Infectious Dz. S1 Exam
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Germ Theory
Particular dz.'s are caused by 1 particular organism
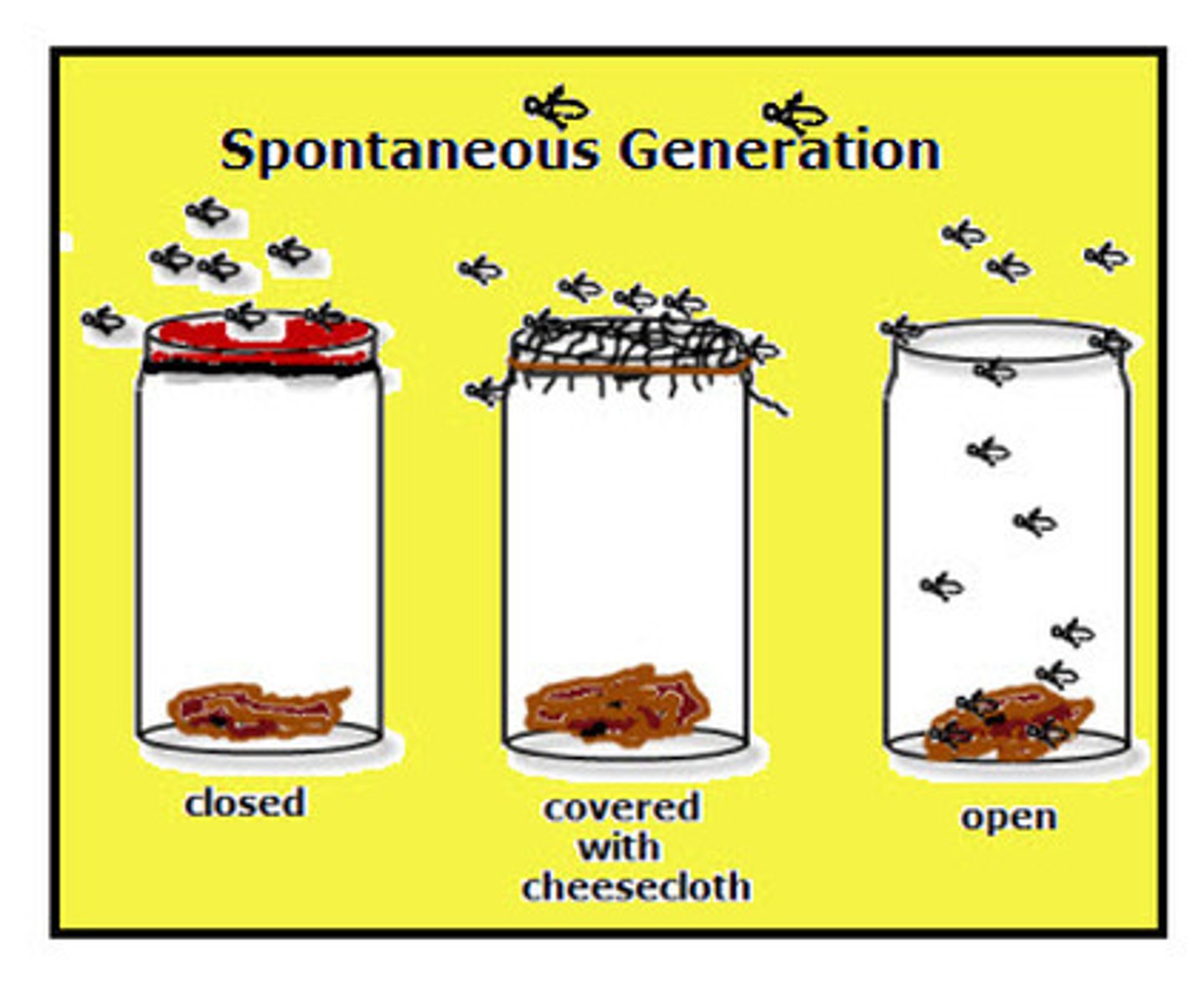
Spontaneous Generation / Abiogenesis
The hypothesis that life arises from nonliving matter spontaneously given the right conditions
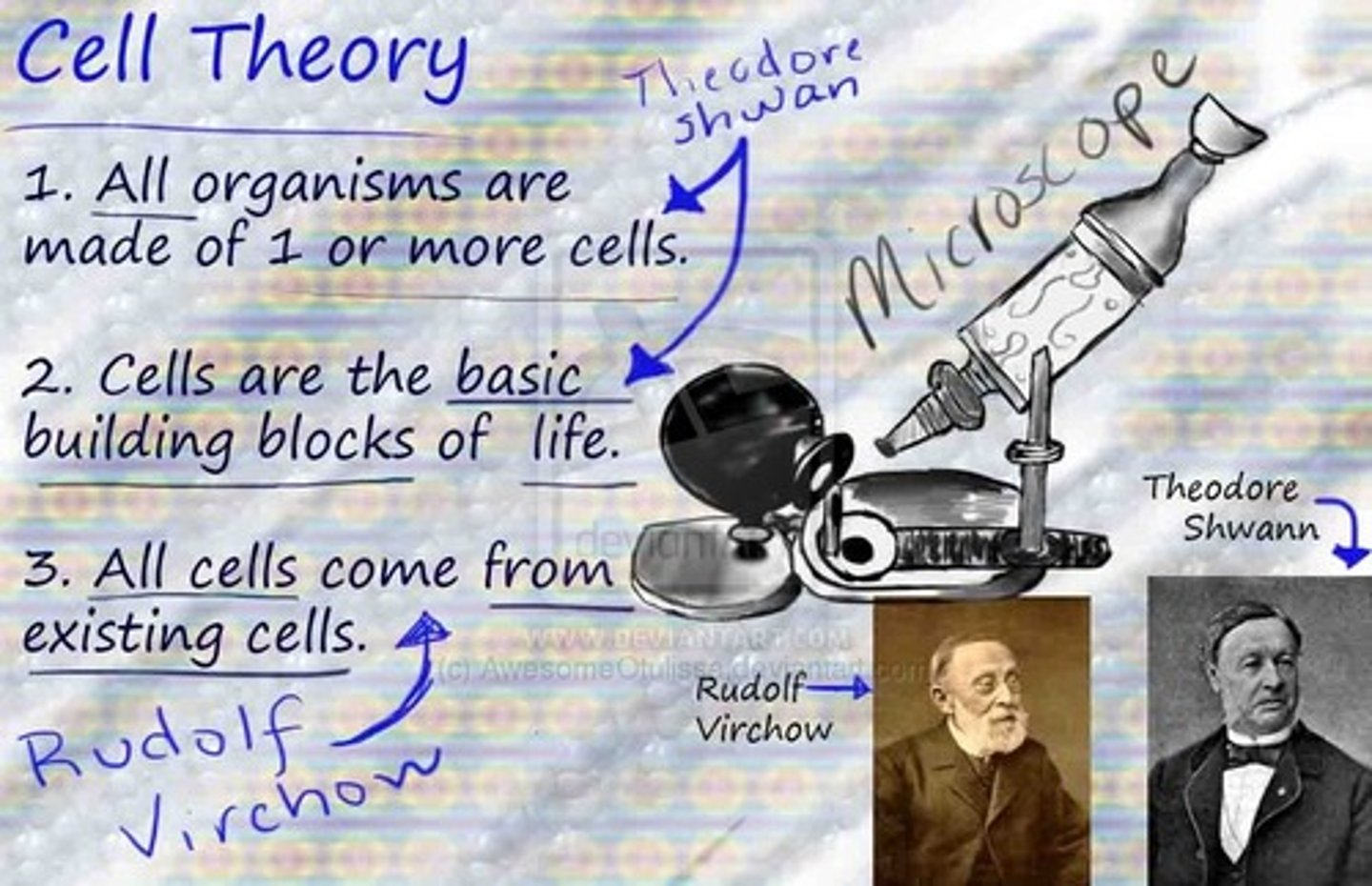
Modern cell theory
- All living things made of 1+ cells
- Cells = organism's basic unit of structure & function
- Cells are derived only from other existing cells
Miasma Theory
Theory that bad air (toxic from vapor) causes illness.

