Chapter 7: Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Good leaving groups are the conjugate bases of:
Conjugate bases of strong acids are good leaving groups
SN2 reactions proceed via _______________, because the nucleophile can only attack from the ___________.
Inversion of Configurations; Back Side
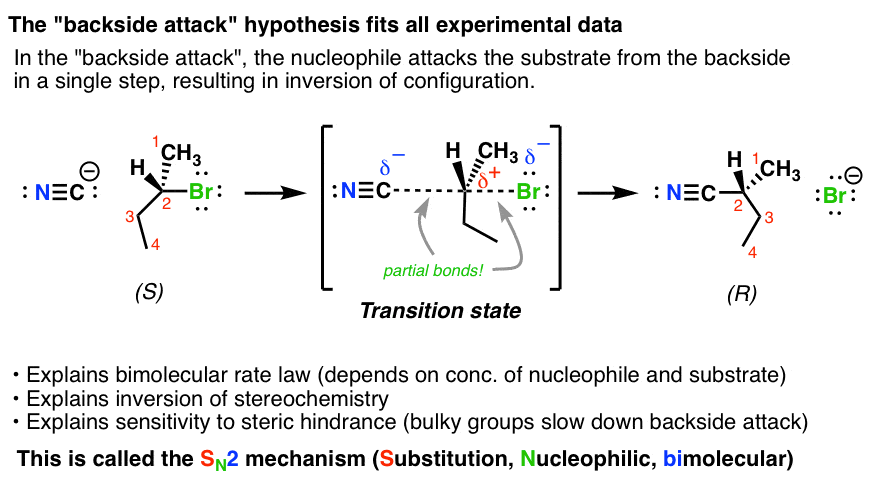
What is an SN2 reaction?
An SN2 reaction is a type of nucleophilic substitution reaction where a nucleophile