Java Stream API
1/54
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What is the Java Stream API?
A feature introduced in Java 8 that allows processing sequences of elements using functional-style operations.
Which package contains the Stream API?
java.util.stream
What is a stream in Java?
A sequence of elements that supports sequential and parallel aggregate operations.
Is a stream a data structure?
No, it's not a data structure; it doesn't store data but operates on data from a source.
What are the main types of streams in Java?
Stream<T>, IntStream, LongStream, and DoubleStream
What is the difference between intermediate and terminal operations in streams?
Intermediate operations return a new stream; terminal operations produce a result or side effect and terminate the stream.
Give examples of intermediate operations.
map(), filter(), sorted(), distinct(), limit(), skip()
Give examples of terminal operations.
collect(), forEach(), reduce(), count(), anyMatch(), allMatch()
What is the purpose of filter()?
Filters elements based on a given predicate.
What does map() do in streams?
Transforms each element in the stream using a function.
What is flatMap() used for?
Flattens nested structures into a single stream.
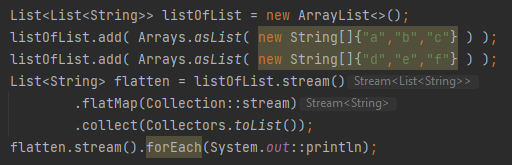
What is collect() used for?
Performs a mutable reduction on the elements and returns a collection or result.
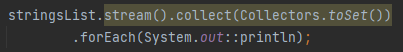
What is Collectors.toList()?
A collector that accumulates the stream elements into a List.
What does forEach() do?
Performs an action for each element in the stream.
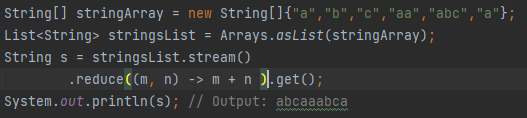
What is reduce() in streams?
Combines elements of the stream into a single result using an associative accumulation function.
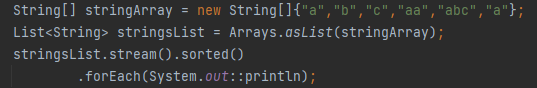
What does sorted() do in streams?
Sorts elements based on natural order or a provided comparator.
How do you create a stream from a collection?
Using collection.stream() or collection.parallelStream()
How do you create a stream from an array?
Using Arrays.stream(array)
What is the difference between Stream.of() and Arrays.stream()?
Stream.of() creates a stream from varargs or single values; Arrays.stream() specifically works with arrays.
What is a parallel stream?
A stream that uses multiple threads to process data concurrently.
How do you create a parallel stream?
Using collection.parallelStream() or stream.parallel()
What is limit(n) in streams?
Truncates the stream to be no longer than n elements.
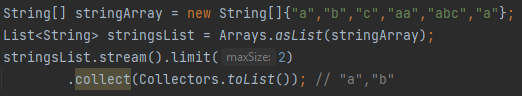
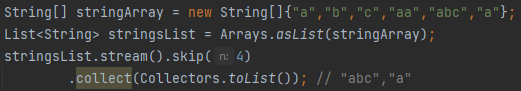
What is skip(n) in streams?
Skips the first n elements of the stream.
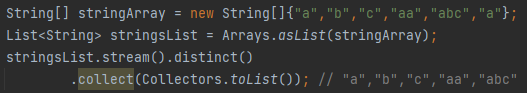
What is distinct() in streams?
Removes duplicate elements from the stream.
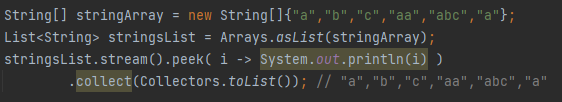
What does peek() do in streams?
Provides a way to see the elements as they flow through the stream, mainly for debugging.
Are streams reusable in Java?
No, streams can be consumed only once.
What happens if you try to reuse a stream?
An IllegalStateException is thrown.
What is lazy evaluation in streams?
Intermediate operations are not executed until a terminal operation is invoked.
What is short-circuiting in streams?
The ability to terminate stream processing early when a result is found (e.g., anyMatch()).
What is anyMatch()?