Oral Candidiasis (Thrush)
CA: Candida albicans
MOT: - direct contact w/ others (saliva)
Si/Sx: - white patches in mouth/tongue -dysphagia -erythema, soreness
Dx: -Hx -PE
Tx: -antifungal (clotrimazole)
Cutaneous Candidiasis (Vaginal yeast infection)
CA: Candida albicans
MOT: -direct contact w/ others (skin)
Si/Sx: - vaginal area rashing, pustules, pruritits, burning, white patches
Dx: -Hx -PE
Tx: - antifungal topical (hydrocortizone) -drying powders
Cutaneous Anthrax
CA: Bacillus anthracis
MOT: - endospore -> open skin wound
Si/Sx: - wound - blister/black ulcer (eschar) -pruritis
Dx: -Hx -PE -methylene blue stain -lab culture -blood test
Tx: -PCN or eryhthromycin
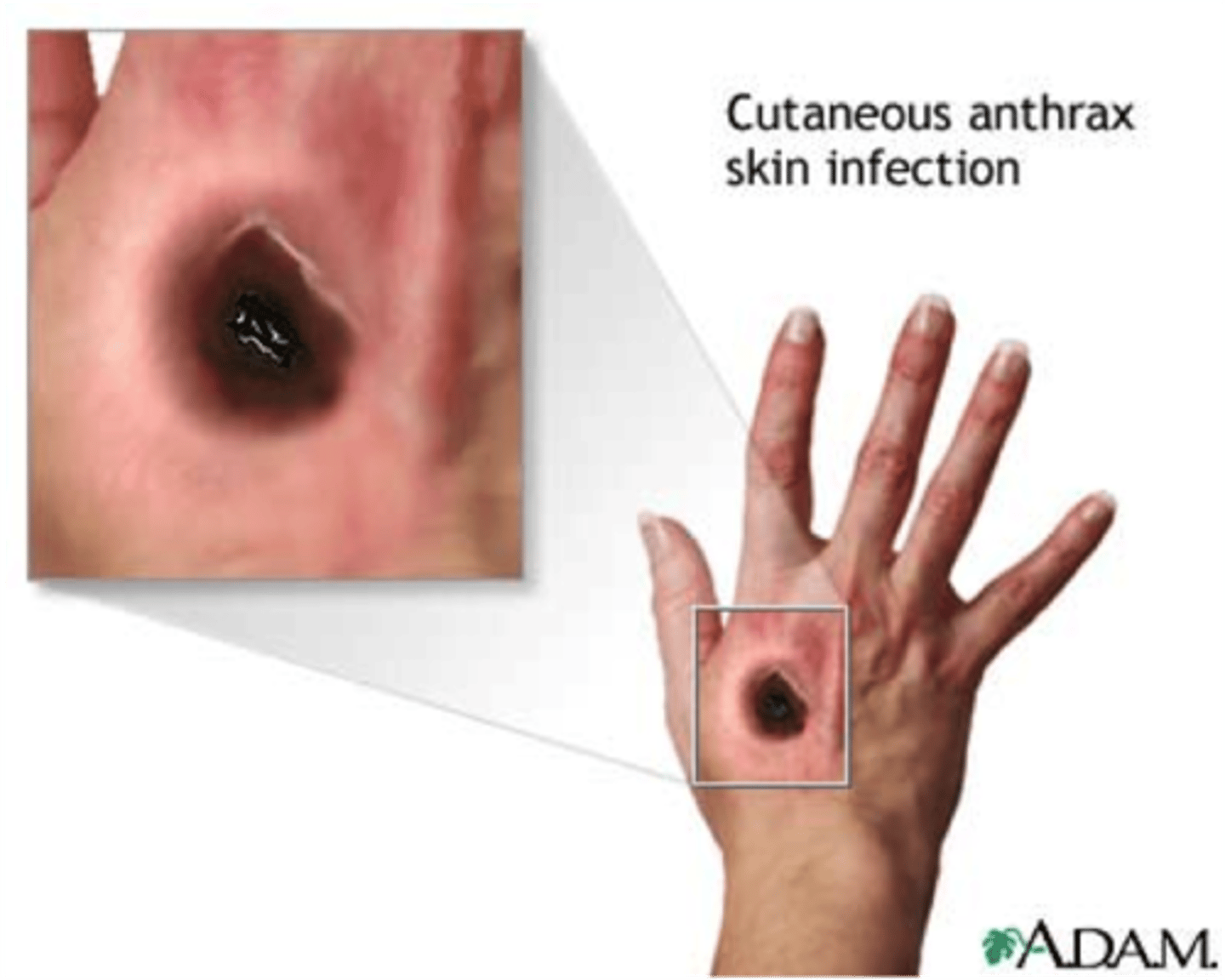
Inhalation Anthrax
CA: Bacillus anthracis
MOT: - airborne spores -consuming/exposed to contaminated meat/animal products
Si/Sx: - nausea -SOB -coughing blood -high fever -chest discomfort
Dx: -Hx -chest x-ray -Blood samples
Tx: -ABX (ciprofloxacin)
The Tineas (Ringworm)
CA: dermatophytes
MOT: Direct contact w/ infected skin, soil, animals
Si/Sx: -pruritis/stinging -red, scaly rash -cracking/peeling of skin -blisters -bald spots
Dx: -PE -Hx -skin scraping/cultures
Tx: -antifungal (clotrimazole)
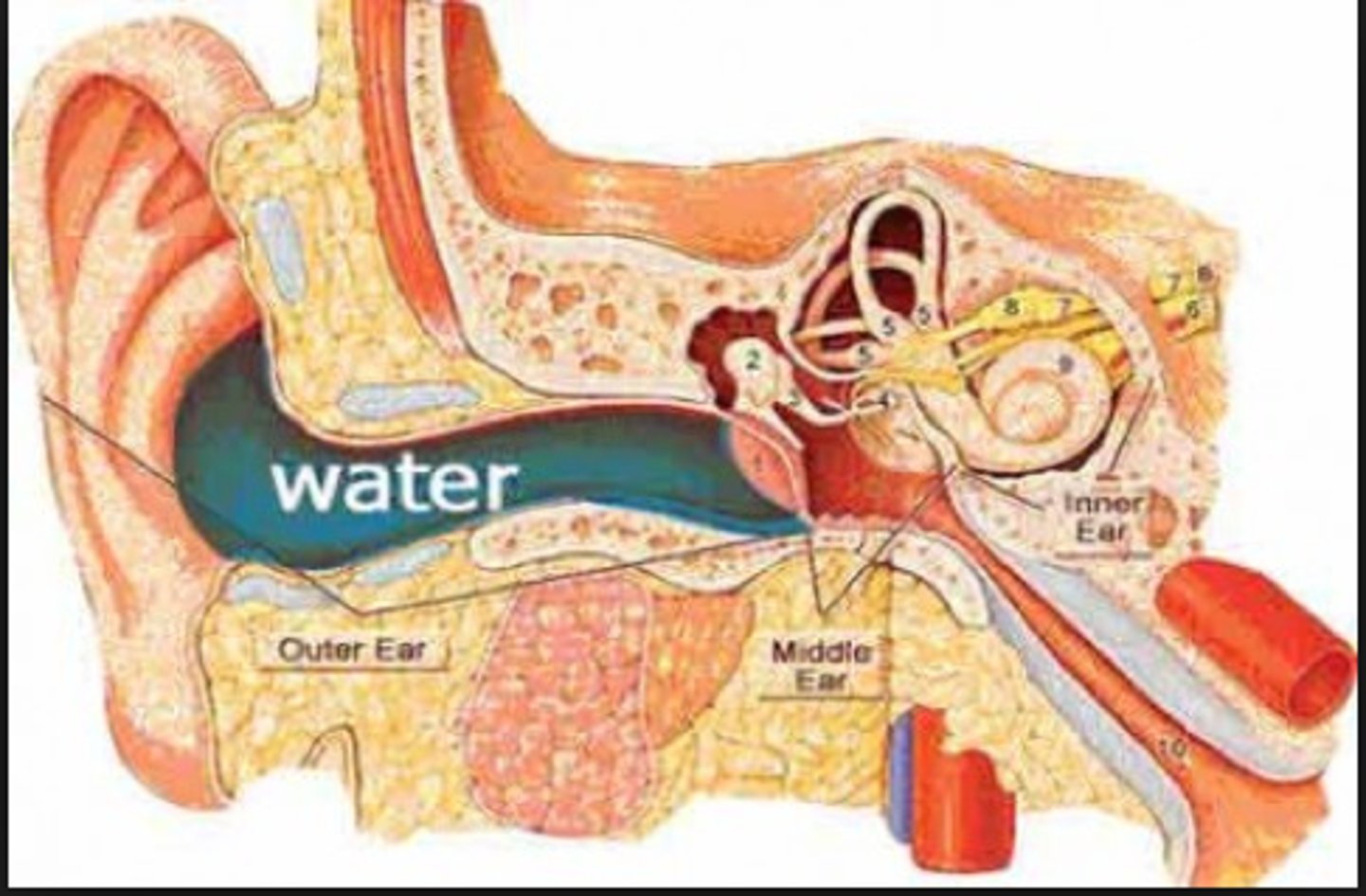
Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear)
CA: Pseudomonas aeruginosa /Staphylococcus aureus
MOT: - contaminated water enters ear
Si/Sx: -ear inflammation -muffled/loss hearing -extreme pain
Dx: -Hx -PE
Tx: -topical ABX / ear drops (ciprofloxacin, hydrocortisone)
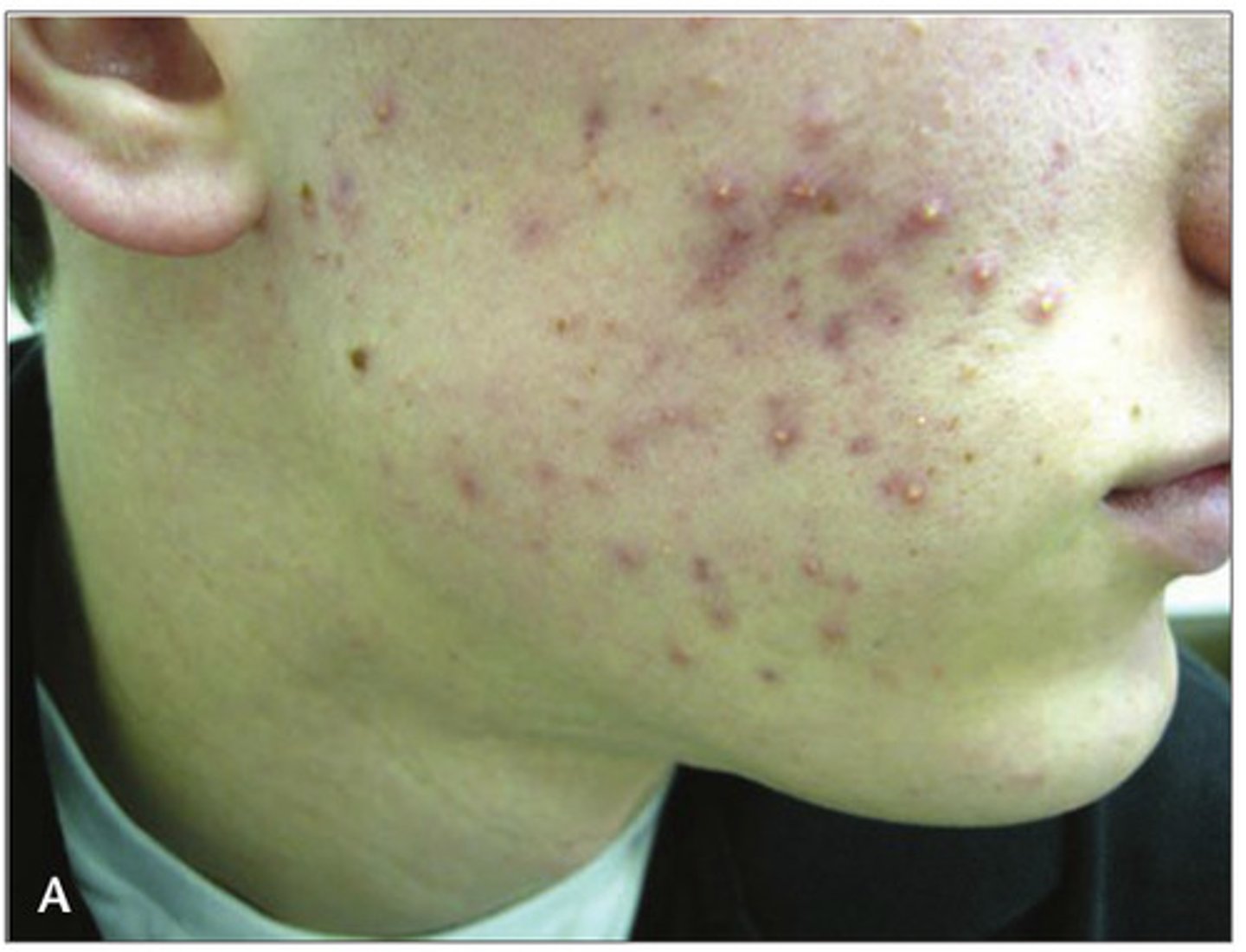
Acne vulgaris
CA: Cutibacterium acnes
MOT: - not contagious
Si/Sx: -papules/pustules -whitehead/blackheads -inflammation, crusting, scarring
Dx: -Hx -PE
Tx: -cleanser -Vit. A derivatives (accutaine) -ABX (clindamycin)
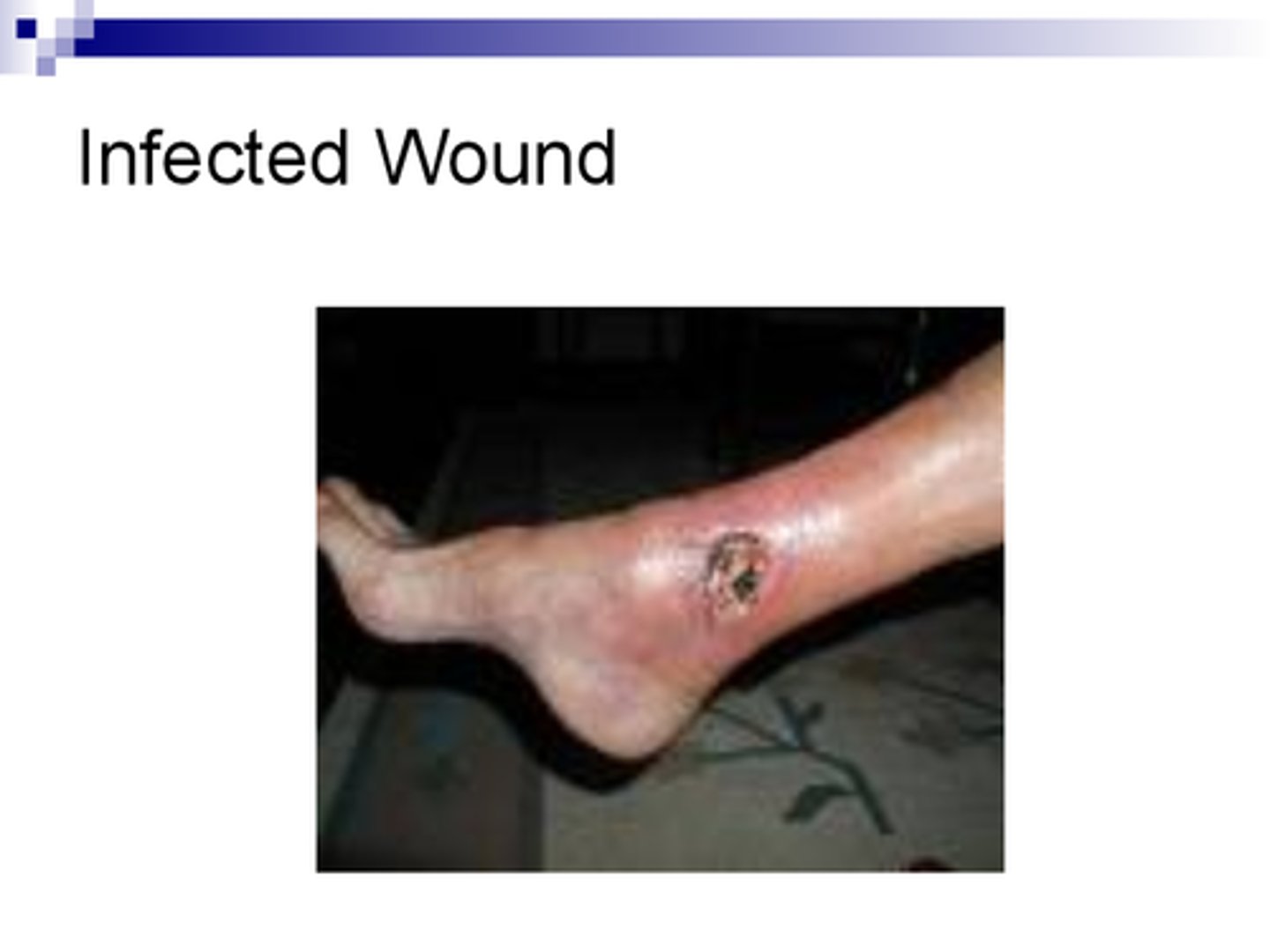
Wound infections
CA: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
MOT: -direct contact of contamination to wound
Si/Sx: -inflammation -scabbing -green/blue pus
Dx: -wound cultures -PE -Hx -C+S
Tx: - Ciprofloxacin)
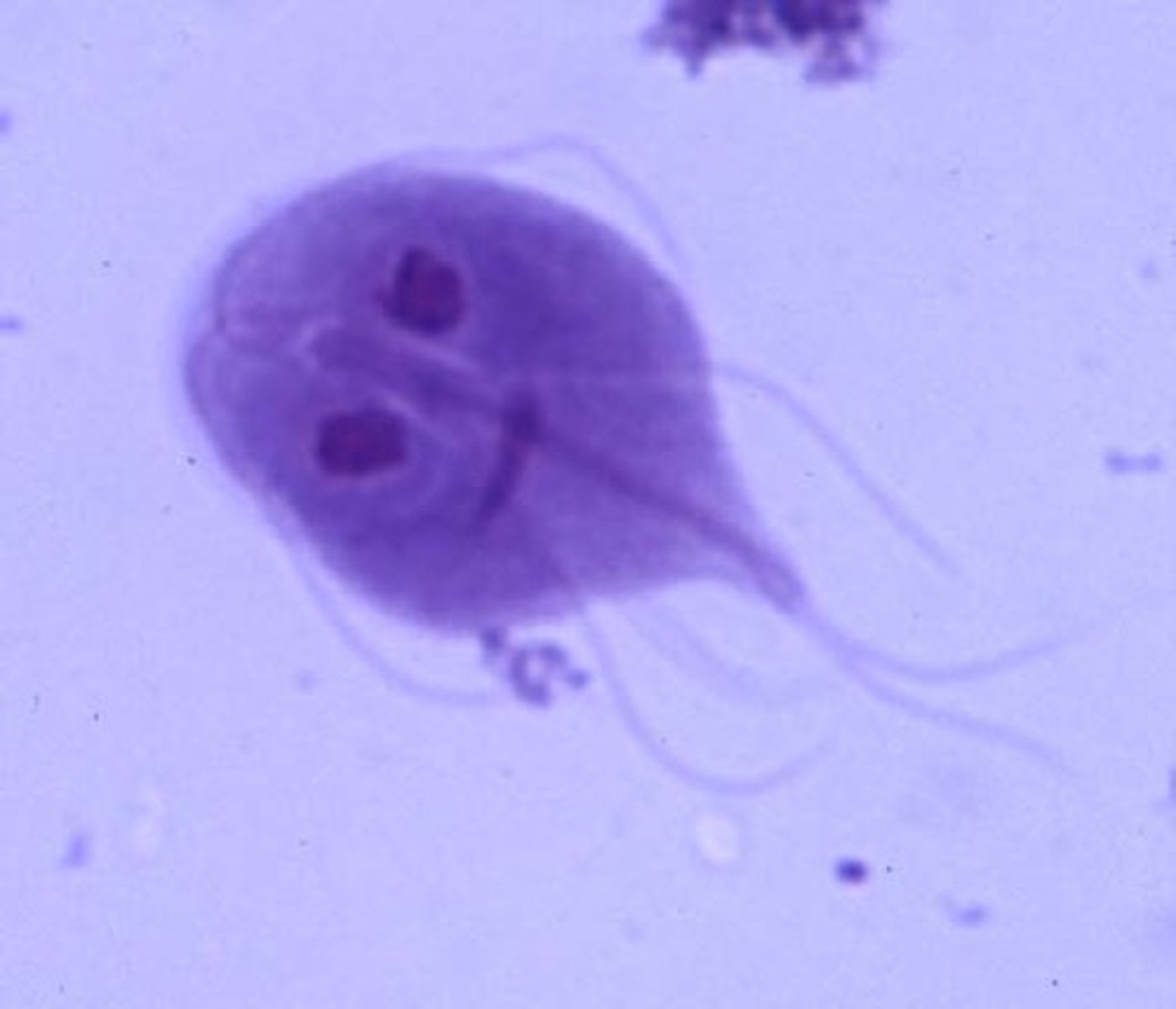
Giardiasis (beaver fever)
CA: Giardia lamblia (protozoan parasite)
MOT: -fecal-oral (exposure to contaminated water/food)
Si/Sx: -N/D -abdominal cramps -sever dehydration
-greasy stool
Dx: -stool sample -Hx -PE
Tx: -Azole
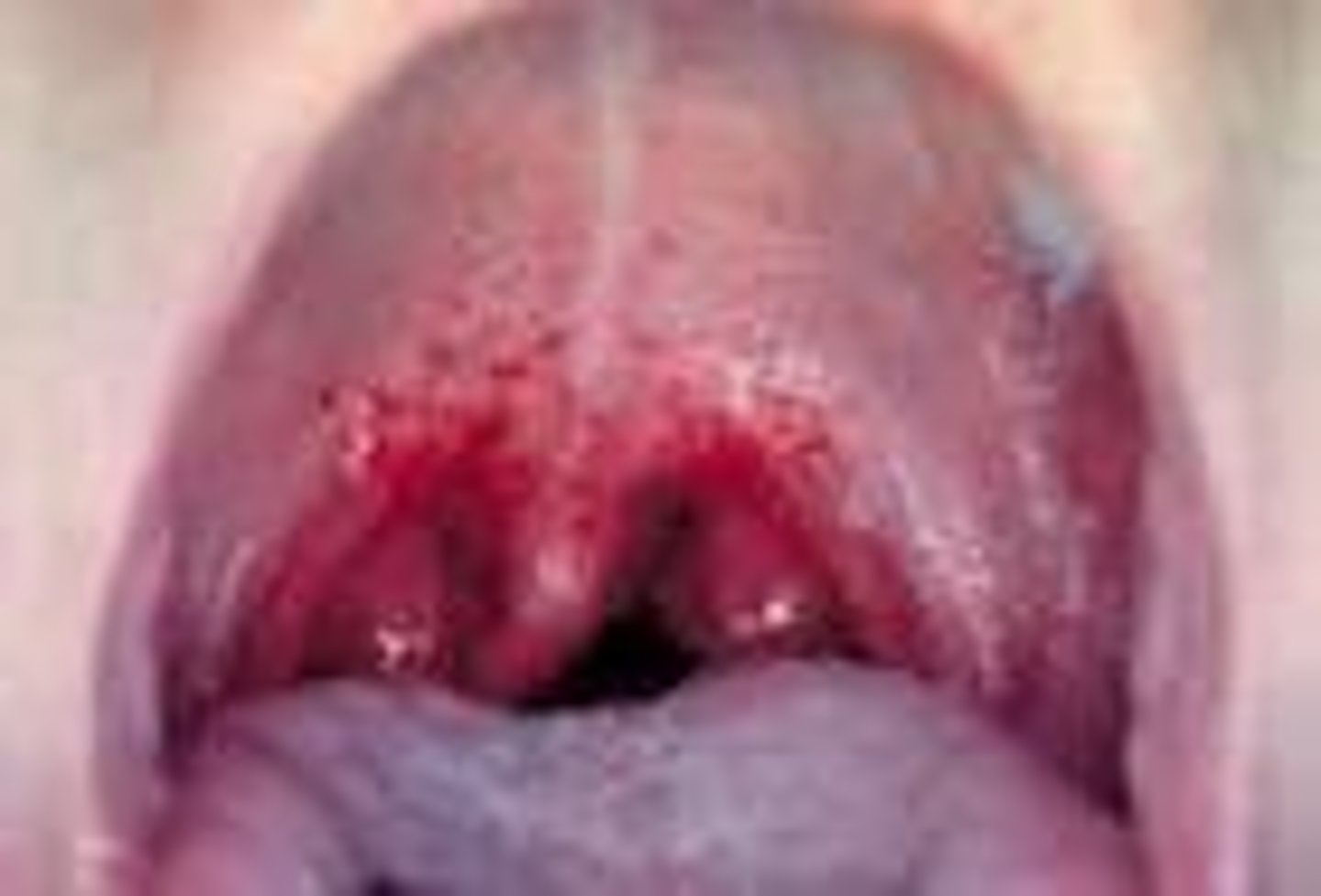
Strep Throat
CA: Streptococcus pyogenes
MOT: -resp. droplets -direct contact w/ infected indv.
Si/Sx: -reds spots in mouth -sore throat -F -dysphagia
Dx: -strep test strip/throat culture
Tx: -ABX (PCN, amoxicillin) -children's Tylenol
Cholera
CA: Vibrio cholrae
MOT: -exposure/consumption of contaminated water/food
Si/Sx: -watery D/N -severe dehydration
Dx: -stool sample -rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs)
Tx: -IV fluids (electrolyte replacement) -oral rehydration

Puerperal fever (Childbed fever)
CA: Strep pyogenes
MOT: -following L+D, tearing of perineum /genital/urinary tract
Si/Sx: -high F -vaginal bleeding -severe abd pain -leg inflammation -pelvic pain
Dx: -PE -Hx -C+S -ABX testing
Tx: -ABX (Augmentin) -Pain relievers (ibuprofen)