attacks an electrophile from the back side, leading to the inversion of configuration at the carbon center. The strong nucleophile forms a new bond to the sp3-hybridized carbon while the leaving group detaches in a concerted fashion
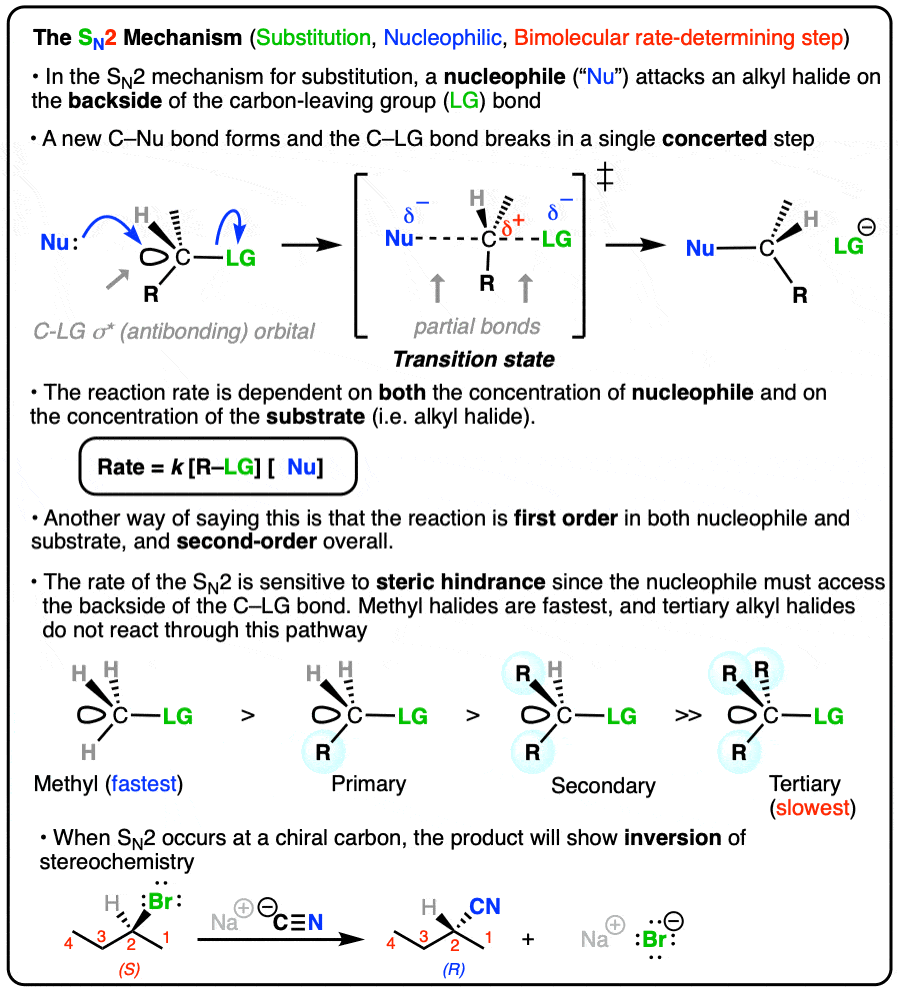
What is a concerted reaction? (Commonly used in SN2)
A chemical reaction that occurs in a single step, where bond breaking and forming happen simultaneously without any intermediates
