General IM Knowledge - The Rotation Series
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
CRAB:
HyperCalcemia
Renal dysfunction
Anemia
Bone pain
How do you diagnose multiple myeloma?
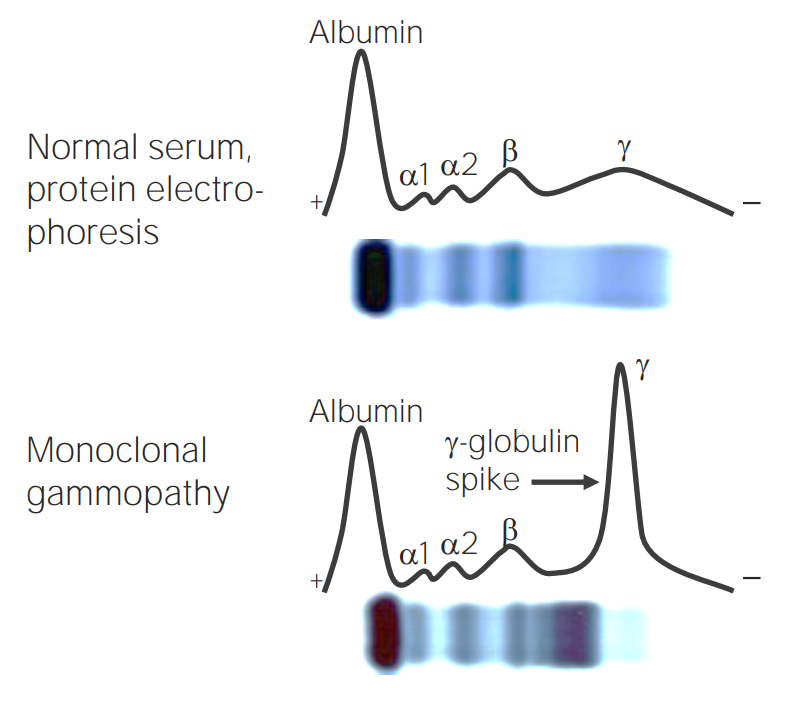
Gamma-globulin protein spike!
What lab values could point us to Multiple Myeloma?
Lasix!
Blocks the Na+/K+/2Cl- transporter in the ascending loop of Henle
What is the drug store name for furosemide? What is the MOA?
Fevers/Chills?
Chest pain?
SOB?
Abdominal pain?
Nausea and vomiting?
Pooping? (normal bowel movements)
Hobbies?
What are good questions to always ask when you see a patient in the hospital?
PIRATES:
P: Pulmonary/Post-op
I: Ischemia
R: Rheumatic
A: Anemia
T: Thyroid
E: Electrolytes/Ethanol
S: Sepsis
What are the most common causes for AFib?
Embolic stroke
Rapid Ventricular Response (RVR) → HR>10
What are the most common complications of AFib?
Left atrial appendage
What is the location that thrombi typically form?
CHAS2VASC score!
Score > 2 = start anticoagulants
What is the score that we can use to estimate the risk of stroke? At what score are anticoagulation drugs indicated?
CHF
HTN
Age > 65
DM
Stroke
Vascular disease
Sex category (Female = 1 point)
What does the CHADS2VASC score stand for?
HASBLED score
What score estimates the risk of bleeding with anticoagulation?
Rate control mediacations: Dilitiazem, verapmil, beta-blockers
Anticoagulant: Apixiban, Rivaroxaban, Warfin
What medications do we use to treat A-Fib?
TRUE!
The AFFIRM trial showed that rate control = rhythm control
True or False: Rate control = Rhythm control, how do you know?
The RACE II trial showed that lenient rate control (HR < 110) is better than strict rate control (HR < 80)
The **** trial shwed that *** rate control (HR < ***) is better than *** rate control (HR < ***)
Cardioversion
SHOCK
How do you treat an afib patient who is hemodynamically unstable?
Tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy
If a patient has prolonged afib with RVR leading to CHF, what is this called?
