Glycolysis: Phases, Enzymes, and Glucose Utilization Pathways
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
Preparatory and payoff
What enzymes use up ATP in glycolysis?
hexokinase and phosphofructose kinase
What enzyme produces NADH in glycolysis?
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
What enzymes produce ATP in glycolysis?
phosphoglycerate kinase, pyruvate kinase
What is the importance of glucose?
Used as fuel to produce ATP
Oxidative respiration
Allows for more ATP produced per glucose molecule
What is glucose a precursor for?
- amino acids
- membrane lipid
- nucleotides
- cofactors
4 major pathways of glucose utilization
1) Structural polymers: extracellular matrix and cell wall polysaccharides
2) Storage: glycogen, starch, sucrose
3) oxidation in PPP: Ribose 5-phosphate
4) oxidation in glycolysis: pyruvate
Feeder pathways for glycolysis
D-glucose, D-fructose, D-Mannose, D-galactose
Preparatory phase
First 5 steps: phosphorylation of glucose and its conversion to two high energy 3 carbon sugars
-activation via phosphorylation and primes them for phase 2
Preparatory phase - ATP
Uses up 2 ATP
Payoff Phase
Steps 6-10: Oxidative conversion of two glyceraldehyde 3-phosphates to pyruvate and the coupled formation of ATP and NADH.
Payoff phase - ATP
Produces 4 ATP and 2 NADH
Oxidoreductase
transfer of electrons
-dehydrogenase or oxidase
Transferase
group transfer reactions
-transaminase, kinase, polymerase
Hydrolases
hydrolysis reactions
-peptidase, protease, phosphatase, lipase, esterase
Lyases
cleavage of covalent bonds by elimination
-decarboxylases, aldolases, and syntases
isomerases
group transfer WITHIN a molecule
-isomerase, mutase, epimerase, racemases
Ligases
covalent bond synthesis power by ATP hydrolysis
-synthase, carboxylase, ligase
1) Phosphorylation of glucose
-traps glucose in the cell by tagging it with a charged group
-irreversible
-coupled to ATP hydrolysis so highly favored
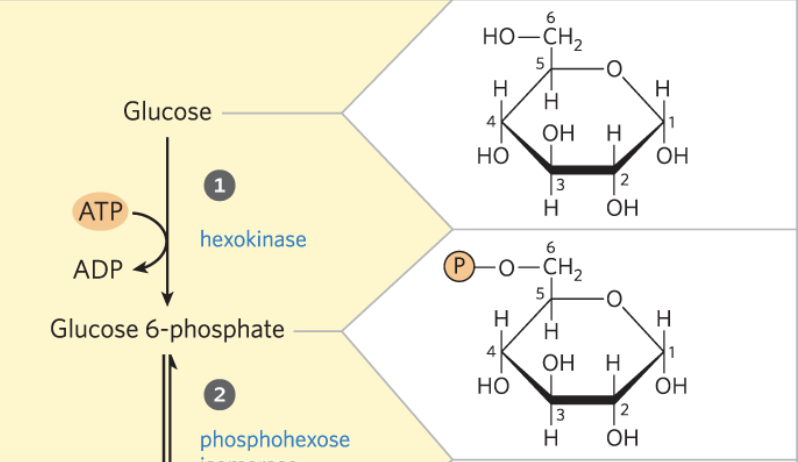
1) Phosphorylation of glucose - R&P