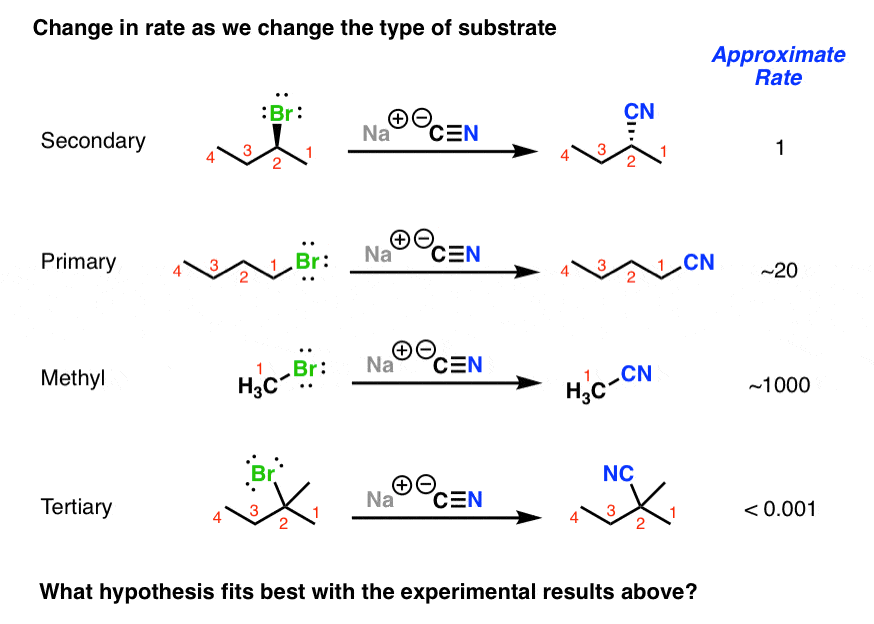
SN2 reactions cannot be performed with what type of halides? Why?
SN2 reactions cannot be performed with tertiary halides. The nucleophile cannot “back-side attack” due to the steric hindrance around the carbon atom bearing the halogen
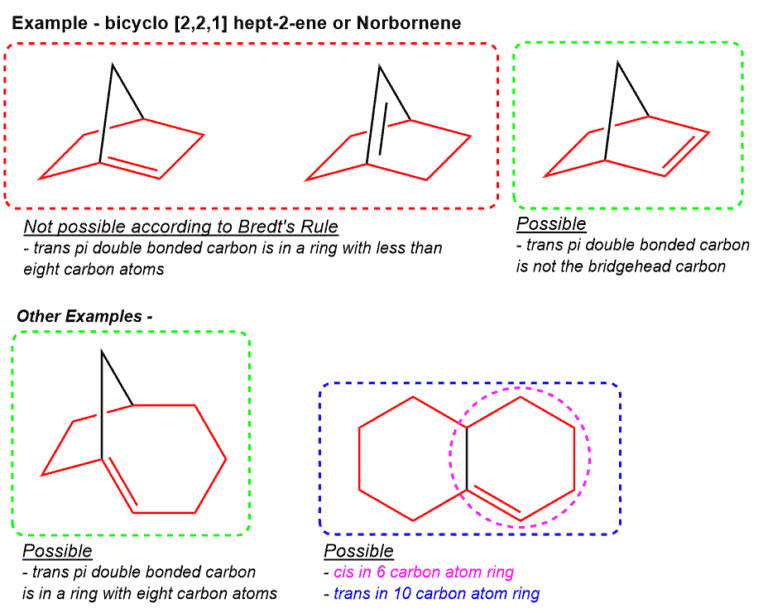
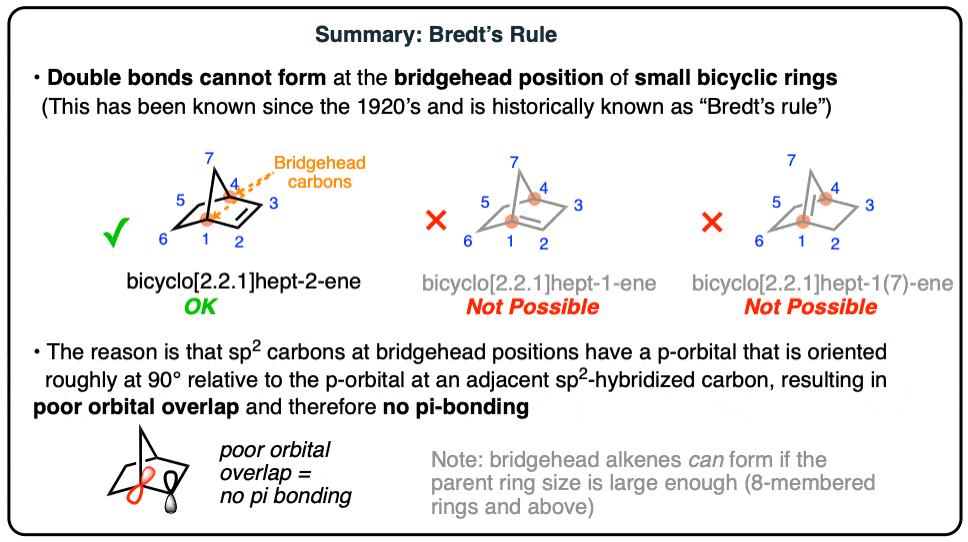
What is Bredt’s rule?
It is not possible for a bridgehead carbon of a bicyclist system to possess a