NVCC PSY 230 Exam2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is puberty
Hormonal and physical changes by which people become sexually mature and reach adult height.
What hormonal changes occur for puberty?
Adrenal androgens released, cause pubic hair development, skin changes, body odor, and feelings of sexual desire.
HPG axis activated. (Hypothalamus, pituitary, and gonads) testosterone and estrogen (M&F- quantities differ) released.
Primary sexual characteristics
Physical changes that are directly involved in reproduction.
secondary sexual characteristics
physical changes of puberty that are not directly involved in reproduction
Potential problems for early-maturing girls
Higher risk of anxiety, depression, risk taking behavior, truancy. Culture plays big role as well.
General order of Physical changes at puberty, girls
Initial breast elevation
Beginning of growth spurt
Appearance of pubic hair
Genital changes
Peak of growth spurt
Menstruation
General order of Physical changes at puberty, boys
Changes in genitals
Appearance of pubic hair
First ejaculation
Peak of growth spurt, followed by more growth
Growth of facial hair
Increased size of larynx and vocal chords cause voice to deepen
Attainment of adult height
Piaget formal operations
12-adult; ability to think abstractly; thinking operates in a formal, logical manner
Kohlberg's theory of moral development
preconventional, - obey to avoid punishment or gain reward.
conventional, - good boy/girl, law & order
postconventional- flexibility to rules based on societies need
Elkind: Adolescent Egocentrism
personal fable, invincibility fables, imaginary audience
Risk factors for risk-taking in adolescence
Prior emotional problems, poor family relationships, executive function challenges, peer pressure
Factors that help teens flourish
Superior executive functions, feeling connected (to anything- school, family, church, etc. sense of purpose)
What are some cultural differences in teens' relationships with their families
Immigrant family have to work out world-view issues as well. Sometimes kids have to act as parents and act as adults at a young age. Can also give extreme closeness to family, as children see parents making large sacrifices for them and working hard.
What is the difference between a crowd and a clique? Gang?
Crowd- large teenager group.
clique- small (~6) peer group of teens with shared attitudes and activities.
Gang- close knit delinquent peer group usually formed in economic deprivation; offer protection
What is emerging adulthood?
- late teens to late 20s. Newer term due to longevity and need for education
What are the tasks of emerging adulthood?
Re-center lives, take control on our own (out of parents reach), feel like an adult outside of other defining terms
Marcia's four identity statuses
Identity diffusion: drifting aimlessly without any goals toward adulthood.
Identity foreclosure: adopts identity without self exploration or thought, often handed down by authority (parents)
Moratorium: engaged in healthy, exciting search for adult self. Can involve anxiety. Critical stage
Identity achievement: end point. Thought through and made goals.
What is flow?
Csikszentmihalyi's term for feeling total absorption in a challenging, goal-oriented activity.
What are current trends in young adult romantic relationships?
Average age of marriage increasing, putting off relationships, more on/off relationships, putting these off until establishing a career is what's pushing the timeline back.
What types of relationships are most likely to last?
Shared interests & flow, one partner more dominant, one more submissive. Believing your partner has a great personality, emotionally stable. Embodies our "ideal self"
What are adult attachment styles?
Secure- capable of genuine intimacy
Avoidant/dismissive- unable to get close
Preoccupied/ambivalent insecure- needy and engulfing
*can change styles over time.
What is the "deinstitutionalization of marriage"? What alternatives exist?
Transformation of the meaning of marriage from a standard adult "institution" to an optional choice.
What are some ethnic/geographic difference in marriage?
Iran: male led, marriage is only life path. Women subservient to men. Some changes happening- more women are enrolling in university, and can now initiate a divorce.
India: Arranged marriages losing favor. Elopements happening.
How does marital satisfaction change over time? Ups and downs
Most common pathway of marital happiness in the West is the U shaped curve.
First years- clear cut attachment. Moving into working model of marriage = steep decline (first 4 years). Curve swings up at empty-nester phase, and even higher at retirement. Elderly couples fight less than middle-aged ones.