Glucose to Glucose 6-phosphate
1) Phosphorylation of glucose - enzyme
hexokinase - transferase (phosphate)
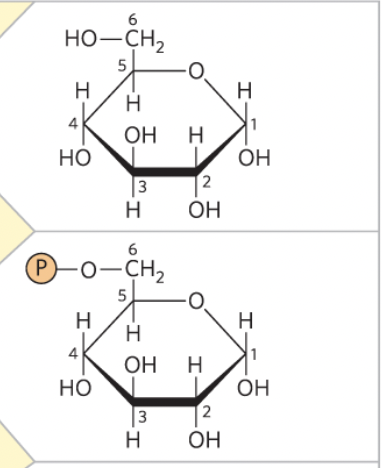
Glucose -> Glucose 6-phosphate
enzyme and step
1) hexokinase - transferase
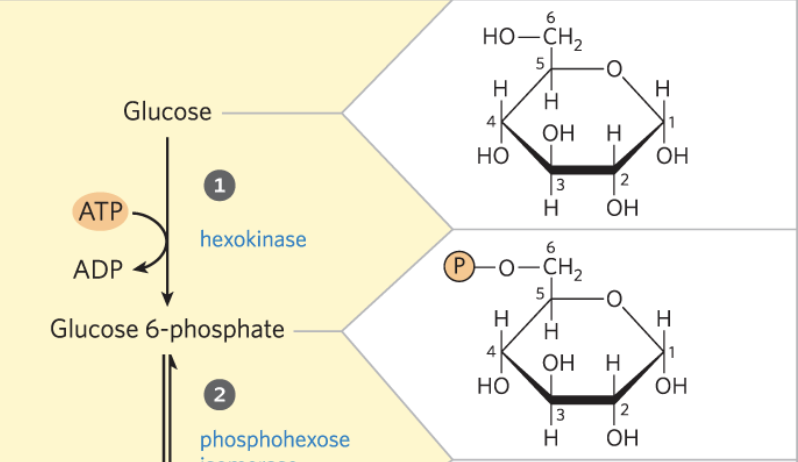
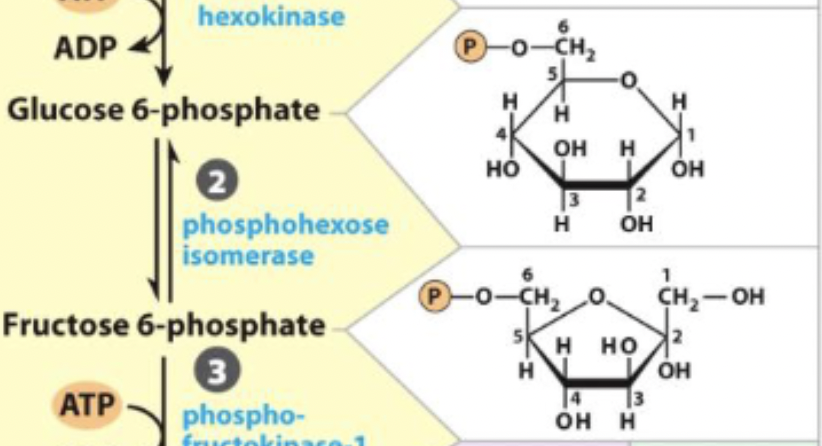
2) Phosphohexose Isomerization
-converts 6C hexagon ring to a 6C pentagon ring
-preps for symmetrical cleavage
-reversible, regulated by [F6P]
![<p>-converts 6C hexagon ring to a 6C pentagon ring</p><p>-preps for symmetrical cleavage</p><p>-reversible, regulated by [F6P]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b5b7c38d-da50-405c-a011-a413b53fea5a.png)
2) Phosphohexose Isomerization - R&P
Glucose 6-phosphate <-> Fructose 6-phosphate
2) Phosphohexose Isomerization - enzyme
phosphohexose isomerase
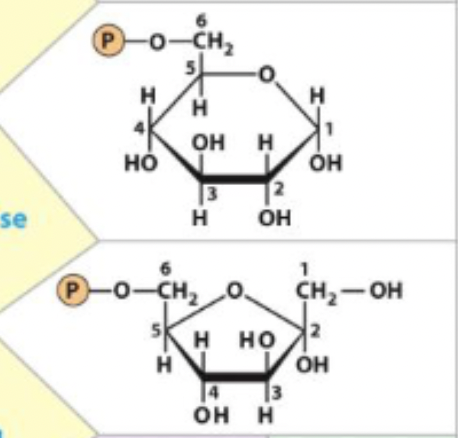
Glucose 6-phosphate <-> Fructose 6-phosphate
enzyme and step
2) phosphohexose isomerase
3) 2nd Priming Phosphorylation