Unstable angina, NSTEMI, and STEMI
What are the 3 different types of acute coronary syndrome?
Unstable angina does not have elevated troponin levels
How can you differentiate unstable angina from NSTEMI & STEMI?
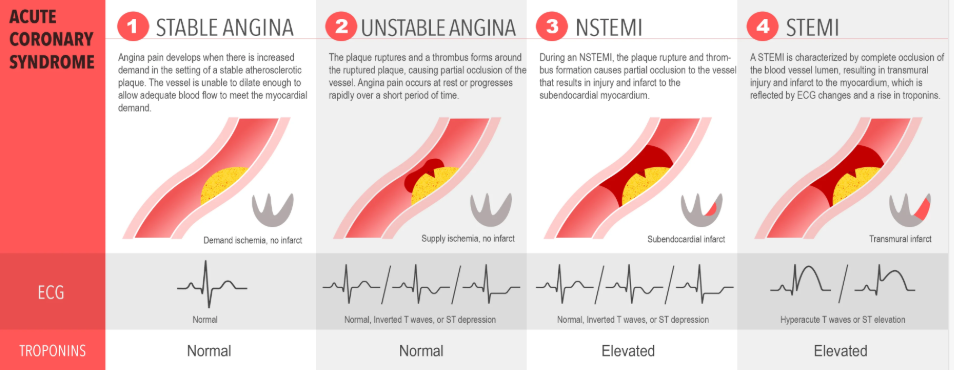
Name the disease from left to right
4 hours
How long does it take before troponin starts to rise after an MI?
Aspirin 325 mg → 81mg daily
What treatment should IMMEDIATELY be given if an MI is suspected?
Medical managment
Stent (PCI)
CABG
What are the 3 types of treatment for MI?
Radiation of pain to the RIGHT arm
What historyu finding is most spefic for acute MI?
the RIGHT arm
Pain radiating to which arm is more specific for an acute MI?
Costochondritis/MSK issue
Chest pain with tenderness to palpation to chest wall is most likely what?
Substernal Chest pain
Worse with exertion
Relieved with rest or nitroglycerin
(3 = typical, 2 = atypical, 0-1 = non-cardiac)
What are the 3 features of typical chest pain?
Demand ischemia!
Type 2 MI
If a patient has elevated troponins and signs of ischemia but you dont think it’s from a primary ACS what are we thinking?
Oxygen supplementation
Nicotine cessation (STOP SMOKING!)
What are the only two COPD treatments that reduce mortality?
88% - 92%
What is the goal O2 sat for COPD patients?
Reversal of hypoxic pulmonary vasculature!
Can cause respiratory failure
Why is giving COPD patients more oxygen bad?
Long Acting Muscarinic Antagonist → Long Acting Beta agonist → Inhaled Corticosteroids
LAMA (Tiotropium) → LABA (Salmeterol) → ICS (albuterol)
*For asthma do the opposite!
What is the typical progression of inhaled treatments?
Change in sputum
Increasing dyspnea or SOB
What is the criteria defining COPD exacerbation?
Duoneb
Ipratropium-albuterol (Short-acting muscarinic antagonist, and short-acting beta-agonist)
What is the nebulized treatment we often give in the hospital?
Steroid, azithromycin
What medications do you give for COPD exacerbation?
5 day
per the REDUCE trial
How long should we give steroids for COPD exacerbation?
Decreases inflammation
Why is azithromycin useful for COPD exacerbations?
O2 sat < 88%
or
PaO2 < 55
What are the indications to start O2 in COPD?
IMPENDING RESPIRATORY FAILURE!!
You may need to intubate
*They literally have such low airflow we cant hear it anymore
An asthma/COPD patient start to look worse, but their wheezing goes away and PCO2 rises to 40 (normal)… what is going on?
