Chemistry - Biochem lipids
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/22
Last updated 12:30 AM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Lipid
* Range of biomolecules like fats, oils, steroids, and phospholipids
* Hydrophobic, but soluble in non-polar solvents
* Reduced molecules
* Hydrophobic, but soluble in non-polar solvents
* Reduced molecules
2
New cards
Lipids are essential
They contain stored energy, and because they are more reduced than carbohydrates, they can undergo more oxidation, release twice the energy.
But, due to their insolubility they take way longer to be broken down, meaning the energy is released slowly.
They also play an important structural role, being part of the membranes that bind cells.
But, due to their insolubility they take way longer to be broken down, meaning the energy is released slowly.
They also play an important structural role, being part of the membranes that bind cells.
3
New cards
Excess lipids in diet
The low solubility of lipids often results in their deposition in the walls of main blood vessels. This restricts blood flow, a condition called **atherosclerosis**.
A diet too rich in lipids can lead to excess accumulation, (through the transformation of fats into adipose tissue), resulting in obesity.
A diet too rich in lipids can lead to excess accumulation, (through the transformation of fats into adipose tissue), resulting in obesity.
4
New cards
Cholesterol
A molecule that is insoluble in blood, and transported with either low density lipoprotein, or high density lipoprotein.
When transported with LDL, cholesterol increases deposition in the walls of the arteries. This is caused by saturated and trans fats.
When transported with LDL, cholesterol increases deposition in the walls of the arteries. This is caused by saturated and trans fats.
5
New cards
Essential fatty acids
omega-3-poly-unsaturated fatty acid (fish oil or flax seeds), which cannot be produced by the body, but must be taken in ones diet!
6
New cards
Uses and abuses of steroids
Often lipids are present in contraceptive pill formulations, which are steroid treatments.
They are also present in male steroid hormones called androgens, with testosterone as the main hormone. Used for balls and boob cancer. Androgens are also known as anabolic steroids. Have also been used for performance enhancing drugs.
They are also present in male steroid hormones called androgens, with testosterone as the main hormone. Used for balls and boob cancer. Androgens are also known as anabolic steroids. Have also been used for performance enhancing drugs.
7
New cards
Structures of different lipids
* triglycerides
* Phospholipids
* Steroids
* Phospholipids
* Steroids
8
New cards
Triglycerides
Esters formed by condensation reactions between **glycerol** and **three fatty acids**.
It is formed when 1 glycerol condenses with *three* fatty acids, to form the *tri*glyceride. (the fatty acids don’t have to be the exact same)
* An esterification reaction takes place between an acid -COOH group and each -OH group in glycerol, eliminating water as each ester link forms.
It is formed when 1 glycerol condenses with *three* fatty acids, to form the *tri*glyceride. (the fatty acids don’t have to be the exact same)
* An esterification reaction takes place between an acid -COOH group and each -OH group in glycerol, eliminating water as each ester link forms.
9
New cards
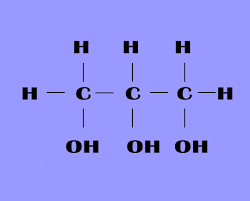
Glycerol
A molecule with three carbon atoms, each of which has an alcohol group.
10
New cards
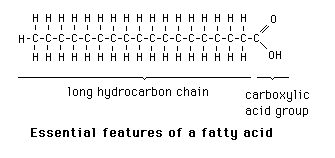
Fatty acids
Long chain carboxylic acids R-COOH.
They are different, allowing for different fats and oils.
* The length of their hydrocarbon chain: the most abundant fatty acids have an even number of carbon atoms with chains between 12 and 22 carbon atoms long.
* The number and position of carbon-carbon double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain
* fatty acids with no double bonds are said to be **saturated**
* fatty acids with a single double bond are described as **mono-saturated**
* fatty acids with several double bonds are descrbed as **poly-saturated**
They are different, allowing for different fats and oils.
* The length of their hydrocarbon chain: the most abundant fatty acids have an even number of carbon atoms with chains between 12 and 22 carbon atoms long.