-another activation via addition of phosphate
-first committed step of glycolysis (must become pyruvate)
-irreversible and favored
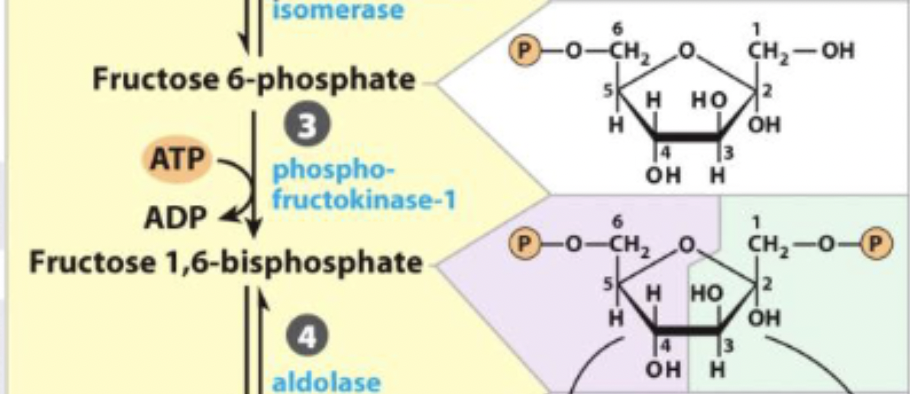
3) 2nd Priming Phosphorylation - R&P
Fructose-phosphate → Fructose 1,6-biphosphate
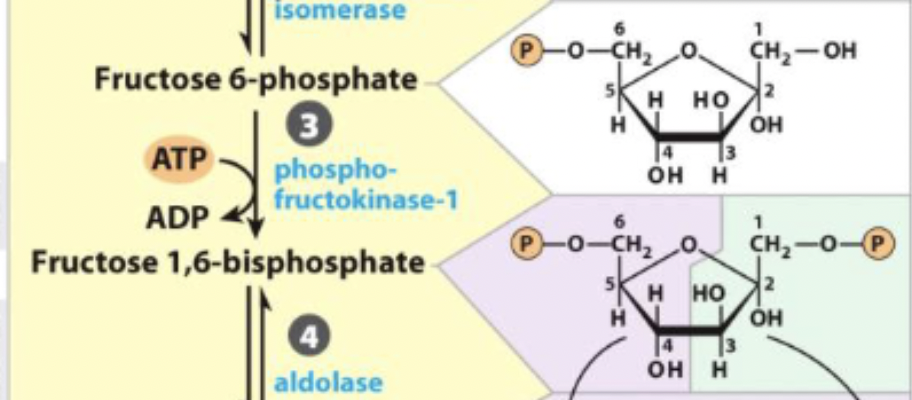
3) 2nd Priming Phosphorylation - enzyme
phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) - transferase
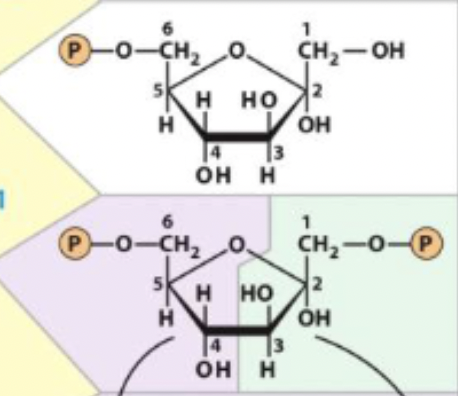
fructose-6-phosphate -> fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
enzyme and step
3) phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) - transferase
4) Aldol Cleavage of F-1, 6bp
6 carbon sugar to 2 high energy 3-carbon sugars
reversible (reverse is aldol condensations) and unfavorable
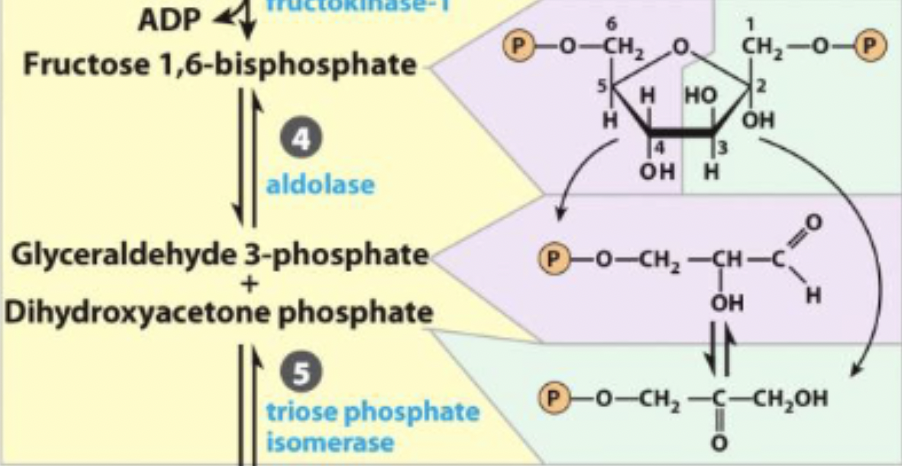
4) Aldol Cleavage of F-1, 6bp - R&P
Fructose 1,6-biphosphate ←→ Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
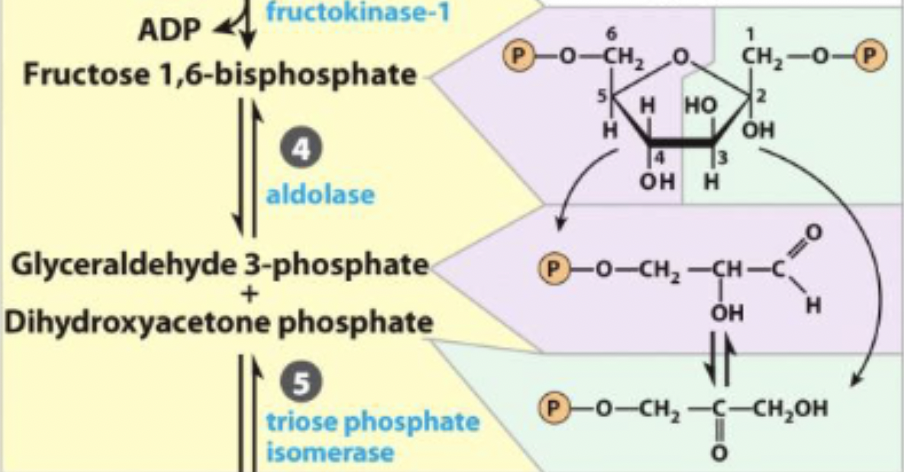
4) Aldol Cleavage of F-1, 6bp - enzyme
aldolase - lyase