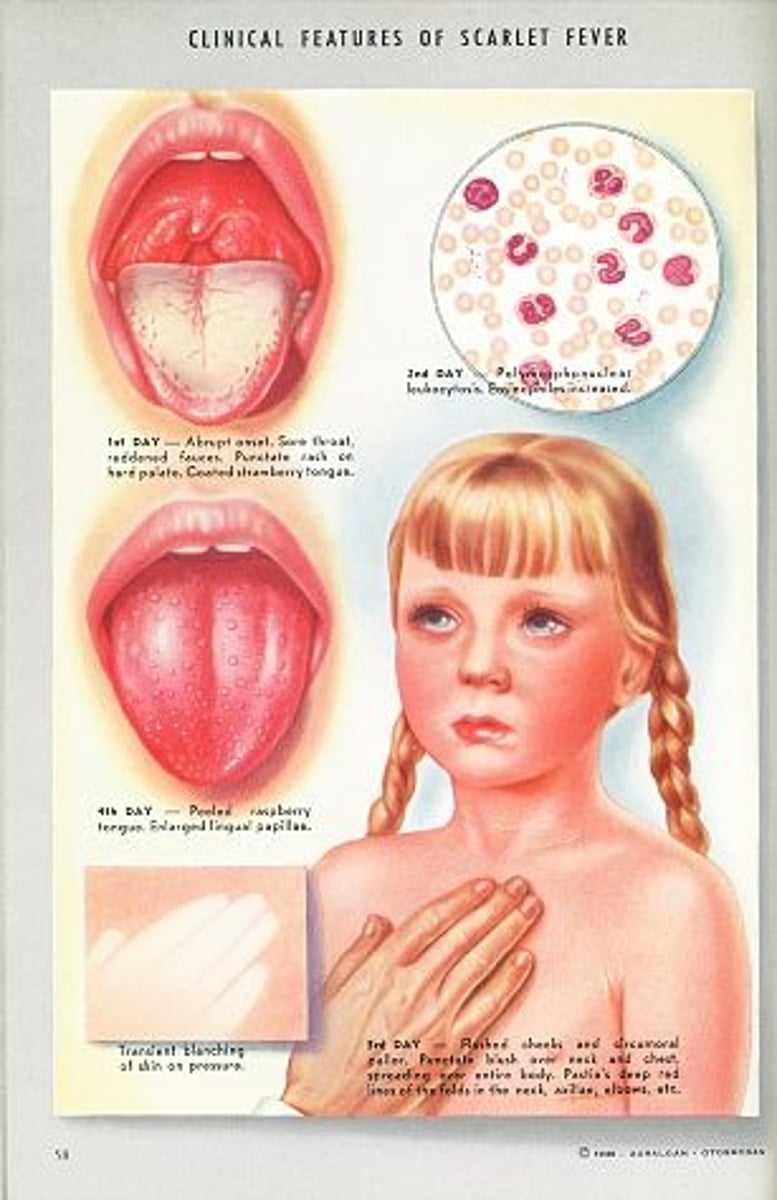
Scarlet Fever
CA: Streptococcus Pyogenes
MOT: -resp. droplets
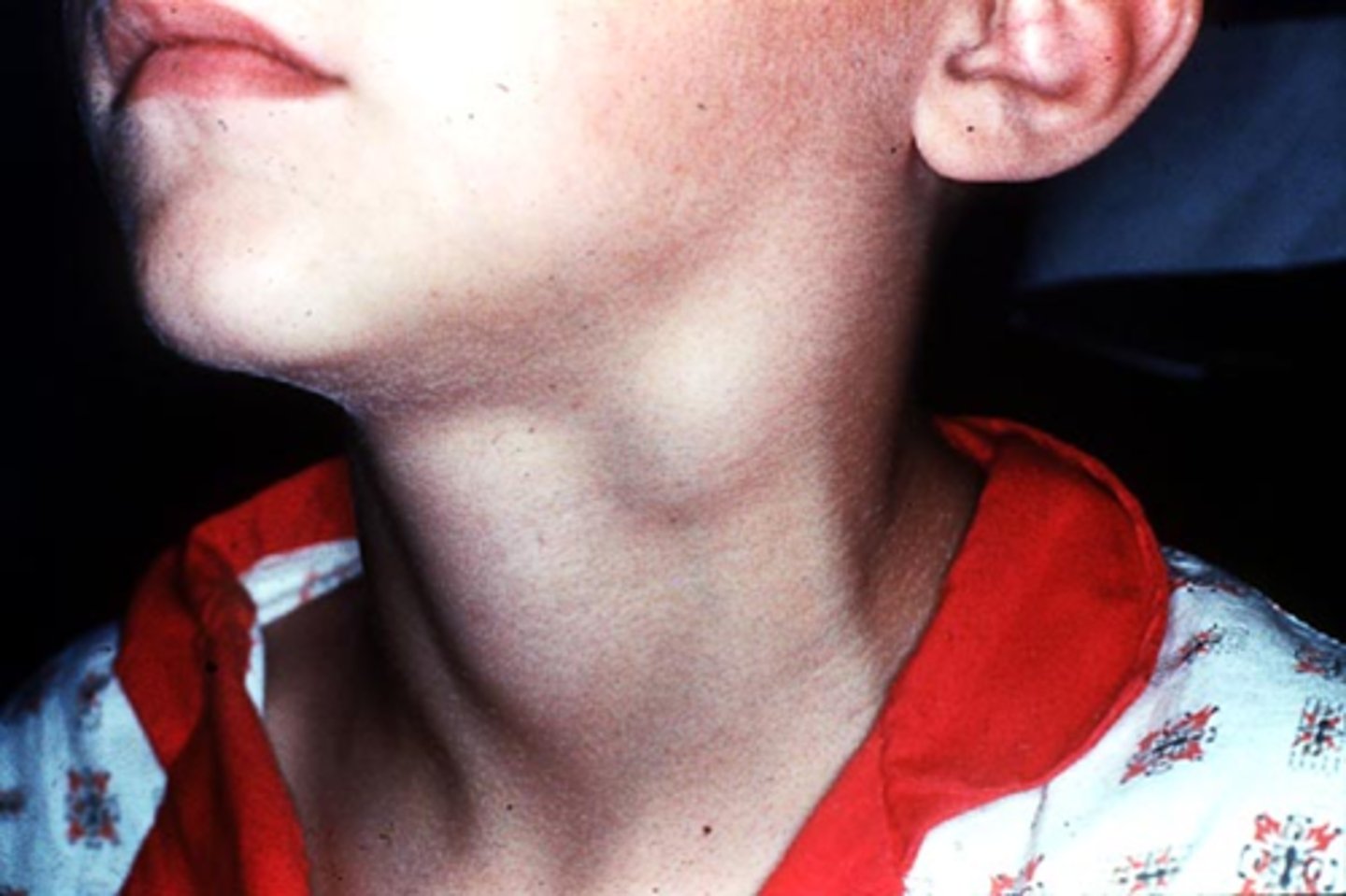
Si/Sx: -F/N -red, sore throat -dysphagia -englarged neck glands -abd. pain
Dx: -Strep A testing
Tx: -ABX (penicillins) -analgesic (tylenol)
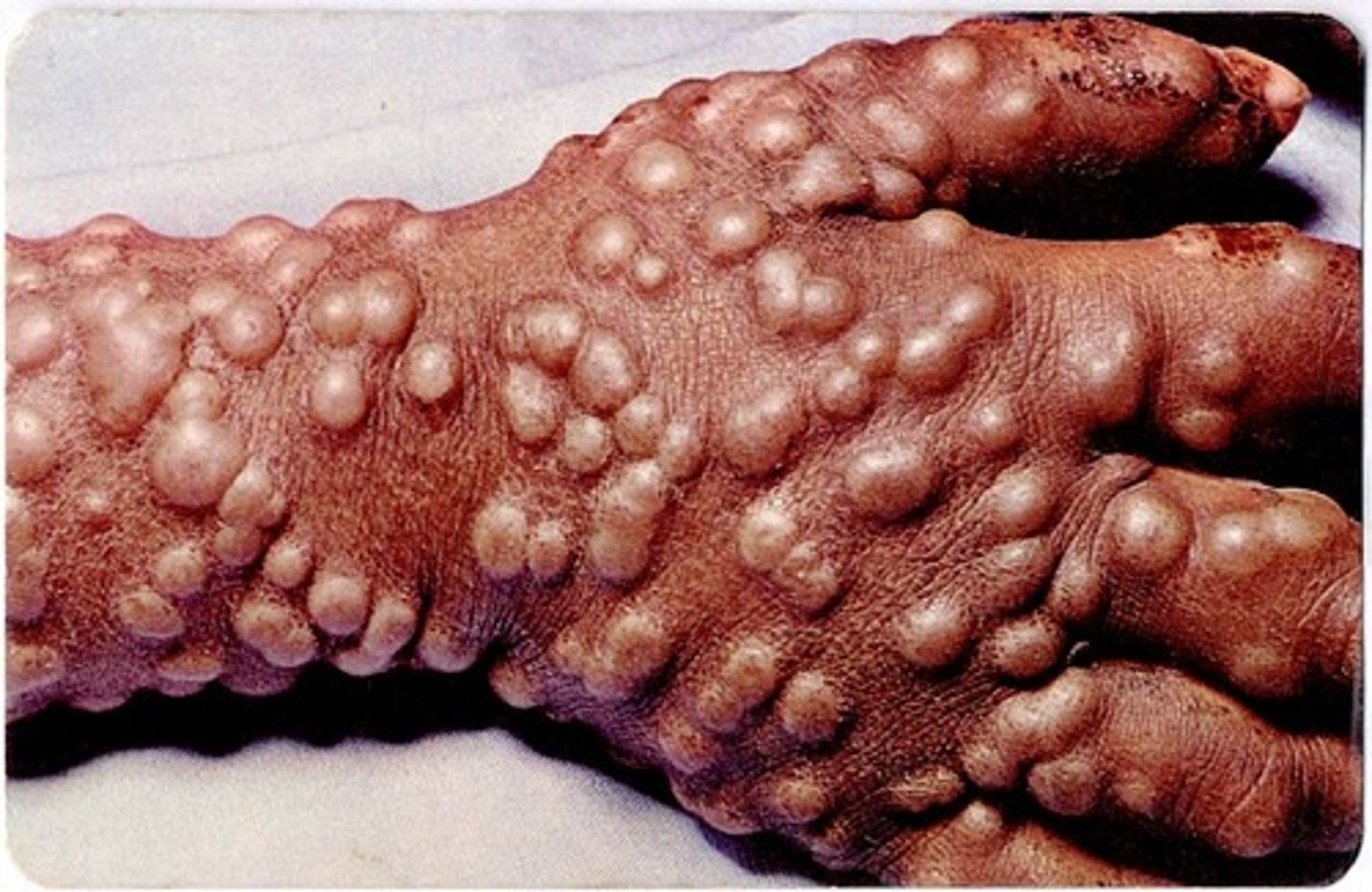
Small pox
CA: Variola virus
MOT: -airborne droplets -direct contact
Si/Sx: -many pustules -F -fatigue -inflammation -rashes -back/muscle pain
Dx: -Hx -PE -tissue sample test
Tx: -no proven tx. -vaccination for prevention -tenbexa (brincidotovir) tablets
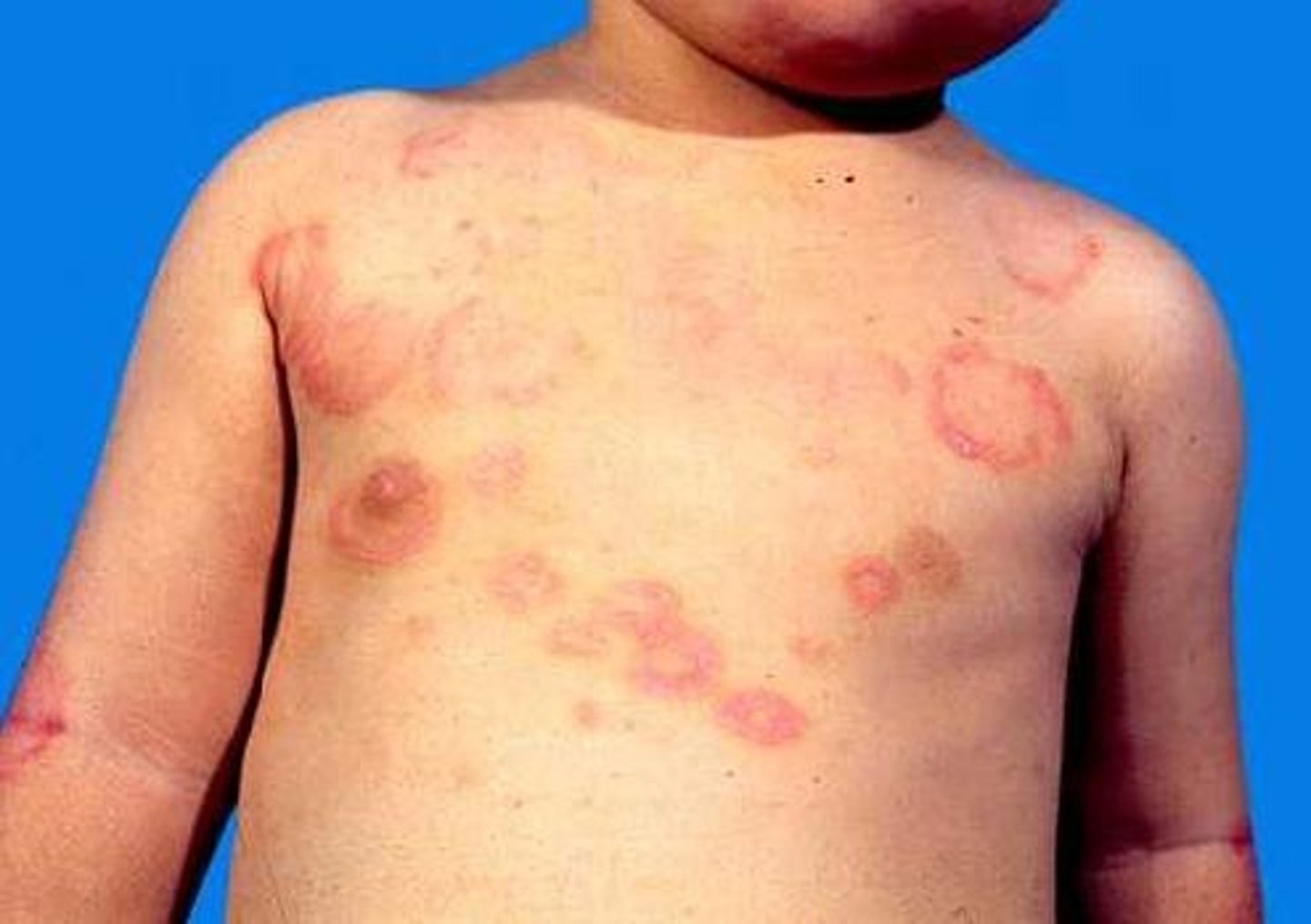
Rheumatic Fever
CA: Group A Strep
MOT: -airborne resp. droplets
Si/Sx: -F -fatigue -arthritis -rashes -chest pain
Dx: -Hx -PE -blood test
Tx: -ABX (PCN) - Anti-inflammation drugs (ibuprofen)
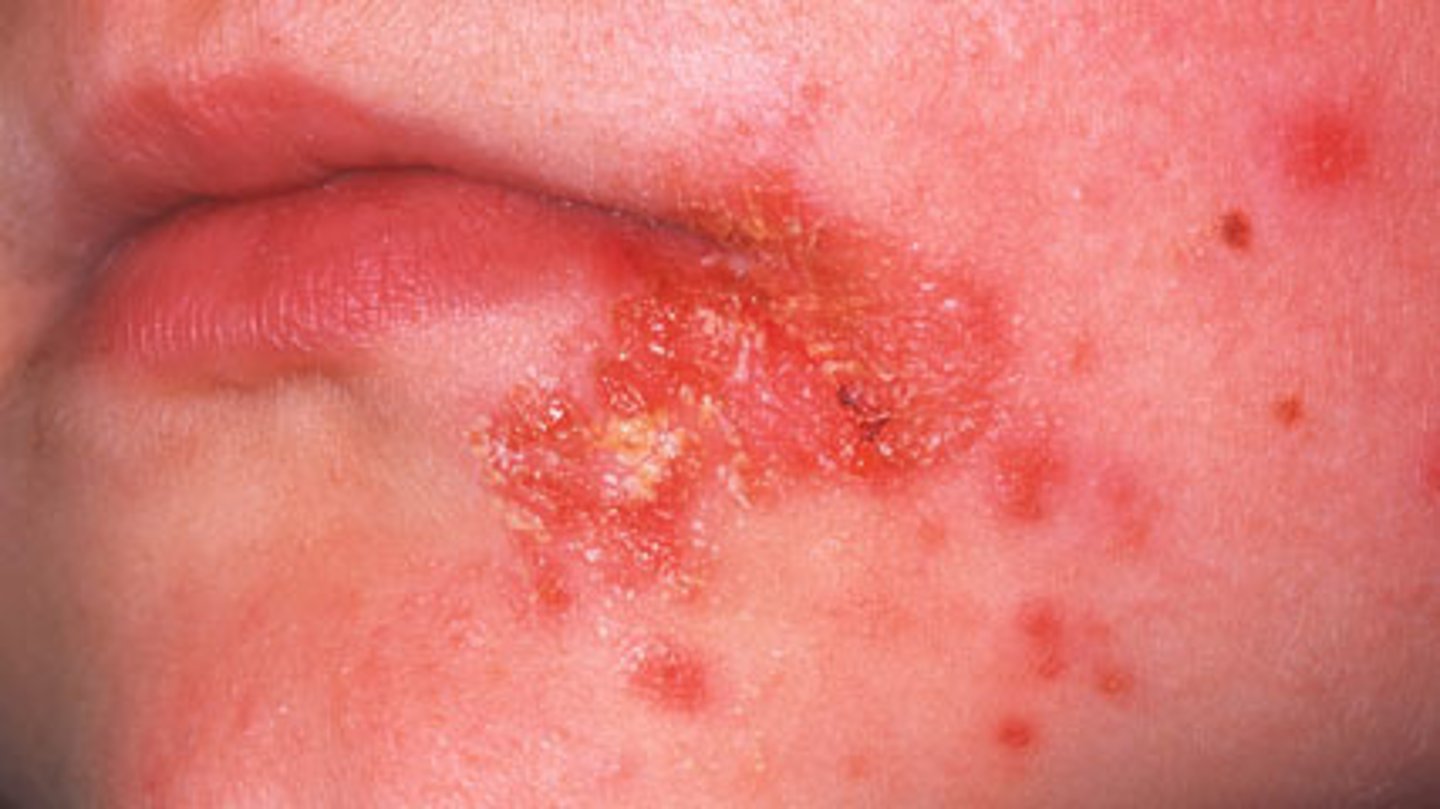
Impetigo
CA: Staphylococcus aureus / Strep pyogenes
MOT: -direct skin-contact
Si/Sx: -erythemic sores around mouth&nose -golden crusting -rashes/blisters
Dx: -Hx -PE -bacterial cultures
Tx: -ABX (mupirocin ointment) -PCN
Toxic Shock Syndrome
CA: strep pyogenes -Group A strep
MOT: -direct contact w/ vaginal device
Si/Sx: -high F/N/V -decreased BP -rashing
- HoTN
Dx: -no exact test -blood/urine sample -swab of lesion
Tx: -ABX (clindomycin) -unhealthy tissue removal -med. ventilation
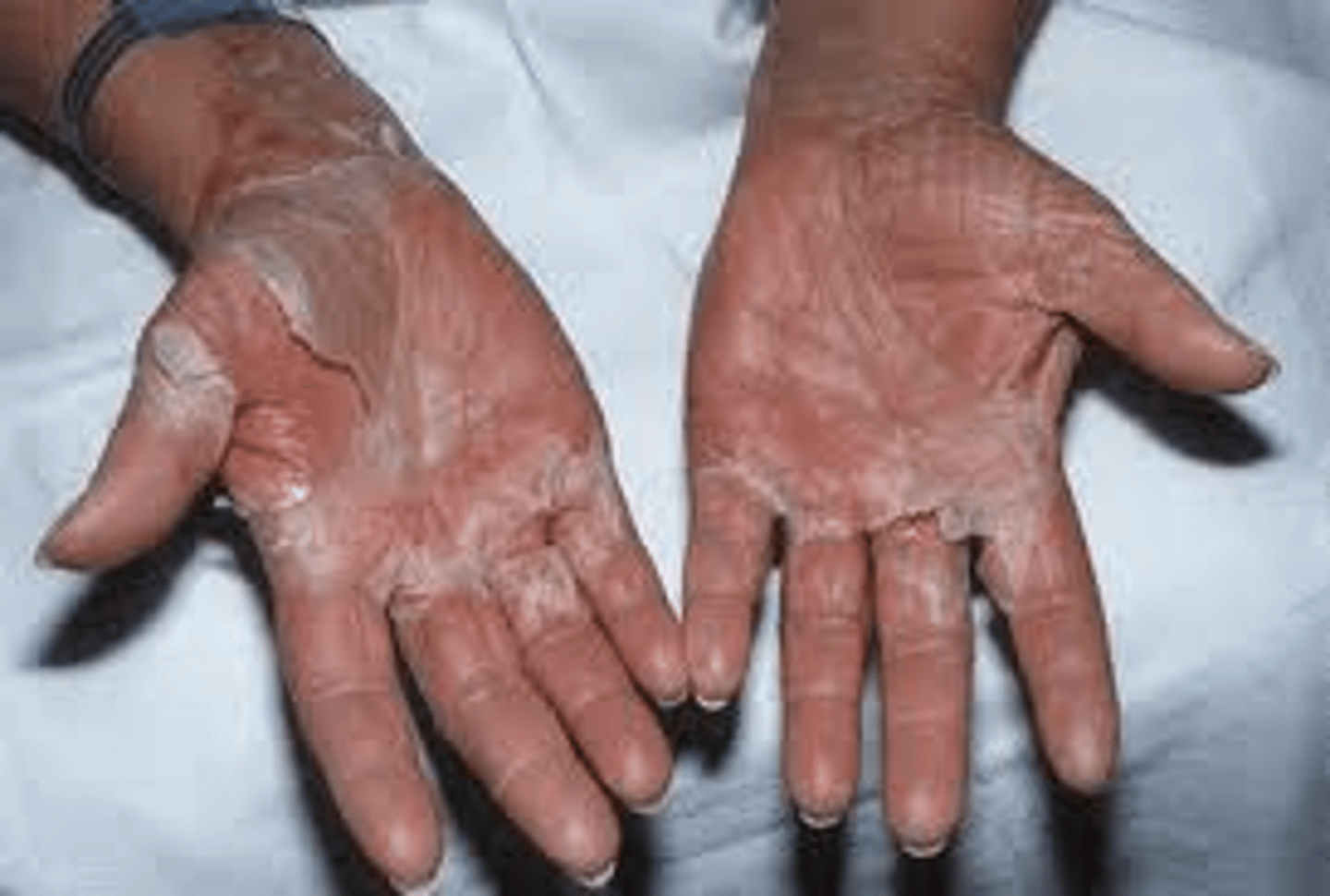
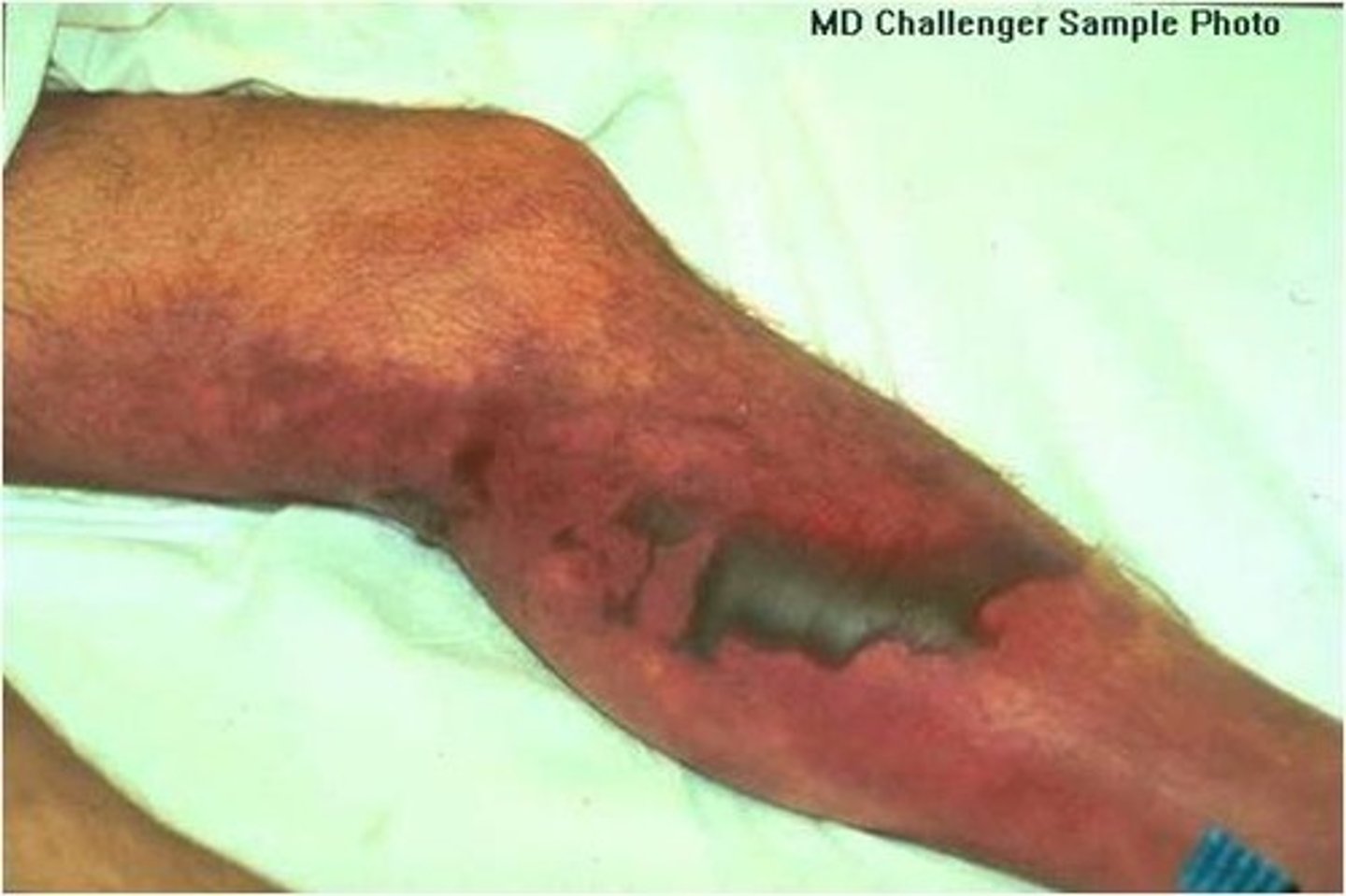
Necrotizing fasciitis
CA: Group A Strep - Staphylococcus areus
MOT: -not contagious -bact. exposure
Si/Sx: -small, painful, red lumps/bumps that spread
-bruise area w/ dark center -F/C -decreased BP
Dx: -Biopsies (tissue samples) -bloodwork -CT/MRI scan
Tx: -surgery (debridement) -IV ABX
Ascariasis
CA: Ascaris lumbricoides & Ascaris suum (roundworms, parasitic)
MOT: - fecal-oral
Si/Sx: - severe abd pain -fatigue -worm in vomit/stool -Wt loss
Dx: - Stool exam -CXR -MRI -Blood tests
Tx: -antiparasitics (Ivermentin)