* The number and position of carbon-carbon double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain
* fatty acids with no double bonds are said to be **saturated**
* fatty acids with a single double bond are described as **mono-saturated**
* fatty acids with several double bonds are descrbed as **poly-saturated**
11
New cards
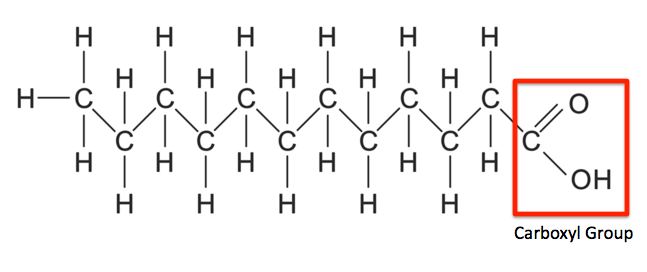
Saturated fatty acids
* CnH2n + 1COOH
* Carbon-carbon single bonds
* Tetrahedral bond angles (109.5), leading to significant London dispersion forces (ergo packed closely together)
* Form saturated triglycerides, with high melting points.
* Known as fats - butter and lard
* Carbon-carbon single bonds
* Tetrahedral bond angles (109.5), leading to significant London dispersion forces (ergo packed closely together)
* Form saturated triglycerides, with high melting points.
* Known as fats - butter and lard
12
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acids
* Contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds
* 120 bond angles, with kinks in the chains (therefore not packed as closely together)
* Form unsaturated triglycerides, which have weaker intermolecular forces with lower melting points
* Known as oils - corn oil, cod liver oil
* 120 bond angles, with kinks in the chains (therefore not packed as closely together)
* Form unsaturated triglycerides, which have weaker intermolecular forces with lower melting points
* Known as oils - corn oil, cod liver oil
13
New cards
Addition reactions
Unsaturated fatty acids are able to undergo addition reactions by breaking the carbon-carbon double bond(s) and adding incoming groups to the new bonding positions created on the carbon atom.
Iodine is able to react with unsaturated fats in this way. The higher the number of double bonds per molecule, the larger the amount of iodine that can react.
Iodine is able to react with unsaturated fats in this way. The higher the number of double bonds per molecule, the larger the amount of iodine that can react.
14
New cards
iodine number
the number of grams of iodine which reacts with 100 grams of fat.
The measure of the amount of unsaturation in the fat.
The measure of the amount of unsaturation in the fat.
15
New cards
Hydrogenation
Similar reaction to the addition of iodine, but with hydrogen.
Often carried out by the food industry to increase the saturation of oils. This produces trans fats.
Often carried out by the food industry to increase the saturation of oils. This produces trans fats.
16
New cards
Rancidity of fats
When fats are stored for long periods of time, they can undergo chemical change which causes them to become **rancid**.
This is characterized by bad smell, taste, texture, or appearance.
It can be caused by either:
* Hydrolytic rancidity
* Oxidative rancidity
This is characterized by bad smell, taste, texture, or appearance.
It can be caused by either:
* Hydrolytic rancidity
* Oxidative rancidity
17
New cards
Hydrolytic rancidity
* Occurs when the fat breaks down by hydrolysis reactions, using the water present in - food. The site of reactivity is the ester linkages in triglycerides.
* Occurs readily in heat
* Catalyzed by the enzyme lipase, and can be favoured in the presence of certain bacteria.
* The rancid smell and flavour is due to the release of free fatty acids.
* Can be reduced by refrigeration
* Occurs readily in heat
* Catalyzed by the enzyme lipase, and can be favoured in the presence of certain bacteria.
* The rancid smell and flavour is due to the release of free fatty acids.
* Can be reduced by refrigeration
18
New cards
Oxidative rancidity
* Occurs when unsaturated fats react with oxygen from the air
* Site of reactivity is the carbon-carbon double bonds in unsaturated triglycerides
* The process known as auto-oxidation, is often accelerated by light and enzymes or metal ions, proceeding via a free-radical mechanism and so yields a mixture of products.
* Characteristic of fats and oils that have a high proportion of carbon-carbon double bonds, such herring fish.
* Can be controlled by the addition of **antioxidants**.
* Site of reactivity is the carbon-carbon double bonds in unsaturated triglycerides
* The process known as auto-oxidation, is often accelerated by light and enzymes or metal ions, proceeding via a free-radical mechanism and so yields a mixture of products.