Sternberg's triangular theory of love
The ideal in our culture is consummate love- combines passion, intimacy and commitment.
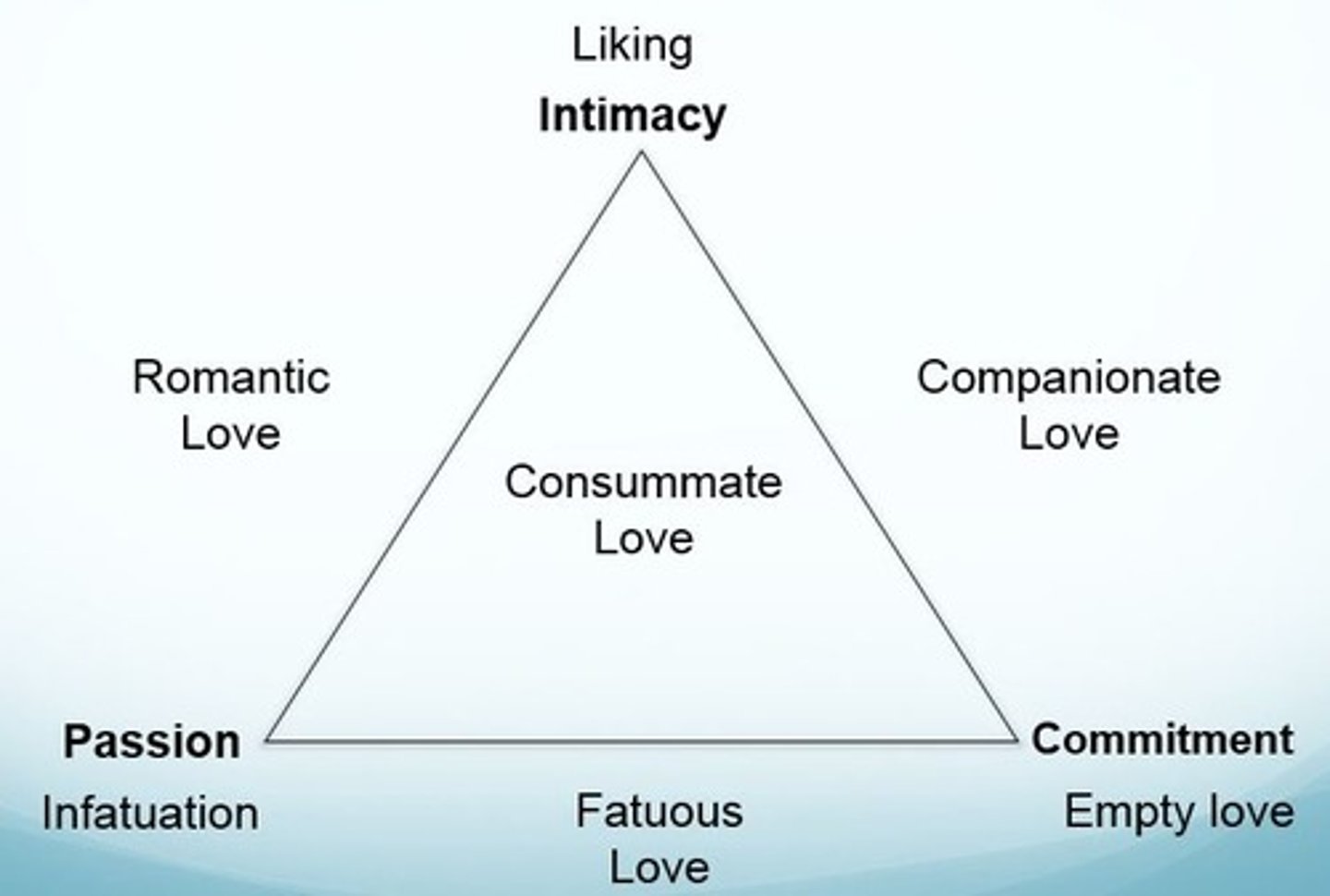
What type of communication do happy couples engage in?