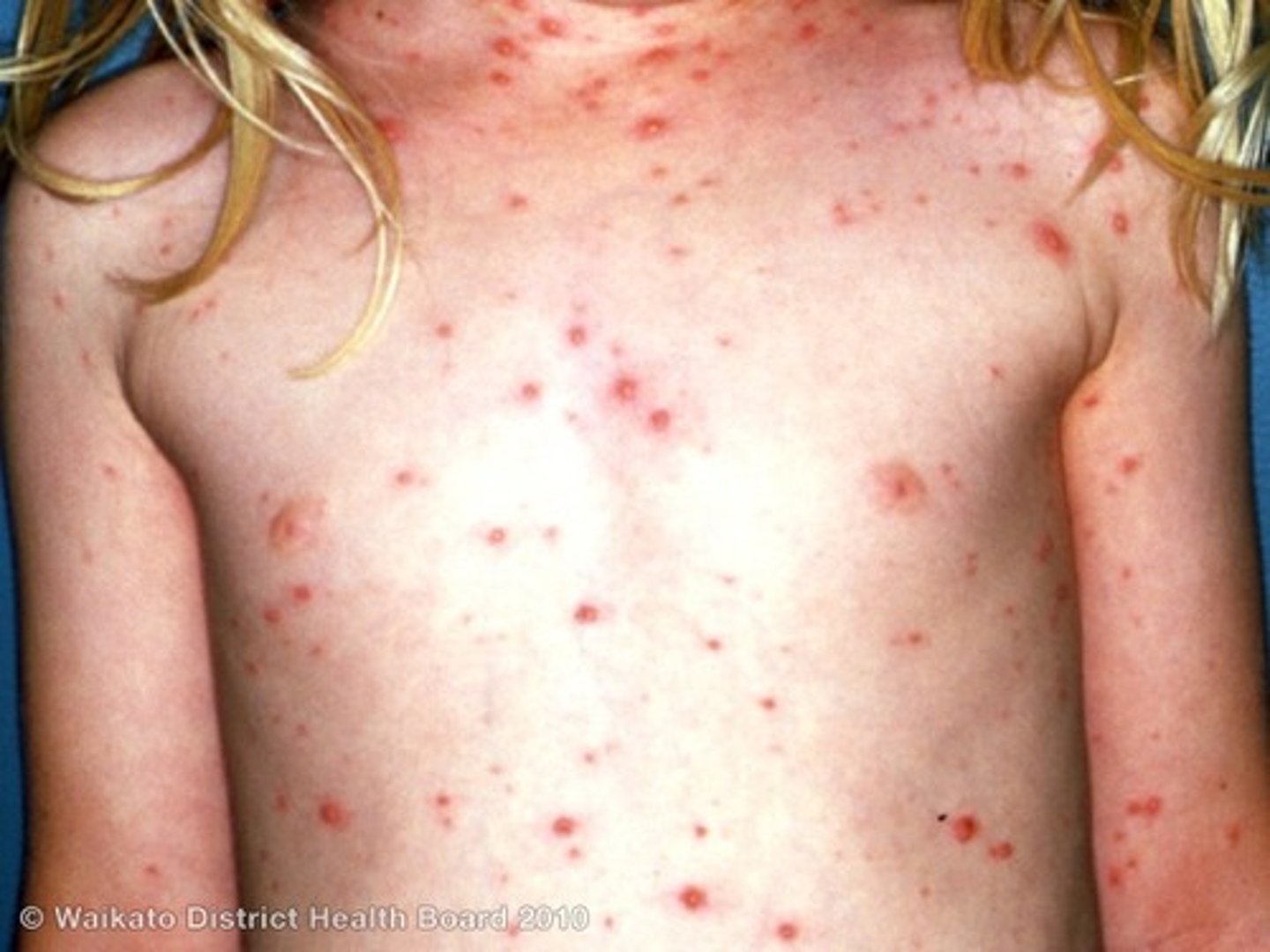
Chicken Pox
CA: Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) -Kids
MOT: -direct skin-skin contect -airborne (resp. droplets)
Si/Sx: -F/C -many oozing vesicles to crusting scabs -pruritis
Dx: -PE -Hx
Tx: - VZV Vaccination
SSSS (staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome)
CA: Staph aureus
MOT: -direct skin-skin contact -kids <6
Si/Sx: -F -fluid-filled blisters -peeling/redness of skin
-tiredness
Dx: -PE -Hx -Biopsy
Tx: -IV ABX (clindamycin) -fluid replacement
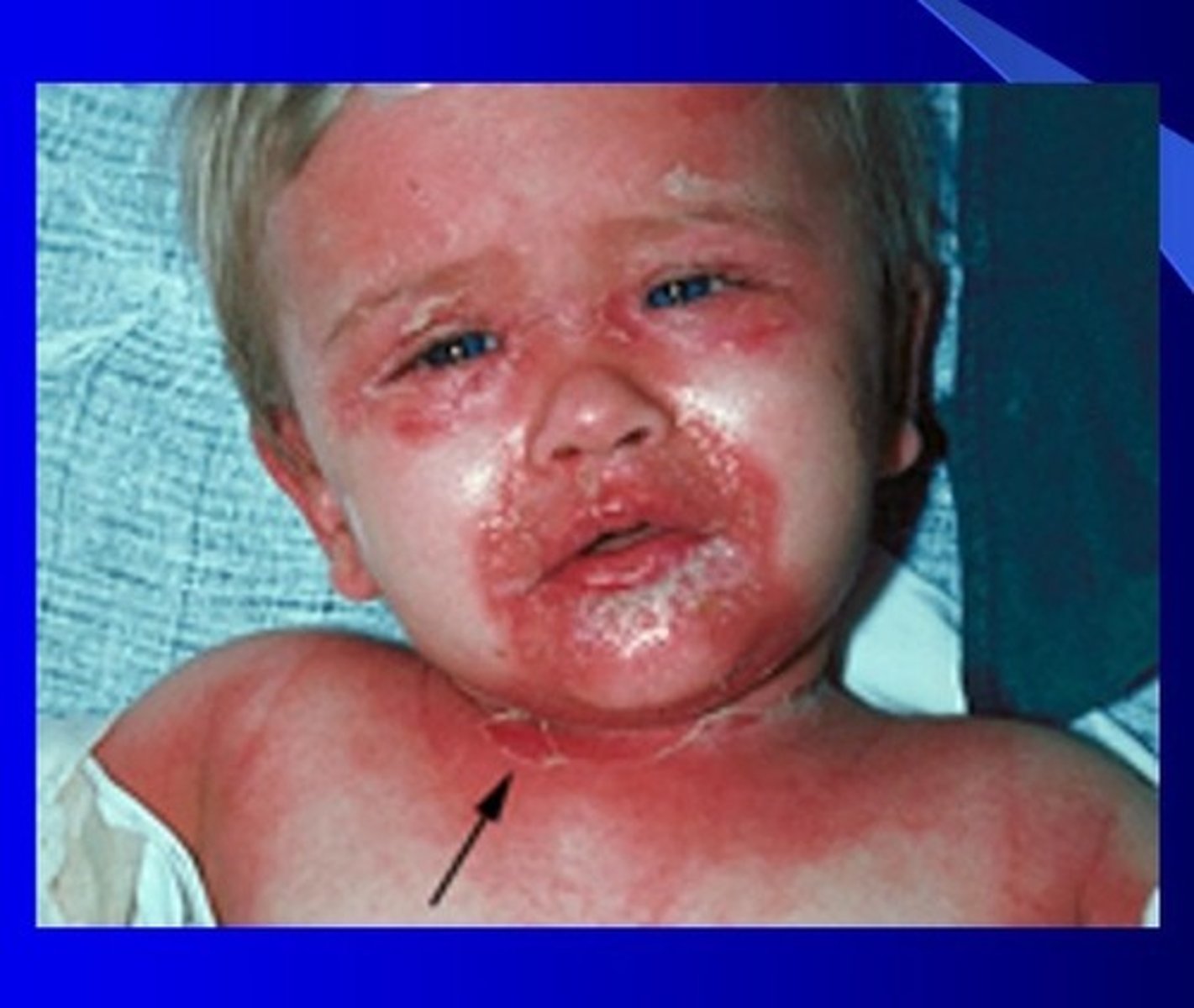
Cellulitis
CA: Staph & Strep
MOT: -skin contact w/ bact.
Si/Sx: -inlammation -swollen lymph nodes -fatigue
Dx: -PE -Hx
Tx: -topical ABX -injectable ABX (vancomycin)