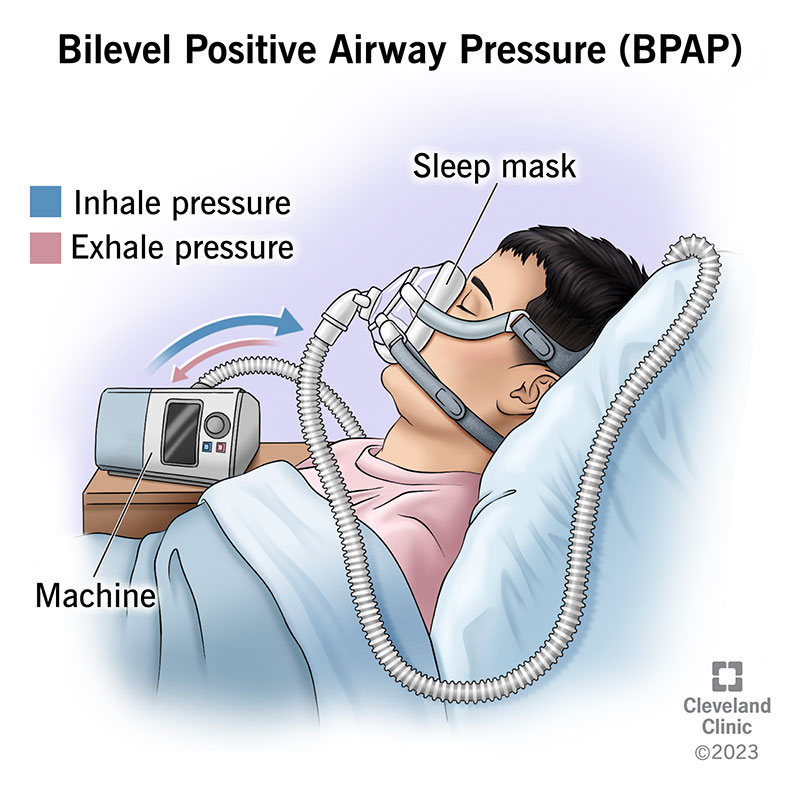
BIPAP!
(Not CPAP → cpap only gives oxygen and does not ventilate)
What is a non-invasive ventilation you can use before intubation?
FEV1/FVC < 0.7
FEV1/FVC ratio that defines obstructive lung disease = ?
Hepatic encephalopathy
Ascities
SBP
Variceal bleed
Hepatorenal syndrome
What are the complications of cirrhosis?
Decompensated cirrhosis!
If a patient presents with a complication to cirrhosis, what is this called?
Non-adherance to meds
Infection
Bleed
Hypokalemia
Overdiuresis
What are the triggers for decompensated cirrhosis?
Lactulose (titrated to 2-3 bowel movements/day
Rifaximin if refractory
How do you treat hepatic encephalopathy?
1 = sleep disturbance
2-3 = confusion with asterixis
4 = coma
What are the stages of hepatic encephalopathy?
Spironolactone + Furosemide in 5:2 ratio
Large volume paracentesis if needed
How do you treat ascities?
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Any cirrhotic patient with ascites and fever needs to be ruled out for what condition?
Diagnostic
Therapeutic
What are the two types of paracentesis?
PMNs > 250
What is the criteria for diagnosing SBP in ascites fluid?