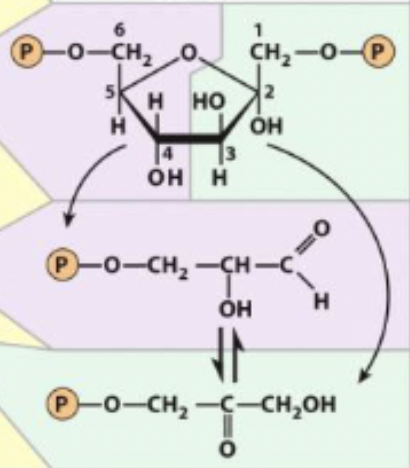
Fructose 1,6-biphosphate ←→ Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
enzyme and step
4) aldolase - lyase
ketone moves from C2 → C1
matches the 3 carbon sugars so glycolysis applies to both
completes prep phase
reversible
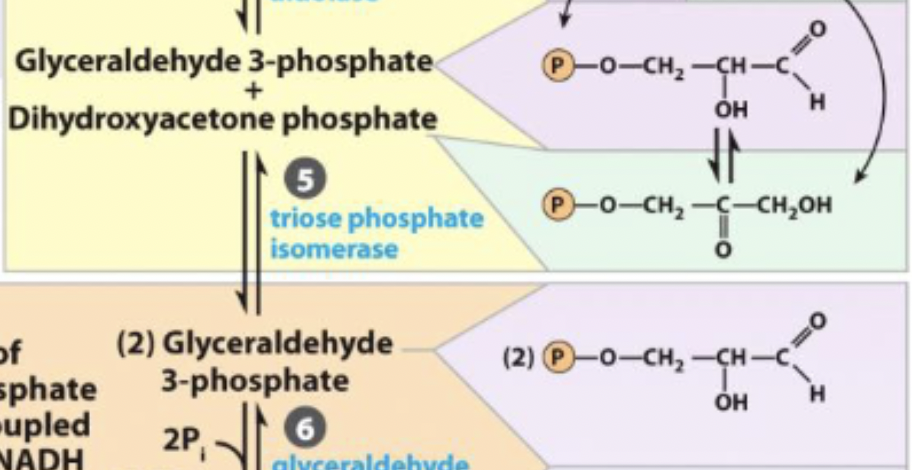
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
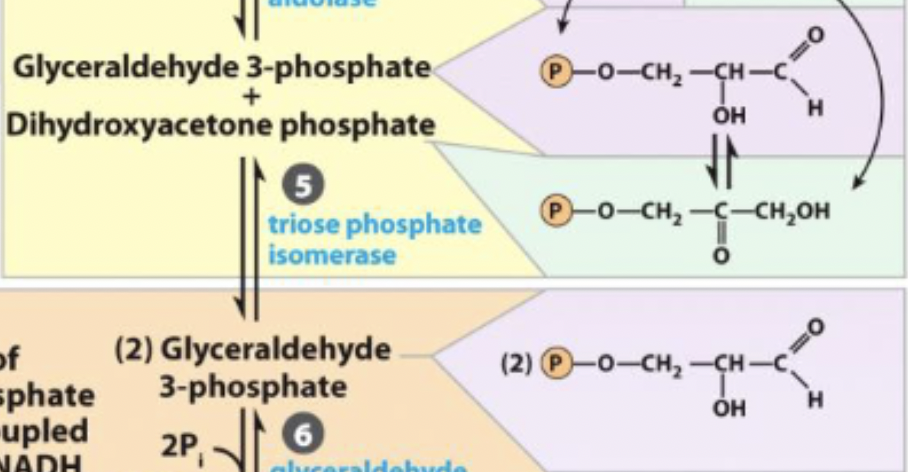
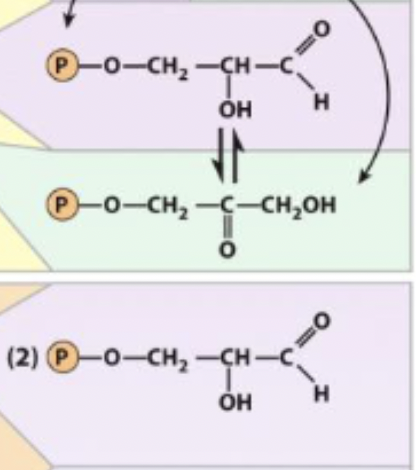
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
enzyme and step
5) triose phosphate isomerase
triose phosphate isomerase
generation of high energy phosphate compound
first step of payoff and first energy yielding step: 2 NADH per glucose
coupled with step 7
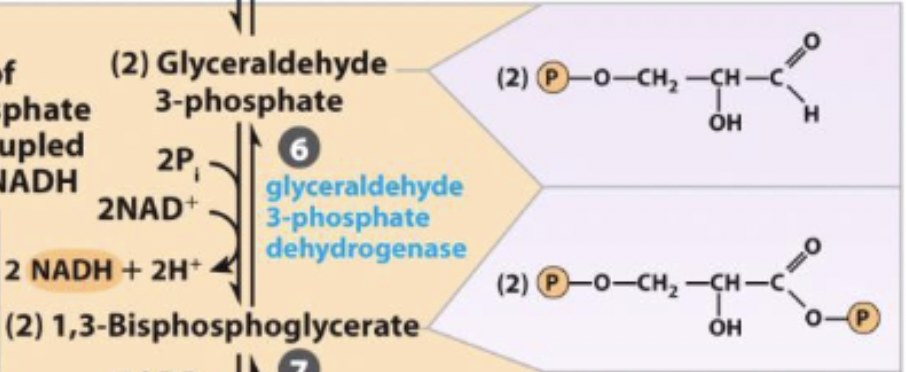
Glyceraldehye 3-phosphate +. inorganic phosphate + NAD+ ←→ 1,3-Biphosphoglycerate + NADH + H+
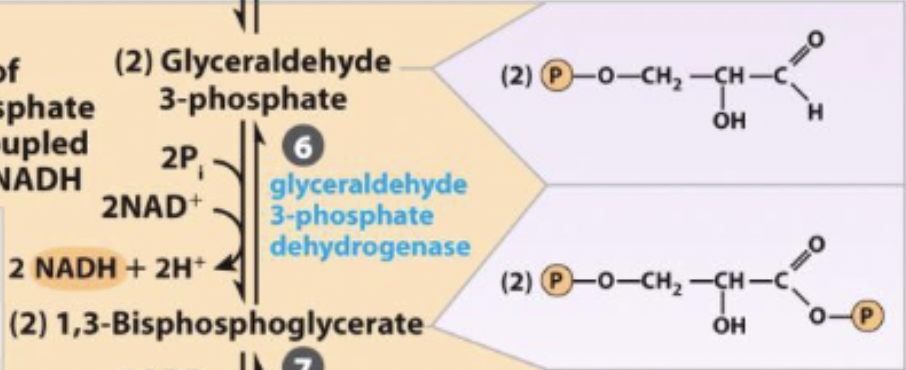
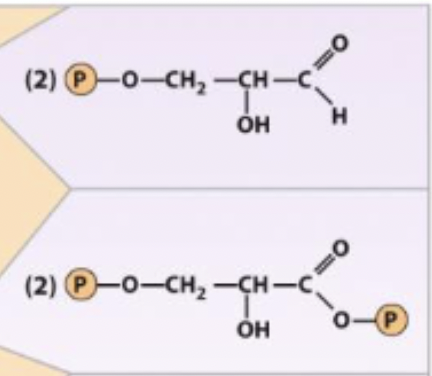
Glyceraldehye 3-phosphate +. inorganic phosphate + NAD+ ←→ 1,3-Biphosphoglycerate + NADH + H+