* Characteristic of fats and oils that have a high proportion of carbon-carbon double bonds, such herring fish.
* Can be controlled by the addition of **antioxidants**.
19
New cards
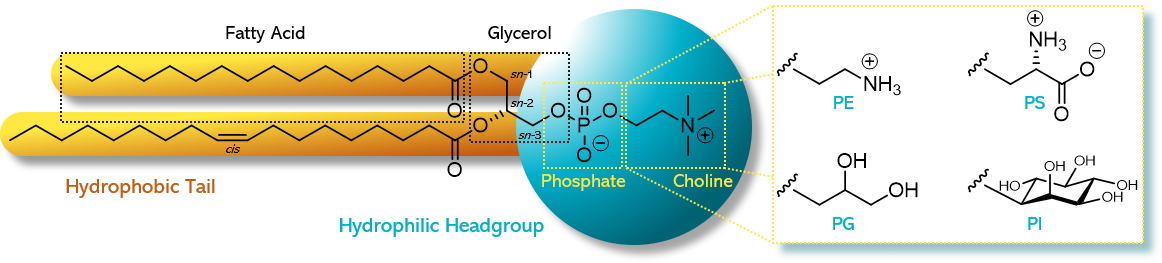
Structure of phospholipids
* Derived from fatty acids and glycerol
* have only **two** fatty acids condensed onto the glycerol molecule.
* The third -OH position of the glycerol is condensed with a phosphate group.
* The most common phospholipid is lecithin.
* have only **two** fatty acids condensed onto the glycerol molecule.
* The third -OH position of the glycerol is condensed with a phosphate group.
* The most common phospholipid is lecithin.
20
New cards
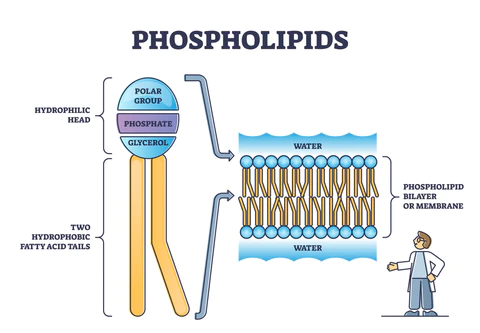
Phospholipid structure
* Hydrophilic head (phosphate group)
* Two hydrophobic groups (the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids)
* Form a **phospholipid bilayer**, which maximizes the interactions between the polar groups and water, while create a non-polar, hydrophobic interior.
* Two hydrophobic groups (the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids)
* Form a **phospholipid bilayer**, which maximizes the interactions between the polar groups and water, while create a non-polar, hydrophobic interior.
21
New cards
Hydrolysis of fats and phospholipids
* Triglycerides and phospholipids are broken down in hydrolysis reactions to yield their component molecules
* Use water
* Either catalyzed by lipase, or set in acidic conditions
* Occurs during digestion of lipids in the gut
* Lipid digestion is slow
* Hydrolysis reactions are also responsible for hydrolytic rancidity
* Soap is made through saponification, which is a reverse esterification
* Use water
* Either catalyzed by lipase, or set in acidic conditions
* Occurs during digestion of lipids in the gut
* Lipid digestion is slow
* Hydrolysis reactions are also responsible for hydrolytic rancidity
* Soap is made through saponification, which is a reverse esterification
22
New cards
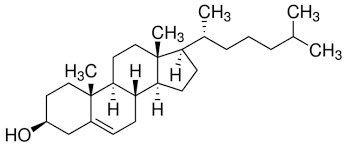
Structure of steroids
* Lipids with a structure consisting four fused rings, known as a **steroidal backbone**
* On of the most important steroids is cholesterol
* On of the most important steroids is cholesterol
23
New cards
Cholesterol as a steroid
* A precursor in the synthesis of biomolecules or other steroids
* Provides fluidity and permeability to the structure of cell membranes
* The hydroxyl group interacts with the polar head groups of phospholipids in the membrane
* The non-polar rings and hydrocarbon chain interact with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer.
* Provides fluidity and permeability to the structure of cell membranes
* The hydroxyl group interacts with the polar head groups of phospholipids in the membrane
* The non-polar rings and hydrocarbon chain interact with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer.