Lab Practical 3- Sea turtle anatomy and satellite data
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Chelonia mydas
Green Sea Turtle

Caretta caretta
Loggerhead Sea Turtle
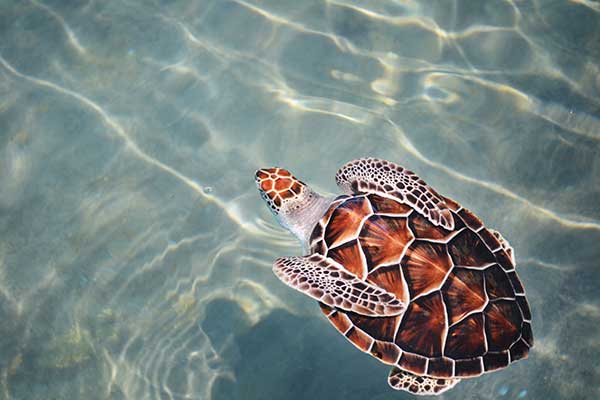

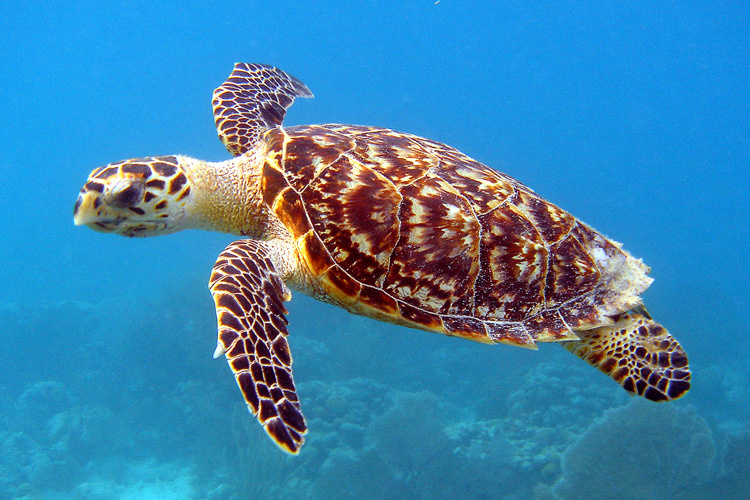
Eretmochelys imbricata
Hawksbill Sea Turtle

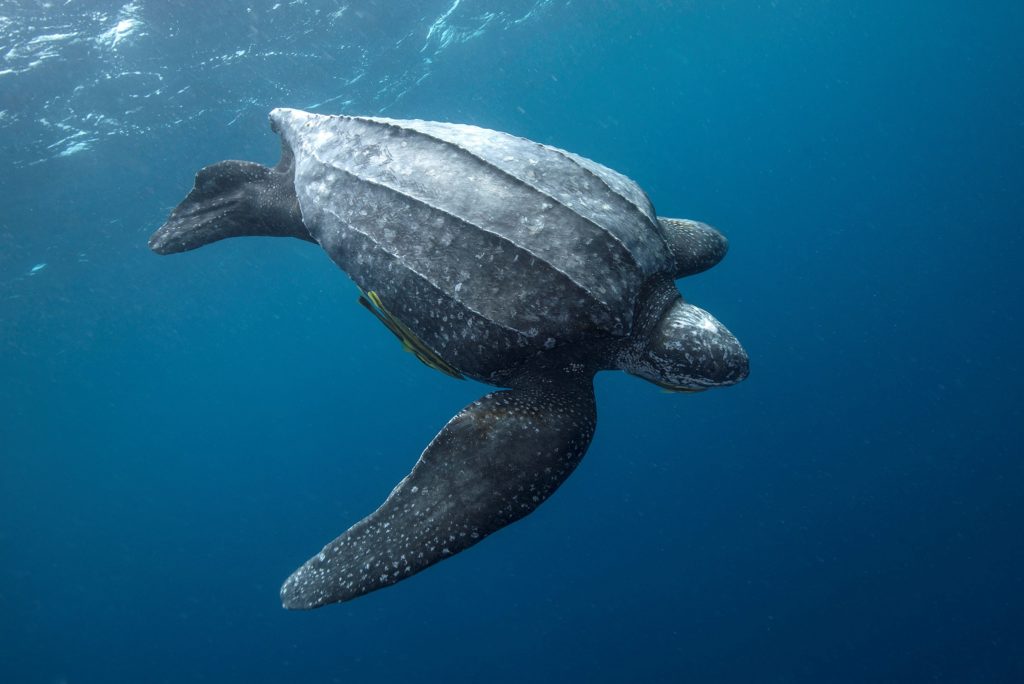
Dermochelys coriacea
Leatherback Sea Turtle

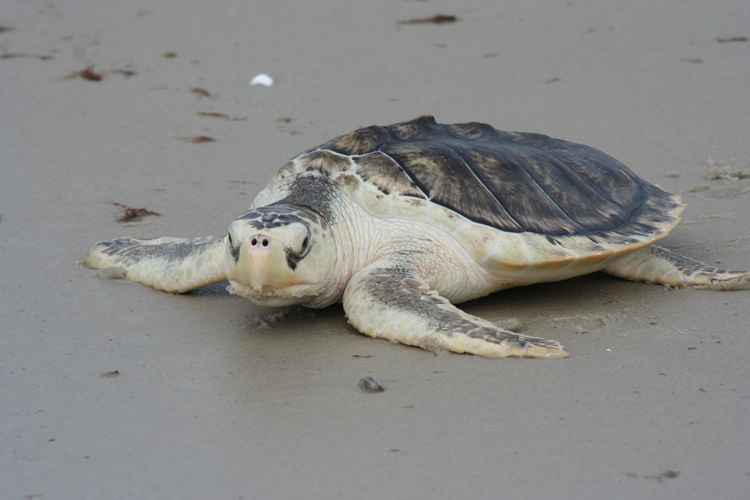
Lepidochelys kempii
Kemp's Ridley Sea Turtle

Lepidochelys olivacea
Olive Ridley Sea Turtle

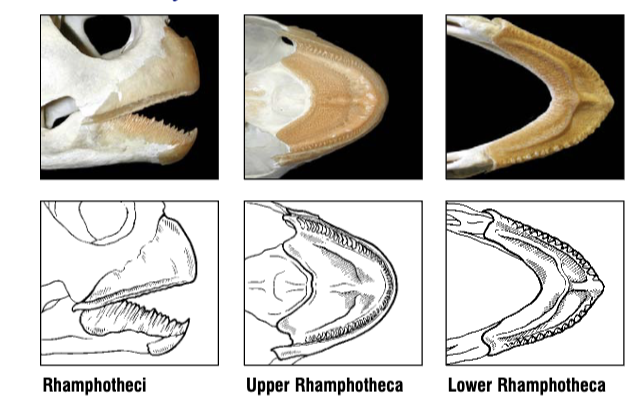
What species does this beak belong to? What do they eat?
Green Sea Turtle, Chelonia mydas
They eat seagrass, algae, and other marine vegetation.