High ratio of positive to negative comments, don't get personal when they disagree, sensitive to partner's need for 'space'
What is the demand-withdrawal pattern of communicating?
One partner in the relationship uses emotional requests, criticism and complaints to create change. The other partner uses withdrawal, defensiveness and passive inaction to avoid the conflict and/or changes.
Common reasons for divorce and tasks of divorced adults
Communication problems, lack of attachment, being denigrated and controlled.
Must move, possibly new job, housework burdens rise, legal hassles
How does parenthood affect an adult?
Makes couples less intimate, produces more traditional marital roles (heterosexual couples), differences in rearing methods
Common experiences of new mothers? New fathers?
Moms: Destroys pre-child fantasies of parenthood (e.g. I'll never ____!), moments of wonderful and terrible, stress.
Dads: Confusion as role or nurturer or disciplinarian, work more to provide more or be physically present more, playing in 'rough and tumble' ways, involvement skewed to play activities.
How are women's careers different than men's? (continuity, occupations, wages)
More erratic and less continuous, women earn less, gender-defined jobs
Super's lifespan theory of careers
What are two strategies for career happiness?
Match career to personality, find an optimal workplace (both intrinsic and extrensic career rewards)
The Big 5 personality traits (OCEAN)
Openness to experience, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism (trend toward either mental health or disturbance),
Erikson: Generativity v stagnation
generativity- nurturing the next generation, caring for others, enriching other's lives
When mid-life adults have not cared about others will feel stagnant, or without a life purpose.
Commitment scripts
type of autobiography produced by highly-generative adults that involve childhood memories of feeling special; being unusually sensitive to other's misfortunes; having a strong, enduring mission from adolescence; and redemption sequences
Redemption sequences
examples of devastating events that turned out in a positive way
What maturity and happiness changes occur in midlife
maturity and happiness increase
What's the WAIS & what does it tell us?
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. Measures adult IQ, includes verbal and performance scales
What were the findings of the Seattle Longitudinal study?
showed that we reach intellectual peak in midlife. Verbal scores decline slower than timed ones.
What is the difference between crystallized and fluid intelligence and how do these change in midlife?
Crystallized- knowledge base
Fluid- ability to quickly master new intellectual abilities
midlife- fluid declines rapidly, crystallized continues until around 60, then dips in all except negotiating relationships
What are some strategies to keep mentally fit?
stay fit, mental stimulation (involving people) matters, keep learning
Postformal thought
relativistic, feeling-oriented, question-driven
a uniquely adult form of intelligence that involves being sensitive to different perspectives, making decisions based on inner feelings, and being interested in exploring new questions.
What roles do grandparents play in today's society?
family watchdog, mediators, cheerleaders, family cement, a few are caregiving grandparents
What is parent care?
adult children's care for disabled elderly parents
What is the "sandwich generation," and what are the characteristics of this role?
women pulled between care of kids and elderly parents.
Menopause
Age related process that occurs around age 50 in which ovulation and menstruation stop due to drop in estrogen.
Sexual changes with age
blood flow decreases, takes longer to produce lubrication, vaginal walls thin, shortens and narrows.
What memory changes occur in later life?
Expanding crystallized memory, becoming wise, declining ability to recognize new faces, names of new places.
Can remember if they've seen something before, word recollection much more difficult (analogous to multiple choice v fill in the blank). More attribution errors.
Especially poor at divided attention tasks.
What is the information-processing perspective on memory change?
Limited memory-bin space, but working memory gets worse. Possibly due to decline of the executive processor (turns material into memories). Deterioration of the frontal lobes.
What is the memory-systems perspective?
Procedural memory- automatically remember. E.g. ride a bike.
Semantic memory- basic factual knowledge.
Episodic memory- ongoing events of daily life.
Episodic is first to go because it requires frontal lobe use, which declines with aging. prin
Socioemotional selectivity theory
principal that in old age, we tend to make the most of every moment.