Returns true if any element in the stream matches the given predicate.
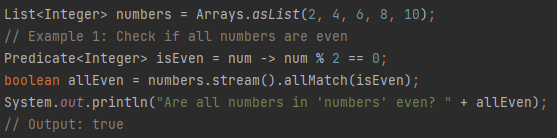
What is allMatch()?
Returns true if all elements match the predicate.
What is noneMatch()?
Returns true if no elements match the predicate.
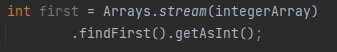
What does findFirst() do?
Returns an Optional describing the first element of the stream.
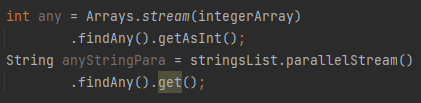
What does findAny() do?
Returns an Optional describing any element of the stream (useful for parallel streams).
What is Optional in Java?
A container object which may or may not contain a non-null value.
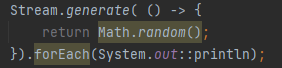
What is the role of Stream.generate()?
Creates an infinite stream using a Supplier.
What is the role of Stream.iterate()?
Creates an infinite sequential ordered stream from a seed and a function.
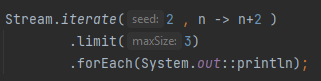
How do you limit infinite streams?
By using limit(n) to avoid infinite loops.
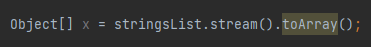
How do you convert a stream to an array?
Using stream.toArray()
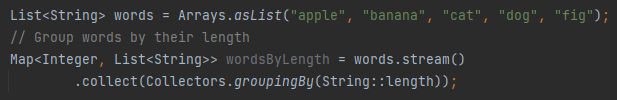
What is Collectors.groupingBy() used for?
To group elements by a classifier function.
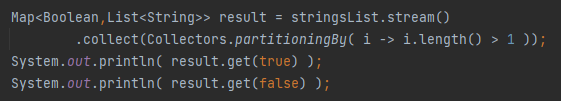
What is Collectors.partitioningBy()?
Divides elements into two groups based on a predicate.
What is the difference between map() and flatMap()?
map() transforms each element; flatMap() flattens nested structures.
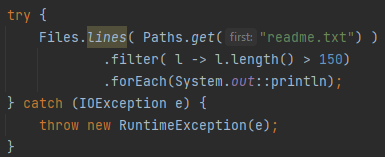
Can you perform file I/O using streams?
Yes, using Files.lines(Path) returns a Stream<String> of lines from a file.
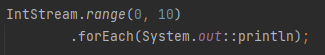
What is IntStream.range()?
Creates a sequential stream of int values in a given range.
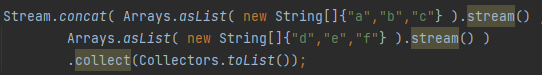
What is Stream.concat()?
Combines two streams into one.
How do you sum values in a stream?
Using mapToInt().sum() or reduce()

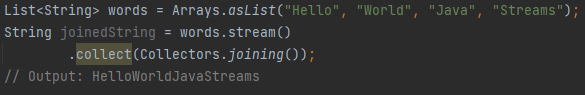
What is Collectors.joining() used for?
Concatenates the elements of a stream into a single String.
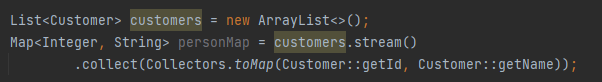
How do you convert a stream to a map?
Using Collectors.toMap()
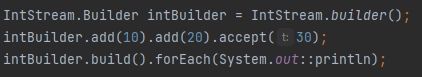
What does Stream.builder() do?
Allows step-by-step construction of a stream.
What is the advantage of Stream API?
Improves code readability, encourages functional programming, and enables parallel processing.
Can exceptions be thrown inside streams?
Yes, but they must be handled (e.g., wrapped in try-catch or use custom utilities).
What happens if a stream pipeline throws an exception?
It terminates the pipeline unless the exception is caught.
What is Stream.empty()?
Creates an empty stream.
What is BaseStream?
A common interface for all primitive and object streams.
What are primitive specializations in streams?
IntStream, LongStream, and DoubleStream for better performance with primitives.