Snout rounded, outer keratin smooth and delicately built.
What species does this beak belong to? What do they eat?
Hawksbill Sea Turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata
They eat sponges and other omnivorous substances.
Snout narrow and pointed with sharp alveolar edges.
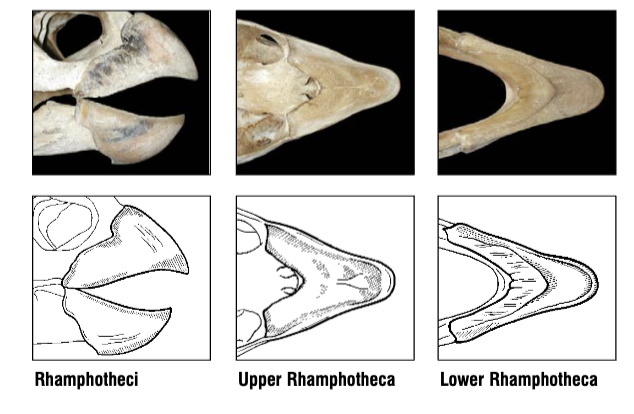
What species does this beak belong to? What do they eat?
Loggerhead Sea Turtle, Caretta caretta
They eat crabs, sponges, mollusks, vegetation, and other invertebrates.
Rhamphotheci robustly constructed with sharp
alveolar edges. U-shaped cutting surface is found along the
posterior margin
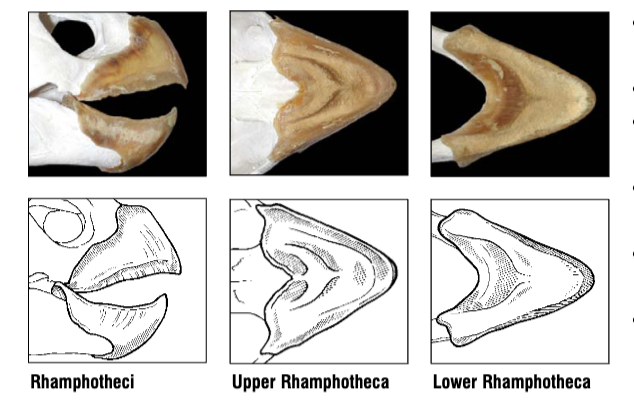
What species does this beak belong to? What do they eat?