Hot tub folliculitis
CA: Pseudomonas aerginosa
MOT: -spread through contaminated hot tub/pool
Si/Sx: - red nodules -acne -pustules
Dx: -PE -Hx
Tx: -Silver sulfadiazine cream
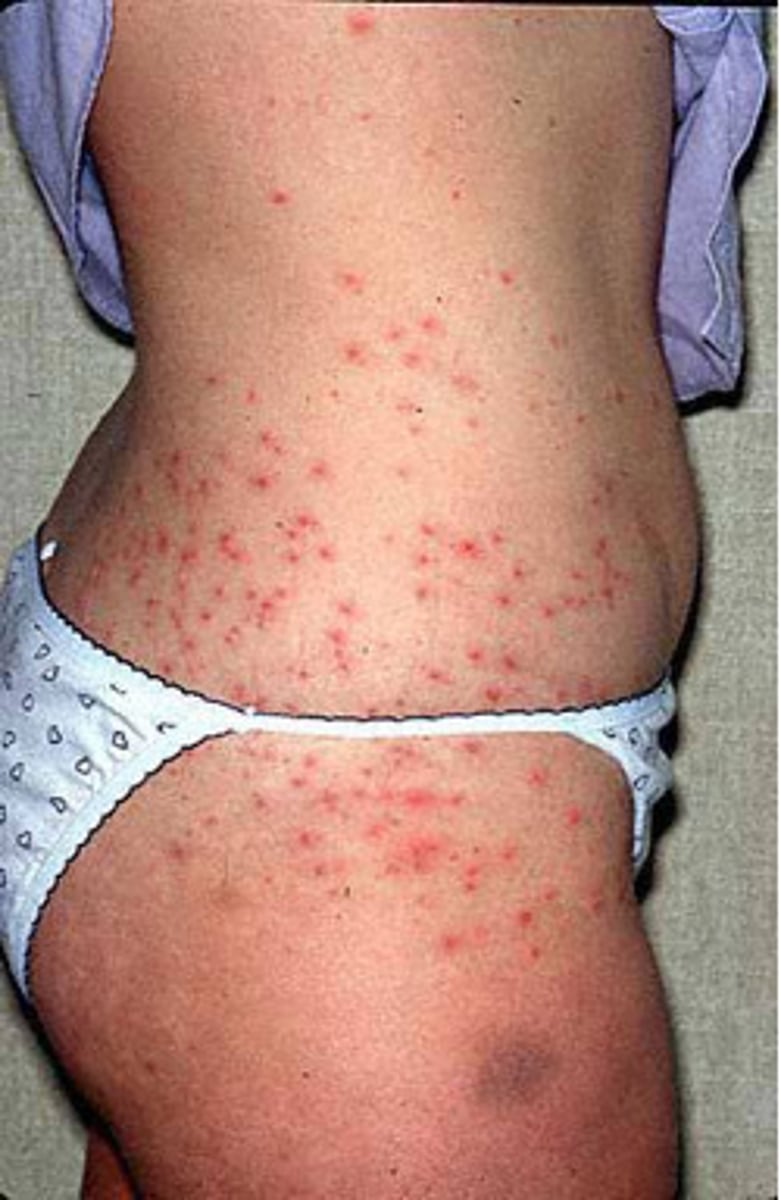
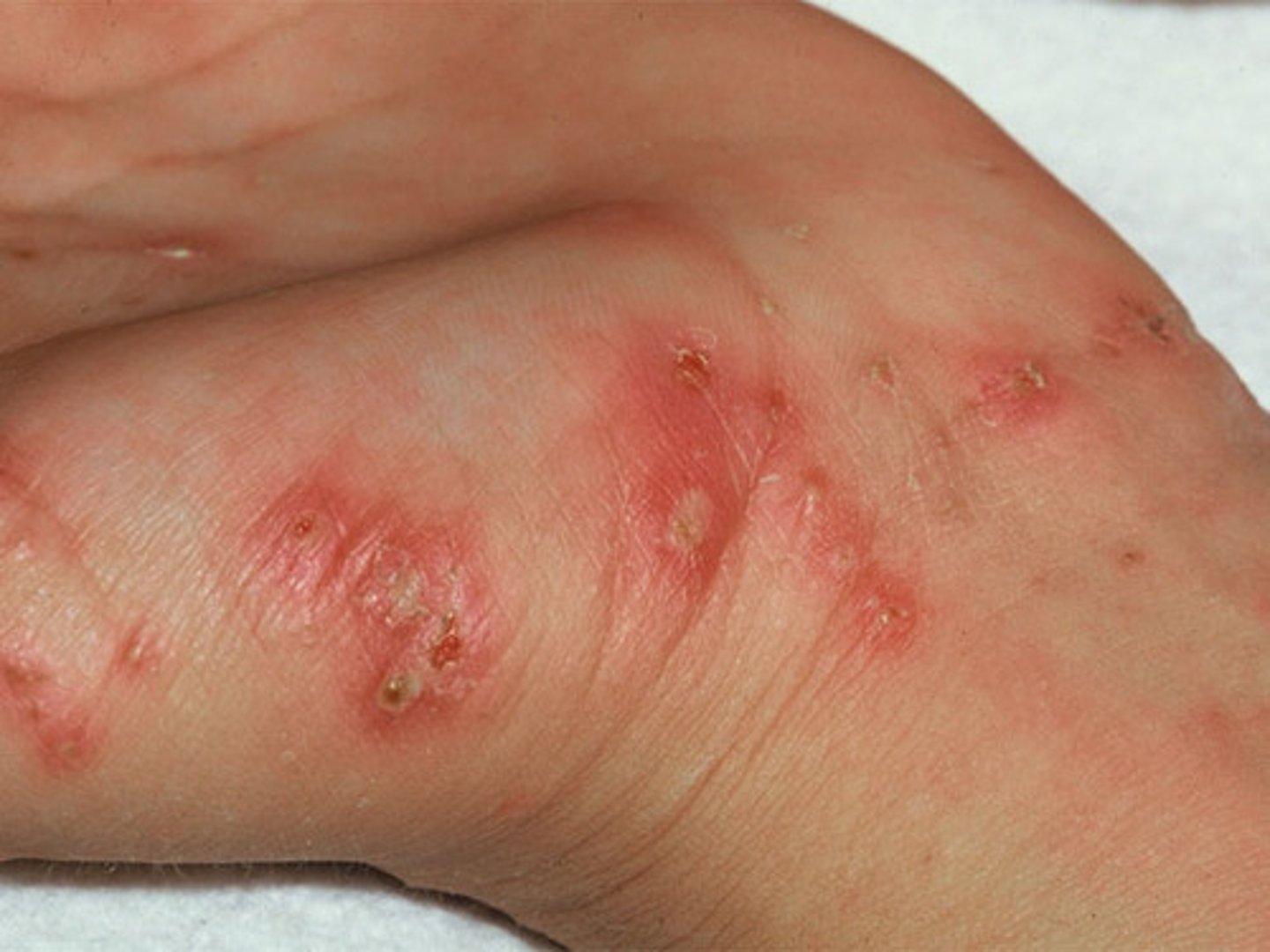
Scabies
CA: Scarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
MOT: -direct skin contact
Si/Sx: -intense pruritis -pimple-like rashing
Dx: -PE -Hx
Tx: -permethrin cream and malathion
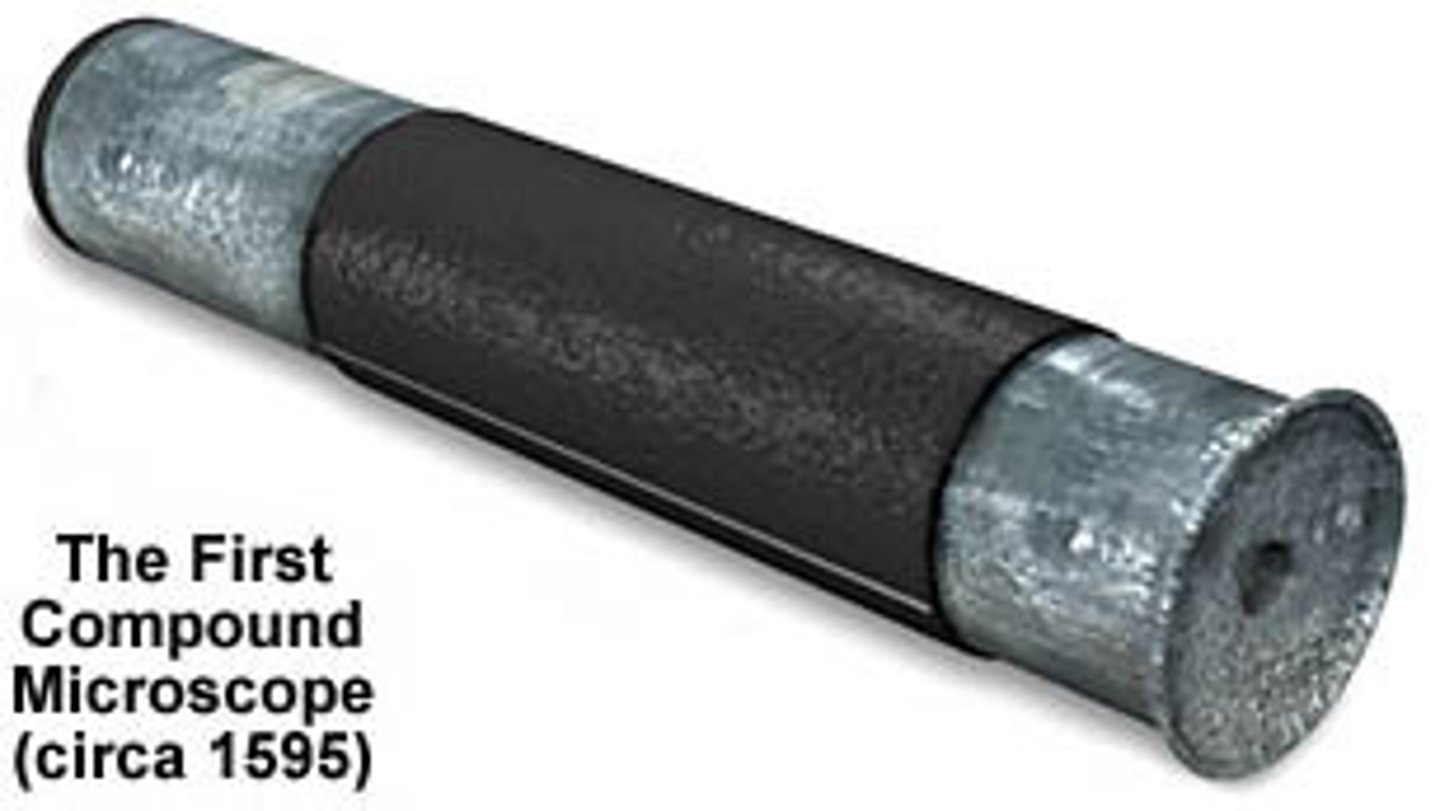
Hans Lippershay
(late 1500s)
- filled 1st patent on microscope

Hans Lippershay, Hans Janssen, and Zacharias Janssen (father and son)
(Late 1500s)
- made spectacles, binoculars, and professional scopes

Hans Janssen
(Late 1500s)
- credited for inventing the microscope
Robert Hooke
(mid 1600s)
- coined the term 'cell'
- first to view non-living tissue
- published 'micrographia' - 1st to document images at that small magnification
- 100x mag

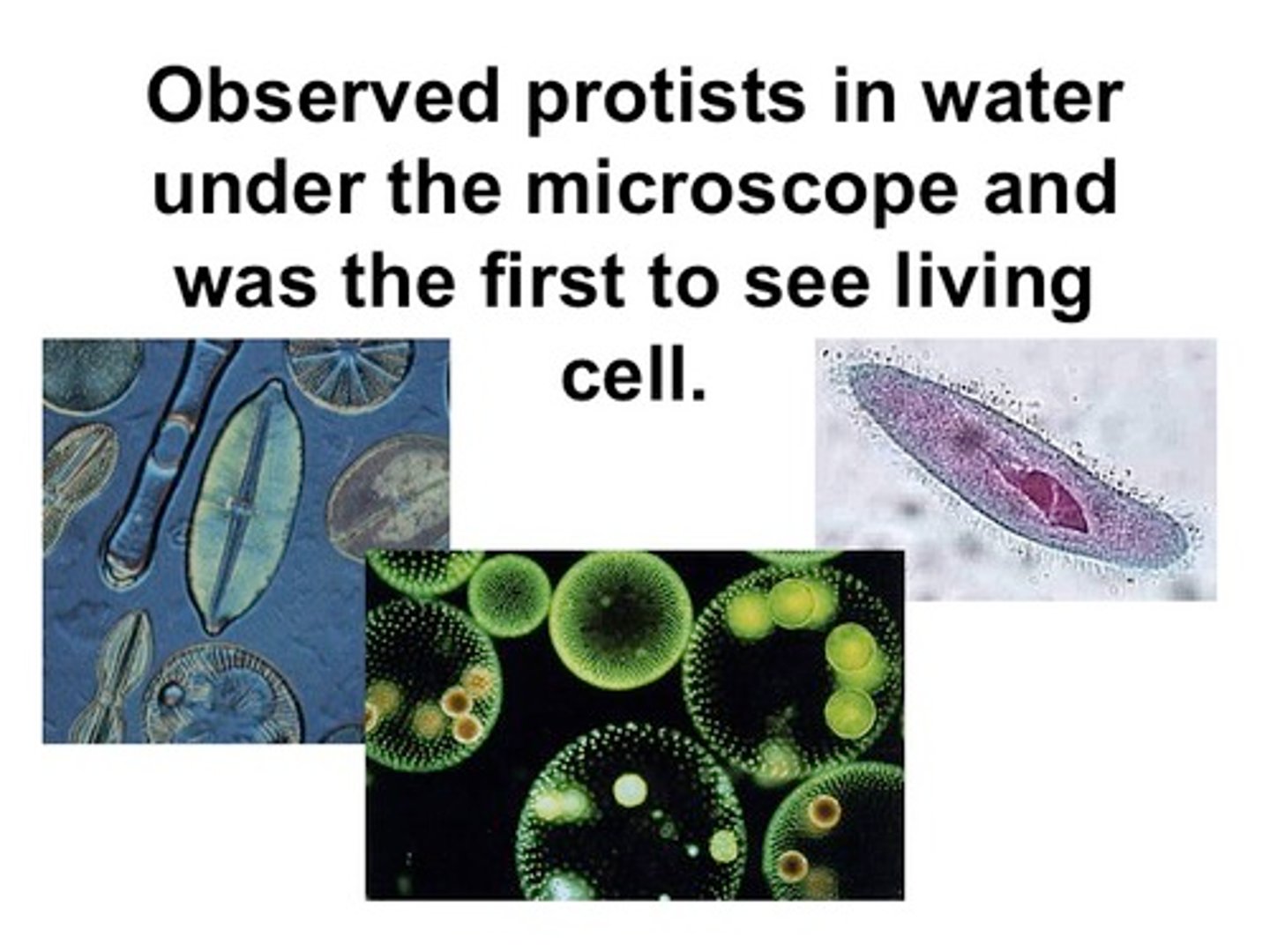
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
(late 1600s)
- 'Father of Microbiology'
- Made own microscope at 200x
- 1st to view and stain living tissue
Aristotle
(BC era - 384-322BC)
- The Philosopher' and 'The 1st Teacher'
- Theorized Spontaneous Generation/'Abiogenesis'