C=C double bond if it involves a trans pi-bond being incorporated in a small ring
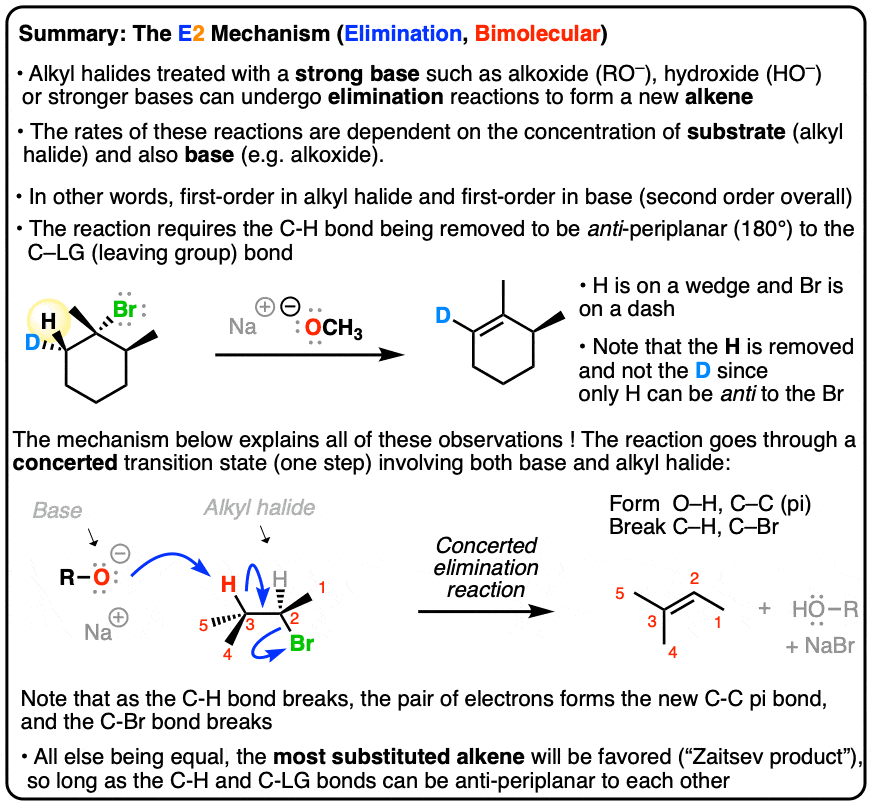
E2 reactions are ___________ and generally favor the more substituted alkene, called the __________
Regioselective; Zaitsev Product
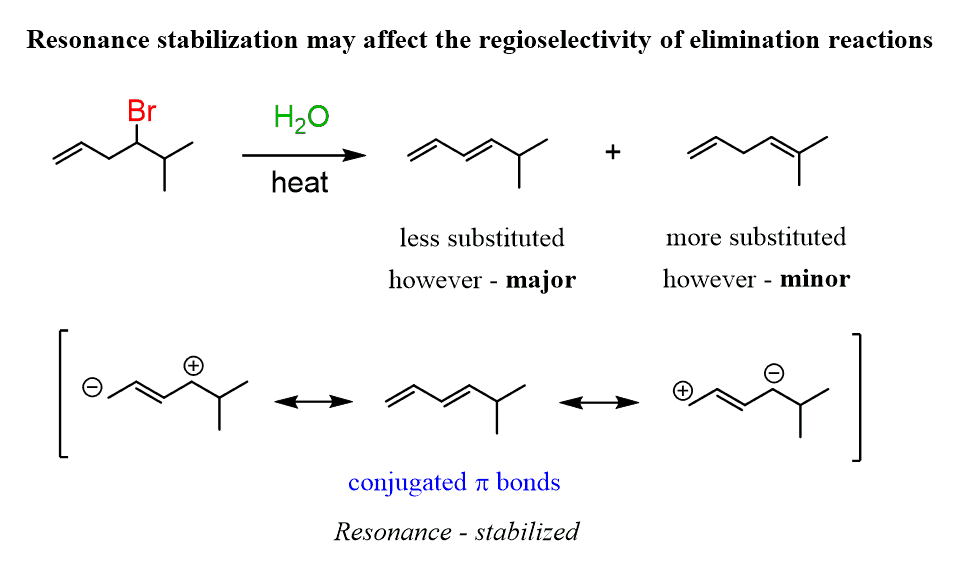
What is regioselective?
Regioselective is a bond forming in a specific location on a molecule
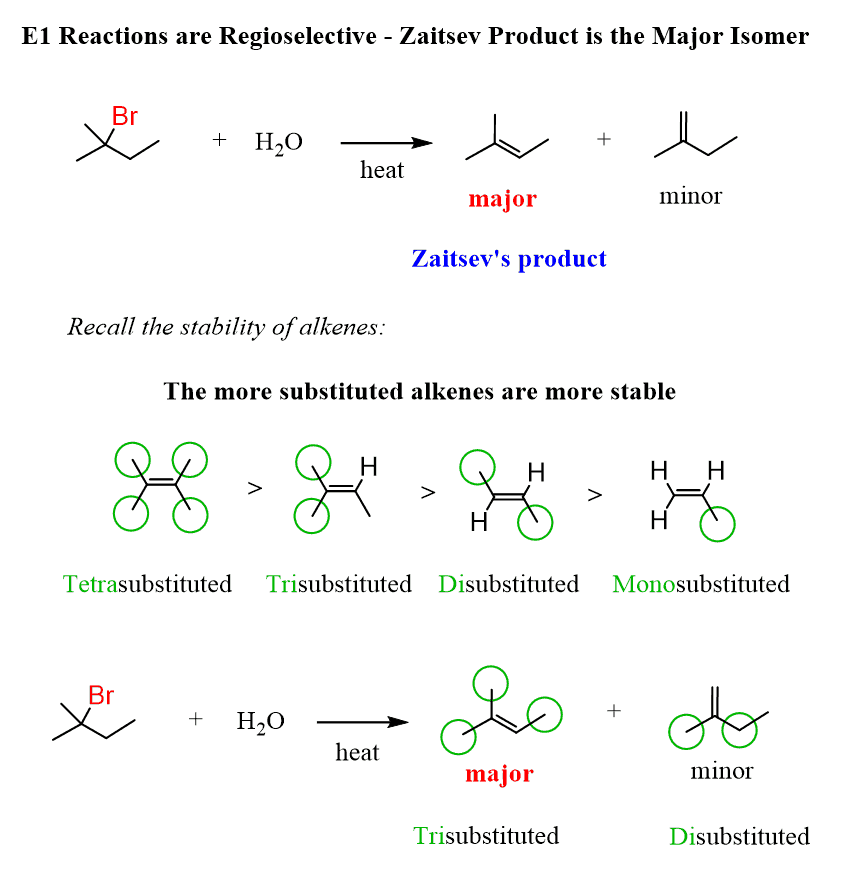
What is the zaitsev product?