Kemp's Ridley Sea Turtle, Lepidochelys kempii
Eat mollusks, urchins, and fish
The rhamphotheci are heavily constructed with thick alveolar surfaces. Both upper and lower jaws come to anterior
hook-like points. Sharp U-shaped ridge marks the posterior border.
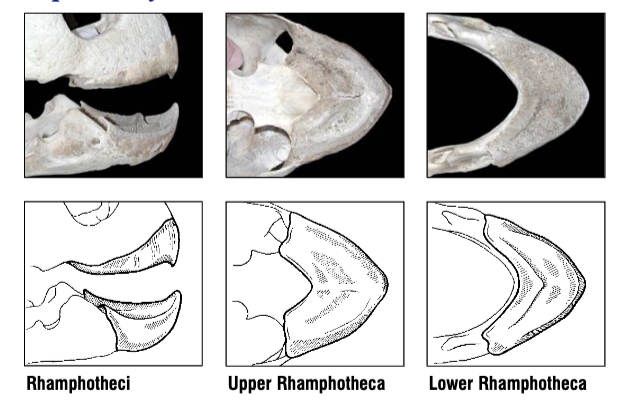
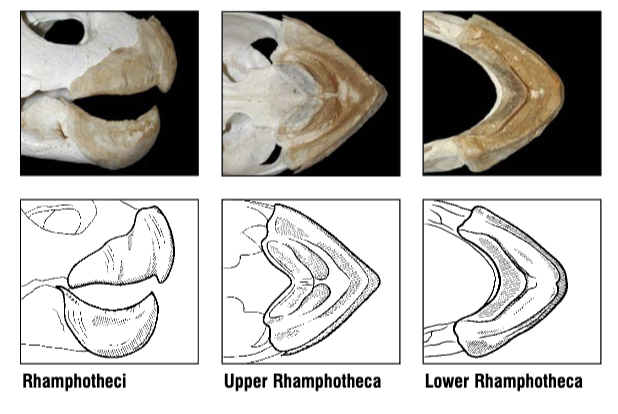
What species does this beak belong to? What do they eat?
Olive Ridley Sea Turtle, Lepidochelys olivacea
They eat jellyfish, urchins, crustaceans, and fish.
Rhamphotheci are heavily constructed with thick
alveolar surfaces. Both the upper and lower rhamphotheci are
pointed at the anterior midline. Lower rhamphotheca has a sharp, wide, V-shaped ridge running posteriorly along the buccal margin.
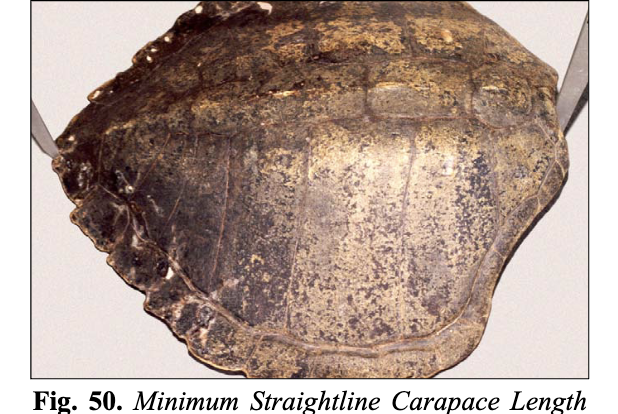
How is the Minimum Carapace Length (SCLmin and CCLmin) measured?
Minimum Carapace Length (SCLmin and CCLmin), also known as notch-to-notch length, is measured from the mid-point of the nuchal scute to the notch where the two most posterior marginal scutes meet. SCL is with a caliper, CCL is with a measuring tape.

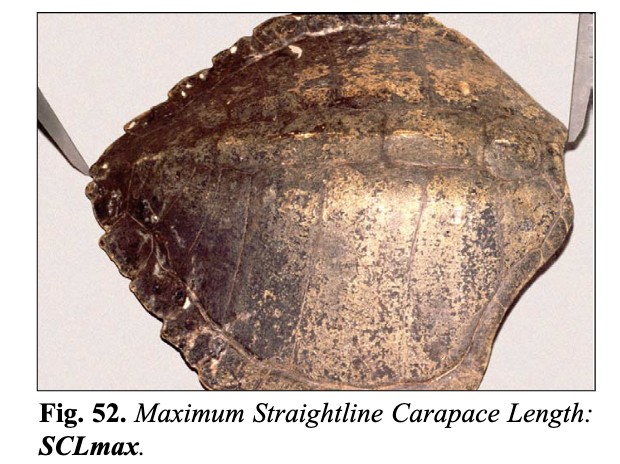
How is the Maximum Carapace Length (SCLmax and CCLmax) measured?