enzyme and step
6) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase - oxidoreductase
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase - oxidoreductase
Produces 2 ATP per glucose by transferring phosphate group to ADP
reversible because of coupling with step 6
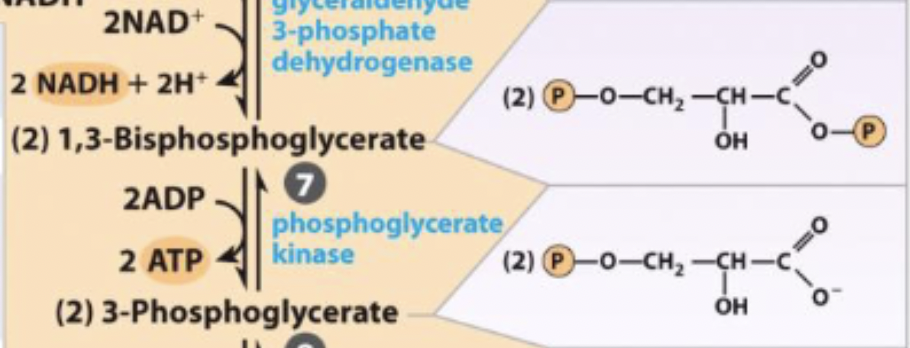
7) 1st production of ATP - R&P
1,3-Biphosphoglycerate ←→ 3-phosphoglycerate
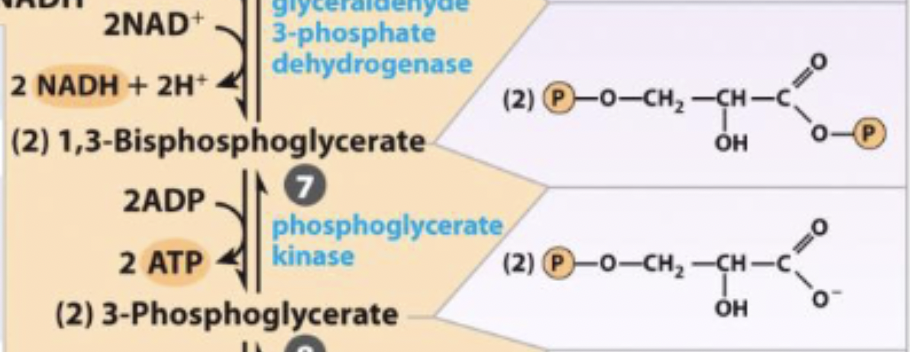
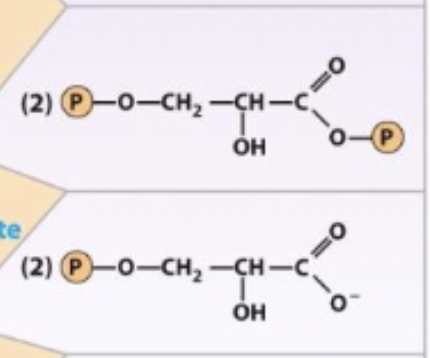
1,3-Biphosphoglycerate ←→ 3-phosphoglycerate
enzyme and step
7) phosphoglycerate kinase - transferase
phosphoglycerate kinase - transferase
swaps C3 phosphate with phosphate on His on enzyme to switch PO3- group to C2
generates high energy phosphate compound
reversible
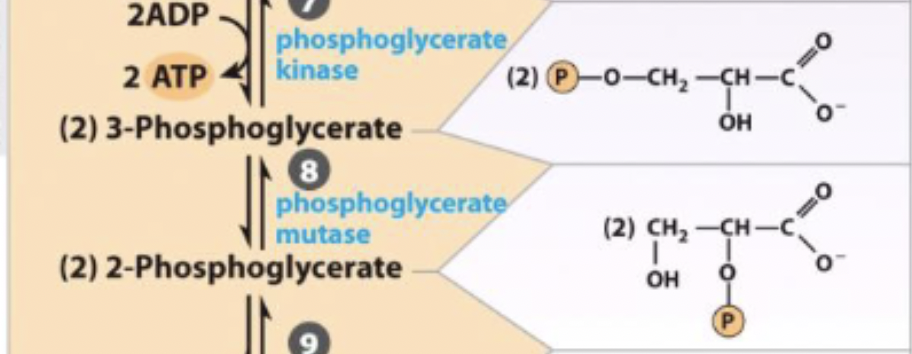
3-phosphoglycerate ←→ 2-phosphoglycerate
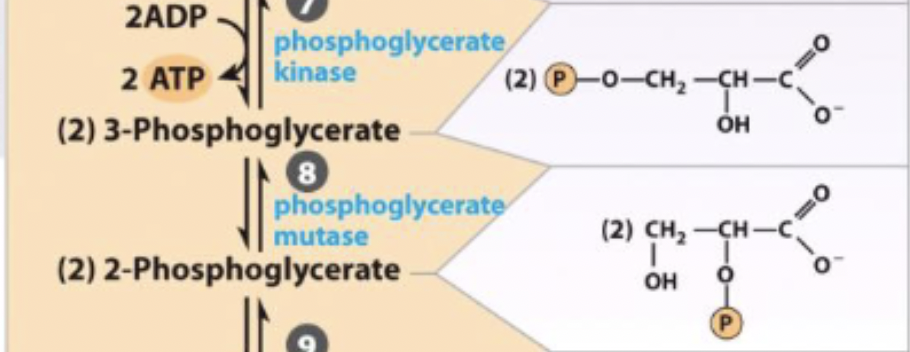
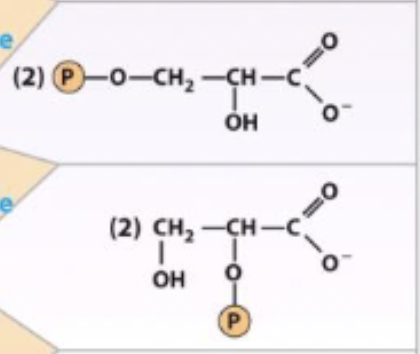
3-phosphoglycerate ←→ 2-phosphoglycerate
enzyme and step
8) phosphoglycerate mutase - isomerase