Zaitsev product is the major alkene product formed in an elimination reaction, where the more substituted alkene is preferentially formed. The one with more double bonds will be more stable and therefore more common
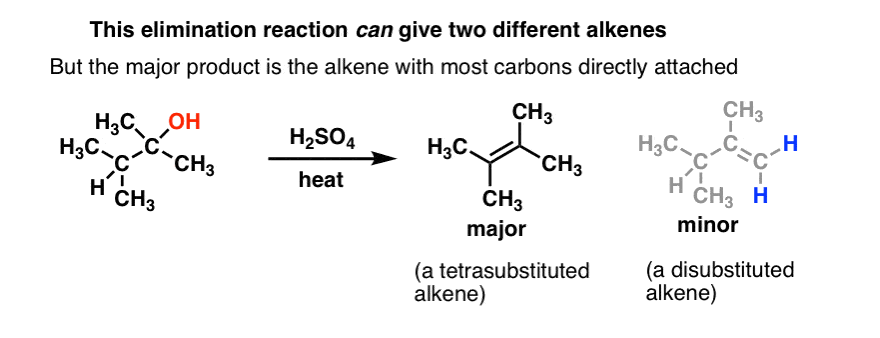
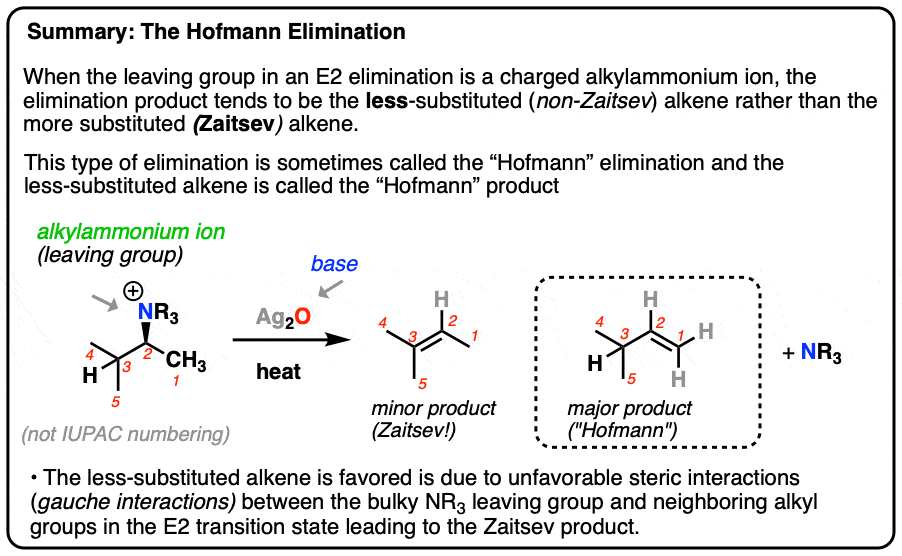
What is the Hofmann product?
Hofmann elimination is an elimination reaction of an amine to form alkenes. The least stable alkene (the one with the fewest substituents on the carbons of the double bond), called the Hofmann product is formed
If the beta position has two different protons, the resulting E2 reaction can be stereoselective, because the _______ isomer will be favored over the _______ isomer (when applicable)
The trans isomer will be favored over the cis isomer
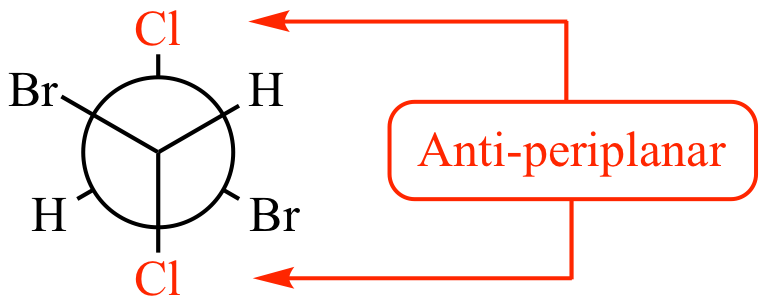
If the beta position only has only one proton, an E2 reaction is said to be __________, because the proton and the leaving group must be _________ to one another
If E2 has one proton, it is stereospecific because the proton and leaving group must be anti-periplanar to one another
What is stereospecific?