Maximum Carapace Length (SCLmax and CCLmax), also sometimes called greatest length,
is from the anterior-most part of the carapace to the posterior-most tip of the carapace on the same side. SCL is with a caliper, CCL is with a measuring tape.

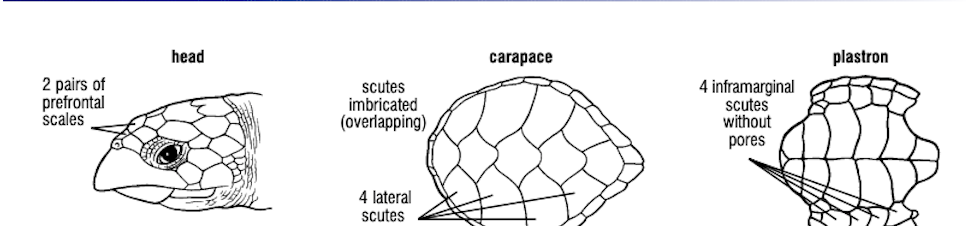
What turtle species has 2 pairs of prefrontal scales, 4 lateral scutes, and 4 inframarginal scutes without pores?
Eretomochelys imbricata, the hawksbill
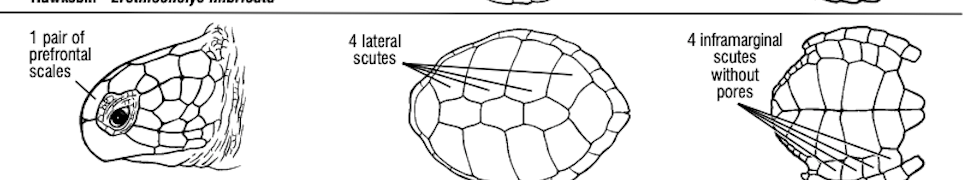
What turtle species has 1 pair of prefrontal scales, 4 lateral scutes, and 4 inframarginal scutes without pores?
Chelonia mydas, the green sea turtle.
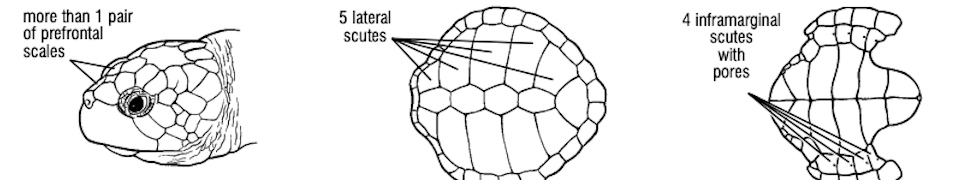
What turtle species has more than 1 pair of prefrontal scales, 5 lateral scutes, and 4 inframarginal scutes with pores?
Lepidochelys kempii, Kemp’s ridley
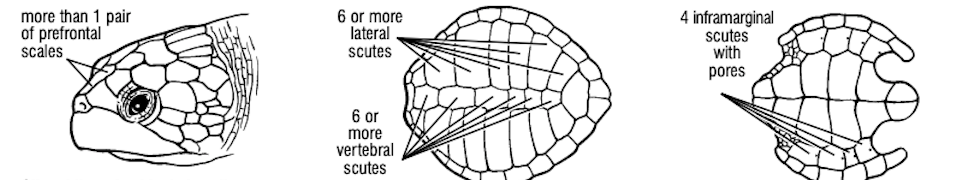
What turtle species has more than 1 pair of prefrontal scales, 6 or more lateral scutes, 6 or more vertebral scutes, 4 inframarginal scutes with pores?
Lepidochelys olivacea, Olive ridley
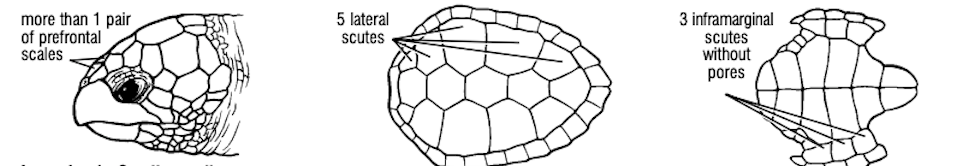
What turtle species has more than 1 pair of prefrontal scutes, 5 lateral scutes, and 3 inframarginal scutes without pores?
Caretta caretta, the loggerhead
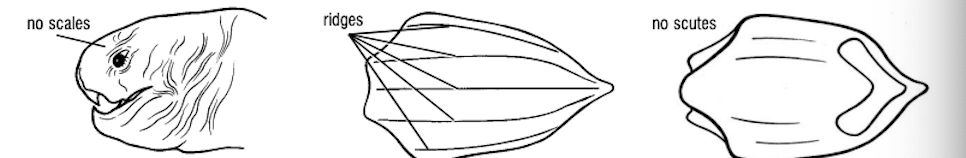
What turtle species has no scales or scutes?