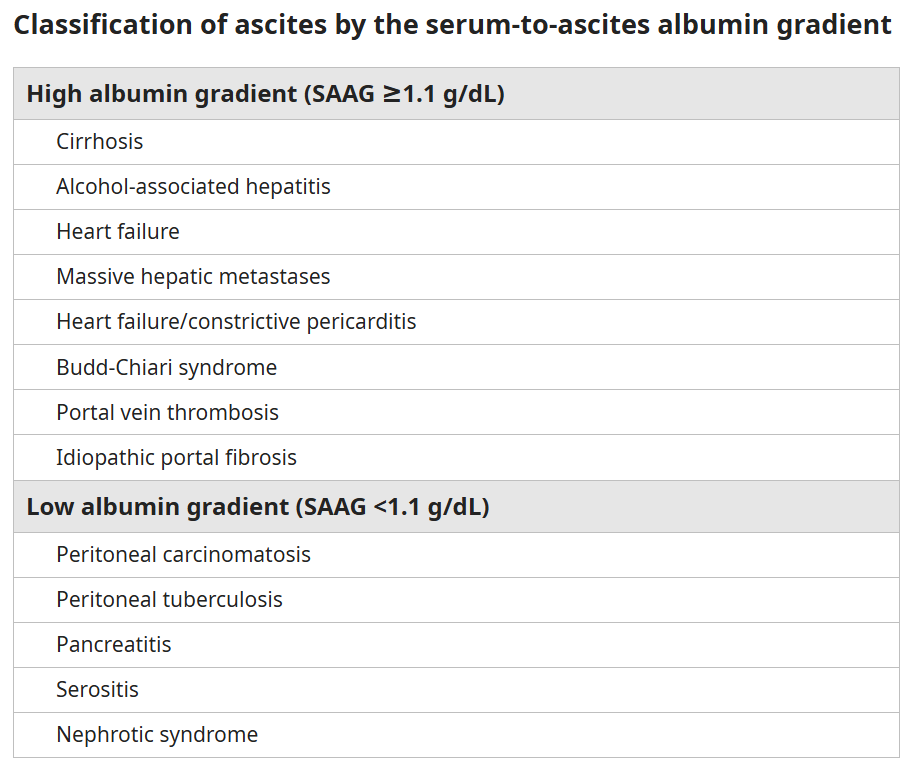
SAAG > 1.1 - Portal hypertension!!
Serum Ascites Albumin Gradient
How can you tell if ascites fluid is from portal hypertension or another etiology?
Octreotide
Ceftriaxone
PPI
2 large bore IVs
Consult GI for banding of varices
When the patient is stable you can use beta blockers for prophylaxis!
What is the treatment for variceal bleed?
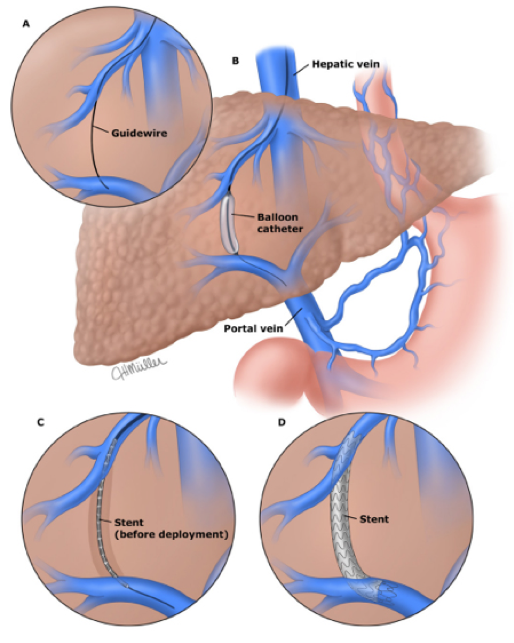
TIPS!
What is the procedure that can reduce risk of variceal bleed by decreasing portal pressure?
Worsened hepatic enecephalopathy!
The liver is not processing the ammoniu
What is the expected complication of TIPS?
FALSE!
It is more of a marker of damage/inflammation NOT function
True or false: AST/ALT a marker of liver function
PT/INR
Bilirubin
Albumin
Platelets
What are the actual measures of liver function?
MELD - Na
If >15 start thinking about transplant
What score is used to determine the degree of cirrhosis and need for transplant?
Hepatocellular → Elevated AST ALT, with minimal ALP/Bilirubin elevation
Cholestatic → Significantly elevated ALP bilirubin, but minimal AST/ALT elevation
What are the two patterns of liver injury
VAID
Viral hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis
Ischemic (shock liver)
Drug-induced
What condition can cause AST/ALT in the thousands?
Anti-smooth muscle Ab (ASMA)
What is the antibody for autoimmune hepatitis?
Anti-mitochondrial Ab (AMA)
What is the antibody for primary biliary cholangitis?
Encephalopathy
INR > 5
*If they meet the criteria consider a transplant
What is the criteria for acute liver failure?