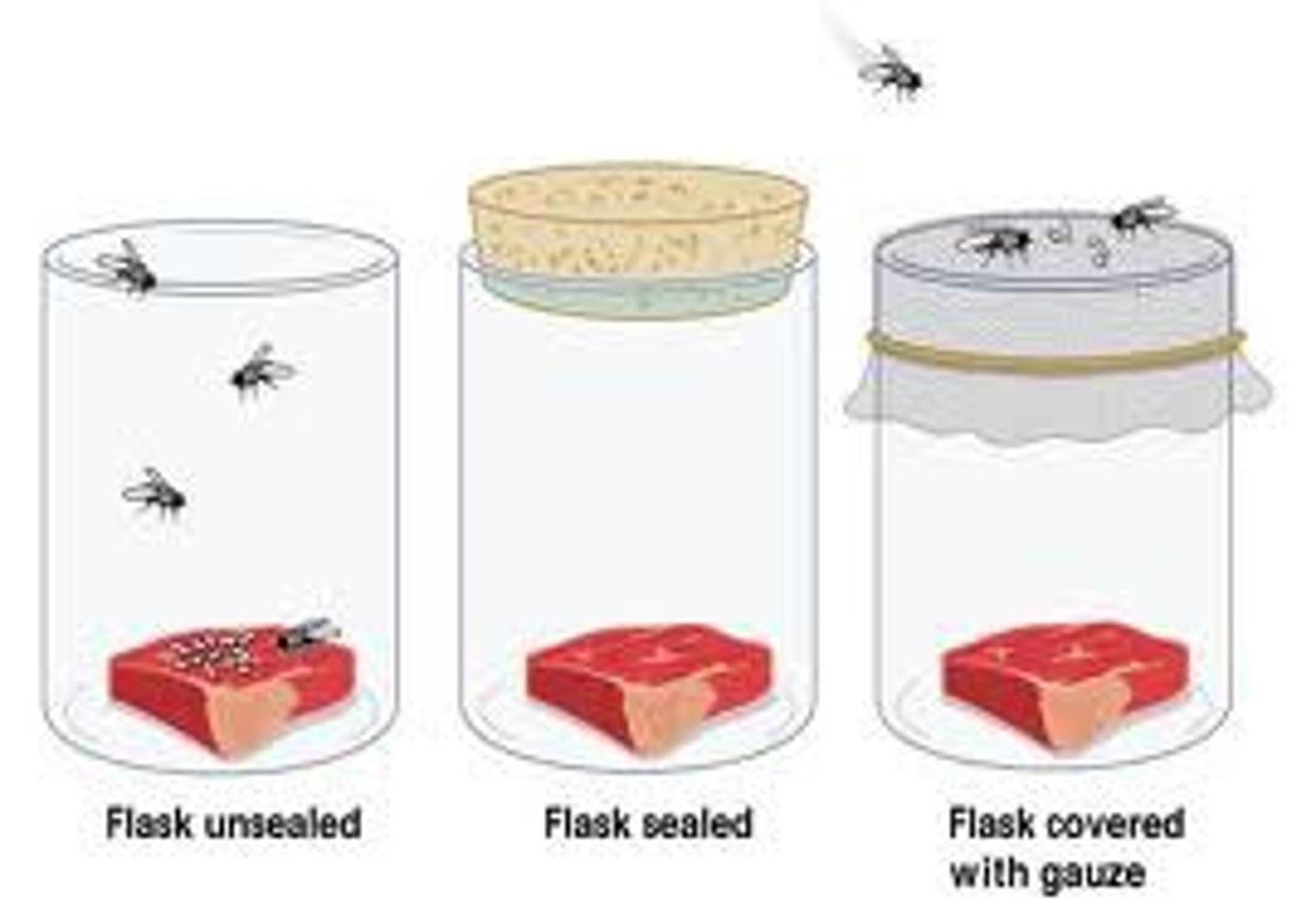
Francesco Redi
(mid 1600s)
Hypothesized Biogenesis
(w/ meat & maggots experiment)
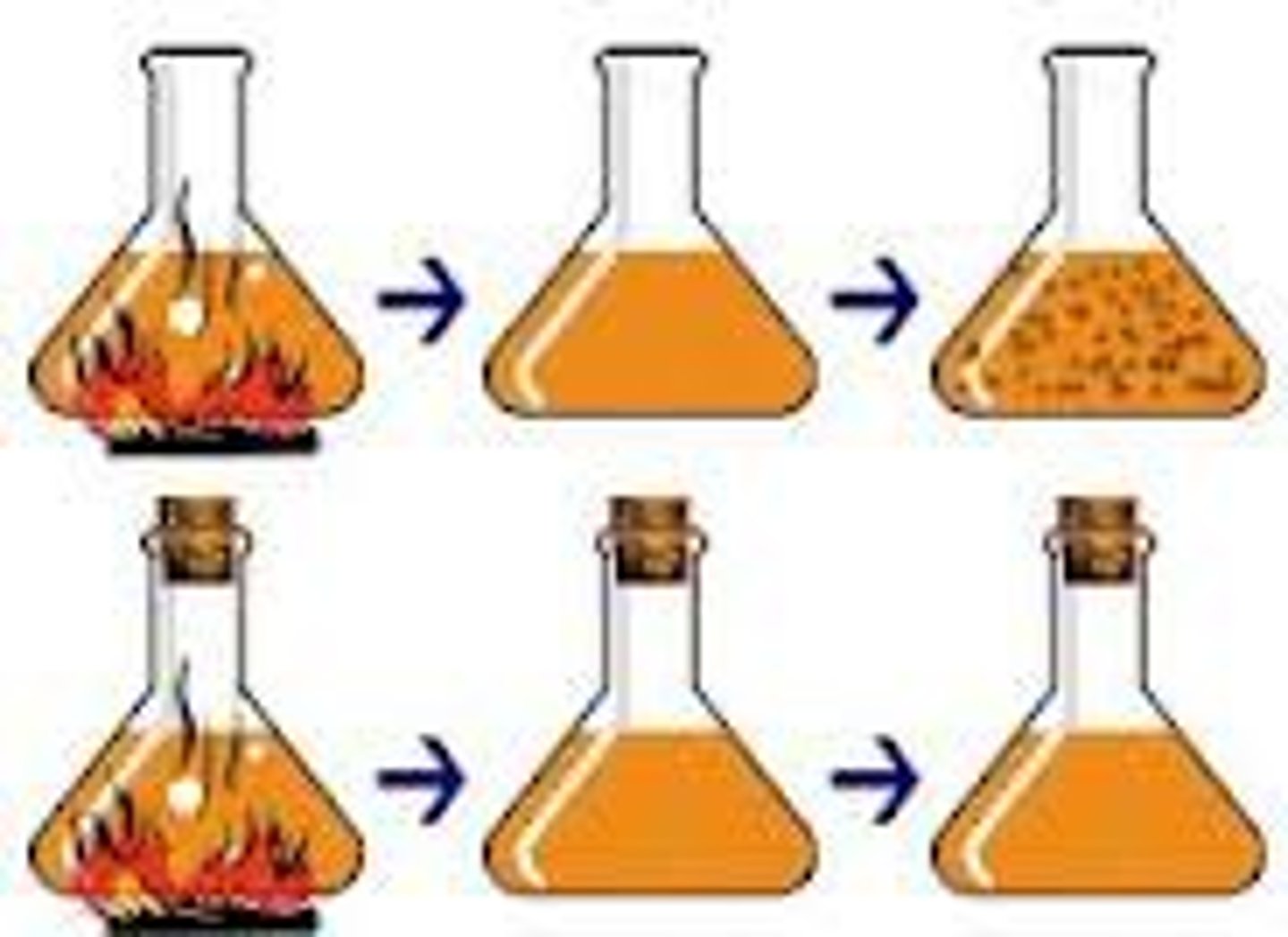
John Needham
(mid 1700s)
- Supported Abiogenesis (w/ broth boil experiment)
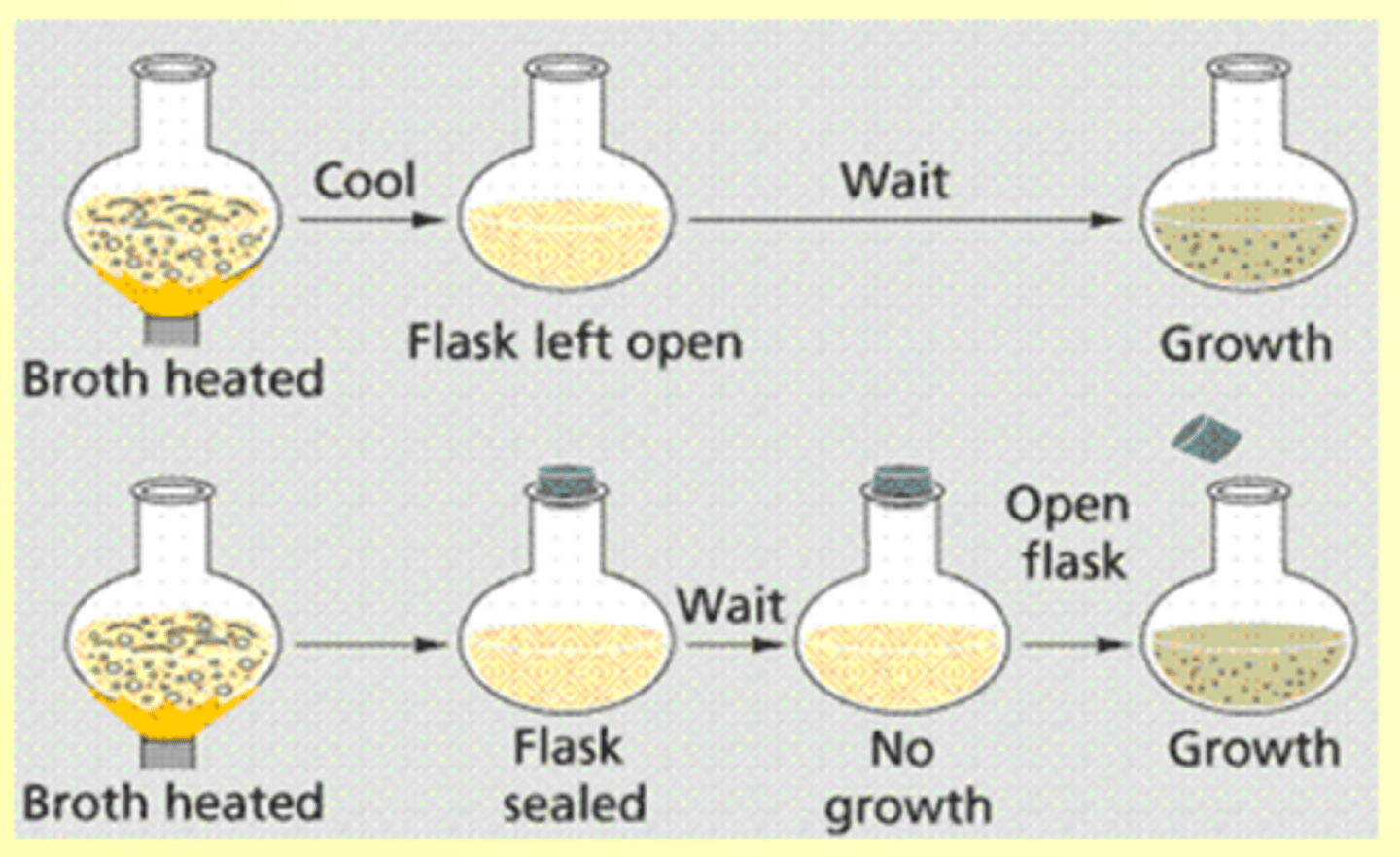
Lazzaro Spallanzani
(mid 1700s)
- Proved Biogenesis by correcting John Needham's experiment
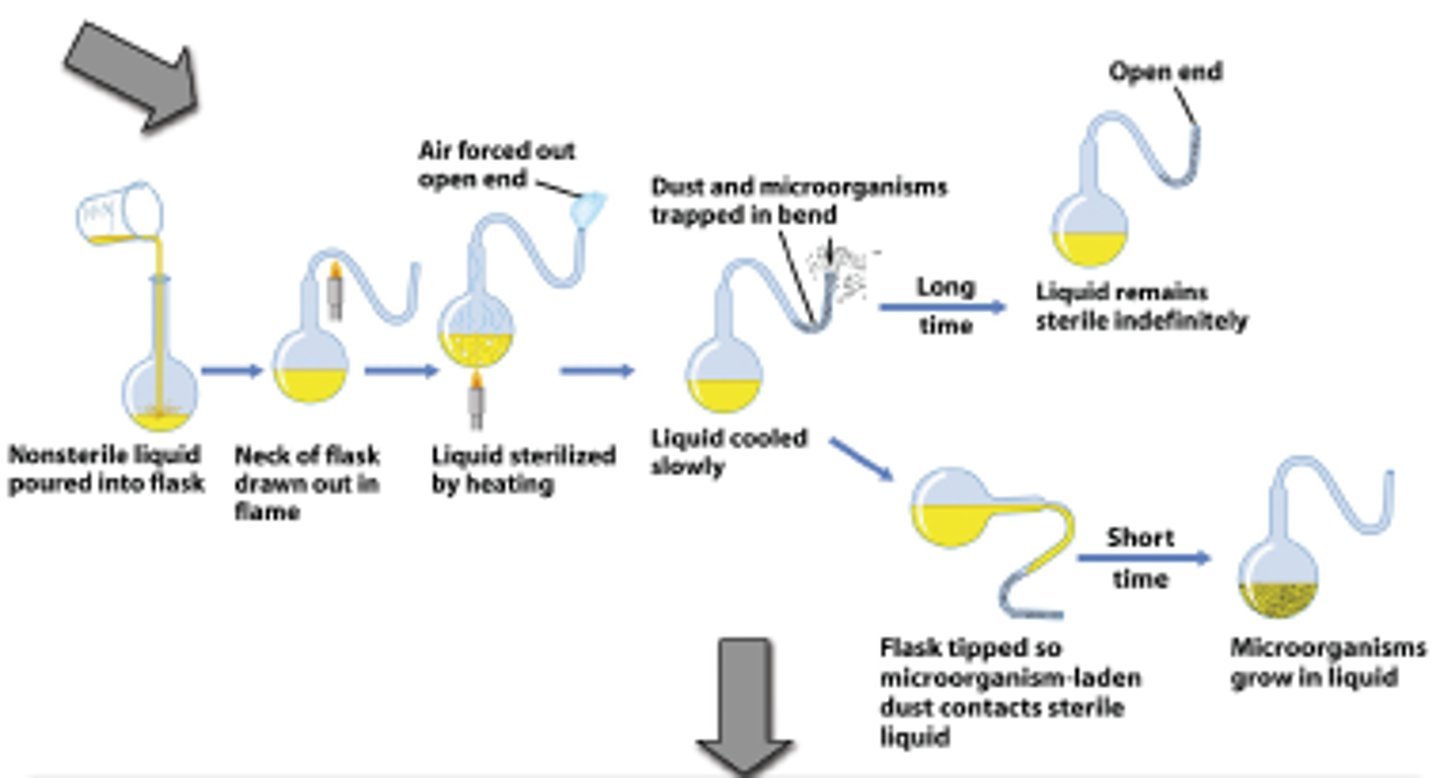
Louis Pasteur
(mid 1800s)
- 'Father of Microbiology'
- Proved Biogenesis with Germ Theory of Diseases
- Invented Swan-neck-flask
- Gun-Cotton Theory
- Pasteurization
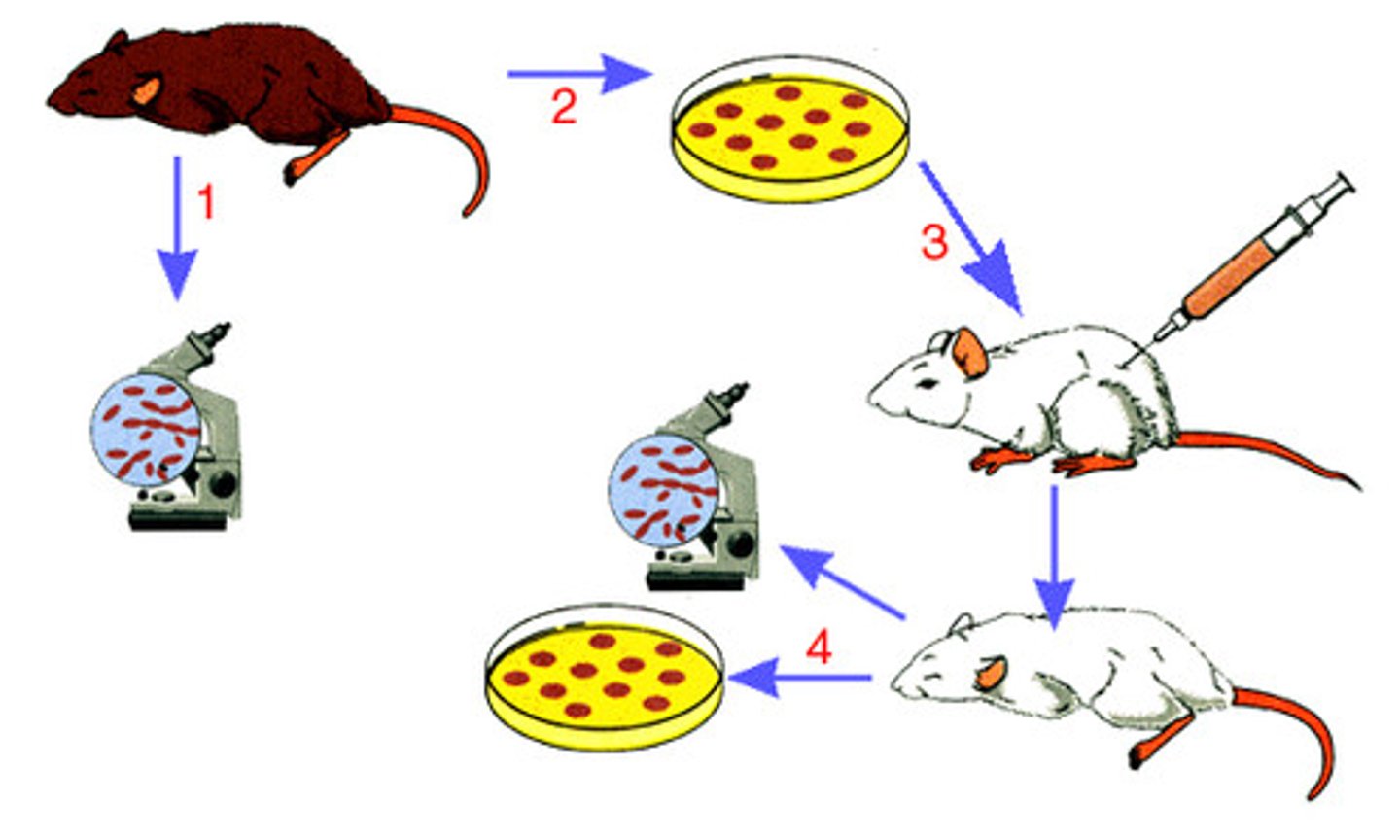
Robert Koch
(Late 1800s-early 1900s)
- Discovered Bacillus anthracis (1876) & Mycobacterium tuberculosis (1882)
- Supported Germ Theory
- Koch's Postulates
Ignaz Semmelweis
(mid 1800s)
- Proposed handwashing for physician & med students to prevent infection of OB pts
- Many OB pts deaths from puerperal fever (Group A strep)

Joseph Lister
(Mid 1800s)
- 1st to use aseptic technique w/ surgical pts
(w/ chemical agent Phenol)
- Inspired Joseph Lawrence to make Listerine