Dermochelys coriacea, leatherback
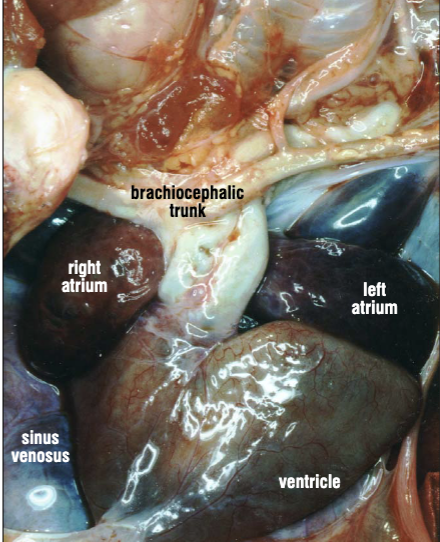
What are the four chambers of a sea turtle heart?
Left atrium, right atrium, ventricle, and sinus venosus
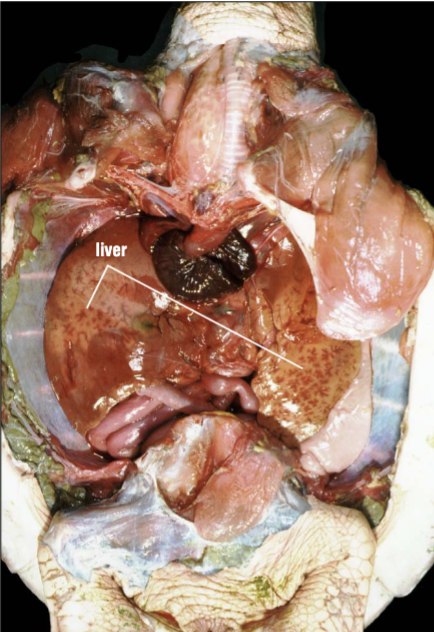
Which side of a sea turtle liver is larger? Where is the liver?
The right lobe is larger, and the liver is on each side of the heart.
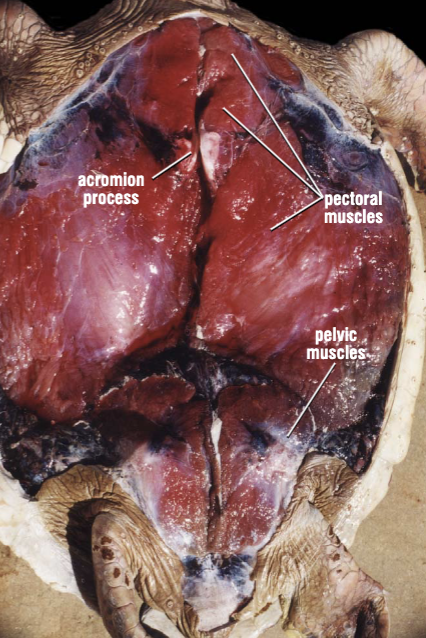
Where is the acromion process?
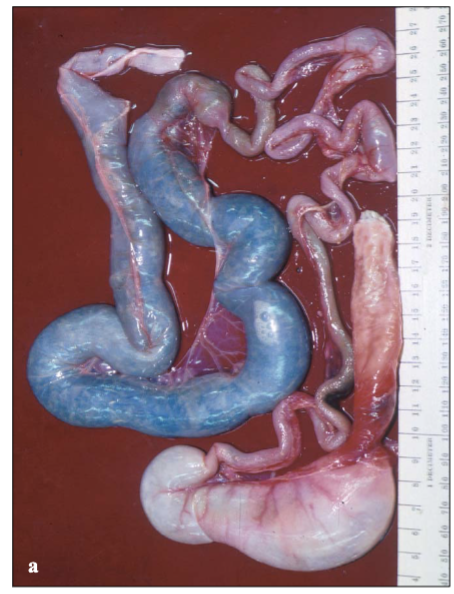
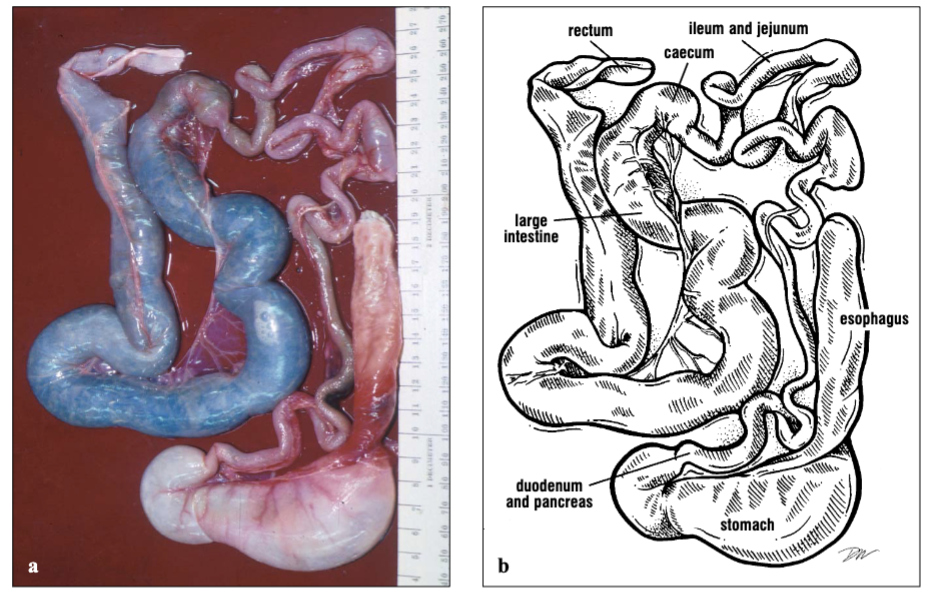
Name the parts of this hawksbill turtle’s GI tract.