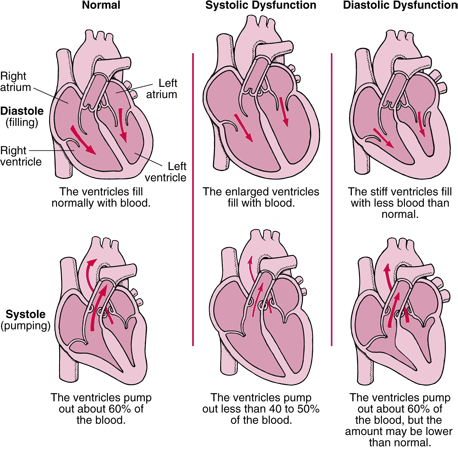
Systolic (HRrEF) → Eccentric
HFmrEF
Diastolic (HFpEF) → Concentric
What are the different classifications of CHF?
HFrEF → <40%
HFmrEF → 40%-50%
HFpEF → > 50%
What are the ejection fraction cut offs for CHF?
Ischemic → HTN, Smoking, obesity, DM, MI
Non-Ischemic → Drug use, viral cardiomyopathies
What are the two broad categories of causes of systolic HF?
Beta blockers
ACE inhibitors
Spironolactone
SGLT2 inhibitors, ICDs (implantable cardiac defibrilators), CRT (cardiac resynchronization therapies), and Bidil in African American populations
What treatments decrease mortality in SYSTOLIC HF?
NONE! → Treat the underlying condition
The mcc is HTN
What treatments decrease mortality in diastolic HF?
JVD!
In practice look at the IVC on POCUS
What physical exam maneuver has the highest sensitivity for volume overload? What about in clinical practice?
BNP!
What is the test with the highest sensitivity for CHF exacerbation?
BNP < 100
Meaning they are probably not volume overloaded enough
What is the BNP cut-off that can rule out CHF?
because adipocytes degrade BNP
What is the reason BNP may be falsely low in obese patients?
K > 4
Mg > 2
*For every 10mEq given, raises their serum K by 0.1, and for every 1 g of Mg goes up by 0.1
What is the goal K and Mg in patients who are being diuresed?
2-2.5x home does
Per DOSE trial
How much Lasix should you give for CHF exacerbation?
6 hours!
LaSIX
How long does Lasix last?
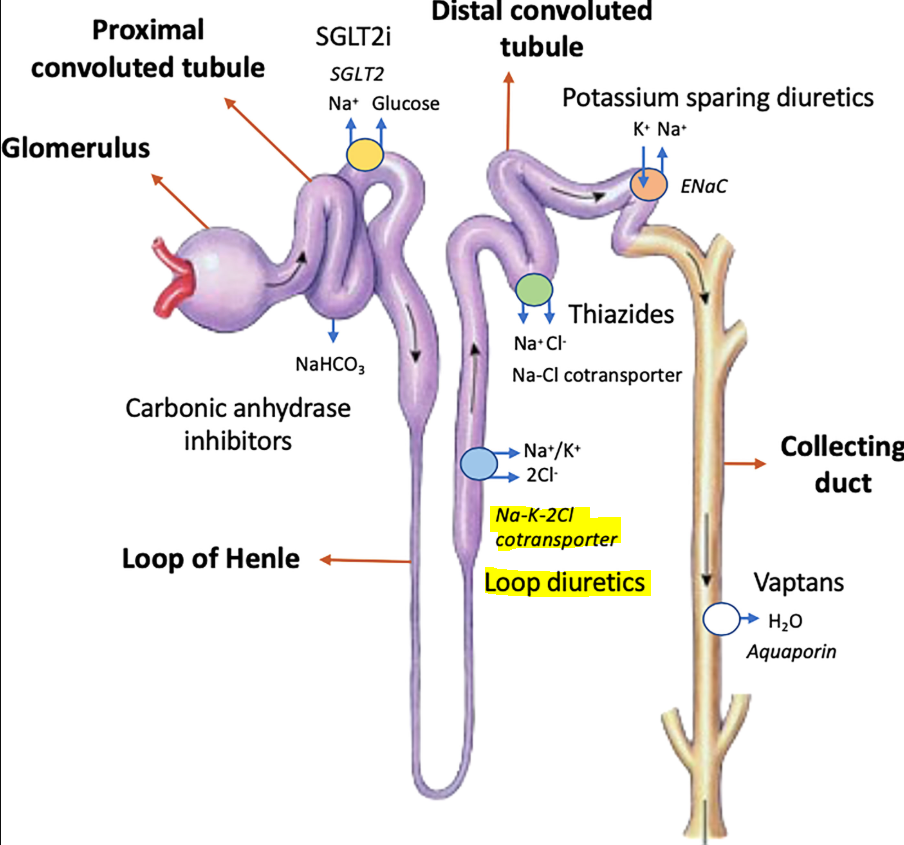
Furosemide!