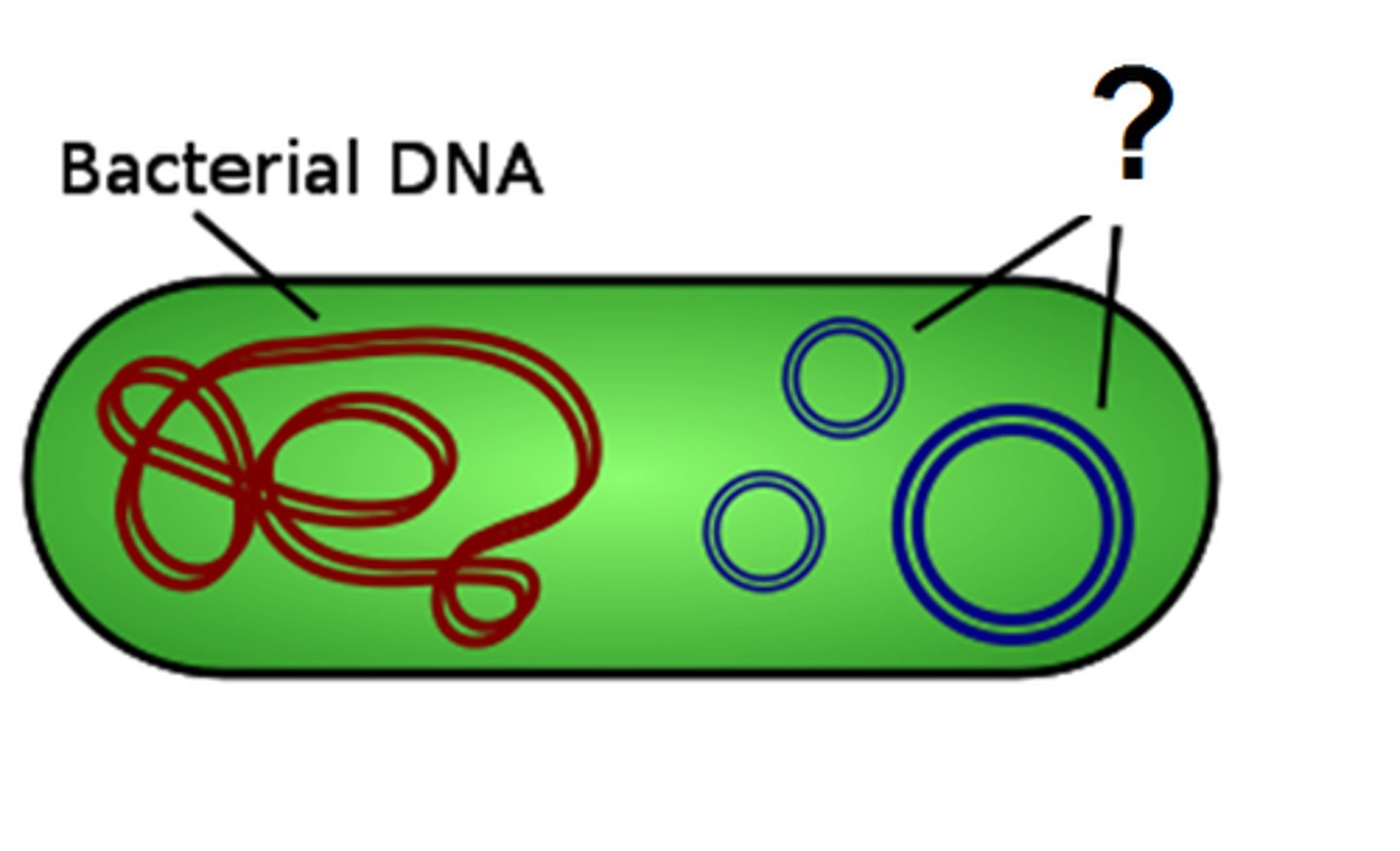
Plasmids
Circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently of the main chromosomes of bacteria
Bacillus (rods)
- Anthrax (rectangular)
- Diphtheria (club)
- Tetanus (swollen)
- Rat Bite fever (chain)

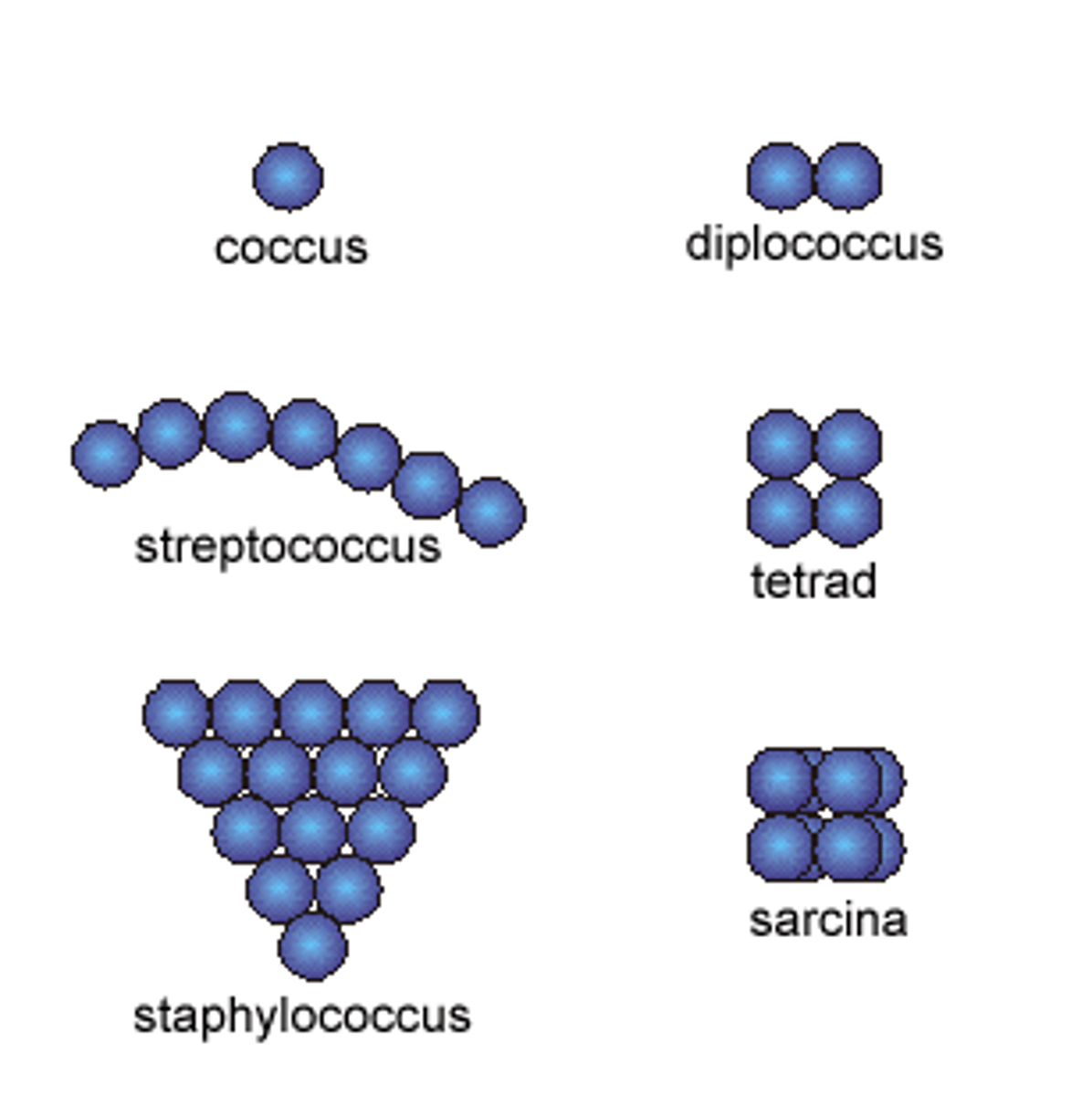
Coccus (Spherical)
- Pneumonia (diplococcus)
- Gonorrhea (diplococcus)
- Strep Throat (chain)
- Non-pathogenic (packet)
- Food poisoning (cluster)
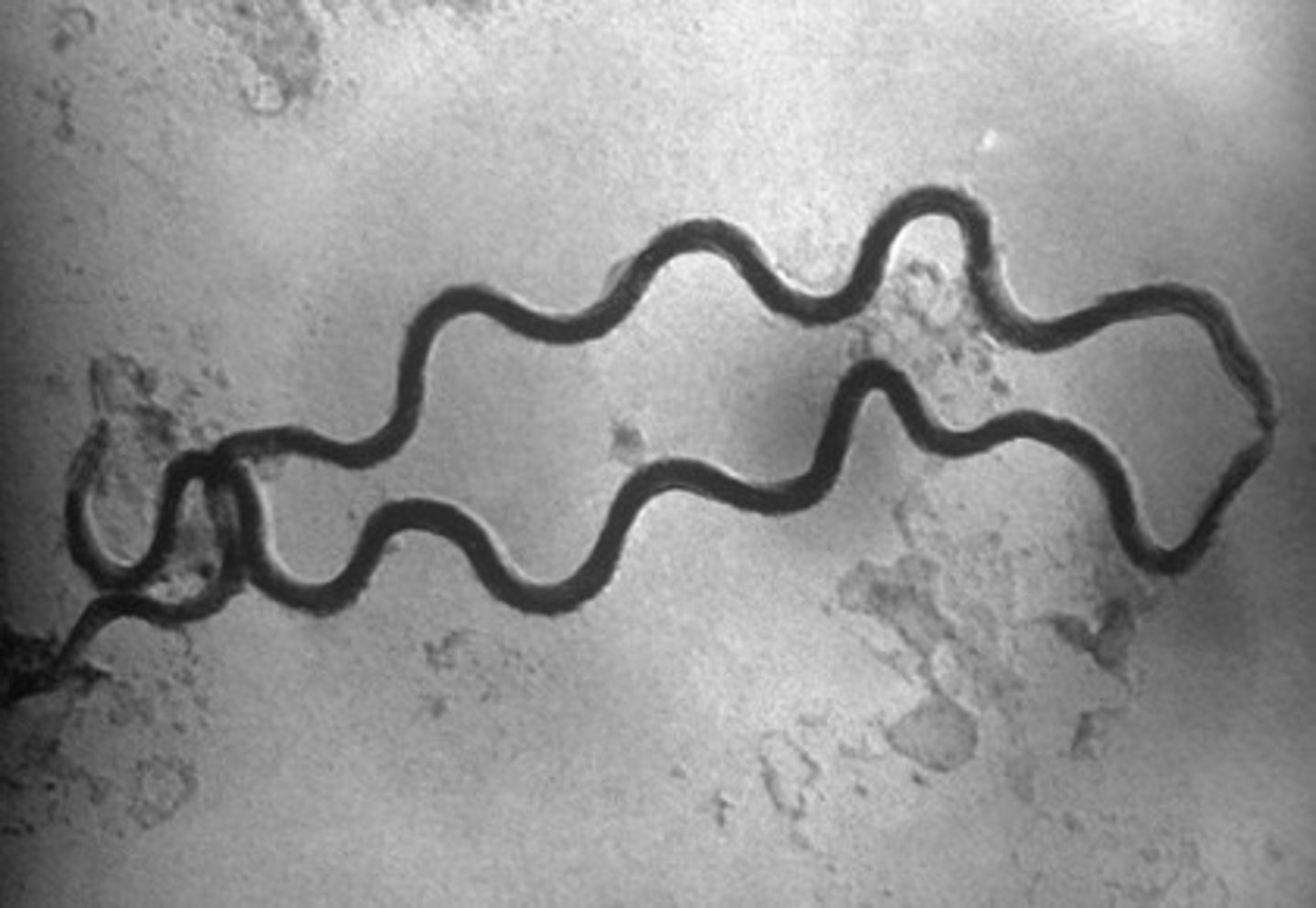
Spiral
- Cholera (single spiral)
- Rat Bite Fever (Corkscrew & Flagellum)
- Syphilis (Corkscrew, No flagellum)
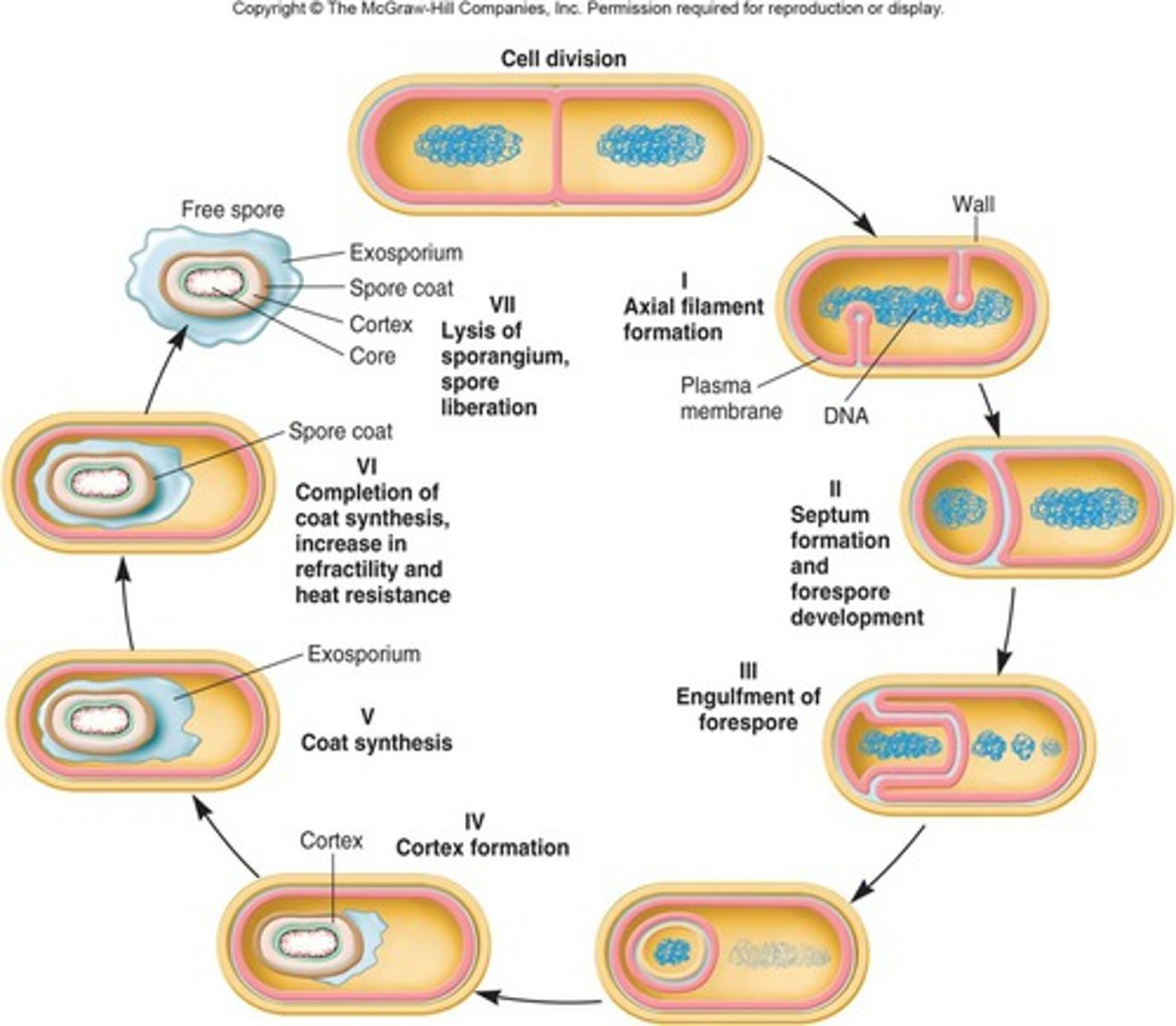
Sporulation
- formation of endospores (when conditions become unfavorable for vegetative cell)
- protective coat formedf
fomites
any object/surface likely to carry infection

variolation
inoculation of smallpox into the skin
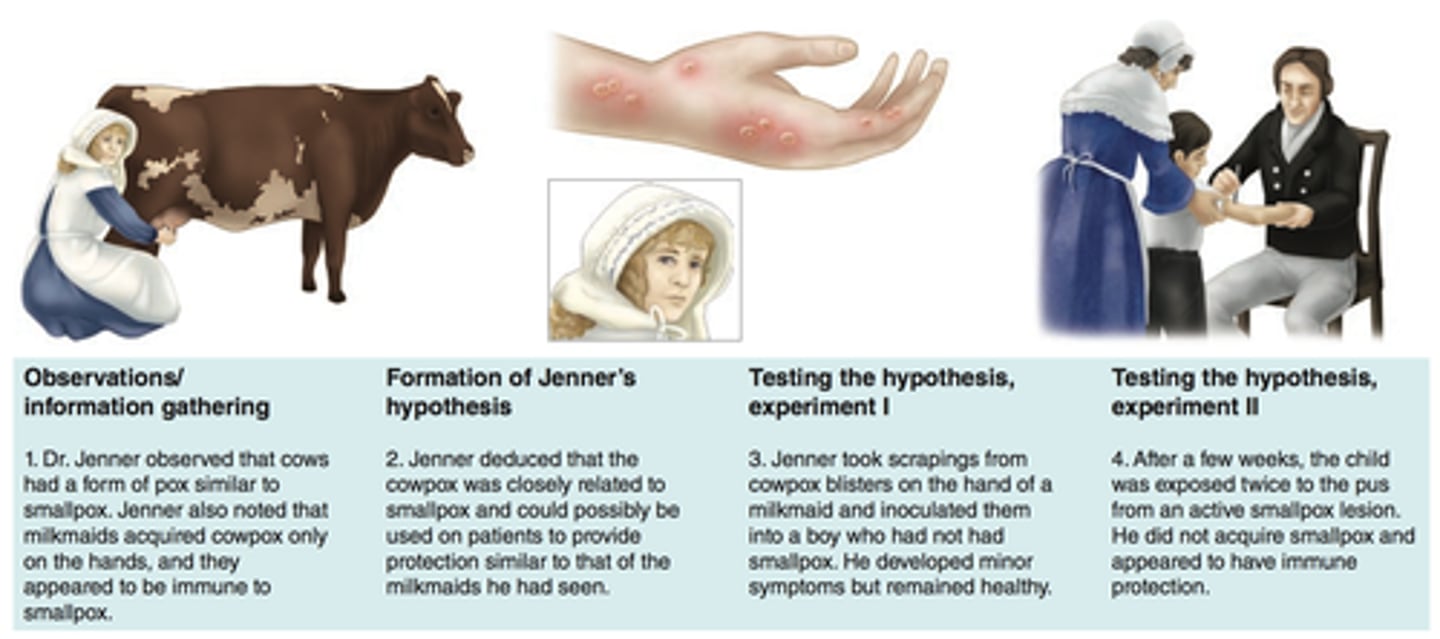
inoculation
Injecting person with small dose of a virus to help build immunization to a dz.
febrile
fever