Esophagus, stomach, cecum, rectum, duodenum and pancreas, ileum and jejunum, small intestine, and large intestine
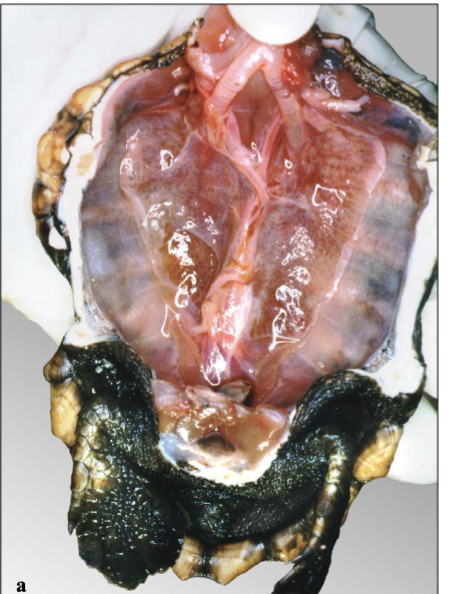
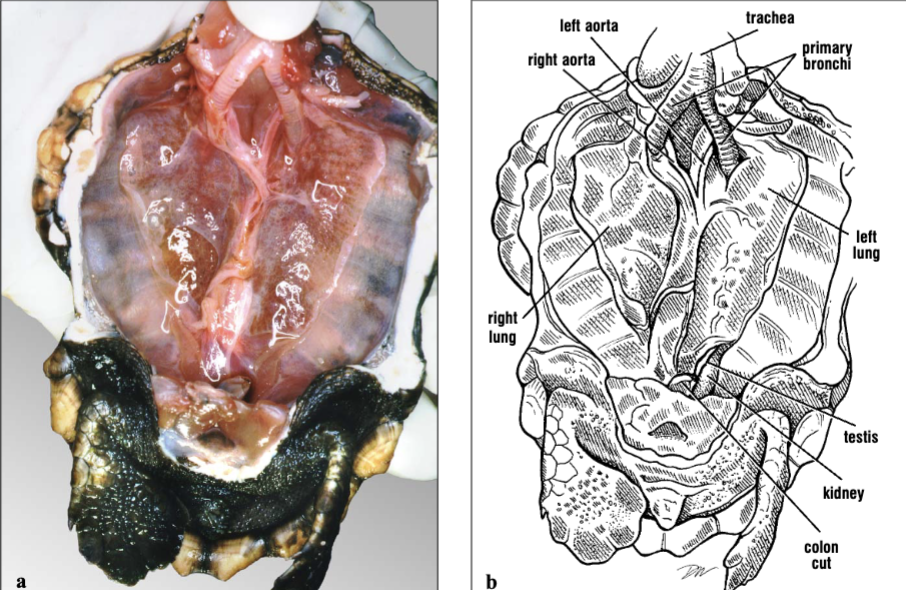
What is the largest organ that can be seen in this picture? What are the tubes at the anterior end of this turtle?
The lungs can be clearly seen, and the trachea is the tube-like structure at the anterior end.
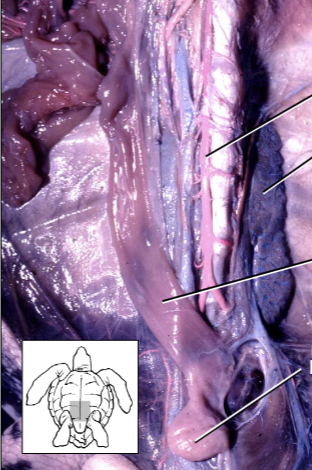
Which one of these lines points to the kidney?