A sulfonamide loop diuretic that blocks the Na-K- 2Cl- channel
What is the common name for Lasix? What is the MOA?
140-180 mg/dL
Per the NICE-SUGAR trial
*Helps to prevent any hypoglycemic events from occuring
What is the goal glucose range for hospitalized diabetic patients?
Typically NONE except insulin
What outpatient diabetes medication should you continue while inpatient?
Lactic Acidosis!
What are people worried about when using metformin in patients with renal impairment?
Fear of hypoglycemia if patients develop AKI
Pancreas issues (GLP-1, DDP-4 → cause insulin secretion)
Euglycemic DKA
HF (-glitazones)
Why do we hold most outpatient ORAL diabetic medications on admission?
SGLT2 Inhibitors
What is a diabetic medication that has mortality benefit in HFrEF?
<7%
<8% in elderly
What is the goal A1c in most adults?
ACCORD trial!
What landmark trial showed that strict A1C goal <6% was not better than lenient <7-8%?
No!
It reduces microvascular complications
Does good control of blood glucose reduce macrovascular complications?
Fluids, insulin, and K+
What is the treatment for DKA?
Urine: Ketones
Serum: Beta-hydroxybutyrate
What can you find in urine and serum that can help diagnose DKA?
Anion gap!!
We want to close it and make it <12
What value do you trend while treating a patient with DKA?