LAD
lymphadenopathy (swelling of lymph nodes)
Dessication
drying something

Biofilm key features
- slime layer & hydrogels
- The Extracellular matrix
- EPS (Extracellular polymeric substances)
(mostly polysaccharides/sugar)
Planktonic cells
freely floating cells living in an aquatic environment

Sessile cells
planktonic cells that have attached to a surface
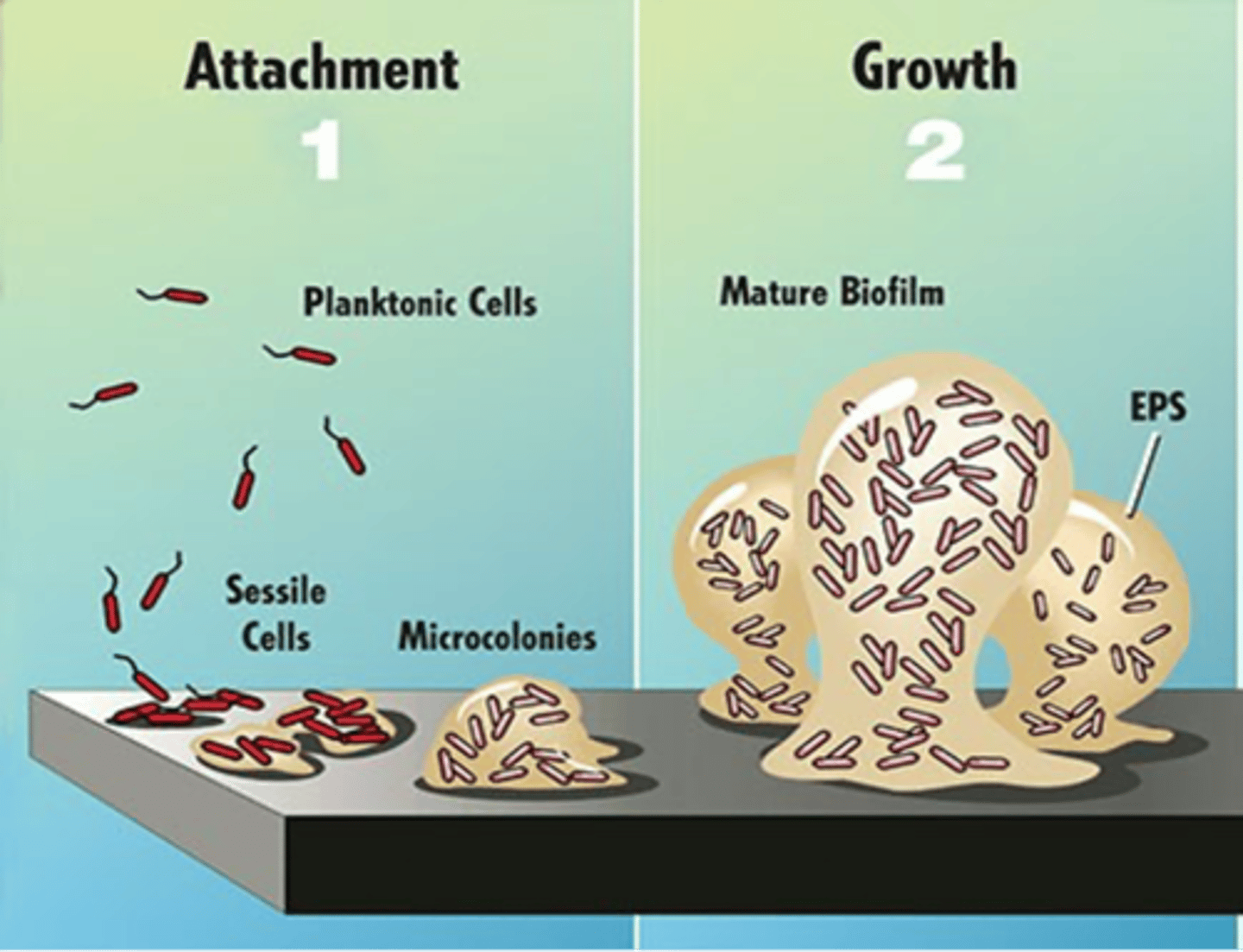
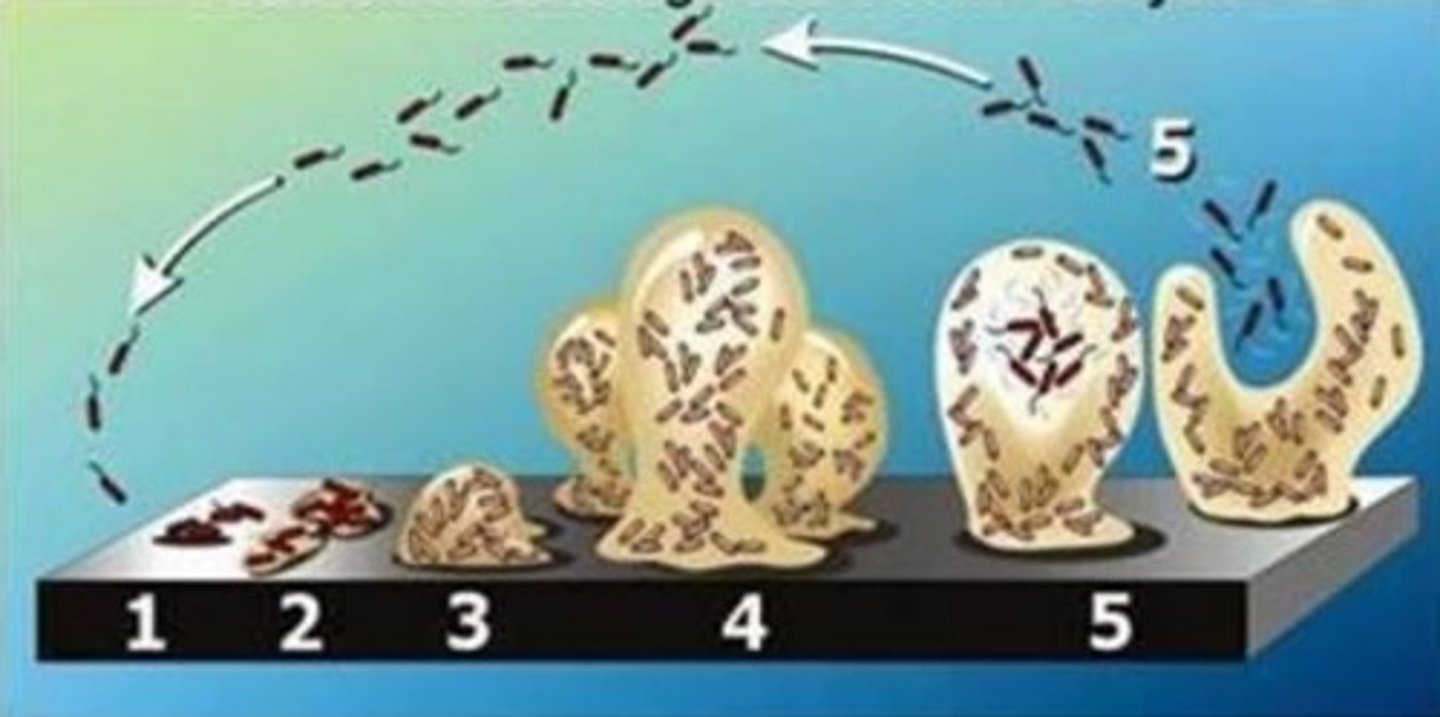
Biofilm formation stages:
1. Reversible Attachment (sec)
2. Irreversible Attachment (sec-min)
3. Maturation / binary fission (hrs-days)
4. Maturation (hrs-days)
5. Dispersion (days-weeks)

Quorum
specific # of bacteria needed for biofilm formation
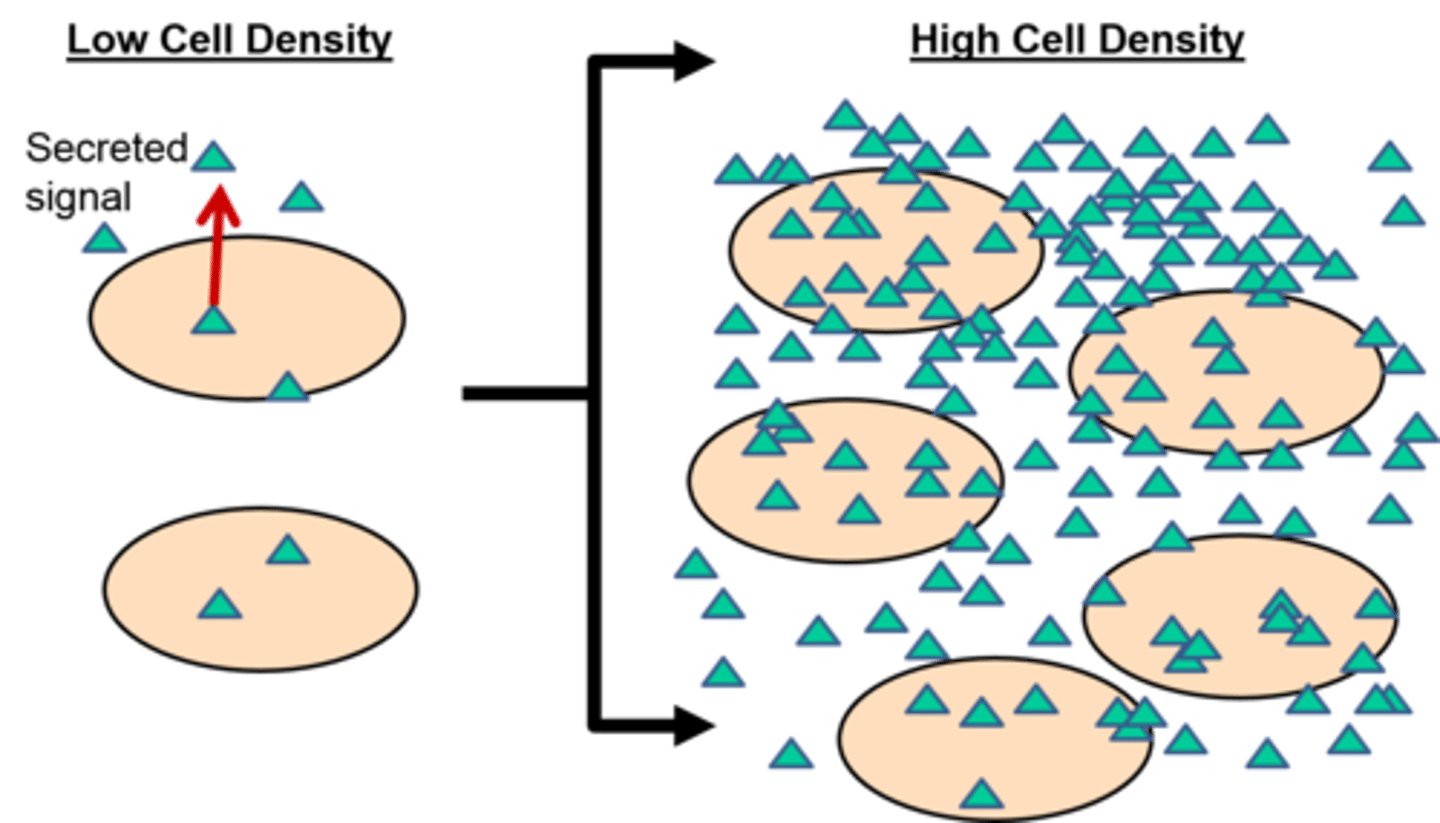
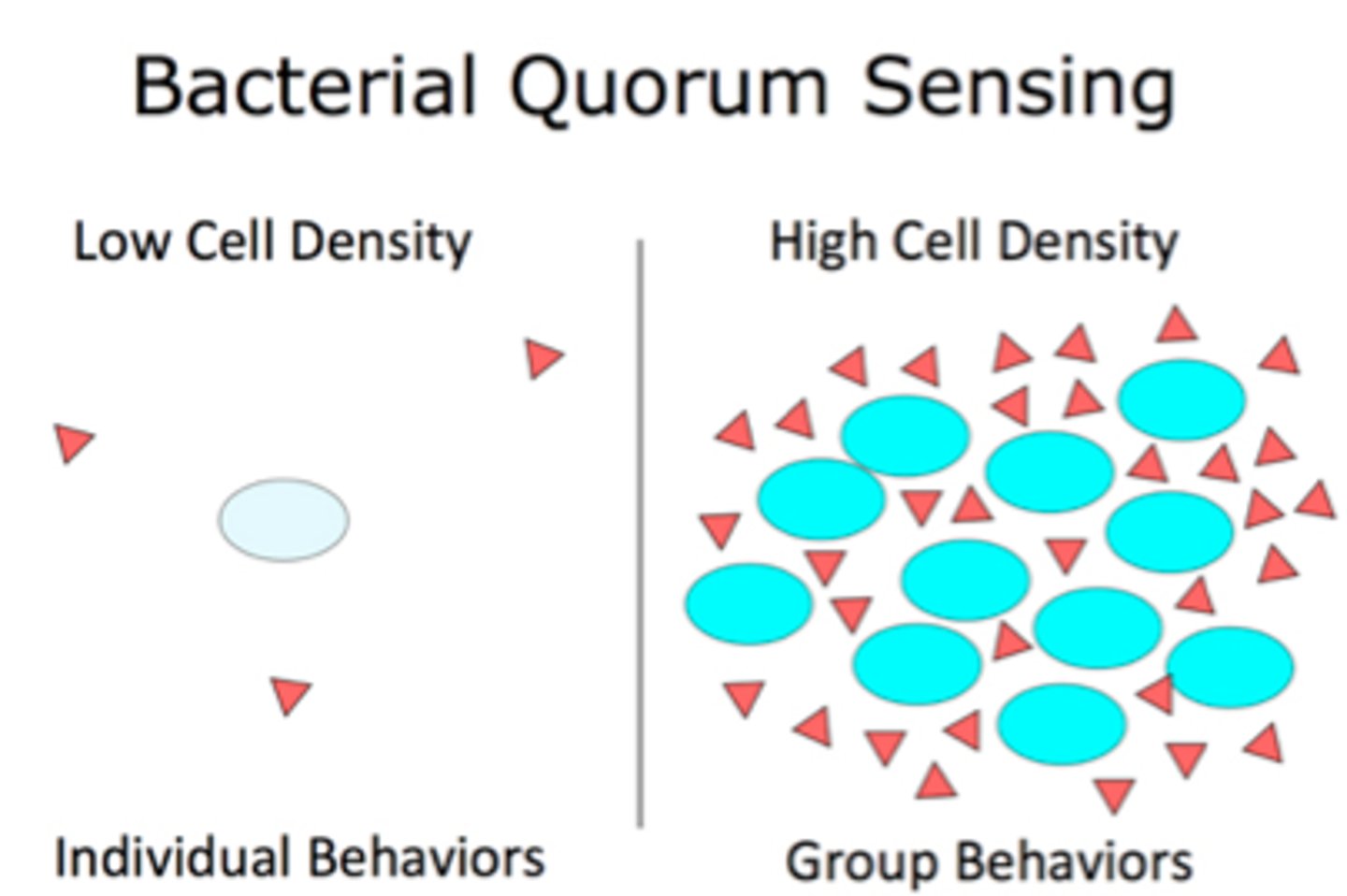
Quorum sensing
when cells in a biofilm coordinate activities by communicating w/ chem. signals until a quorum is reached
mucins
major component of mucus that lubricates & helps protect body from infections
BSL-1
Virulence: non-pathogenic
Ex.: (non-pathogenic E.Coli)
Lab Practices: open lab bench/table
Safety Equipment: lab coats, gloves, eye protection
Facility Construction: sink available, lab doors separate

BSL-2
Virulence: moderate hazard, varying severity
Ex.: Staph. aureus, HIV, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Lab Practices: lab access restricted during work
Safety Equipment: lab coats, gloves, eye protection
Facility Construction: self-closing doors, sink/eyewash ready

BSL-3
Virulence: airborne, potentially lethal
Ex.: (Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
Lab Practices: restricted access, surveillance, & immunizations
Safety Equipment: lab coats, gloves, eye protection, face shields, mask
Facility Construction: sink available, 2 sets of self-closing doors, & exhaust/air circulated
BSL-4
Virulence: Most dangerous
Ex.: (Ebola, Hantavirus, Marbury virus)
Lab Practices: change clothing & shower before leaving, decontaminate all
Safety Equipment: positive pressure suit connected to HEPA filtered airline
Facility Construction: lab isolated from facility, exhaust & decontamination system
Hemolysis
the breakage of RBCs by bacteria
(Alpha, Beta, & Gamma)
Alpha Hemolysis
Availability: Greenish discoloration
Hemolysis: Partial breakdown
Hemolysin production: partially effective
Mechanism: when H2O2 is produced & reacts w/ hemoglobin
Ex.: (Strep. pneumonia & Viridians streptococci)
Pathogenicity: May/may not be
Diagnostic tool: To ID certain species
Antibiotic Susceptibility: may be affected
O2 Requirement: facultative anaerobes or aerotolerant O2
Beta Hemolysis
Availability: Clear zone/ halo
Hemolysis: Complete breakdown
Hemolysin production: fully effective
Mechanism: when exotoxins produce & lyse w/ RBCs
Ex.: (Group A Strep, Strep. aureus)
Pathogenicity: often is
Diagnostic tool: To ID certain species
Antibiotic Susceptibility: may be affected
O2 Requirement: aerobic or facultative anaerobic O2
Gamma Hemolysis
Availability: No change
Hemolysis: none
Hemolysin production: none
Mechanism: none
Ex.: (Enterococcus faecalis or some Strep strains)
Pathogenicity: May/may not be
Diagnostic tool: To ID certain species
Antibiotic Susceptibility: may be affected
O2 Requirement: anaerobic or facultative anaerobes O2