The second from the top. The kidney is the dark greyish organ.
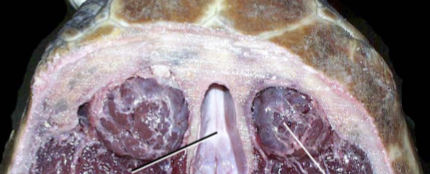
Which one of these lines points to the brain? Which one points to the salt gland?
The black line points to the brain, and the white line points to the salt gland.
What is a scute?
Scutes are keratinous epidermal structures that grow above the carapace bones.
What are dermal ossicles?
Dermal ossicles are bony plates that reside deep to the skin in the leatherback carapace.
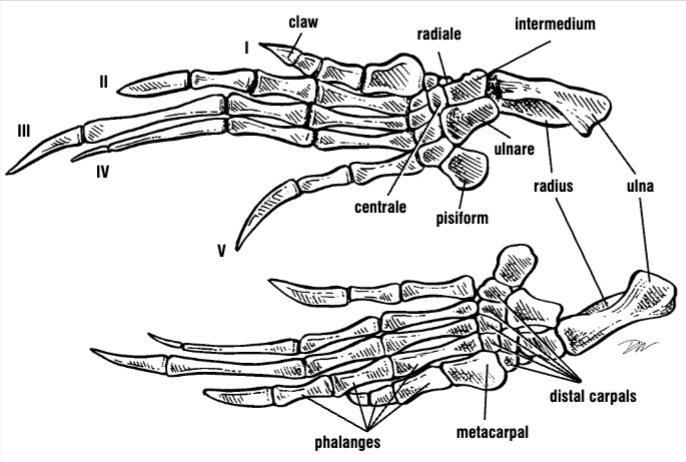
What bones are sea turtle flippers comprised of?
What is albumen?
Essentially egg white- it is a substance with mostly water, some ash, and some lipids.
As they are laid in the nest, sea turtle eggs are developmentally paused at the tiny _____ stage.
Gastrula
Oxygen demand peaks as sea turtle embryos enter the _____ stage, where they begin thrashing within the nest.
Pipping.
What are the developmental stages of sea turtle eggs?
Day 1 - Gastrula
Day 10 - Embryo
Day 20 - Eye spot
Day 30 - Identifiable turtle
Day 40 - Identifiable sea turtle
Day 50 - Pipping
What is the rhamphotheca?
It is the turtle’s keratinaceous beak-like structure, upper and lower jaw in Chelonoids.
How does the diet of Chelonia mydas (Green sea turtle) affect the rhamphotheca structure?
The adults are herbivores. For this, the beak is rounded and the keratin is smooth on the outside. The edge and inner beak is full of serrations and spike-like cusps.
How does the diet of Eretomychelys imbricata (Hawksbill turtle) affect the rhamphotheca structure?
They are omnivores, but prefer to eat sponges. For this, they have a narrow pointed snout with sharp alveolar edges.
How does the diet of Caretta caretta (Loggerhead sea turtle) affect the rhamphotheca structure?
They eat mollusks, crustaceans, sponges, and vegetation. For this, they have a U-shaped cutting surface on the posterior margin of the beak, sharp alveolar edges, and a wide crushing surface within the mouth that helps them break down mollusks and crustaceans.
How does the diet of Lepidochelys kempii (Kemp’s Ridley) affect the rhamphotheca structure?
They eat mollusks, urchins, and fish. For this, they have a beack with thick alveolar surfaces, wide crushing surfaces, and U-shaped ridge marks on the posterior margin.
How does the diet of Lepidochelys olivacea (Olive ridley) affect the rhamphotheca structure?
They eat jellyfish, urchins, crustaceans, and fish. For this, they have a wide and heavy rhampotheca with a thick alveolar surface and a V-shaped ridge along the buccal margin.
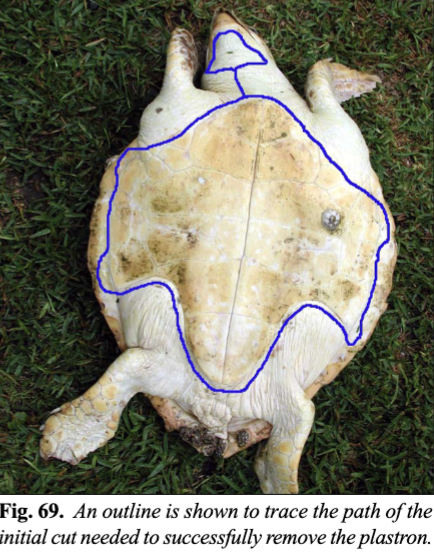
How does one access the internal anatomy of sea turtles?