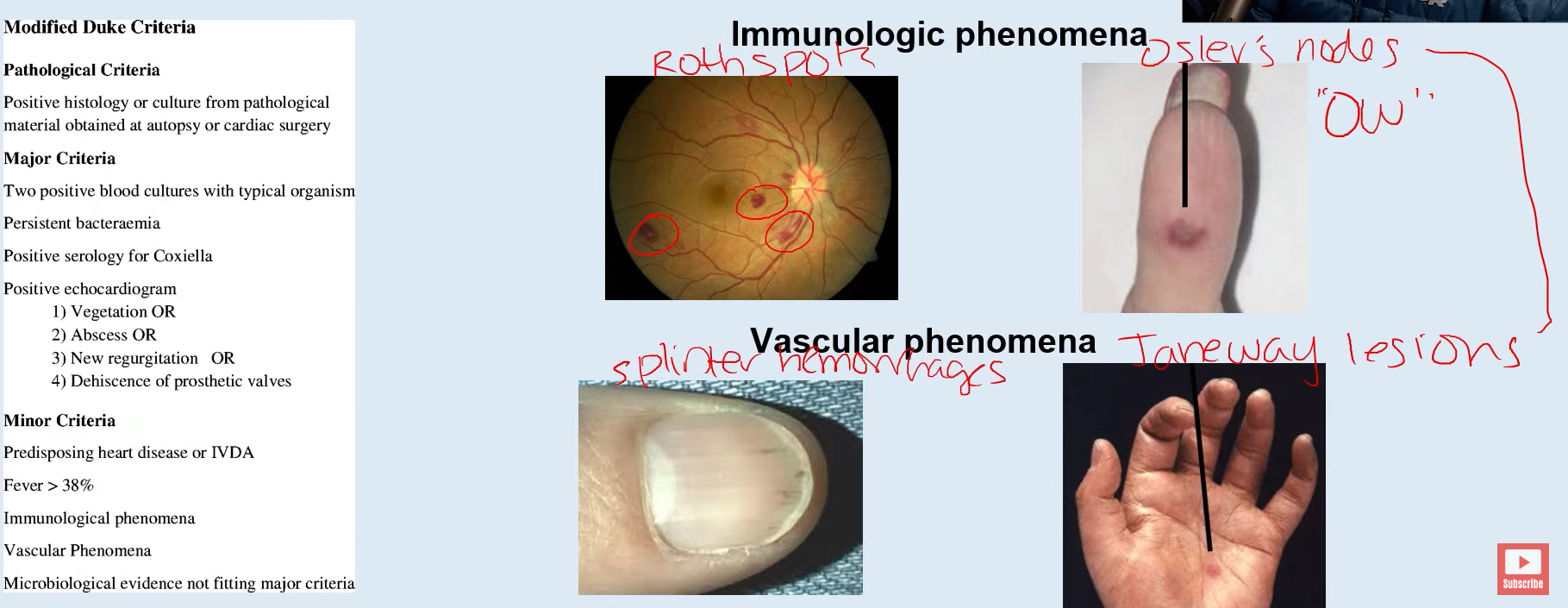
Duke criteria!
What criteria do we use to diagnose endocarditis?
They are “stickier” than gram negative!
I.e. staph aureus or strep need repeat blood cultures
Why do we have to keep repeating blood cultures for gram positive organisms?
Heart rate!
What is the first vital sign to change in acute GI bleed?
Two large-bore IVs!
All patients with GI bleed need two what?
18-gauge or larger
Smaller number is bigger (i.e. 16,14,…)
What size defines a large bore IV?
Usually no!
It’s too long, therefore there is a lot of resistance
Can you give rapid fluid resuscitation through a central line?
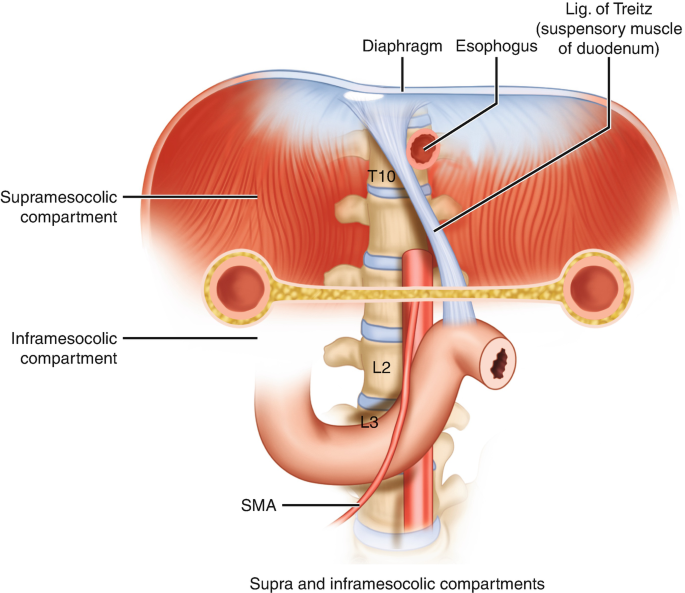
Ligament of Treitz!
What is the cut-off point for upper and lower GI bleed?
Melena
Hematemesis
Coffee-ground emesis
What are presenting symptoms of upper GI bleed?
Hematochezia
What are the presenting symptoms of lower GI bleed?
The passage of dark tarry stools containing blood
Define Melena
The passage of fresh bright red blood in the stool
Define Hematochezia
DiverticulOSIS bleeds
Diverituclitis hurts
Does diverticulosis or diverticulitis bleed?
Colonoscopy with banding
CT angiogram with IR embolization
What are two treatment approaches to active lower GI bleed?
HGB > 7 g/dL
Per TRICC trial
What is the transfusion goal for hemoglobin?