Chapter 1.2 - Homeostasis and Feedback Control
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
homeostasis
state of relative constancy in the internal environment, maintained by negative feedback loops
basic pathway of homeostatic feedback
sensor to integrating sensor to effector
set point
normal value of a physiological variable (ex: normal blood pH)
negative feedback loop
system of sensor, integrating center, and effector that works together to produce a change in the opposite direction of a physiological variable
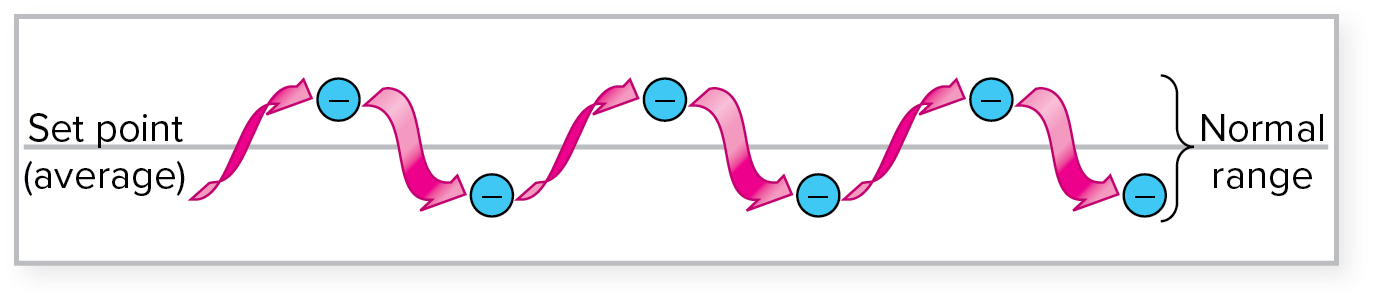
dynamic constancy
when physiological variables fluctuate over time, but maintain an average of the set point
positive feedback
when the effectors amplify the changes that stimulated the effectors (ex: thermostat increasing temperature in response to rising temperature)
how do positive and negative feedback loops work together?
positive feedback loops amplify the negative feedback response
intrinsic regulatory mechanisms
regulatory mechanisms built into the organ
extrinsic regulatory mechanisms
regulation of an organ by the nervous or endocrine systems
negative feedback inhibition
the ability for a negative feedback loop to reduce its own activity (ex: insulin decreases blood glucose and also inhibits its own production in order to prevent blood glucose from falling too far)