The plastron must be removed first, with cuts around the periphery of the plastron along the sea formed by the marginal and inframarginal scutes, along the posterior and axillary body, then to the head region.
How can you identify males and females based on external anatomy?
Mature males have long tails with cloacal openings near the tip, while females have short tails. Males also have long curved claws and the mid ventral plastron becomes soft during mating season.
Describe the internal anatomy of each sea turtle gender.
Immature males have gonads, but their tails are not noticeably longer than females so gonads must be examined to determine sex. The gonads are posterior to the lung and ventral to the kidneys.
Females have round, yellow follicles. If they have nested previously, the ovary will have round, flat, white structures and less compact ovaries.
What is a neophyte nester?
It is a female sea turtle that is nesting for the first time.
What is the function of papillae?
It is to keep a turtle’s food traveling down to the stomach instead of escaping. They eat slippery foods like jellyfish, so this helps prevent slippage.
True or false: Scutes are numbered from the posterior end to the anterior end.
False. They are numbered front to back.
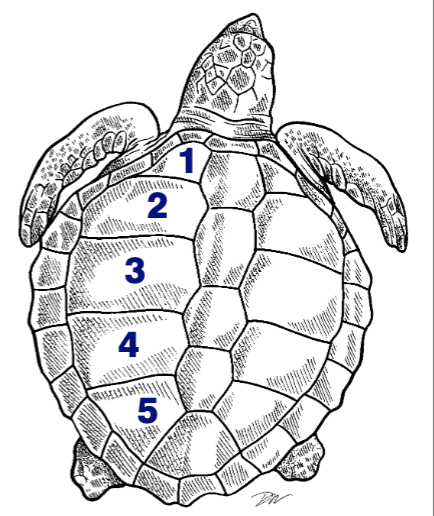
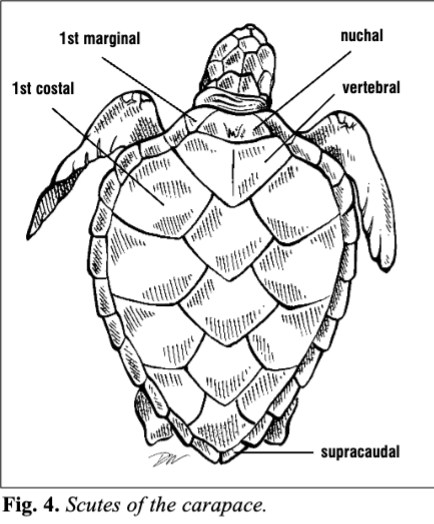
Name and order all of the carapace scutes.
The lastmarginal scutes on each side are termed supracaudals or postcentral.
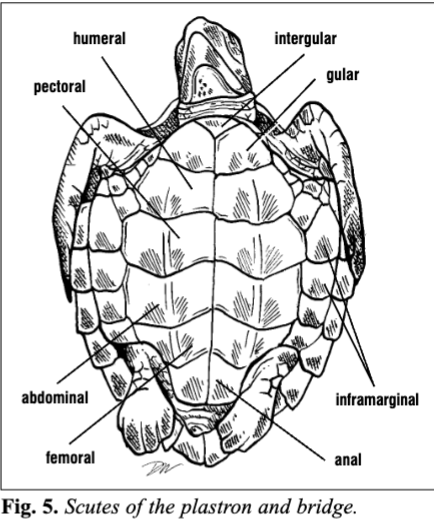
Name and order all of the plastron scutes.
How do satellite transmitters (Satellite Relayed Data Loggers) work?
They are attached to marine mammals with glue. They continuously collect, compress, and store data before transmitting the information to a satellite. The data are then relayed to ground stations, which process the information, compute the location from which the message was received, and place the location and raw data in a database. They last about a year and cost $3-6,000
How do radionavigation devices work?
They also store and transmit data, however, because radio waves don’t travel easily through water, data collected during dives must be stored for later transmission when the animal surfaces. In addition, transmission requires than an antenna be in the “line of sight” of the transmitter, making tracking over long distances difficult.
How do bioacoustic tracking devices work?
Bioacoustic tracking methods are based on the face that different species produce different sounds. Scientists can use underwater listening systems to track not only a variety of marine mammal species, but even individuals. As with radio navigation devices, bioacoustic tracking requires that researchers be within range of the animal in order to collect data.
What kinds of animals can be tagged?
A wide variety of marine animals can be tracked using tags, such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sea otters, sea turtles, sharks, and fish.
Why is tagging data useful?
It can give insight into how often and for how long an animal is on land, how deep they can dive, and migratory behaviors. This can help conservation efforts to know what areas to focus on ie. preventing boat traffic on whale migration routes or protecting a critical sea lion mating beach.