phosphoglycerate mutase - isomerase
forms an enol by removing a water
generate high energy PEP to form a good phosphate donor
reversible
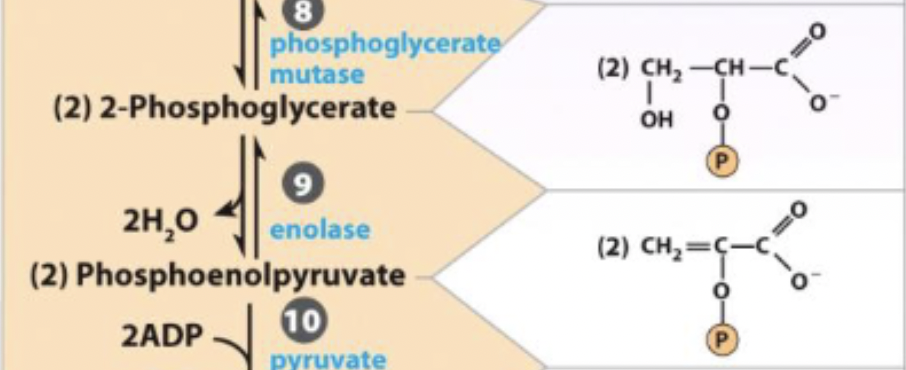
2-phosphoglycerate ←→ H2O + phosphoenolpyruvate
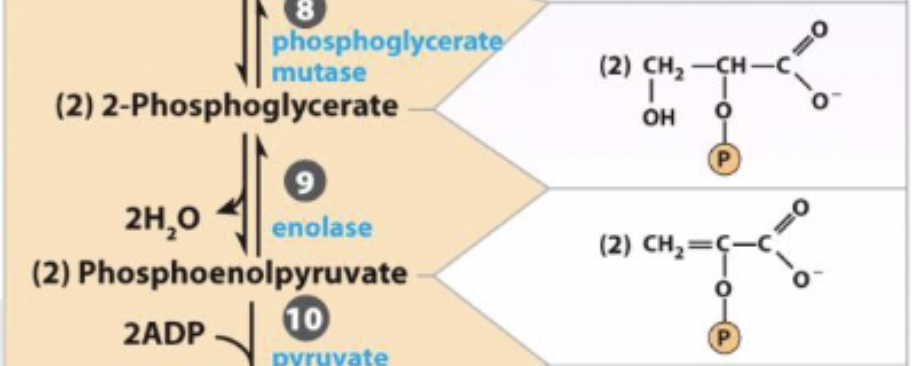
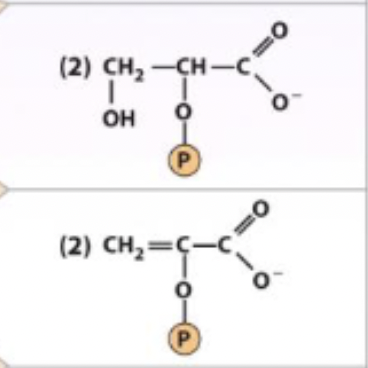
2-phosphoglycerate ←→ H2O + phosphoenolpyruvate
enzyme and step
9) enolase - hydrolase
enolase - hydrolase
forms ATP from PEP
generates 2 ATP per glucose
keto-enol tautomer intermediate
irreversible and favored
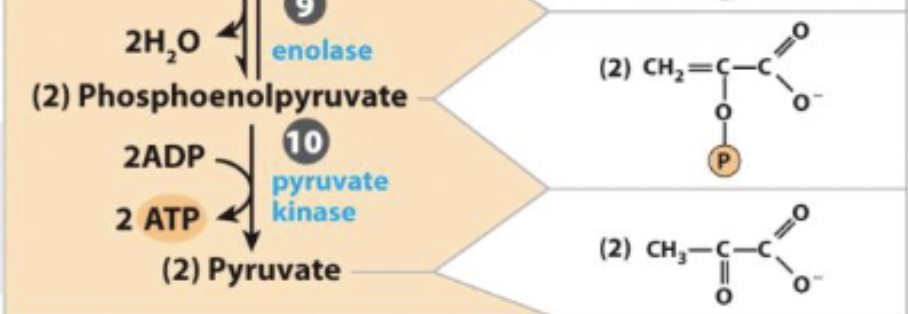
10) 2nd production of ATP - R&P
phosphoenolpyruvate ←→ Pyruvate
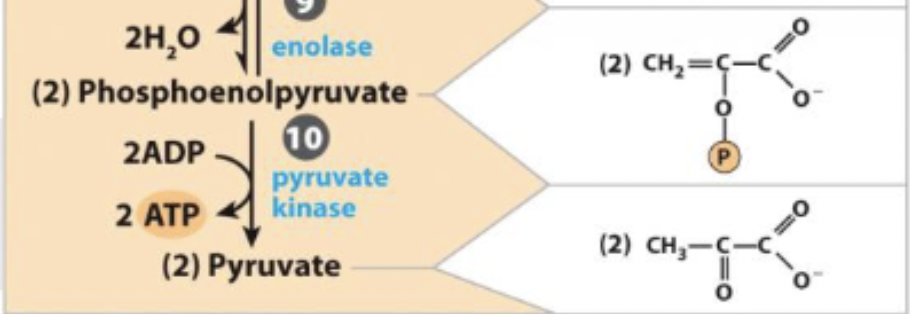
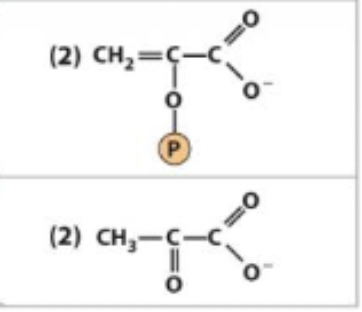
phosphoenolpyruvate ←→ Pyruvate
enzyme and step
10) pyruvate kinase
PEP
phosphoenolpyruvate
10) 2nd production of ATP - enzyme
pyruvate kinase
Substrate-level phosphorylation
When an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule, often to form an ATP
What is consumed by glycolysis?