A stereospecific reaction is when the starting materials differing only if their configuration are converted into stereoisomeric products
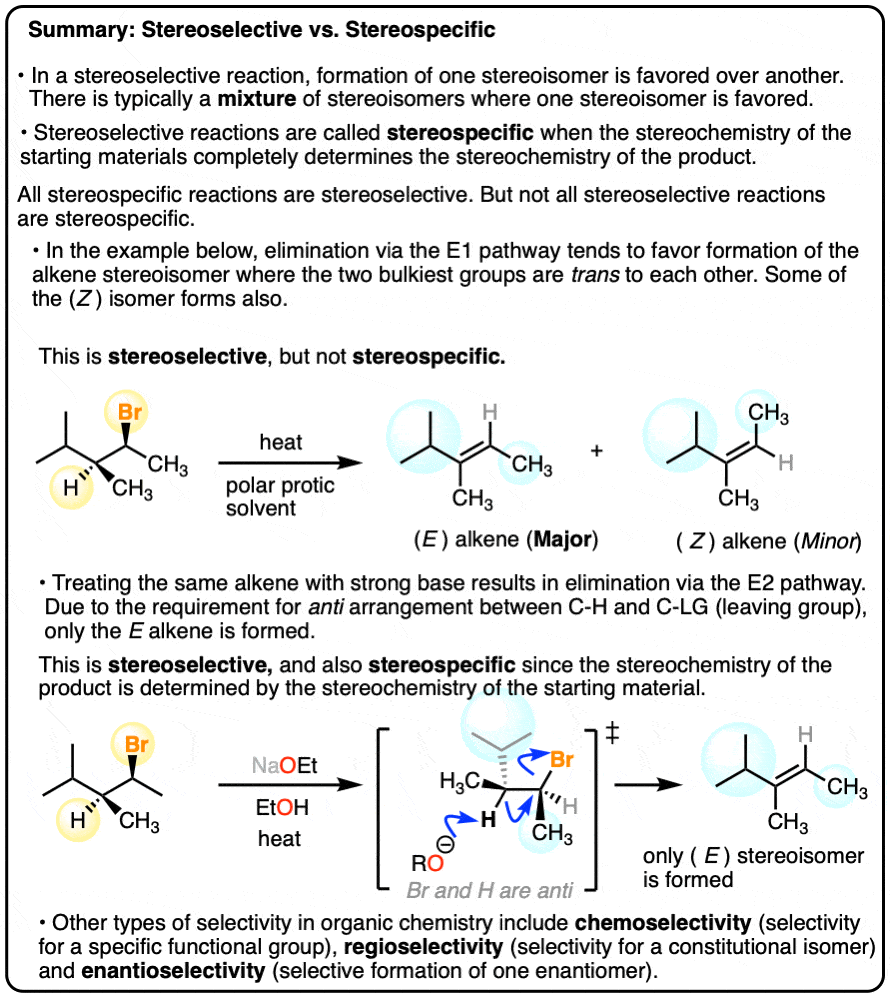
What is anti-periplanar?
Anti-periplanar is a arrangement of atoms where they are opposite of each other across a single bond, typically linear, with a dihedral angle of 180 degrees
Unimolecular nucleophilic substitutions are known as:
Unimolecular nucleophilic substitutions = SN1 reactions
What are the two core steps to an SN1 reaction?
Loss of a leaving group to give a carbocation intermediate
Nucleophilic attack
What is solvolysis?
Solvolysis is the resulting SN1 process when a solvent molecule functions as the attacking nucleophile
Zaitsev v.s. Hoffman products?
Zaitsev's rule predicts that the more substituted alkene (Zaitsev product) is the major product in elimination reactions, while Hofmann's rule (or anti-Zaitsev) predicts the less substituted alkene (Hofmann product) is favored, particularly with bulky bases.
What are E1 reactions?
E1 reactions are Unimolecular elimination reactions
SN1 processes are favored by what type of solvents?
SN1 processes are favored by polar protic solvents
What are polar protic solvents?
SN1 and E1 processes are observed for ___________, as well as __________ halides
SN1 and E1 reactions are observed for tertiary alkyl halides, as well as allylic and benzylic halides
Substitution and elimination reactions often compete with each other. What three steps are required to predict the products?
Determine the function of the reagent
Analyze the substrate and determine the expected mechanism(s)
Consider any relevant regiochemical and stereochemical requirements
When alcohols react with HBr to give alkyl halides, what are the 2 pathways?
For primary and secondary substrates: SN2 pathway
For tertiary substrates: SN1 pathway