Erikson: integrity v despair
(late 60s+) to reach integrity, one must review lives and make peace with what they've done; but does not involve dwelling on the past. Should have sense of purpose.
What is the traditional retirement age? How has this changed over time? What are some cultural differences in retirement?
Traditional 65. Now 66. For people born after 1970, it's 67. Some places (eg. Bangladesh, Jamaica, Mexico) have no retirement.
What is age discrimination
illegally laying off workers or failing to hire or promote them based on age
How are the elderly "at risk"?
Lack of pension, income & other assets. Probable future cutbacks on Social Security. (1950- 16 workers to 1 retiree; soon will be 2 to 1).
Age discrimination.
What helps widows cope with their loss?
finding self-efficacy. Life traumas can promote emotional growth. Friends seem more important than children in seeing how widows adjust.
What is the socioeconomic/health gap that has been documented by researchers? What are the real implications of this gap?
Disparity between rich and poor in health. At age 55, only 5% of ppl in top quarter of income distribution reported being in poor health; bottom quarter odds were 1 in 3.
What are ethnic and gender differences in aging and disease?
Women live longer, but are more frail. Men live more health years.
Sensory impairments: vision, hearing
Vision- problems seeing in dim lighting; sensitive to glare; trouble seeing close objects. presbyopia is age-related difficulty seeing close objects
Hearing- Loss of hearing high pitched tones. presbycusis is age-related hearing loss.
What is dementia? What is the process of dementia? What are the two main causes?
Avg time from diagnosis to death is 4-10 yrs.
Vascular- impairments in vascular problems- small strokes.
Neurocognitive (Alzheimer's)- neurofibrillary tangles replace neurons; development of protein bodies (senile plaques)
How are we currently treating Alzheimer's?
mental exercise, physical exercise, trying to dissolve plaques
What options exist for elderly care?
Nursing home, assisted living, day-care programs, home health services, continuing-care retirement community (ultimate person-environment fit)
Thanatology
The study of death and dying
Cultural differences in death and dying
Kubler-Ross's stages of dying- what are the stages and what are the criticisms of the theory?
denial, anger, bargaining, depression & acceptance
What is middle knowledge
Idea that terminally ill people can know they're dying yet simultaneously not grasp or come to terms emotionally with that fact.
What is a "good death"
minimize pain & fear; be close to loved ones; enhance spirituality; feel life has meaning
Dying trajectory
fact that hospital personnel make projections about when and how someone will die, and will organize their care to the prediction
End-of-life instruction
courses for medical professionals devoted to how to provide the best palliative care.
Palliative-care
any intervention designed not to cure illness but to promote dignified dying
Hospice care
providing backup care that allows people to die with dignity at home. provide scheduled care, 24 hr help in crisis, as well as bereavement counseling
Advance directives- what are the variations
any written document spelling out instructions with regard to life-prolonging treatment at end of life.
Living will
durable power of attorney for health care
DNR- when impaired, consulting dr and family
DNHospitalize- specific to nursing homes. States mentally impaired resident not be transferred to hospital for emergency care.
What is euthanasia? Passive v active?
What are the guidelines for physician-assisted suicide in Oregon where it is legal?
1. an adult (age 18 or older), an Oregon resident, capable (able to make and communicate health care decisions), and diagnosed with a terminal illness (incurable and irreversible) that will lead to death within six months.
-if these are fulfilled, then:
1. the patient must make two oral requests to his physician, separated by at least 15 days; must provide a written, witnessed request to dr (two witnesses); confirmation of prognosis, determination of if capable by 2 dr; if either believes the patient's judgment is impaired by a psychiatric or psychological disorder, must refer the patient for a psychological examination; must inform the patient of feasible alternatives to assisted suicide, including comfort care, hospice care, and pain control; and dr must request, but may not require, the patient to notify his next-of-kin of the prescription request.
What is the "age-based rationing of care"?
controversial idea that society should not use expensive life-sustaining technologies on the very-elderly.