1 glucose, 2 ATP, 2 NAD+
What is produced by glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 4 ATP, 2 NADH
glycolysis reactants
Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + Pi
glycolysis products
2 Pyruvate + 2 NADPH + 2H+ + 2 ATP
2 possible fates of pyruvate
fermentation & aerobic respiration
What cause fermentation of pyruvate?
no O2
What is the goal of non-oxidative pyruvate fermentation?
NADH + H+ → NAD+
Yeast fermentation of pyruvate
ethanol fermentation (produces CO2, NAD+, and ethanol) using
pyruvate decarboxylase
alcohol dehydrogenase
Animal fermentation of pyruvate
lactic acid fermentation (produces NAD+ and L-Lactate) using lactate dehydrogenase
Where does glycolysis take place?
muscle and brain
Where does gluconeogensis take place?
Liver
glycolysis v. glucogenesis
different because both contain irreversible rxns. They are catalyzed with different enzymes and have different methods of regulation
“cost“ of gluconeogenesis
4 ATP, 2 GTP, 2 NADH
glucogenic amino acids
amino acids that can be used in gluconeogenesis
ketogenic amino acids
can be converted to acetyl CoA → keto bodies which can be used for energy in fasting conditions
-Both L’s
5 amino acids that are both keto- and glucogenic
PITTT
-Phe, Ile, Tyr, Trp, Thr
Pentose Phospate Pathway (PPP)
Another path for glucose 6-phosphate that produces ribose 5-phosphate, NADPH, and CO2
ribose 5-phosphate
used to make nucleotides and coenzymes
NADPH
important reductant to produce fatty acids and sterols
2 phases of PPP
oxidative and non oxidative
Oxidative phase of PPP
Glucose 6-phosphate to ribose 5-phosphate, also producing NADPH
glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
type and location
oxidoreductase in step 1 of oxidative phase of PPP
glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase job
oxidizes alcohol to carbonyl and reduces NADP+ to NADPH + H+
lactonase
type and location
hydrolase in step 2 of oxidative phase of PPP
lactonase job
break the cyclic structure by using water to cleave the ester bond
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
type and location
oxidoreductase in step 3 of oxidative phase of PPP
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase job
Reduction reaction to produce NADPH and oxidation of an alcohol to a ketone
-also produces CO2
phosphopentose isomerase
type and location
isomerase in step 4 of oxidative phase of PPP
Phosphopentose isomerase job
convert Ribulose 5-phosphate to Ribose 5-phosphate
Non-oxidative phase of PPP goal
produce Glucose 6-phosphate from Ribose 5-phosphate
how is xyulose 5-phosphate produced from ribose 5-phosphate in non oxidative phase of PPP?
isomerase to ribulose 5-phosphate
epimerase
how are ribulose 5-phosphate and xyulose 5-phosphate epimers?
C3 chiral center has flipped stereochemistry
general order of PPP non-oxidative phase
pentose: ribose 5- phosphate → intermediates → final hexose: Glucose 6-phosphate
What does PPP and gluconeogensis have in common?
A pentose formed by PPP can be converted to glyceraldehyde 3 and using gluconeogenesis enzymes can form fructose 6-phosphate easily converted to glucose 6-phosphate
2 enzymes specific to non-oxidative PPP
transketolase and transaldolase
transketolase
transferase that transfer a ketone from one molecule to another
-requires TPP
transaldolase
transferase
Transketolase transfers how many carbons?
2 (from ketose donor to aldose acceptor)
Transaldolase transfers how many carbons?
3