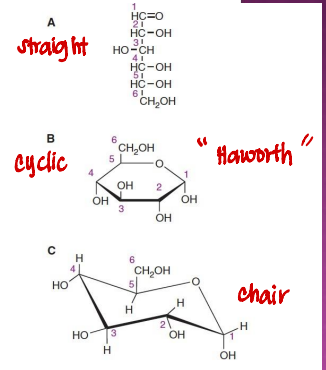
Haworth projection
The cyclic structure of glucose is usually shown using the ______
A. Fischer projection
B. Haworth projection
C. Newman projection
D. Chair projection
From the side and above the ring
In the Haworth projection of glucose, how is the molecule viewed?
A. From below only
B. From the side and above the ring
C. From directly overhead
D. From the edge
Bold and thick
In a Haworth projection, how are bonds closest to the viewer drawn?
A. Thin and dashed
B. Dotted
C. Bold and thick
D. Wavy lines
Their orientation above or below the ring
In the Haworth projection, what do the positions of hydroxyl (–OH) groups indicate?
A. Their color
B. Their orientation above or below the ring
C. Their molecular weight
D. Their electronegativity
They are implied and simplify the structure
Why are hydrogen atoms often omitted in Haworth projections of glucose?
A. They are implied and simplify the structure
C. They are not part of the ring
D. They are unstable
Chair-like conformation
In reality, the ring shape is more like a _____
A. Flat hexagon
B. Chair-like conformation
C. Boat conformation
D. Straight chain
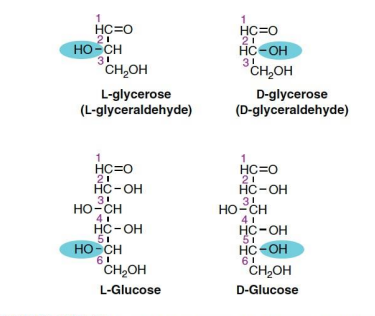
Note the 2nd to the last carbon If OH is in Left (levorotatory) Right (Dextrorolatory)
D- and L-isomerism of glycerose and glucose.
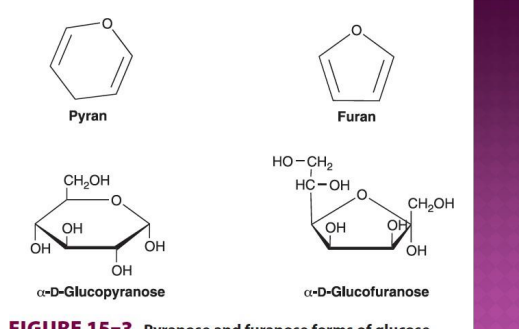
Pyranose and furanose forms of glucose.
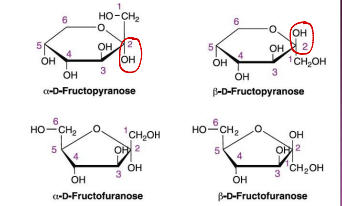
Ketose = 2nd c = 0
Aldose = 1st - = 0
Pyranose and furanose forms of fructose
C-2 epimers
Glucose and mannose are epimers at which carbon?
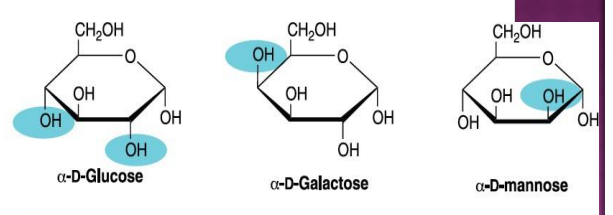
Epimers of Glucose
Epimers
Molecules that differ in the position of H and OH at only one carbon
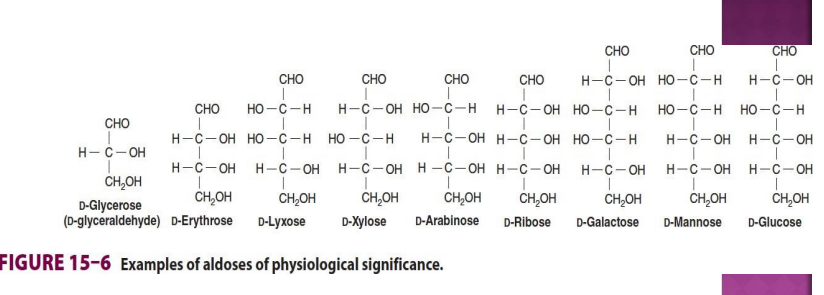
Example of aldoses of physiological significance
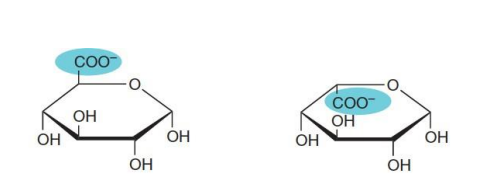
L + D in last C
a-D-Glucuronate (left) and ẞ-L-iduronate (right).
sugar part
non-sugar part
Glycosides are molecules made of __ [2]
glycone
sugar part of glycoside is callled as ____ ?
aglycone
non- sugar part of glycoside is callled as ____ ?
Methanol
glycerol
sterol
phenol
base like adenine
Examples of aglycone (non-sugar part) include ___ [5]
Digitalis
Digoxin
Strophanthus/Ouabain
Cardiac Glycosides examples [3]
Heart failure (CHF)
Cardiac glycosides (like Digitalis, Digoxin, Strophanthus/Ouabain) are used to treat:
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Hypertension
C. Heart failure (CHF)
D. Asthma
Na⁺-K⁺-ATPase
Cardiac glycosides work by blocking which enzyme?
A. Lipase
B. Na⁺-K⁺-ATPase
C. Amylase
D. DNA polymerase
True
[T/F]
Blocking Na⁺-K⁺-ATPase in heart cells causes to stop the potassium from going in and sodium from going out of heart cells
Calcium channels to open → more calcium inside → stronger heart contraction
Increased sodium inside heart cells causes:
A. Calcium channels to open → more calcium inside → stronger heart contraction
B. Potassium channels to open → less contraction
C. No change in contraction
D. Weaker heart contraction
An anti-tubercular (aminoglycoside) antibiotic
Streptomycin is classified as:
A. A cardiac glycoside
B. An anti-tubercular (aminoglycoside) antibiotic
C. A lipid molecule
D. A steroid hormone
Streptomycin
It is an antibiotic made of amino sugars linked by glycosidic bonds.
Hyaluronic acid (connective tissue)
[AMINO SUGAR]
D-glucosamine is part of:
A. Chondroitin (cartilage)
B. Hyaluronic acid (connective tissue)
C. DNA backbone
D. Glycogen
connective tissue
hyaluronic acid is a substance in _____ tissue
cartilage
chondroitin can be found in _____
Chondroitin (cartilage)
D-galactosamine is part of:
A. Hyaluronic acid
B. Chondroitin (cartilage)
C. Glycogen
D. DNA
Chondroitin
D-mannosamine is part of:
A. Chondroitin
B. Hyaluronic acid
C. DNA
D. Glycogen
Macrolide antibiotic
Erythromycin is classified as a:
A. Glycoprotein
B. Macrolide antibiotic
C. Aminoglycoside antibiotic
D. Steroid
Erythromycin
____- is a macrolide antibiotic with a large ring and a ketone group, plus amino sugars linked by glycosidic bonds.
Streptomycin
_____- is an aminoglycoside antibiotic made of amino sugars linked together.